What is currency control and what does it consist of?
This is a set of regulatory measures. The term can also be defined as the management of operations with domestic and foreign currencies in business carried out on the international market. This is extremely important for the legalization of transactions within the framework of foreign economic activity. Typically, the list of such events includes the following:
- a system for regulating the acquisition and settlements in foreign currency on the territory of the state;
- licensing of purchase and sale of valuables;
- monitoring the movement of money across the state border;
- coordination of payments for import and export.
The work of government regulatory structures is organized in such a way that interference in business activities is minimal and does not interfere with law-abiding businessmen.
Basic principles:
- exclusion of unjustified interference of the state and its bodies in foreign exchange transactions of residents and non-residents;
- priority of economic measures in the implementation of state policy in the field of currency regulation;
- unity of foreign and domestic monetary policy of the Russian Federation;
- unified system of VC and regulation;
- provision by the state of protection of the rights and economic interests of residents and non-residents when carrying out currency transactions.
Criticism
Since the mid-2010s, the Russian authorities have been intensively implementing the ideas of weakening foreign exchange controls. During this time, legislation has undergone several resonant changes, in particular the following:
- cancellation of the transaction passport - a document that the bank prepared for an import or export contract;
- liberalization of requirements for the use of accounts in foreign banks by individuals;
- non-resource non-energy companies were allowed not to return foreign exchange earnings to the country;
- requirements for repatriation (return of money from other states to Russia) of foreign currency earnings extended to loan agreements concluded between residents and non-residents;
- liberalization of foreign exchange transactions, according to which it is possible not to submit a report to those who have no more than 600,000 rubles in foreign currency equivalent in their account or deposit abroad;
- launch of the “One Window” system, designed to simplify life for participants in foreign economic activity regarding the regulation of the nuances of internal control, as well as interaction with tax and customs authorities.
At the same time, in some areas the currency legislation has become stricter:
- new reasons for fines for violating the requirements for repatriation of funds have appeared;
- control over the foreign accounts of Russian companies has been strengthened, including the repatriation of foreign currency earnings - even for minor delays, companies risk running into fines;
- tax authorities began to use the “sleeping” exchange control norm;
- individuals and organizations were required to report on the movement of funds in non-bank financial institutions and through foreign electronic wallets if the amount of incoming transfers exceeds 600,000 rubles per year.
Compliance with some requirements of currency regulation is sometimes brought to the point of absurdity, Forbes said: “Among the loudest is the imposition of a fine on a citizen whose payment was stuck in a foreign bank and returned not to the Russian bank, but to another financial organization abroad.”
The Center for Strategic Development called for the abolition of currency controls. According to the organization’s specialists, currency restrictions and, in particular, requirements for the repatriation of Russian and foreign currency received by companies under foreign trade contracts, interfere with cross-border business and do not contribute to the stability of the Russian currency. However, the Bank of Russia actively opposes the liberalization of foreign exchange controls. The Central Bank is convinced that without the requirement for mandatory repatriation of foreign currency earnings, the fight against money laundering and the financing of terrorism is unthinkable.
Why do we need currency control?
The main goals of VK activities can be identified:
- regulation of foreign exchange transactions;
- checking contracts with non-residents for compliance with basic requirements;
- eliminating the risk of providing false reports and inaccurate information contained in them.
For organizations that are going to use foreign economic activity (foreign economic activity) in practice, it is necessary to understand exactly what it is, why currency control is needed and what it means for the bank. If you adhere to deadlines, prepare documents correctly and follow up on transactions in a manner regulated by law, the company will be able to avoid penalties and not waste unnecessary time.
What applies to foreign exchange transactions at the legislative level?
Currency transactions are defined by Law No. 173-FZ of December 10, 2003. Article 1 lists the basic terms and the concept of foreign exchange transactions. According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, foreign exchange transactions include:
- acquisition, alienation by a resident from a non-resident (or vice versa) of any currency, securities, their use for payment;
- purchase, alienation of currency values between residents (this can be a gift, purchase and sale, inheritance);
- import into Russia and export from Russia of securities, currency, including rubles;
- acquisition, alienation of securities and currency between non-residents;
- transfer of securities and currency from a Russian account to a foreign one or vice versa;
- transfer of Russian currency from Russia abroad or vice versa, making a transfer to a resident’s account or as to one’s own;
- transfer by a non-resident of currency or securities from a Russian account to a foreign one.
