Definition of Accounting Entries
An accounting entry is a method of recording business transactions in different accounts. The amounts are equal. Every business entity undergoes several payments and trade transactions every day, including:
- settlements with suppliers;
- payment of taxes;
- transfer of funds for the purchase of devices;
- ensuring the transportation of goods.
Accounting records can also be called a tool for recording income and expenses. Financial activities are reflected using double entry:
- Debit contains information about income from various sources;
- The Credit includes information about expenses, including wages and settlements with counterparties.
Credit and debit accounts are interconnected. They are presented in a single table, which is also known as a correspondent account.
All values in the statements must match the information in the primary documents. In other words, transactions that are reflected in the journals are necessarily confirmed by appropriate documentation.
Opportunities for generating reports
Data available in the system
The following data is directly stored in the R/3 System:
- Records of general ledger accounts used, debtors and creditors
- Data on opening balances and turnover of accounts for the period in company code currency and alternative currencies
- Data on initial balances and turnover on personal accounts for the period for each of the views (OGK codes) in the currency of the company code and alternative currencies
- Separate entries for the general ledger accounts and personal accounts, separately - open positions, separately - cleared
- Headings and positions of posted documents
Posting classification
There are two types of accounting records:
- simple, which reflect two accounts (debit and credit);
- complex - include more than two accounts.
Postings are used depending on the trading operation.
Postings are also divided according to the nature of the information reflected - into real, conditional and clarifying. Real ones are used to reflect business transactions, for example, the calculation and payment of wages. Conditionals arise as a result of accounting methodology. But in reality this operation was not performed. Used to transfer or clarify indicators.
There can be several examples:
- closing the sales account and determining the financial result;
- production costs include management costs. The latter are accounted for in the “General business expenses” account, while no business facts occur.
Clarifying entries involve maintaining corrective records, as well as records for writing off the calculation difference in the production process accounts. They, in turn, are divided into two categories:
- additional ones, which increase the amount of turnover on the account; regular ink is used when drawing up;
- reversal – when calculating the totals, the red amount is subtracted and drawn up in red ink.
ORGANIZATION OF ACCOUNTING IN R3
Organizational units of accounting
To ensure simultaneous information support for several organizations, the concept of “Company Code” was introduced in R/3. A company code represents an organization that maintains accounting records in R/3 and produces a separate balance sheet. For a company code, all the parameters necessary for accounting must be specified - chart of accounts, base currency in which accounting is maintained, etc.
If there is a need to maintain full accounting records for an organization’s area of activity or division, R/3 allows you to use the concept of “business area”. Several business areas can belong to a company code.
Balance sheets and other accounting reports can be obtained for both an organization (company code) and a division (business area). The concept of the R/3 chart of accounts makes it possible to unify accounting at the holding's enterprises, taking into account their characteristics. Company codes located in the same country can use a common chart of accounts. In this case, part of the accounts can be used only by part of the company codes. Details of the account, such as the currency in which the foreign exchange account is maintained or the details of the bank in which the bank account is opened, the fields filled in and displayed in the account entries, may differ from one company code to another.
Fiscal year and posting periods
The fiscal year in R/3 may not correspond to the calendar year. Its parameters are set when setting up the system for each company code. The financial year is divided into periods. The default setting for Russia is to use a calendar fiscal year with twelve periods corresponding to calendar months and four additional ones. Additional periods can be used for year-end closing postings and balance sheet preparation.
To protect data, periods can be closed for a certain type of posting.
Examples of accounting entries
An example of correspondence between two accounts: wages were paid to employees from the cash register in the amount of 500,000 rubles. The operation is reflected by the following posting: On the debit of the account - 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”, on the Credit - 50 “Cash” - 500,000 rubles.
If transactions affect more than two offsetting accounts, they can be presented in two ways. One account can be debited and several accounts credited. In this case, the total amount credited does not differ from the amount of the debited account.
Example:
The company's account was credited with revenue in the amount of 100 thousand rubles and the amount from the sale of equipment - 50 thousand rubles:
Debit of account 51 “Current accounts” - 150 thousand rubles;
Credit to account 90 “Sales” - 100 thousand rubles;
Credit to account 91 “Other income and expenses”, in this case the subaccount “Other income” is used - 50 thousand rubles.
Complex wiring can be presented in the form of two simple ones:
For debit - 51 “Current accounts”, for Credit - 90 “Sales” - 100 thousand rubles;
Debit 51 “Settlement accounts” Credit 91 “Other income and expenses (subaccount “Other income”)” - in the amount of 50 thousand rubles.
Let's consider another option, when several accounts are debited and one is credited at the same time. In this case, the debit amount is equal to the credit amount.
As an example:
Materials were received from the counterparty in the amount of 50 thousand rubles, as well as equipment for installation in the amount of 50 thousand rubles. A complex accounting entry is reflected as follows:
Debit account 10 “Materials” - 10 thousand rubles;
Debit of account 07 “Equipment for installation” - 50 thousand rubles;
Credit to account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” - 60 thousand rubles.
