Purchasing goods for the principal: algorithm for re-issuing an invoice
When purchasing goods for the principal, the chain of interaction for issuing an invoice differs from that described above:
- the supplier issues an invoice in your name (as an agent) and registers it in its sales book;
- you enter it in part 2 of your invoice journal;
- then, on your behalf, issue an invoice with similar indicators to the principal (indicate the actual supplier as the seller) and record it in Part 1 of the accounting journal;
- The principal records the invoice received from you in his purchase ledger.
Familiarize yourself with the position of the Ministry of Finance on the nuances of issuing agency invoices.
If an agent purchased goods for several principals and the invoice contains data for the entire purchase, when re-issuing an invoice to each principal, the agent must transfer information only on those goods (services or works) that were intended specifically for this principal (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated April 18 .2014 No. GD-4-7/ [email protected] ).
Read about deducting VAT from the principal when purchasing goods through a chain of intermediaries here.
Export of commodities confirmed 180 days
Input VAT on raw materials, works and services can be deducted after confirmation (or non-confirmation) of the 0% rate. Wherein:
- separate accounting of incoming VAT is maintained;
- input VAT accepted for deduction on such goods is reflected in the VAT return: in Section 4 - if the documents are collected within 180 calendar days,
- in Section 6 (updated declaration) - if the documents are not collected within the period of 180 calendar days,
- in Section 5 - if the right to deduction arose after confirmation or non-confirmation of the 0% rate.
Changes in 1C regarding deductions:
- Accepted for deduction when purchasing non-commodity goods for export;
- Blocked until confirmation 0% - accounting for input VAT only for transactions at a rate of 0% for which confirmation is required (export of raw materials, works, services);
- Distributed – maintaining separate accounting of incoming VAT for general expenses. The share of input VAT related to the 0% rate in the VAT Distribution and when it is carried out, the input VAT also acquires the methods Accepted for deduction and Blocked until 0% is confirmed.
VAT deductible on export:
- when the rate is confirmed as 0% - accounting for input VAT only for export transactions is carried out on account 19 using the method Blocked until confirmation of 0% ;
- as a result of separate accounting of VAT on total expenses - the share of incoming VAT related to exports is determined in the VAT Distribution and when it is carried out, the incoming VAT also acquires the method Blocked until confirmation 0% .
It is reflected in Section 4, page 030 and Section 8 in the usual manner, as are deductions in the domestic market (column 16 of the Purchase Book).
page 010 Operation type code:
- code “01” Shipment or purchase of goods, works, services, rights, incl. transactions taxed at a rate of 0%;
- code “25” Registration of invoices in the purchase book in relation to tax amounts previously restored when performing transactions taxed at a rate of 0%. In the purchase book in gr. 9 our organization must be indicated, not the supplier (Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated September 20, 2016 N SD-4-3/17657).
Document Formation of purchase ledger entries – checkbox Submitted for deduction of VAT 0% .
Cost of purchases according to the invoice (column 15 of the Purchase Book):
- the total amount of the invoice indicated in gr. 9 invoices on the “Total payable” page (including VAT).
p. 180 Amount of tax accepted for deduction (column 16 of the Purchase Book):
- amount of VAT to be deducted.
With separate accounting, as a rule, VAT will be partially deducted. Verification algorithm in the Federal Tax Service: “VAT charged by the seller may exceed the VAT declared by the buyer for deduction.”
How can an intermediary, forwarder, or developer issue an invoice?
The procedure for filling out an invoice by intermediaries (developers, forwarders) is indicated in the table:
| Line number (columns) of the invoice | Content |
| Line 1 |
The serial numbers of such invoices are indicated by each taxpayer in accordance with their individual chronology of invoicing |
| Line 1a | The serial number of the correction made to the invoice and the date of this correction. When drawing up an invoice, before making corrections to it, a dash is placed in this line |
| Line 2 |
|
| Line 2a |
|
| Line 2b |
|
| Line 3 | The intermediary indicates the full or abbreviated name of the shipper in accordance with the constituent documents. If the seller and shipper:
When drawing up an invoice for work performed (services provided), property rights, the seller puts a dash in this line. When drawing up an invoice by a commission agent (agent) purchasing goods and materials from two or more sellers on his own behalf, the full or abbreviated names of the shippers and their postal addresses are indicated (through the sign “;” (semicolon)) |
| Line 4 | The intermediary indicates the full or abbreviated name of the consignee in accordance with the constituent documents and his postal address. When drawing up an invoice for work performed (services provided), property rights, the seller puts a dash in this line. When the principal (principal) draws up an invoice issued to a commission agent (agent) selling 2 or more goods and services buyers on his own behalf, the full or abbreviated names of consignees and their postal addresses are indicated (through the sign “;” (semicolon)) |
| Line 5 |
|
| Line 5a | Details of the invoice or act on which the invoice was drawn up |
| Line 6 |
|
| Line 6a | The address of the buyer indicated in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, within the location of the legal entity, the place of residence of the individual entrepreneur indicated in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs - when the principal (principal) draws up an invoice issued to the commission agent (agent) selling goods and services on his own behalf |
| Line 6b | The intermediary indicates the INN and KPP of the taxpayer-buyers through the sign “;” (semicolon) |
| line 7 | The intermediary indicates the name of the currency for the goods listed in the invoice and its digital code in accordance with OKV (All-Russian Classifier of Currencies) |
| Line 8 | The line is filled in when issuing an invoice under a government contract for the supply of goods (performance of work, provision of services), a contract (agreement) on the provision of subsidies from the federal budget to a legal entity, budget investments, contributions to the authorized capital (if any) |
| Box 1 |
|
| Box 1a | The column is intended to reflect the code of the type of product in accordance with the unified Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the EAEU. The data is indicated in relation to goods exported outside the territory of the Russian Federation to the territory of a member state of the EAEU; If there is no data, a dash is placed |
| Columns 2 and 2a | If there is an indicator, a unit of measurement (code and the corresponding symbol (national) in accordance with sections 1 and 2 of the All-Russian Classifier of Units of Measurement) (if it is possible to indicate it). If there are no indicators, a dash is placed |
| Column 3 | Quantity (volume) of goods (work, services) supplied (shipped) according to the invoice of the principal (principal) based on the accepted units of measurement (if it is possible to indicate them) |
| Column 4 | The price (tariff) of a product (work performed, service rendered), transferred property right per unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it) under an agreement (contract) excluding VAT, and in the case of using state regulated prices (tariffs) that include VAT, taking into account the amount of tax. If there is no indicator, a dash is placed |
| Box 5 | The cost of the entire quantity (volume) of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice of GWS without VAT |
| Box 6 | The amount of excise duty on excisable goods. If there is no indicator, the entry is made: “Without excise tax” |
| Column 7 | Tax rate |
| Column 8 | VAT amount |
| Column 9 | The cost of the entire quantity of goods and materials supplied (shipped) according to the invoice, including VAT, and in the case of receiving a payment amount, partial payment on account of upcoming supplies of goods and materials - the received amount of payment, partial payment |
| Columns 10 10a | Country of origin of the product (numeric code and corresponding short name) in accordance with the All-Russian Classifier of Countries of the World. These columns are filled in for goods whose country of origin is not the Russian Federation |
| Box 11 | Registration number of the batch of goods subject to traceability |
| Columns 12 and 12a | In these columns you need to reflect the unit of measurement of the product that is used for traceability. It is determined according to the All-Russian Classifier of Units of Measurement |
| Box 13 | Quantity of goods in specified units |
Note! Sellers of goods subject to traceability must issue invoices in electronic form (clause 1.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And buyers of goods subject to traceability must ensure the receipt of electronic invoices via telecommunication channels (clause 1.2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Adjustment invoice for the return of goods (accounting with the Seller) (valid until 01/01/2019)
From 01/01/2019, return goods using the Sales Adjustment .
Find out more Processing a return to the buyer from 01/01/2019
How is the operation of returning goods recorded in the seller's accounting?
- if part of the goods is returned, this means that ownership of the goods has not been transferred, so the seller needs to reverse the proceeds using the “red reversal” method.
How to reflect the transaction to the seller in 1C?
- using the document Adjustment of implementation - type of operation Adjustment by agreement of the parties.
Adjustment scheme for VAT accounting
Step 1. Reflection of the return of not accepted goods (quantity adjustment).
Step 2. Issuance by the seller of an adjustment invoice to reduce the quantity of goods as agreed by the parties.
Step 3. Acceptance of VAT for deduction by the seller for the difference associated with a decrease in the quantity of goods according to the adjustment invoice. The deduction is reflected in the purchase book in the period when the adjustment is made as agreed by the parties. The deduction can be reflected no later than three years from the date of drawing up the adjustment invoice (clause 13 of article 171, clause 10 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Step 4. Drawing up and submitting to the Federal Tax Service a VAT return for the quarter in which the adjustment took place, where the amount of the VAT difference for the adjustment SF:
- taken into account on page 120 of Section 3,
- reflected in page 180 of Section 8.
page 010 Operation type code - code “18” Drawing up or receiving an adjustment invoice in connection with a change in the cost of shipped goods (works, services), rights.
pp. 020-030 Number and date of the seller’s invoice (column 3 of the Purchase Book) - indicates the number and date of the “primary” seller’s invoice for which the CSF is issued.
pp. 060, 070 Number and date of the seller’s adjustment invoice (column 5 of the Purchase Book) - is indicated in exact accordance with the number and date of the seller’s adjustment invoice.
p. 170 Cost of purchases according to the invoice (column 15 of the Purchase Book) - data from gr. 9 KSF on the page “Total decrease” (including VAT) when the seller reflects the KSF purchases for a decrease in value in the book.
p. 180 The amount of tax accepted for deduction (column 16 of the Purchase Ledger) is the amount of VAT to be deducted when the seller reflects the CSF purchase book for a decrease in value (corresponds to the amount of tax under column 8 of the CSF on the page “Total reduction”).
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
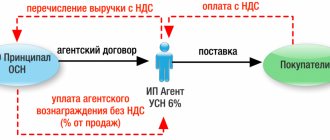
When does an agent need to issue an additional invoice?
In addition to shipping invoices (the procedure for issuing which is described above), the agent must issue another one to the principal. This need arises for agents who pay VAT.
This is due to the fact that for an agent - a VAT payer, income for tax purposes is the remuneration under the agency agreement (clause 1 of Article 156 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore, for its amount the agent:
- issues an invoice to the principal (as in the normal sale of goods, work or services);
- registers it in the sales book with code 01 (Articles 168–169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The costs transferred by the agent to the principal under the agency agreement (related to its execution) do not form an object of VAT taxation - the agent does not need to take into account their amount when calculating income tax (subclause 9, clause 1, article 251, clause 9, article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
Find out when and how consolidated invoices can be issued in agency relationships.
VAT tax agent
The right to deduction arises only from tax agents - VAT payers:
- when purchasing goods, works, services from a foreign person on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- when leasing federal (municipal) property from government bodies;
- from shipowners.
The right to deduction arises when the following conditions are simultaneously met:
- goods, works, services were accepted by the tax agent;
- the service is used by a tax agent for activities subject to VAT;
- VAT is paid to the budget by the tax agent.
Tax agents have the right to deduct VAT in the tax period when it was actually paid (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 23, 2013 N 03-07-11/44418, dated January 13, 2011 N 03-07-08/06), arbitration practice (Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated January 28, 2013 N A56-71652/2011 and dated March 21, 2012 N A56-38166/2011).
Can an NA claim a deduction for advance payments transferred to foreigners (clause 12 of article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 9 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)?
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation thinks - NO! Since the deduction can only be made in the tax period in which the work (services) was accepted for accounting. There is no invoice issued by the seller necessary to accept the deduction (clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 04/06/2016 N 03-07-08/19500).
The tax agent cannot exercise the right to transfer the deduction for 3 years, only during the period when the conditions for applying the deduction are met (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 17, 2016 N 03-07-08/67622).
Control ratio for VAT tax agents
Checking compliance with the control ratio (CR) of the Federal Tax Service:
- If codes 1011711 and 1011703 are present in Section 2 p. 070, then this CS must be carried out. If it is not fulfilled, then this indicates an overstatement of the amount of VAT to be deducted.
News for tax agents on VAT
As of January 1, 2018, a new clause 8 of Art. 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Federal Law of November 27, 2017 N 335-FZ). According to it, VAT taxpayers purchasing:
- raw animal skins,
- scrap and waste of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, secondary aluminum and its alloys,
become tax agents for VAT.
Invoice and agent report: what to look for
When preparing an invoice, it is important for the agent to ensure that the information indicated there is identical to the data reflected in another important document - the agent’s report. The invoice data and the agent's report should not differ in information about the quantity of goods, their price and other indicators.
The presence of discrepancies may indicate:
- about arithmetic or technical errors made - in this case you will have to start correcting an incorrectly drawn up document;
Find out the algorithms for correcting erroneous data in an invoice on our website .
- adjustments to the price and/or quantity that have occurred that have not been taken into account by the agent, which requires the execution of an additional agreement to coordinate the changes and an adjustment invoice.
Inconsistencies in documents may be caused by:
- discounts provided by sellers and not taken into account by the agent when compiling the report;
- revision of prices in the conditions of initial shipment of goods at preliminary prices;
- in other cases (when returning goods, identifying shortages or discrepancies in quality, etc.).
The articles posted on our website will help you correctly correct errors that arise in your current business activities:
- “How to make a correction in a work book - sample”;
- “Corrections in the cashier-operator’s journal - sample”.
Results
The agent, as a link between the principal and a third party (buyer or supplier), is responsible for re-invoicing. An agent selling on his own behalf the goods of the principal in invoices issued in the name of buyers indicates himself as a seller. Using such a document, the buyer can safely claim a VAT deduction. If the agent purchases goods or services on behalf of the principal, then when re-invoicing he must indicate information about the supplier on pages 2, 2a and 2b.
Download step-by-step instructions for re-invoicing here .
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.