Residents are individuals with Russian citizenship or people who permanently reside in the Russian Federation. Residents include organizations and companies registered in Russia, foreigners with a residence permit, and consular missions of the Russian Federation located abroad.
Non-residents are foreigners, representative offices of foreign states, interstate and intergovernmental organizations (their branches) in Russia. Non-residents can be companies registered and operating in other countries.
Law No. 173 Federal Law establishes that there are no restrictions on currency transactions between non-residents and residents. Article 9 of this law establishes restrictions only on foreign exchange transactions for payments for goods that were purchased from a Russian company. Payment can be made in rubles.
Who carries out currency control in the Russian Federation
The system is multi-level and is not represented by one person. The leading structural unit is the Government of the Russian Federation. It is developing a regulatory framework that addresses issues of foreign exchange transactions by domestic counterparties and foreigners. Other entities carry out supervisory activities over the implementation of legally established requirements.
Let's consider which authorized structures are responsible for implementing currency control (for example, banks), their responsibilities in Russia:
- Central Bank of Russia.
- Federal customs and tax services.
- Individual entrepreneurs (those in the register of investment advisers) and legal entities - managers, brokers, investment advisers, registrars, dealers, depositories.
- VEB.RF is a state development corporation.
- Authorized banks.
Commercial banks of the Russian Federation perform the functions of VC agents in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation and instructions of currency control authorities. Typically, this activity includes:
- accounting of international contracts;
- checking documents justifying the operation;
- identifying facts of violations of laws;
- informing authorities and currency control agents about currency transactions and identified violations in the manner prescribed by law;
- carrying out transactions not related to commercial activities.
Almost all banking structures provide consultations for business representatives regarding VC.
How is the legality of a transaction using currency confirmed?
The list of documents to confirm the legality of a transaction varies. The number of securities, as a rule, depends on the type of transaction. The bank requests documents from the client, who, in turn, is obliged to provide them within the established time frame.
In accordance with Art. 23 173-FZ, currency control authorities and agents have the right to request documents from companies within a period of at least 7 working days. The exact period is counted from the moment the company receives the request.
The list of documents sent by the company at the request of currency control authorities and agents is specified in the same article of the federal law. The list is provided in an exhaustive form, but it is not necessary to fully apply it in every case. The documents requested for verification include the following:
- Identification.
- Certificate of registration as an individual entrepreneur.
- Data on registration of a legal entity (for residents).
- Information about property rights.
- Certificates of registration with the tax authority.
- Registration documents.
- Draft documentation related to currency transactions.
- Documents and data issued by credit institutions - statements, bank control statements.
- Customs declarations.
- Transaction passport.
- Insurance contracts.
- Written notifications about the assignment of claims to a factor (financial agent).
Agents and currency control authorities have the right to request only those documents that directly relate to a specific transaction. Moreover, all documents must be valid at the time of their submission to the control authorities. The data is provided in the original or in a copy certified in a special form.
How to pass it
Features and recommendations, compliance with which will help to successfully complete the process:
- In agreements concluded between participants in foreign trade activities, all conditions, including deadlines, must always be spelled out in detail.
- Cash payments must be made within the terms established by the agreement. The legal entity is obliged to identify the funds received by the bank within 15 working days (provide the bank with documents justifying the receipt of money). If the amount under the agreement exceeds 6 million rubles, it is subject to mandatory bank accounting.
- Additionally, it will be necessary to provide a certificate of supporting documents.
How to open a foreign currency account
Opening is necessary for conducting operations by a legal entity and entrepreneur, such as:
- settlements with international partners in foreign currency without conversion;
- obtaining borrowed funds;
- investments in foreign organizations;
- acquisition of shares, bonds and other securities;
- payment for real estate;
- purchase and storage of foreign currency;
- receiving interest on deposits;
- remuneration of company employees under labor and civil law contracts.