Complex wiring can also be presented in the form of two simple ones:
For Debit - 10 “Materials”, for Credit account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” - 10 thousand rubles;
Debit account 07 “Equipment for installation” Credit account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” - 50 thousand rubles.
Complex postings significantly reduce the number of accounts, and this allows you to reduce the time for performing analytical and accounting functions.
How to prepare accounting entries for specific business transactions?
Examples of accounting entries for wages
Payroll transactions reflect the following: Debit personal income tax, other deductions and payment of wages, credit - accruals. Accounting entries are made for each employee.
Payroll accounting is carried out on the basis of the following important principles:
- accurate recording of the number of employees and the time they worked;
- correct withholding amounts, including budgetary and extra-budgetary funds;
- monitoring the performance of work by employees;
- correctness when posting labor transactions in accounting.
Table with examples of salary postings:
Payroll posting table.
Renting premises in the accounting department
All actions with the leased property are reflected by both the lessor and the tenant.
To fill out a lease agreement, an agreement form drawn up on the basis of the principles of Chapter 34 of the Civil Code is used. The contract specifies the validity period. If the period is not specified, it is considered that the contract was concluded for an indefinite period. In Russia, when renting for a period of more than a year, state registration is required.
General work log: sample filling and step-by-step guidance for drawing up the document are in the article at the link.
The contract has two parts: main and additional. The additional one includes various payments, such as housing and communal services. In rare cases, housing and communal services fees are included in the general rent. By law, rental expenses are recorded in accounting on a monthly basis.
These expenses are considered as ordinary activities and are taken into account in accounts 20-29 and 44, depending on the activities of the organization.
Table of accounting entries for renting premises with answers:
Table: Accounting for the lessor when recognizing rental income as income from ordinary activities.
Table: Accounting for the lessor when recognizing rental income as other income.
Table: Tenant's accounting.
Examples of accounting entries for wholesale and retail trade
The economic activities of wholesale and retail organizations require the execution of many transactions; they are related to the sale of goods, finished products, as well as services.
Find out the procedure for writing off accounts payable with an expired statute of limitations in this article.
Posting table with trading examples:
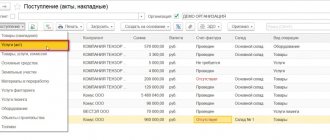
Table: Receipt of goods from the supplier.
Table: Sales of goods at the time of payment.
Table: Sales of goods at the time of shipment (OPT).
Table: Sales of goods at the time of shipment (Retail).
Accounting entries for beginners under an assignment agreement
An assignment agreement is a replacement of a creditor under an obligation. There are three parties to the contract. The accounting of the parties is as follows:
- debtor – all debt transactions are reflected in analytical accounting. Costs identified during the validity of the assignment agreement are reflected in other expenses. Changing the lender will not affect financial accounting;
- assignor - the assignment agreement does not generate either income or expenses. But the fact of execution of the operation increases its liquidity;
- assignee - when assigning a debt, records it in debit as a receivable for the amount of the debt, then displays it as a credit in anticipation of the transfer of funds.
The following table with examples for an assignment agreement will help beginners make accounting entries:
Table: Postings under the assignment agreement.
Cash transactions in accounting
Cash transactions involve receiving, issuing and storing cash. Accounting for cash transactions is based on the regulations of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What is depreciation of fixed assets in simple words? The answer is here.
When maintaining a cash register, the following documents are used:
- cash receipt order - to record cash receipts;
- expense cash order - to record cash expenses;
- cash book – takes into account all movements on the cash register.
Table of accounting entries with answers:
Table: Cash transactions in accounting entries.
Provision of services
An organization can either provide services to third parties or use the services of a third party. Accounting for accounting entries in this case will be different.
The main tasks are the following:
- reliable and complete information content of all transactions performed;
- providing information to all participants in the process;
- avoiding a negative outcome for these operations;
- proper documentation;
- competent reflection of expenses in the process of operations;
- receiving monetary profit from the transaction.
Table with answers for business transactions related to the provision of services to third parties:
Table: Provision of services to third parties.
Table: Obtaining services from a third party.
How to prepare accounting entries for fixed assets?
An organization that has fixed assets on its balance sheet is obliged to take them into account in the balance sheet. It is worth noting some features in this process:
- accepting a fixed asset for accounting, its initial cost is determined;
- a fixed asset has a useful life - this is the period during which it generates income;
- it is necessary to depreciate the fixed asset, i.e. write off its partial cost;
- revaluation is not mandatory, the organization has the right to carry it out;
- expenses for capital or current repairs of fixed assets are recorded on debit expense accounts;
- write-off of a fixed asset occurs in the event of non-receipt of profit or its disposal.
Table of accounting entries for fixed assets with examples:
Table: Accounting entries for fixed assets.
Closing of the year
According to the law, a period is defined for which all economic activities of the organization are carried out; this period lasts from January 1 to December 31. Based on this period, January 1 is the new reporting date, and December 31 is the final one.
