Production accounting in 1C 8.3 Accounting is simplified, but has its own characteristics. Within the framework of the article, we will step by step consider the sequence of production of products in 1C 8.3:
- what settings need to be made if production is recorded in 1C;
- sequence of registration of operations for production of products;
- what production transactions are generated in 1C 8.3.
For more details, see the online course: “Accounting and tax accounting in 1C: Accounting 8th ed. 3 from A to Z"
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
Options for accounting for finished products in 1C
Before setting up production accounting in 1C 8.3, you need to decide how the cost will be calculated.
Calculation of cost in 1C depends on the use of planned cost and subconto Products . In 1C it is possible to calculate:
- using subaccount Products on account 20.01: with planned prices;
- without planned prices;
- with planned prices.
The planned cost determines:
- share of distribution of direct costs;
- cost of products during the month before calculating the actual cost.
Learn more Comparison of cost calculation options, their differences and recommendations for use
Sale of finished products: postings
The volume of sales is understood as GP shipped to consumers regardless of the fact of payment. The sale is fixed both by prepayment and with payment after shipment:
| Operations | Wiring | |
| D/t | K/t | |
| Sale of GP before payment | ||
| The actual cost of the shipped GP was written off | 90/2 | 43 |
| Reflected revenue for shipped GP | 62 | 90/1 |
| VAT charged | 90/3 | 68/VAT |
| Payment received | 51 | 62 |
| Selling GP on prepayment | ||
| Advance received from buyer | 51 | 62/AB |
| VAT on advance | 76 | 68/VAT |
| The shipped GP was taken into account at FS (actual cost) | 90/2 | 43 |
| Sales revenue taken into account | 62 | 90/1 |
| Offset of prepayment | 62/AB | 62 |
| Recovered VAT from advance payment | 68 | 76 |
| VAT charged on sales | 90/3 | 68 |
Production accounting settings in 1C - step by step for dummies
Accounting policy according to accounting
Setting up accounting policies for accounting purposes is set in the Main - Settings - Accounting Policies section.
During production, set the Product Output when setting up Activities, the costs of which are taken into account on account 20 “Main production” .
And also determine the settings for writing off general business expenses and using planned costs in 1C.
Setting the planned cost
If you do not pre-set planned prices for GP (or semi-finished products), set the price manually in the Shift Production Report document.
the type of planned prices in the section Administration - Program Settings - Accounting Parameters - link Type of planned prices.
Set the planned price using the document Setting item prices in the Warehouse - Prices - Setting item prices section.
- Setting the planned production price
- Setting item prices
Specification Definition
To automatically fill in materials for production in 1C, it is recommended to enter specifications for their write-off per unit of production.
Set the specification of the item in the item card using the Specifications in the section Directories – Goods and Services – Nomenclature.
Learn more Determination of specifications for the write-off of materials for production
Unfinished production
If production expenses were incurred during the period, but there was no output (semi-finished products, production services), or it was incomplete, then account 20 is not closed, the value of work in progress (WIP) remains on it and is transferred to the next month. Accounting for work in progress can be configured in the form of the organization’s accounting policy, on the “WIP” tab. The default method is usually “In the absence of release, consider direct expenses as WIP expenses”:
If, in the accounting policy, the WIP accounting method “Using the WIP Inventory” document is selected, then if there is work in progress, it will be necessary to enter the “WIP Inventory” document before closing the month. Here you manually indicate the amounts of work in progress for each item group:
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
Product release in 1C 8.3 Accounting sequence
In 1C, product release can be reflected in two ways:
- with the write-off of materials according to the specification: production of products and accounting for the costs of its production are carried out simultaneously when posting the document Production Report for the shift .
- production of products and accounting for the costs of their production are carried out simultaneously when posting the document Production report for the shift ;
Production of products in 1C without specifications step by step
Let's look at production in 1C 8.3 for dummies step by step using an example.
On January 26, the materials were written off for production according to the invoice request:
- blanks for soles - 2,000 pcs.;
- fabric - 500 m².
On January 30, women's sandals “Kate” were produced (1,000 pairs).
On January 28, the materials were written off for production according to the invoice request:
- eco-leather “Lazur” - 250 linear m.;
- insoles - 500 pairs;
- shoe decorations with rhinestones - 1,000 pcs.
On January 29, women's sandals “Megan” (500 pairs) were produced.
On January 30, Design Academy LLC provided services for developing the design of women's shoe models. The cost of services is 53,100 rubles. (including VAT 18%).
The Organization has approved the planned cost of production:
- women's sandals “Kate” - 230 rub./pair;
- women's sandals "Megan" - 270 rub./pair.
Accounting is maintained using the Products on account 20.01.
Write-off of materials for production
Write off materials for production in 1C Women's sandals "Megan" with the document Requirement-invoice in the section Production - Production - Requirements-invoices.
checkbox on the “Materials” tab . the Products subconto on account 20.01 can only be filled out on the Cost Account .
Postings
The write-off of materials for the production of women's sandals "Kate" is recorded in the same way.
Reflection in accounting for design development services
When purchasing services in 1C, use the document Receipt (act, invoice) to reflect the transaction type Services (act) in the section Purchases – Purchases – Receipt (acts, invoices).
Design development services provided:
- for the Nomenclature Group Women's Footwear ;
- Cost item Design development , Type of expense - Material costs .