Typically, opening an account is free for business representatives. You only need to pay for servicing a specific package of services. First of all, you need to go to the official portal of the bank and leave an electronic application. Then you will need to provide a complete list of documentation. The verification is usually carried out within 1-3 business days, after which an agreement is signed for servicing the account by the banking organization.
Open a business account at SEA BANK and receive up to 6% on your account balance!
How to convert currency to rubles
To account for transactions in foreign currency, the date on which you should take the Central Bank exchange rate and convert the currency into rubles is very important. As already mentioned, in Russia, accounting for foreign exchange transactions is carried out exclusively in rubles, and since exchange rates are constantly changing, it is important to know the “correct” moment of converting currency indicators into rubles.
Thus, in order to be reflected in accounting and reporting, the cost values of liabilities and assets of a legal entity expressed in foreign currency, as well as the amount of reserves in foreign currency, must be converted into rubles.
In accounting for foreign exchange transactions, only the official exchange rate of the Central Bank of a given currency to the ruble is used to convert cost indicators into Russian rubles. The exception is cases when, in order to convert the value of a monetary obligation or a tangible asset into rubles, a special law or agreement establishes a different rate at which the amount payable must be recalculated.
The date of conversion of currency indicators into rubles is different for each operation. Most often, the date of conversion at the official exchange rate is the moment when the business operation is carried out. In the case where over the course of a month (or a shorter time period) an enterprise carries out a large number of similar transactions in foreign currency, and the official exchange rate has not undergone significant changes, it is possible to keep records of transactions in foreign currency of this type at the rate averaged over a given period of time.
PBU 3/2006 clearly defines all the moments when currency amounts should be converted into rubles:
- On the date of the business operation (when cash flows), as well as on the reporting date (balances at the cash desk/account), it is necessary to convert into rubles all cash/non-cash currency at the cash desk/on the foreign exchange account. Also, in a number of situations, the value of funds may be recalculated as the exchange rate changes.
- Cash/non-cash currency is recalculated at the rate existing at the reporting date in order to reflect the data in the financial statements.
- As of the date of the business transaction, the value of fixed assets, intangible and other non-current assets accepted for accounting, as well as the value of inventories and other assets, with the exception of cash, is recalculated.
- On the date of recognition of foreign currency income or expenses, they are recalculated into rubles. As for the date of recognition of travel expenses, it coincides with the moment of approval of the traveler’s advance report.
- On the date of recognition of costs that form the cost of fixed assets, intangible and other non-current assets, the amount of investments in foreign currency in these non-current assets is recalculated into Russian rubles.
- If an enterprise has received an advance payment in the form of a deposit or an advance payment, then these funds are accounted for in accounting in Russian rubles at the exchange rate at the time of receipt of the specified amounts.
- If the prepayment was paid by the company (in the form of transfer of a deposit or payment of an advance against the delivery of assets or for expected expenses), then this payment will be reflected in the accounting records in rubles at the rate prevailing on the date of payment.
After non-current assets, transferred or received advances have been reflected in accounting, their value is not recalculated when the exchange rate changes.
Read about what points you need to pay special attention to when organizing accounting for foreign economic activity in the article “Features of accounting for foreign economic activity .
What operations fall under VC
The objects of regulation are the norms of legislation relating to transactions. For example, Russian residents are prohibited from paying each other in foreign currency. The only exception is the Russian ruble and a number of transactions provided for by law. It turns out that transactions carried out between constituent entities of the Russian Federation and foreign enterprises in any monetary units are subject to currency regulation.
The list of currency transactions is determined by clause 9 of Article 1 of the Law on Currency Regulation and Currency Control 173-FZ.
All foreign exchange transactions are subject to exchange control, including:
- loans, credits;
- foreign trade transactions;
- provision of services;
- sale or acquisition of a property share of a legal entity;
- processes relating to the alienation and purchase of securities;
- transfers by residents of the country to their own accounts or to the accounts of other residents opened abroad.