You can read how to independently draw up an accounting certificate about correcting an error and writing off a debt here.
Closing the year sums up all the annual financial results of the organization. That is, it resets the balances on accounts 90 and 91, and closes account 99. As a result, the total, profit or loss is taken into account on account 84.
Closing is done on a full year basis. In accounting, the year end is shown as December 31st. After closing, the organization begins a new period with zero financial balances.
Table with examples:
Table: Closing transactions.
Examples of accounting entries for taxes and state duties
Tax expenses and state duties are displayed in the period of actual payment. Based on the purpose of the payment, you need to consider:
- write-off of costs for core activities;
- posting of costs to other expenses if they are not related to the main activity;
- accounting as part of the property.
Payment of taxes and state duties is carried out from the organization's current account. When paying, you must take into account all the payer's details and the correct purpose of the payment.
Examples of postings are clearly shown in the following table:
Table: Postings for taxes and duties.
Loans issued
The organization has the right to issue a loan to a third party organization or individual. Such a transaction must be certified in writing on both sides as a loan agreement. The loan agreement usually specifies the interest level, the period of validity of the agreement, and the payment schedule.
If the interest level is not determined, you can take the current refinancing rate as a basis. The loan agreement can also be interest-free, which must also be stated in the agreement.
The loan can be issued either in cash or in kind; it is worth noting that VAT is not assessed for a cash loan. The amount of interest received is included in sales revenue or other income. This does not affect financial results.
Table: Accounting entries for loans and credits.
Acquiring
Acquiring is non-cash payments with the buyer through an intermediary, which is the bank, on the basis of a concluded agreement between the organization and the acquiring bank.
This operation has the following features:
- use of a POS terminal for processing bank cards;
- The POS terminal is listed on an off-balance sheet account (if provided by a bank), or as a fixed asset (if acquired as an asset of an organization);
- proceeds from the sale are credited to the account in an amount reduced by the amount of the acquiring bank's commission, but the entire amount of proceeds is indicated in the income;
- the acquiring bank's commission is included in the costs.
Accounting entries for acquiring in the table:
Table: Accounting entries for acquiring.
Accounting is equipped with a large number of entries; an experienced accountant knows that the reflected data must be correct and literate, in accordance with established rules. First of all, the accountant must understand the importance of this and be aware of the responsibility that lies with him.
If information is distorted or trying to avoid providing it, the manager and accountant will be held liable under Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
How to prepare accounting entries correctly? Watch the following video for recommendations:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ng4Ifp0Mgog
Don't forget to add "FBM.ru" to your news sources
Last news
Who keeps the accounting records?
Accounting records are required to be used by all business entities - both large companies and individual entrepreneurs using a simplified taxation system. Some organizations are subject to annual audits, so it is very important for them to keep their accounting records in order. These include the following categories:
- joint stock communities;
- insurance companies;
- financial and credit groups;
- securities companies;
- non-state pension funds.
Who is responsible for mistakes
Serious recordkeeping violations may result in the following sanctions:
- tax;
- administrative;
- payment of fines.
Responsibility for errors lies with the chief accountant, as well as the head of the company. If an error is identified in the papers, it is necessary to correct them immediately, as the sanctions can be serious.
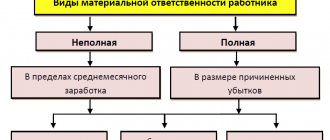
The chief accountant is responsible for the damage caused to the direct employer. He acts as a financially responsible person. The procedure for its collection is specified in the employment contract with the employee.
If this information is not reflected in the contract, only penalties can be applied to the accountant, the amount of which does not exceed his monthly salary.
Financial liability is regulated by federal laws and the labor code. An employment contract cannot contradict the laws. It is prohibited to collect an amount greater than that specified in the code.
The manager is also the financially responsible person. All damages that may be recovered from him are indicated in the Labor Code (Article 277). Similar conditions apply to the probationary period.
Every day, companies conduct several transactions. Significant transactions also include transfers between accounts, so all actions must be reflected in the computer database. Some organizations continue to keep records in paper journals.
Postings make it possible to track how, what and in what amount were transferred between correspondent accounts. Using this information, you can get an idea of income and expenses, as well as the company's activities as a whole. Some enterprises carry out mandatory audits of their accounting records. It is necessary to make sure that all postings do not diverge from the primary documentation. This will avoid the application of sanctions.
1C: Accounting 8
“1C: Accounting 8” is the most popular accounting program that can take accounting automation to a whole new level. A convenient product and services connected to it will allow you to effectively solve the problems of the accounting department of any business!
- Support of different tax systems, maintaining accounting and tax records, submitting reports;
- Inventory accounting, batch accounting, settlements with counterparties, extracting primary documents;
- Payroll calculation, accounting of cash transactions;
- Integration with other 1C programs and websites;
- Working with electronic certificates of incapacity for work (ELS).
Try 30 days free Order
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter