Introduction to direct and indirect taxes
Taxes levied on taxpayers can be divided into the following types:
- at the place of receipt (Article 12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): federal (clause 2);
- regional (clause 3);
- local (clause 4);
See this article for more details.
- by applicability: general;
- special;
- straight;
- from individuals;
The tax system of the Russian Federation is built using a combination of direct and indirect taxes. Direct taxes are collected directly from the income received or the value of the taxpayer’s property. Such taxes go to the appropriate budget immediately after transfer. For them, the law determines the percentage of income withdrawal. A number of direct taxes provide payment benefits, and sometimes complete exemption.
Indirect taxes are imposed on goods and services. Either the entire tax or part of it is included in the price. The owner who sells goods or services receives these tax amounts, which he then reimburses to the state. Thus, indirect taxes are practically paid by the buyer, and the seller is an intermediary in the payment of indirect taxes, but it is he who is asked about the timeliness and correctness of its transfer. Indirect taxes are related to the consumption of goods or services.
Direct taxes are easier to calculate and control (unlike indirect taxes). At the same time, indirect taxes allow flexible distribution of the tax burden.
Calculation methods and example
Calculation of the mineral extraction tax based on the amount of minerals extracted is limited: for gas, coal, oil; in other cases, the tax base will be cost based. The quantity is determined directly or indirectly.
The direct method is used where it is possible to rely on the readings of measuring instruments that take into account quantitative production. To these must be added the actual losses during production. Actual losses are determined by the difference between the calculated production indicator and the actual one.
The indirect method is calculated based on the PI content in the mining product. Mineral raw materials themselves are taken into account using instruments. The calculation methodology is fixed in the LNA. It cannot be changed during the entire production period if the technological characteristics of production do not change. How to calculate the mineral extraction tax by quantity is stated in Art. 338, 339 NK.
The value of PI is determined to calculate the tax at sales prices, with or without subsidies. Subsidies appear in the calculations of the miners who actually receive them. These methods are applied if the miner had a sale in the reporting month.
Another calculation method. It applies if there were no sales in the reporting month. Methods for determining value are characterized by Art. 340 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- The cost of mined PI = the number of mined PI*the cost of a unit of PI production.
- Cost of a unit of production PI = revenue / sales volume or Cost of a unit of extracted PI = estimated cost / volume of production.
The estimated value of PI is calculated according to NU data, using the same methodology as the income tax base. Direct and indirect costs are taken into account.
An example (conditional) of cost calculation. The company extracts construction sand. It has no subsidies. In the past period she had realization. The organization pays VAT to the budget. Production for the period amounted to 50,000 tons, of which sales - 35,000 tons. Sales price - 300 rubles/t. The cost of delivering sand is 150,000 rubles.
Calculation:
- 300 / 1.2 = 250 rub./t - selling price excluding VAT.
- 35,000 * 250 = 8,750,000 rub.
- 8750000 – 150000 = 8600000 rub. — revenue.
- 8600000 / 35000 = 245.71 rubles. — the cost of one mined ton.
- 245.71 * 50000 = 12285500 rub. — mineral extraction tax base.
- 12285500 * 5.5% = 675702.50 rub. — Mineral extraction tax.
Note: the rate of 5.5% is established by art. 342 paragraphs 2 paragraphs. 4.
Property tax, or what is included in direct taxes
Direct taxes allow you to manage the country's economy. They selectively influence industries and contribute to the creation of better conditions for the work of organizations in areas of activity that require state support. They can also create unfavorable conditions for areas of the economy whose development is unacceptable for the state.
Direct taxes include:
- for individuals: personal income tax;
- on property;
- for motor transport;
- to a plot of land;
- Personal income tax for employees;
What is the tax base?
The tax base is:
- quantity of minerals extracted during mining:
oil
- natural gas
- gas condensate
- coal
- multicomponent complex ores in the Krasnoyarsk Territory;
The tax base is determined by the taxpayer independently in relation to each mineral resource extracted. That is, if a company extracts marble and granite, then its own tax base is calculated for each.
The cost of extracted minerals is determined:
- based on the sales prices of extracted minerals;
- based on sales prices without taking into account subsidies from the budget to compensate for the difference between the wholesale price and the estimated cost;
- based on the estimated cost of extracted minerals.