Results
Currency regulation and control bodies in the Russian Federation consist of:
- from the Government of the Russian Federation and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, combining the functions of regulation and control;
- sectoral and intersectoral executive authorities (currency control bodies), whose competence includes certain aspects of currency legal relations;
- currency control agents - authorized banks and structures equivalent to them, as well as Vnesheconombank. Agents carry out functions of control and collection and transmission of information in the field of currency regulation.
It is impossible to single out a single main body of currency control and regulation.
In terms of powers and functionality, the Government of the Russian Federation and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation are in an equivalent position. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
In what cases is a contract registered?
To legally consolidate and regulate foreign trade activities, certain types of agreements must be registered with an authorized bank. The requirements are imposed by law and apply to export transactions the amount of which is equal to or exceeds 6 million rubles. And also to import transactions and loan agreements, the amount of which is equal to or exceeds 3 million rubles.
Those. Such transactions will include:
- Item. This includes goods, services, work performed, leasing, rental relations, intellectual property, commodity values along the way and in intermediate territories.
- Contract value. From 3 million rubles when it comes to importing credit agreements and borrowed funds, from 6 million when exporting.
In addition, the agreement is registered if the process is at the planning stage. However, in this case, the counterparties must have a project in their hands. The agreement must contain:
- contract date;
- the subject of the contractual relationship (it is important to describe in detail the product or service being sold);
- currency used, total cost;
- deadlines for fulfilling obligations;
- detailed details of the parties.
Salary in foreign currency: nuances
According to Art. 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages at domestic enterprises must be paid in rubles.
Find out from this publication whether an improperly executed employment contract can lead to an unscheduled labor inspection.
The issuance of earned money in the form of foreign currency is regarded as a violation for the following reasons:
- A change in the exchange rate of the ruble to a given currency may lead to the fact that the real salary will be less than it is established in the staffing table. That is, there will be a deterioration in wage conditions, which is considered a punishable act. Sanctions for such violations are determined by Part 1 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
- Salaries can be paid through a cash desk, and foreign currency can be issued in cash only for business travel purposes. Tax authorities may regard such an operation as a violation of currency laws.
Moreover, citing the fact that such payments are a violation of labor laws, tax authorities during audits may generally exclude such payments from expenses.
It is allowed to pay wages in the following currency:
- resident employees, if they actually perform their labor duties outside the territory of the Russian Federation (clause 26, part 1, article 9 and part 2, article 14 of law No. 173-FZ, letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 04.04.2018 No. OA-4-17 / [email protected] );
- non-resident employees (Part 2 of Article 14 of Law No. 173-FZ, letter of the Federal Tax Service dated January 12, 2018 No. OA-4-17 / [email protected] ).
Find out more about who can receive a salary in foreign currency from this article.
Will an employer be fined if he evades wage indexation, the publication “Fine for non-indexation of wages - under what article and by how much?” will tell you..
Documents for currency control
To register a contract, you will need the following documentation:
- agreement (extract from the contract) or a draft prepared by the parties;
- data on deadlines for fulfilling obligations;
- other information that may be required by the bank.
If the contract is transferred for servicing to another authorized bank, it is important to indicate the unique contract number and other information necessary for the transfer. When there has been an assignment of rights under a transaction, such a document must be provided.
When fulfilling or terminating obligations, changing the person in the obligation, changing the amount of obligations under a registered contract, residents are required to draw up and submit to the bank a certificate of supporting documents. Also, the functions of the currency control department in the bank include requesting data on ongoing transactions. This includes the following information:
- transaction type code;
- unique contract number;
- return time information on expected repatriation times.
How is currency control carried out in practice?
Currency control services are provided by all credit organizations operating in the cash settlement services segment. Consequently, this service is mandatory in most cases. In order to understand the principle of currency control, it is enough to simulate a typical situation.
If a company earns money in foreign currency, then on the way to receiving money it passes one serious obstacle. This obstacle is currency control. That is, the company will not be able to withdraw money or dispose of it in any other way until it proves the nature of its legal origin.
Regulation is carried out in order to control the implementation of transactions: companies and entrepreneurs are checked for facts of money laundering, terrorist financing, cooperation with fraudsters, and the purchase and sale of goods prohibited for circulation in Russia.
Currency control using the example of Alfa-Bank →
For companies providing services, currency control always starts with the credit institution. When money from a transaction arrives at the bank, it does not immediately appear in the company’s account—the bank must check the legality and purity of the transaction or individual operation. If the bank doubts the legality of a transaction/individual operation, it will not release the money to the client until the client provides supporting documents.
Documentation submission deadline
If a write-off is carried out, this occurs simultaneously with the provision of a write-off order. Enrollment documents must be provided within 15 working days. The regulated period for transfer to another banking organization or assignment of rights under a transaction is 30 days (excluding weekends).
Supporting documentation is sent within 15 days of the following circumstances:
- months of registration of the declaration for the export and import of goods, execution of documents confirming the fulfillment of obligations under the contract;
- dates of registration of adjustment documents.
Classification of foreign exchange transactions
Classification of currency transactions is carried out according to different criteria. The object includes transactions with rubles, foreign currency, foreign and Russian securities. Operations are classified by subject:
- between non-residents;
- between currency residents;
- between currency residents and non-residents.
Foreign exchange transactions are divided into groups according to the nature of the transaction:
- export-import operations;
- transactions on the client’s bank foreign currency account;
- foreign exchange trading;
- international lending;
- the country's acquisition of foreign currency.
There is another classification of currency transactions performed:
- by deadlines (current, capital, cash transactions with currency);
- active and passive operations (in accordance with accounting);
- operations performed by residents and non-residents;
- aimed at achieving different goals (performed in the entrepreneur’s own interests or in the interests of clients).
There are other types of foreign exchange transactions:
- such transactions that take place through a bank or cash desk;
- purchase of intangible assets, fixed assets, inventories for foreign currency;
- expenses and income in foreign currency;
- fixed assets.
A separate group includes currency conversion transactions, which are carried out for the purpose of exchanging one currency for another. In this case, the difference in rates at the time of the currency transaction must be taken into account. Exchange rates change every day. When converting foreign currency into rubles, an exchange rate difference is formed. Such exchange rate difference must be attributed to the company's expenses or income.
Price
The regulation of certain categories of payments is directly dependent on the total amount under the agreement. For example, for transactions within the framework of recorded contracts (3 million rubles or more), it is necessary to provide information about its unique number and send supporting documents, which include various acts and invoices.
If all points of the agreement are fulfilled (not through settlements), then simultaneously with acceptance for accounting, along with the latest papers, a certificate of supporting documentation is drawn up.
If it is necessary to confirm transactions that are not subject to bank exchange control (less than the amount specified above), only supporting evidence is used, including agreements, declarations, etc.
When the cost of an agreement with foreign partners does not exceed 200 thousand rubles, a simplified monitoring procedure is carried out. You will only need information that relates to currency transactions. Regardless of the contract amount, the banking organization has the right to request additional papers and demand clarification. This is done in cases where the legality is in question.
Currency account: how to keep track of transactions
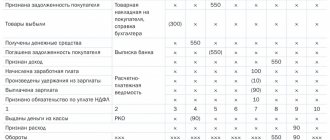
To keep records of foreign exchange transactions for foreign exchange settlements, there is a separate synthetic account 52 in the chart of accounts. The main basis for entering information into accounting for this account is bank statements. The credit of the account reflects transactions involving the transfer and debit of foreign currency funds from the account.
The debit of this active account reflects:
- at the beginning of the month - the balance of non-cash foreign currency;
- during the month - all foreign exchange earnings.
In accounting, currency balances on accounts are reflected in ruble revaluation. Make sure that you recalculate correctly and reflect the revaluation in accounting and tax accounting according to established rules using a Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. You can get demo access to the K+ system absolutely free.
If, when checking bank statements, the company discovers errors when posting or debiting money from a foreign currency account, then they are reflected in the “Claims” subaccount opened to account 76.
For account 52, for the convenience of maintaining analytical accounting, it is customary to open sub-accounts of the 1st and 2nd order. Sub-accounts of the 1st order: 52-1 “Accounts in foreign currency within the state” and 52-2 “Accounts in foreign currency abroad.” Subaccounts of the 2nd order help to maintain separate accounting for accounts opened in different currencies. But most often, 2nd order subaccounts are created to reflect transactions on current, transit and special transit accounts.
A transit account in foreign currency was previously used for the mandatory sale of foreign currency earnings that were transferred by non-residents as payment for services or products. After the sale of the required amount of foreign currency, the remaining amount in the transit account was transferred by the bank to the client’s current account opened in foreign currency. Now the transit account is used to record on it amounts for which information has not yet been submitted to the bank confirming that the foreign currency receipts belong to a specific agreement.
The company's regular (current) account, opened in foreign currency, is credited with its foreign currency earnings, bank interest for the use of available funds and other foreign currency earnings related to business activities. Foreign currency accounts abroad, in accordance with federal legislation, can be opened for transactions related to the movement of capital investments.
A transit special account in foreign currency is opened by an authorized bank independently without the participation of the client. Such an account is needed to record foreign exchange transactions related to the purchase/sale of currency.
Companies usually store all available funds in foreign currency in foreign currency accounts of those banks that have appropriate licenses for the right to conduct foreign exchange transactions issued by the Central Bank. To open a foreign currency account abroad, you will need to obtain appropriate permission from the Central Bank of Russia.
Each bank foreign currency account is usually maintained in the currency that the bank client indicated when opening it. If another currency is received into this account, the bank will independently convert it under the conditions specified in the account servicing agreement. The currency is converted according to the international foreign exchange market exchange rate valid on the day of transfer.
To record currency transactions, active account 55 can also be used. It summarizes information on the availability/movement of money in Russia and abroad, both in Russian rubles and in foreign currency: in check books, letters of credit, on deposits and in other payment forms (except for bills of exchange). For each of the payment forms, 1st order subaccounts are opened for account 55. Analytical accounting is maintained for each letter of credit, deposit, checkbook, etc.
Also, to record foreign exchange transactions (when purchasing currency), organizations can use account 57, called “Transfers in transit.” For account 57, 1st order subaccounts can be opened:
- Currency listed for sale.
- Currency for sale deposited with a banking institution.
- Money in rubles transferred for the purchase of currency (funds before the day of purchase are taken into account here).
Subaccount 52-2 reflects monetary transactions in foreign currency carried out on the company's foreign accounts. The debit of this subaccount reflects:
- operations to receive funds transferred from the company’s current accounts opened with authorized Russian banks;
- unused currency;
- interest accrued by the bank for using the account balance;
- previously erroneously written off and then returned funds.
The account credit reflects:
- transactions for payment for the maintenance of a foreign representative office of the company;
- funds withdrawn for payment of salaries and compensation for travel expenses, as well as for payment of other expenses approved by the estimate;
- account servicing costs;
- transfers to the company's current account opened with a Russian authorized bank.
Bank clients can withdraw currency from their accounts to pay for travel expenses of their employees and with special permission from the Bank of Russia. Also, the enterprise can operate a cash register in foreign currency; transactions in it are reflected in subaccount 50-4 (in the case of foreign economic transactions and business trips abroad). All currency movements at the cash register are reflected in the enterprise's unified cash book. Naturally, all entries are made in rubles.
Exchange differences associated with changes in the ruble exchange rate on different days of valuation of foreign currency assets and liabilities that arise on accounts 52 and 57 are reflected using account 91. Positive exchange differences are visible in the subaccount “Other income” (on a loan), and negative ones - on subaccount “Other expenses” (by debit). The basis for reflecting exchange rate differences is an accounting certificate. Analytical accounting of exchange rate differences is carried out separately from other non-operating income/expenses of the enterprise. For this purpose, a separate accounting register is created.
Find out about codes for types of currency transactions from the material “Directory of codes for types of currency transactions (2022)” .
Does the bank have the right to refuse registration?
The currency agent has every right to refuse to accept the agreement for servicing. Most often, this is due to an insufficiently serious attitude towards the quality of the documents drawn up on the part of entrepreneurs. For example, this happens if the documents:
- were not provided;
- partially transmitted (some of them are missing);
- contain false information;
- do not meet the stated criteria.
If the documentation provided is insufficient and the decision to refuse was made for this reason, professionals must indicate exactly what information was not provided.
Fines for violating currency laws
For violation of the rules for conducting currency transactions, the law provides for administrative liability, and in some cases, criminal prosecution .
The fine for illegal currency transactions is set at 75% of the transaction amount.
For failure to ensure timely receipt of foreign currency earnings to the current account, if the equivalent of unreturned funds in Russian currency does not exceed 9 million rubles, then the fine for organizations and individual entrepreneurs is:
1) 1/150 of the Central Bank key rate of the amount of violation for each day of delay;
2) from 75% to 100% of the transaction amount.
In case of violation, officials will be fined from 20 to 30 thousand rubles.
If the limit of 9 million rubles is exceeded, Article 193 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation comes into play. The severity of the punishment will depend on the amount and the presence of aggravating circumstances.
New exchange control rules
To minimize the occurrence of annoying errors and prevent negative consequences, it is worth carefully studying the legislative framework relating to these issues. Changes that came into force from mid-2022:
- banks are required to point out errors in the agreement;
- control activities under contracts with a total value of less than 200 thousand rubles. carried out in a simplified manner;
- instead of using transaction passports in the process, it is necessary to register contracts;
- enterprises are responsible for specifying deadlines for the execution of all contractual clauses.
Thanks to the innovations listed above, the entire process has been significantly simplified, since it has become much less time-consuming. In addition, the list of mandatory documentation has been reduced, which means that the risks of non-compliance with legislative norms that relate to the circulation of currency, both national and foreign, have been reduced.
Currency control refers to the activities of authorized bodies and agents, which are aimed at ensuring compliance by residents and non-residents of the Russian Federation with the requirements of legislation in the field of foreign trade activities. The process involves the Government of the Russian Federation, the Central Bank, customs and tax authorities, banks and other agents. A certain list of transactions of legal entities must be taken into account by the participants who carry out monitoring. In some cases, banking organizations may refuse registration.
A unique payment instrument for foreign trade settlements is a customs card from SEA BANK.
Responsibility for violation of currency control regulations
Organizations, individual entrepreneurs, and individuals must comply with legislative requirements for compliance with currency control regulations. In most cases, market participants violate reporting deadlines (if we are talking about “pure” market participants). In accordance with Art. 15.25 of the Administrative Code, failure to comply with reporting deadlines entails the following types of administrative liability:
- No more than 10 days - warning or fine: citizens - 300-500 rubles; officials - 500-1000 rubles; legal entities - 5,000-15,000 rubles.
- No more than 30 days - administrative fine: citizens - 1000-1500 rubles; officials - 2000-3000 rubles; legal entities - 20,000-30,000 rubles.
- More than 30 days - administrative fine: citizens - 2500-3000 rubles; officials - 4000-5000 rubles; legal entities - 40,000-50,000 rubles.
Repeated violations committed by citizens, officials, and legal entities imply an increase in the amount of the administrative fine several times. Consequently, delay in fulfilling the requirements of an agent or authorized body can be quite costly for a market player.
5 / 5 ( 1 voice )
about the author
Irina Rusanova - higher education at the International East European University in the direction of "Banking". Graduated with honors from the Russian Economic Institute named after G.V. Plekhanov with a major in Finance and Credit. Ten years of experience in leading Russian banks: Alfa-Bank, Renaissance Credit, Home Credit Bank, Delta Credit, ATB, Svyaznoy (closed). He is an analyst and expert of the Brobank service on banking and financial stability. [email protected]
Is this article useful? Not really
Help us find out how much this article helped you. If something is missing or the information is not accurate, please report it below in the comments or write to us by email