What does he do?
In organizations of different forms of ownership, the work responsibilities of an accountant depend on the structure of the enterprise: the larger it is, the more specialized the accountant’s areas of activity. And vice versa, the smaller the institution, the wider the range of areas of work of the specialist.
Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated February 21, 2019 No. 103n approved the professional standard for the profession of accountant. This document helps to understand how to draw up the functional responsibilities of an accountant and establishes in detail what the employee does:
| Area of activity | Functions |
| Measure accounting objects in money and carry out current grouping of economic activity facts | Measure accounting objects in money and make accounting records. Enter data into accounting registers. Reflect in accounting the results of revaluation of accounting objects. Prepare calculations (reporting, product costs). Compare inventory results with information from accounting registers. |
| Accounting for primary documents on business activities | In terms of primary accounting documents, the accountant’s reporting responsibilities are presented as follows:
|
| Final summary of the facts of economic life | Calculate totals and balances of accounting accounts. Prepare balance sheet and general ledger. Prepare materials for regulatory authorities. Regarding accounting registers:
|
| Formation and provision of accounting (financial) statements | Regarding the formation of information in the accounting system:
Regarding the numerical indicators of reports as part of accounting:
Prepare explanations for the balance sheet and financial results report. Regarding reporting:
|
| Internal control of accounting and reporting | Organize and plan the process. Check the quality of reports. Monitoring the implementation of internal control processes. |
| Tax accounting, preparation of tax calculations and declarations, tax planning | Maintain tax records, calculations, declarations. Calculate and pay contributions. Organize tax planning for the enterprise. Monitor compliance with tax policy requirements. |
| Conducting financial analysis, budgeting and cash flow management | Regarding financial analysis:
Regarding budgeting and cash flow management:
|
ConsultantPlus experts examined whether the employer is obliged to draw up job descriptions for each employee separately or whether he has the right to draw up one instruction for the corresponding position. Use these instructions for free.
Who does the accounting department consist of?
Here I will not consider individual divisions subordinate to accounting - the financial and HR (personnel) departments.
In terms of the problems of working with accounting, these departments cause the least number of problems. The finance department is strictly concerned with the movement of funds, and interaction with them rarely raises questions. Often developers and technical specialists do not interact with him at all.
The HR department, although it belongs to the accounting department, is, in fact, a separate department with its own accounting automation systems and other features. HR rather refers to management accounting.
The main composition of the accounting department is divided into two weighted entities:
- Chief Accountant.
- Accounting rank and file
It is impossible to consider the work of any accounting department without taking into account the chief accountant.
Moreover, it is the chief accountant who is the key figure, since he is personally responsible for correct and timely reporting to the state. All the features of the accounting department and its interaction with other departments directly depend on how the chief accountant understands his responsibility and determines the degree of personal control over document flow, including primary ones.
The rank and file of the accounting department in matters of organizing work and interaction with various specialists is involved only as subordinates and slave employees. And it doesn’t play a special role in building effective cooperation with accounting.
It would seem that the organization of work of other departments is structured in a similar way. Actually this is not true. For example, in the sales department, in addition to the manager’s responsibility for overall performance, there is also the personal responsibility of each manager for interaction with clients. At the same time, there are no such strict rules and clearly defined responsibilities of the department head. Therefore, much more initiative, different approaches to work, etc. are allowed.
It is important to understand that in medium and small businesses, two people are responsible to the state for the activities of the enterprise, reporting and payment of mandatory contributions (tax and social) - the head of the company and the chief accountant. We will talk about the manager later, but now we will focus on the chief accountant.
Job specialization
The functional responsibilities of an accountant depend on the structure of the institution. If the enterprise is small, the specialist becomes a generalist. The job responsibilities of an accountant specialize in a manufacturing enterprise, which has a branched structure.
As a general rule, specialization occurs based on the categories of accounting objects:
The list is completed by the position of the chief accountant - the head of the financial service, who controls the activities and is responsible for their correctness.
What is accounting?
If you start studying reference books and documentation, you will come across many definitions of accounting.
For example, Wikipedia offers the following: Accounting is a staffing and structural division of an economic entity, designed to accumulate data about its property and obligations.
In textbooks, instead of a short but difficult-to-understand text, you will find entire chapters devoted to this definition. But for the non-specialist they also do not provide clarity.
In fact, the accounting department is responsible for the following areas:
- Accounting;
- Tax accounting.
In fact, the current activities of accounting are related to the correct execution of documents that reflect all movements of funds and assets.
And the final goal is reporting to the state: tax, financial and statistical. Internal reporting and management accounting can be maintained without accounting entries, documents and reports of a certain type. While reporting to the state is strictly regulated. This is the main function of any accounting department.
Responsibilities of the employee
The legislator approved two main documents that spell out the responsibilities of an accountant in detailed format:
- Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated August 21, 1998 No. 37 “Qualification reference book for positions of managers, specialists and other employees”;
- Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated February 21, 2019 No. 103n, which approves the professional standard for the accountant profession.
Here is how the main responsibilities of an accountant in a factory or other enterprise are presented:
- keep accounting of property, liabilities and business operations, that is, accounting for fixed assets, inventory, production costs, sales of products, results of economic and financial activities, settlements with suppliers and customers, for services provided, etc.;
- participate in the development and implementation of measures for financial discipline and rational use of resources;
- accept and control the relevant areas of accounting, prepare for accounting processing - these are the responsibilities of an accountant for primary documentation in an organization;
- reflect on the accounting accounts transactions involving the movement of fixed assets, inventory and cash;
- find the causes of losses and costs, take measures to prevent them;
- calculate and transfer taxes;
- develop forms of primary documents for which standard ones are not approved;
- ensure the safety of accounting documents;
- create and maintain databases.
Here is how the responsibilities of the chief accountant in the organization are presented:
- carry out work on organizing the accounting of the institution;
- formulate accounting policies based on structure, industry, and other characteristics;
- lead activities related to the preparation and approval of the working chart of accounts, forms of primary accounting documents, reporting, conducting an inventory, organizing an internal control system;
- coordinate reporting;
- organize the process of maintaining accounting registers, executing estimates, and accounting for property;
- ensure that business transactions are reflected in accounting accounts without violating deadlines;
- coordinate work on timely calculation and payment of taxes and other payments;
- participate in the financial analysis of the enterprise;
- develop measures to improve financial performance results;
- monitor compliance with cash and financial discipline;
- participate in the procedure for processing paperwork regarding shortages, violations in the expenditure of funds and inventory items;
- generate a report on the execution of budgets and estimates;
- organize the safety and transfer of documents to the archive;
- manage department employees.
The profession of accountant and its history
The activities of any company cannot fully function without proper document flow, so in any company there is always a person of this specialty. What are the functions of an accountant? The size of the subject matters directly here. If we talk about small institutions, then all duties are performed by one person - the chief accountant.
In large organizations, a whole department of highly qualified accountants is engaged in conducting business transactions and documenting them, where each is concentrated in a specific area, and also performs the job duties assigned to him. One is responsible for the cash register and payment of wages, the second interacts with foreign exchange transactions, the third manages the warehouse of goods produced. The headquarters is always headed by the chief accountant; his task is to coordinate the work of the entire department and prepare reports. Only he bears full responsibility for the financial activities of the company as a whole. The profession of an accountant is always an advantage, because he can work not only in one place at once, but also keep records of several small companies at the same time.
Interesting fact about the profession
An accountant (from German “Buch” - book and “Halter” - holder) is a specialist in the field of accounting. The first accountants carried out their activities back in Ancient India, only then they were called accountants; they worked, as a rule, on agricultural accounting. The name of the profession itself appeared only in the 15th century by the decision of Emperor Maximilian. Around the same time, the first book on accounting was published - a treatise by the Italian Luca Pacioli “On Accounts and Records”. In his manuscript, he described and organized what an accountant does. In our country, this profession appeared at the beginning of the 18th century by order of Peter the Great.
Rights
The work of an accountant is responsible, requiring the ability to analyze data and process large volumes of information. To perform the functions of the position, the accountant has the following rights:
- get acquainted with the draft decisions of the head of the enterprise in terms of accounting;
- develop proposals for process improvement;
- inform management about identified violations;
- propose measures to eliminate and prevent violations;
- request the required information from departments;
- involve employees of other departments to perform assigned tasks.
Responsibility
An enterprise accountant bears the following responsibilities:
- disciplinary;
- material;
- administrative;
- criminal;
- civil law.
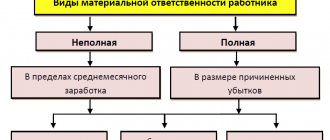
| Type of responsibility | Normative base | Punishment |
| Disciplinary | Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Reprimand, reprimand, dismissal |
| Clause 9, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | Dismissal due to the adoption of an unreasonable decision by the chief accountant, which resulted in a violation of the safety of property, its unlawful use or other damage to the organization’s property | |
| Material | Part 2 art. 243 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | According to the resolution of the plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 16, 2006 No. 52, full financial liability is possible provided that this is allowed by the employment contract with the chief accountant. Otherwise - liability in the amount of the average monthly salary |
| Administrative | Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - gross violation of accounting and reporting requirements | Fine - from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles, for repeated violation - from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles or disqualification for a period of 1 to 2 years |
| Part 1 art. 15.6, Art. 19.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - failure to submit financial statements on time to the Federal Tax Service and statistical authorities | Warning or fine from 300 to 500 rubles | |
| Part 5 art. 14.5, art. 15.5, part 1 art. 15.6, part 2 art. 15.33 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - failure to submit tax returns and other documents to the Federal Tax Service, reports to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation on time | Warning or fine from 300 to 3000 rubles | |
| Part 1 art. 15.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - violation of cash discipline | Fine from 4000 to 5000 rubles |
What is an accountant responsible for?
E.V. Danilova Magazine “Glavbukh”, N 11, June 2001
The accounting profession has always been necessary and important, and in recent years it has also become prestigious. The accountant is aware of all the affairs of the enterprise, since he must reflect financial and economic transactions in accounting and, by correctly taking advantage of the benefits, minimize taxes. How much will be transferred to the budget and whether the company will have to pay fines depends on its work. Therefore, many managers respect accountants and trust them.
But we should not forget that this profession is also associated with financial responsibility. For serious violations in work, both unconscious and accidental, as well as intentional, for using his official position for personal gain, an accountant can be brought not only to disciplinary and administrative, but also to criminal liability. We will tell you how and for what exactly in this article.
Responsibilities of an accountant
Usually, accounting of business transactions is carried out by an accounting service, or, as it is often called, accounting.
It is headed by the chief accountant. But sometimes an organization has such a small staff that all its affairs are managed by one accountant. In this case, the functions of the chief accountant are assigned to him. In addition, accounting can be entrusted to a specialized organization or a specialist accountant. This follows from the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 N 34n (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting). Paragraph 2 of Article 7 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 N 129-FZ “On Accounting” establishes that the chief accountant is responsible for the formation of accounting policies, accounting and timely submission of complete and reliable financial statements.
The chief accountant is appointed and dismissed by the head of the organization, and he reports to him. Well, what to do in case of disagreement? An accountant, by written order of his boss, is obliged to accept documents on controversial transactions for execution, but then only the manager will bear responsibility for the consequences.
Issues related to the work of an accountant at an enterprise are regulated by the Regulations on Chief Accountants, approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR of January 24, 1980 N 59. However, this document is practically not used today. However, it has not been officially canceled, so accountants can be held accountable in the cases provided for here. For example, it is punishable:
- incorrect accounting, which resulted in neglect of accounting and distortions in financial statements;
- acceptance for execution and execution of documents on transactions that were not carried out according to established rules;
- untimely and incorrect reconciliation of transactions on bank accounts, settlements with debtors and creditors;
- incorrect write-off of shortages, accounts receivable and other losses;
- untimely inspections and documentary audits;
- leaving false statements due to the fault of the accountant.
- fine;
- deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities;
- compulsory work, in which the convicted person performs unpaid socially useful work in his free time from his main job;
- correctional labor served at the place of work of the convicted person;
- confiscation of property;
- restriction of freedom when a convicted person is kept in a special institution without isolation from society;
- arrest, that is, keeping a convicted person in conditions of strict isolation from society;
- deprivation of liberty.
Along with the manager, the chief accountant is responsible for non-compliance with the rules and regulations that regulate the financial and economic activities of the enterprise.
In addition, in cases where quarterly and annual reports are not submitted to the relevant authorities on time, the chief accountant is also to blame. As is known, without the signature of the chief accountant, monetary and settlement documents are considered invalid and cannot be accepted for execution. Therefore, the accountant is responsible for the content of these documents.
By the way, instead of an accountant, primary documents can be signed by authorized persons (clause 14 of the Regulations). Their list is approved by the manager in agreement with the chief accountant. A document flow schedule at the enterprise is also drawn up. But only the chief accountant controls the implementation of this schedule, and he is also responsible for its violation.
As for primary documents, accounting registers, accounting reports and balance sheets (before transferring them to the enterprise archive), then, of course, their execution and safety are under the responsibility of the accountant.
It remains to add that in accordance with the letter of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated October 4, 1993 No. 18 “On approval of the Procedure for conducting cash transactions in the Russian Federation,” control over the correct conduct of cash transactions is assigned to the chief accountant of the enterprise. Consequently, the appointment, dismissal and relocation of all financially responsible persons (cashiers, warehouse managers, etc.) must be coordinated with him.
Disciplinary responsibility
Of course, an accountant, like any employee of an enterprise, can be held accountable for violating labor discipline.
This is, first of all, a failure to fulfill all the above responsibilities: after all, for an accountant they are labor duties. Of course, being late, absenteeism, showing up at work while drunk are also violations of discipline for which the employee must be punished. The punishment is determined in accordance with labor legislation. This could be a reprimand, a reprimand, a severe reprimand, or dismissal. Moreover, dismissal is possible only in cases expressly provided for in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Please note that any other measures of liability for violation of discipline cannot be applied to an accountant. For example, the manager does not have the right to fine him or reduce the vacation allotted to him by law. Of course, an employee’s salary can be reduced, but this cannot be made dependent on his misconduct.
When imposing disciplinary sanctions, the head of the enterprise should adhere to a certain procedure. Let's look at this order using a hypothetical example. Suppose an accountant missed one of his working days. An employee can be punished for this one offense no later than six months after it was committed. As soon as the administration finds out about absenteeism, the accountant should be required to provide a written explanation. From this moment on, management has exactly one month to punish the offender. The recovery is formalized by an order for the organization, which the accountant must be familiar with against receipt. Here it must be added that, based on the results of an audit or inspection of financial and economic activities, penalties can be imposed within two years from the date of the offense.
Material liability
The financial liability of the organization's employees is provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
An accountant, like any other employee, is responsible only for direct damage caused to the enterprise, and in an amount not exceeding his monthly salary. Note: an accountant does not directly deal with values. Therefore, he cannot be entrusted with full financial responsibility. Moreover, he does not even have the right to receive money and inventory items for the enterprise by checks. However, an exception has been made for small enterprises: by agreement with the bank, the chief accountant can also perform the functions of a cashier. In this case, an agreement on full financial responsibility must be concluded with him. Example 1
The accountant of Gvozdika LLC signed a power of attorney, according to which an employee of this enterprise was to receive 15,000 rubles from another organization. and bring them to the accounting department. The money had to be delivered urgently, so an agreement on full financial responsibility was not concluded with the employee. The employee received the money, but lost it on the way. The head of the enterprise issued an order in which he obliged the chief accountant to compensate for the damage caused: after all, he signed a power of attorney and sent the employee to collect valuables without concluding an agreement with him on full financial liability. The accountant refused to pay the money and went to court. The matter was decided in his favor. The court indicated that the accountant does not bear any responsibility in this case, since he himself did not service the valuables. The court ruled that the employee who received the goods under a one-time power of attorney should be punished. In this case, the court referred to paragraph 5 of Article 31 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Unlike an accountant, a cashier bears full financial responsibility. Based on Article 121.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the enterprise enters into a corresponding agreement with it in writing. Please note that such contracts can only be concluded with employees who have reached the age of 18 and perform work directly related to the storage of valuables, their transportation, sale, etc.
Example 2
The cashier discovered that 20,000 rubles were missing from the cash register. He reported this to the head of the organization. He decided that the cashier himself was to blame for the loss and demanded a refund from him. The cashier wrote a statement about the theft to the police and indicated in it that the money was stolen by a worker who, two days before the discovery of the loss, changed the wiring in the cash register. However, the head of the organization still went to court with a demand to recover the missing money from the cashier. The court ruled in favor of the employer, and the cashier had to pay 20,000 rubles. Two months after this, law enforcement agencies detained a fitter, who admitted to stealing money from the cash register. The court reviewed the case and found that the cashier was not financially responsible, since he was innocent of the loss. According to this decision, the money was returned to him.
Administrative responsibility
First of all, let us turn to Article 15 of the RSFSR Code of Administrative Offences.
It is established here that officials are responsible for administrative offenses related to failure to fulfill official duties. This rule also applies to an accountant who is an official of the organization. What is an administrative offense? This is an unlawful act or omission that was committed intentionally or through negligence. Intent occurs if the offender was aware that his action was illegal, foresaw harmful consequences, desired or consciously allowed them. Negligence is a situation where the culprit knew about the possibility of harmful consequences, but thoughtlessly hoped to prevent them or did not anticipate such consequences, although he should have and could have foreseen them.
The chief accountant bears administrative responsibility only in cases where he has violated the norms of legislation on taxes and fees, the implementation of which is entrusted to him.
Indeed, sometimes organizations accrue taxes and other obligatory payments at the wrong time or not in full. Then the federal tax police authorities have the right, as a preventive measure, to issue written warnings to the managers, chief accountants and other officials of these enterprises. Accountants who fail to comply with such requirements must pay a fine of up to 100 minimum wages, that is, 10,000 rubles. Let us recall that from January 1, 2001, fines are calculated based on a base amount of 100 rubles. This is stated in Article 5 of Federal Law No. 82-FZ of June 19, 2000 “On the minimum wage.”
Criminal liability
The head of the organization and the chief accountant, as well as persons actually performing their duties, may be held liable under Article 199 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (CC RF).
What accounting offenses does the Criminal Code punish? This is the indication in documents of deliberately distorted data on income or expenses or the concealment of any objects of taxation, if as a result a large amount of taxes was not paid, namely 1000 minimum wages, that is, 100,000 rubles. Well, what is the punishment? Those found guilty are deprived of the right to engage in accounting activities for up to five years. Arrest for a term of four to six months or imprisonment for a term of up to four years is also possible. But in each specific case the punishment is determined by the court.
There are no exact criteria here, but the court always takes into account the mitigating circumstances specified in Article 61 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation: for example, a confession or the fact that the perpetrator has young children. In such cases, the maximum penalty is four months of arrest. In addition, a suspended sentence or deferment of the sentence is possible.
If there are aggravating circumstances listed in Article 63 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the sentence is more severe and there can be no question of any conditional sentence.
If an accountant has repeatedly evaded calculating taxes and the non-payment amounted to a particularly large amount, or he was in collusion with a group of people, then he may be imprisoned for a term of two to seven years. A particularly large amount is 5,000 minimum wages, that is, 500,000 rubles.
Example 3
The accountant deliberately did not take into account part of the tax base, which is why the organization underpaid tax to the budget. This was revealed by the inspection. As a result, 100,145 rubles were collected from the organization. tax and penalties, as well as a fine of 1900 rubles. The tax police opened a criminal case against this accountant under Article 199 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. However, it was later closed because the accountant managed to prove that there was no crime. He proved that he was right in the following way. Although 100,145 rubles were collected from the budget, the amount of unpaid tax is only 95,000 rubles, the rest is 5,145 rubles. - penalties for 65 days of delay. Penalties were calculated as follows: 95,000 rubles. * ((25%/300%)*65 days) = 5145 rub. Note that the refinancing rate did not change during this period and amounted to 25 percent. Thus, the amount of hidden tax is only 95,000 rubles. In accordance with the Criminal Code, this cannot be considered large in size, therefore, there is no corpus delicti.
But let’s assume that the accountant himself did not commit the crime, but only contributed to its commission with advice, instructions, etc. This means that he will be held liable under Article 33 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation as an instigator or accomplice.
It must be said that when deciding whether to punish an accountant, the court always takes into account the accountant’s dependence on the head of the organization. After all, as we have already said, the chief accountant is obliged to carry out the written order of his boss, despite his inner conviction of its illegality. This relieves the accountant of criminal liability. As Part 1 of Article 42 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation states: “It is not a crime to cause harm by a person acting in pursuance of an order or instruction that is binding on him.” In such cases, criminal liability is borne by the person who gave the illegal order, that is, the head of the organization.
Particular consideration should be given to the situation when the chief accountant is employed by government agencies or municipal institutions. He can be attracted if he: abuses his official powers (Article 285 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), exceeds these powers (Article 289 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), illegally participates in business activities (Article 289 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), takes bribes (Article 291 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation) RF), commits forgery (Article 292 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation) or is negligent in his official duties (Article 293 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
When holding accountants criminally liable for such crimes, the court may apply the following sanctions to them:
It remains to add that every accountant need not be afraid of liability and severe penalties.
To do this, he only needs to comply with the rules established by law, as well as fulfill his official duties with the utmost precision and in a timely manner. Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
Example of a job description
The algorithm for accounting activities is fixed in the job description. The employer defines in detail the tasks and functions of the accountant in the document.
The structure of the job description includes the following sections:
- General provisions. Contains information about the employee and qualification requirements. The section indicates the standards and regulations that the specialist knows.
- Responsibilities. The section contains a detailed list of tasks and functions.
- Rights. Informs about the authority of the employee when performing duties.
- Responsibility. Contains a list of penalties for violation of established requirements.
Accounting tasks
The main task of accounting is to provide complete and accurate information about the activities of the organization and its financial situation.
In addition, accounting solves the following problems:
- Creation of the necessary valid information base about the performance of the organization, its condition from the point of view of material support and performance - the formation of financial statements that are required by managers, founders, creditors, and investors.
- Supplying reliable data on the activities of the organization of fiscal authorities to monitor compliance with state legislative norms when the company carries out business operations.
- Early elimination of negative results of the organization’s economic activities, identification of internal economic reserves to maintain its material and financial stability.