Important
: the latter method of assessment is applied in the event that there is no sale of mineral resources in the corresponding tax period.
Examples of direct taxes
The state, represented by the tax service, knows in advance about the amount of tax revenue from a particular direct tax. This is achieved by organizations providing declarations or other reporting documents in which tax is calculated. Examples of such taxes are given below.
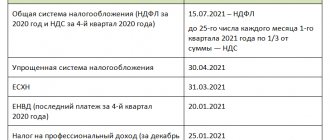
1. Personal income tax (NDFL) is intended to levy a share of their income received in organizations of the Russian Federation. This applies to citizens of the Russian Federation and foreigners working on its territory. The tax rate ranges from 13 to 35%, depending on the type of income received and the status of the person receiving it. The tax goes to regional and local budgets.
For information on how to calculate the tax base, see the publication . ”
Not subject to taxation:
- pensions;
- unemployment benefits;
- maternity benefits;
- donor rewards;
- alimony;
- grants to support science;
- international or Russian awards for the highest achievements in various fields of knowledge and art;
- financial assistance to the family of a deceased employee from the company;
- payments to victims of natural disasters;
- income from the sale of harvested wild berries, mushrooms and other forest gifts of nature;
- income from the sale of houses, apartments and other real estate, provided they have been owned for more than 5 years (for properties purchased before 2016, more than 3 years);
- income from inheritance of property;
- income received as a result of gifts from relatives;
- gifts worth less than RUB 4,000;
- other income under Art. 217 NK.
Read more about income not subject to personal income tax here .
2. Income tax for legal entities, which is the main tax payment for them. Taxpayers for this tax are Russian and foreign organizations operating in the Russian Federation. The object of tax collection is the profit received by the organization as a result of its activities in the production and sale of goods. The tax rate for 2020-2021 is 20%.
Find out how profit before tax is calculated (formula) here.
3. Property tax is levied on companies and individuals.
Property is divided into movable and immovable. The concept of movable and immovable property is given in Art. 130 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Real estate is considered to be everything connected with the land (subsoil, the land itself, buildings and structures that are located on it). For a building to be considered real estate, it must be impossible to move it from its location without destruction. Communications must be connected to it. Movable property is considered to be everything that does not fall under the concept of real estate: money, shares, deposits, collections, cars, weapons, etc.
From 2022, movable property is exempt from taxation.
The base for calculating the tax is its average annual value, with the exception of objects whose value is calculated at the cadastral value (clause 2 of Article 375 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Tax rates are specified in Art. 380 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is a regional tax.
For current information on changes in property tax, see the materials in the special section “Organizational property tax - rates, period, etc.”.
Property tax for individuals provides for the withdrawal of tax on real estate objects specified in Art. 401 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It applies to local taxes. The provisions on the cadastral value of real estate objects also apply here (Article 403 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Tax rates and tax benefits are provided for in Art. 406 and 407 respectively. Tax calculation is carried out by the tax service by sending out receipts for payment.
- Land tax is levied on organizations and individuals who own land plots, taking into account their cadastral value. This is also a local tax. There are land plots in respect of which tax is not levied (clause 2 of Article 389 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax rate is established by Art. 394 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Organizations carry out tax calculation and payment independently. For individuals, the Federal Tax Service calculates the tax by sending them receipts for payment.
For information on the specifics of collecting land tax, see the material “Object of taxation of land tax” .
- Transport tax is classified as regional. It is paid by the owners of cars, airplanes and other vehicles listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 358 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Tax rates are given in Art. 361 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Increasing coefficients are provided (clause 2 of Article 362 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) for cars costing more than 3,000,000 rubles. The Code allows for a 10-fold increase in the tax rate, subject to the adoption of a corresponding law by the regional authorities. In relation to car owners, different tax rates are provided depending on the year of manufacture of the car and its environmental class. The calculation and payment of transport tax by legal entities is carried out independently, and by individuals - on the basis of notifications from the Federal Tax Service.
Who are taxpayers
A taxpayer is one who pays taxes. As you know, taxes affect almost every area of our lives, so it is impossible to find a person who does not pay them.
The calculation of taxpayers-motorists is made on the basis of information available about their transport. They go to the tax service after the car is registered with the traffic police. Legal entities must pay the duty and advance payment themselves, without waiting for the tax office to remind you.
Tax for individuals is calculated according to the formula - the tax base is multiplied by the corresponding rate. From this comes the cost that must be paid to the taxpayer.
For legal entities, everything is calculated differently. During the year, an advance payment is made, and the tax itself is calculated from it. When submitting a report, the organization must make a payment.
What are indirect taxes?
Indirect taxes are classified as such because they are levied not on the manufacturer, but on the final buyer. Indirect tax is included in the price of a product or service. The use of these taxes allows us to collect significant funds for government spending. Indirect taxes are used to tax goods in high demand.
Indirect taxes include:
- value added tax;
- excise taxes
Indirect taxes in the form of VAT provide more than 35% of all revenues to the country's budget. This is a federal tax, the essence of which is that it does not tax the entire cost of a produced good or service, but only the added value that appears at different stages of production.
This tax applies to the sale of most goods and services. The tax is not levied on the following categories of goods and services (Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- from some medical goods and services (subclause 1, clause 2);
- when providing premises for rent to foreign organizations (clause 1);
- from medical care services for a citizen who has an appropriate medical certificate (subclause 3, clause 2);
- from the services of organizations providing preschool education of children (subclause 4, clause 2);
- from food products from canteens in medical and educational organizations (subclause 5, clause 2);
- from services provided by archival institutions (subclause 6, clause 2);
- when transporting passengers in a city or other settlement (subclause 7, clause 2);
- when providing funeral services (subclause 8, clause 2);
- from other types of services (subclauses 9–34 clause 2).
The list of goods whose sales are exempt from VAT is given in clause 3 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If there are transactions subject to and not subject to VAT, the company is obliged to carry out separate accounting of them. The same is necessary in the case of using different VAT rates. The rates used for VAT (Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) are as follows: 0, 10 and 20%.
A preferential rate of 0% is used for export operations, international transport, in the space industry, and when transporting oil and gas (clause 1).
The 10% rate is intended to tax the sale of goods and services:
- for food purposes (subclause 1, clause 2);
- for children (subparagraph 2, paragraph 2);
- medical purposes (subclause 4, clause 2);
- periodical press (subparagraph 3, paragraph 2);
- when transported by plane and other air transport;
- when purchasing breeding stock.
Sales of all other goods and services (except those mentioned above) are taxed at a rate of 20%.
With quarterly income below RUB 2,000,000. a company or individual entrepreneur has the right to apply and receive an exemption from VAT.
Read about how to obtain VAT exemption here.
Indirect taxes in the form of VAT are the most complex and controversial to apply. Therefore, there are quite a lot of lawsuits regarding them.
Indirect taxes in the form of excise taxes were initially intended to be used only to tax goods, the demand for which negatively affects the health of the people purchasing them. This applies to tobacco products and alcohol. By introducing this tax they wanted to reduce the consumption of harmful products. Additionally, it was supposed to be extended to luxury goods.
Currently, excise taxes are included in the cost of the following goods (Article 181 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- alcoholic drinks;
- tobacco products;
- cars;
- motorcycles;
- gasoline and diesel fuel;
- various engine oils;
- kerosene for refueling aircraft;
- natural gas;
- fuel for stoves.
Methods and formulas for calculating the amount of excise taxes can be found here .
Tax rates for each type of excisable goods are set out in Art. 193 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Currently, the rates in the Tax Code are indicated until 2022 inclusive. Indirect taxes in the form of excise taxes are calculated based on the tax base of each excisable product. The amount of excise tax is calculated based on the results of each month of sales (Article 192 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Find out about excise tax rates on fuel here.
what is included in direct and indirect taxes in the table.
What does the concept of “transport tax” mean?
The Tax Code of Russia contains all the detailed information on tax terms and rates. There is even a whole paragraph on this topic. In Russia, each entity can apply its own rules and conditions, change rates and interest.
Each subject of the Russian Federation has a state body that makes the following decisions:
- what date to pay the fee;
- what percentage will be deducted;
- what preferential categories will be applied both for citizens of the Russian Federation and for transport;
- in what order the payment will be made.
Transport tax begins to be calculated as soon as the car is purchased.
In the Code you can find a list that will indicate all the objects that are taxed and not taxed. Since 2013, taxation began to apply to all citizens. Government agencies cannot take the entire amount of road costs, so citizens have to pay a certain percentage, so to speak, for using these services.
This is how indirect taxes appear:
- Increase in the cost of gasoline.
- Increase in car prices.
- Road repair fees.
- Toll roads.
Motorists' funds are deposited into the country's budget. If you turn to the Tax Code, or, more precisely, to Chapter 28, you can find out in what order, amount and terms you need to pay taxes.
Table of direct and indirect taxes
All types of taxes can be summarized in a table:
| Type of tax | Tax name | Budgets | ||
| federal | regional | local | ||
| Direct taxes | For individuals | |||
| Personal income tax | v | |||
| Property tax | v | |||
| Transport tax | v | |||
| Land tax | v | |||
| Water tax | v | |||
| For legal entities | ||||
| Income tax | v | |||
| Personal income tax from employees | v | |||
| Property tax | v | |||
| Transport tax | v | |||
| Land tax | v | |||
| MET | v | |||
| Gambling tax | v | |||
| Water tax | v | |||
| Trade fee | v | |||
| Indirect taxes | VAT | v | ||
| Excise tax | v | |||
Who pays tax and where?
Taxpayers are considered to be all organizations conducting entrepreneurial activities in the gambling business. Individual entrepreneurs cannot pay such a tax - only legal entities act as organizers of gambling.
From July 1, 2009, special play areas were created. In 2019, they were geographically located as follows:
- Altai Territory - “Siberian Coin”
- Krasnodar region - “Krasnaya Polyana”;
- Primorsky Krai - “Primorye”;
- Kaliningrad region - “Yantarnaya”;
- The Republic of Crimea is in the project.
Outside these zones, gambling can only be carried out in bookmakers' offices and betting shops. All operations of the gambling business are regulated by Federal Law No. 244-FZ dated December 29, 2006.
Despite the “legalization” of the gambling business, many casinos have gone online or underground. Such attempts to conduct business are illegal. According to the amendments that came into force in January 2015, the organizer of online gambling bears criminal or administrative liability. In addition, distributing online casino advertising also entails liability for the site owner.
Results
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for a gradation of taxes into direct and indirect. Direct taxes are paid by the taxpayer on his income. Indirect taxes are included in the price of a product or service and are paid by the final buyer. And it is the responsibility of the taxpayer to timely transfer received indirect taxes to the budget.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What affects the amount of tax
The following factors influence the amount of transport tax:
- engine power;
- car category;
- vehicle service life;
- region of residence of the car owner and place of registration of the car itself.
For the calculation, the coefficient and tax rate are important, which are established differently in each region. If the above list is a constant value, then the coefficient and tax rate are regularly increased.
The coefficient increases only when the price of the car exceeds 3 million rubles.
Benefits that help you avoid taxes
In each region, preferential categories may be different, depending on the decision of the regional authorities. Some beneficiaries may be exempt from tax only partially, while some citizens may be completely exempt.
The first category includes:
- war veterans,
- people who eliminated the consequences of the Chernobyl accident,
- disabled people of groups 1 and 2,
- families that are recognized as having many children.
Car owners are required to independently notify the tax service of their rights to use benefits.
You just need to contact the tax service at your place of registration, submit an application, the necessary documents and wait until the status is updated. Along with general benefits, there are also local ones.
They operate for a certain period of time:
- For example, in the Jewish Autonomous Region the tax was canceled for those who suffered from a flood, in Khakassia - from a fire.
- There are many regions where people engage in agriculture. Therefore, farm-owned vehicles may be partially or fully tax exempt.
- Individual entrepreneurs and legal entities in Novosibirsk pay only 10% for transport tax if their cars run on natural gas.
Payment must be made every year by December 1st. It follows that in 2022, payments for 2022 will be made at the rates that were in effect that year.
If the fee is not paid, this will lead to certain consequences - penalties will be charged, and the case may also be transferred to bailiffs, and they will demand payment.