Subconto Products do not fill out either for BU or NU. Accounting for direct costs, with the exception of material ones, is carried out in general according to the Nomenclature Group . They will be reflected in certain products only after distribution.
Postings
Accounting for the release of finished products in 1C 8.3
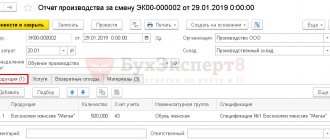
Issue production of women's sandals "Megan" through the document Production Report for a Shift in the section Production - Product Release - Production Reports for a Shift.
Please indicate:
- Cost account — 20.01;
- Products tab : Planned amount - the planned cost of products established by the administrative document of the organization.
- Specification - not filled in if the document Requirement-invoice .
Accounting for finished products in 1C - postings
The production of women's sandals "Kate" is designed in a similar way.
Bringing the cost of production to the actual cost
At the end of the period, when all information on costs has been collected, when performing the Month Closing procedure through Operations – Period Closing – Month Closing, the amount of planned expenses is compared with actual ones. Operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26 adjusts the cost of production for the difference between plan and actual.
Costing
If the Subconto Products, planned prices , then direct costs for the product group that are not reflected in certain products are distributed in proportion to the planned cost .
Let us determine the share of each type of product:
Distribution of costs for design development between product names:
Direct costs for which the Products , for example, materials , will be included in the cost of the product name indicated in the subconto.
In the example, the actual cost calculated at the end of the month is greater than the planned cost. Therefore, the planned cost is brought to the actual cost.
Regulatory regulation
Work in progress and finished products in mass and serial production are assessed according to (clause 27 of FSBU 5/2019):
- direct costs (excluding indirect ones);
- planned (normative) costs (set by the organization based on the usually required volumes of raw materials, materials and other resources under normal load conditions of production capacity).
The difference between actual and planned costs reduces (increases) costs in the period of occurrence, i.e., in the period when materials are written off for production.
In tax accounting, products are accounted for at actual cost (Articles 318, 319 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Valuing inventories at planned cost only makes sense if there is a reliable calculation that is regularly revised. The difference between plan and fact will indicate that unplanned (negative) events occurred during the production process: for example, the utilization of production facilities is disrupted - they are not working at full capacity.
Production of products in 1C according to specifications step by step
Let's look at the sequence of product release according to specifications in 1C 8.3 Accounting using an example.
The organization produces women's shoes.
On January 23, women's sandals “Kate” were produced (1,000 pairs). Materials are written off for production according to specification No. 1, consumption rate for 1 pair:
- blanks for soles - 2 pcs.;
- fabric - 0.5 m².
On January 28, women's sandals “Megan” (500 pairs) were produced. Materials are written off for production according to specification No. 1, consumption rate for 1 pair:
- eco-leather “Lazur” - 0.5 linear meters;
- insoles - 1 pair;
- shoe decorations with rhinestones - 2 pcs.
On January 30, Design Academy LLC provided services for developing the design of women's shoe models. The cost of services is 53,100 rubles. (including VAT 18%).
The Organization has approved the planned cost of production:
- women's sandals “Kate” - 230 rub./pair;
- women's sandals "Megan" - 270 rub./pair.
Accounting is carried out without using the subaccount Products on account 20.01.
Production of finished products
the production of women's sandals "Kate" in 1C with the document Production Report for the Shift in the section Production - Product Output - Production Reports for the Shift.
Please indicate:
- Cost account — 20.01;
- Products tab : Planned amount - the planned cost of products established by the administrative document for the organization .
- Specification — a list of materials used in the production of products. The data is used to automatically populate the tab Materials.
When the Specification , click the Fill the Materials tab will automatically be filled in with data on the materials used, their quantity, accounting accounts, cost item, product and item group.
Leave Products column
Accounting for finished products in 1C - postings
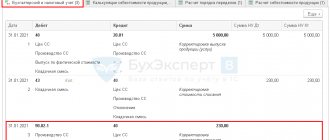
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 43 Kt 20.01 - capitalization of manufactured finished products at planned cost;
- Dt 20.01 Dt 10.01 - write-off of materials.
The production of women's sandals "Megan" is designed in a similar way.
Bringing the cost of production to the actual cost
At the end of the period, when all information on costs has been collected, when performing the Month Closing procedure through Operations – Period Closing – Month Closing, the amount of planned expenses is compared with actual ones. Operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26 adjusts the cost of production for the difference between plan and actual.
Costing
If costs are taken into account using the boiler method without subconto Products , then all direct costs accounted for on account 20.01 are distributed in proportion to the planned cost within the product group between product names, including material ones. Even if they are precisely defined by product names in the document Shift Production Report on the Materials .
Let us determine the share of each type of product:
Distribution of direct costs, incl. material between product names:
In the example, the actual cost calculated at the end of the month is greater than the planned cost. Therefore, the planned cost is brought to the actual cost.
We looked at production accounting in 1C 8.3 Accounting step by step, we sequentially examined how to keep records of finished products according to specifications and without specifications in 1C.
Closing the period and calculating the actual cost
Closing cost accounts and calculating the actual cost of manufactured products (semi-finished products) is carried out at the end of the month through routine operations.
Previously, routine operations must be carried out to calculate depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets, repay the cost of workwear, write off deferred expenses, calculate wages and payroll taxes. You can use the routine processing “Month Closing” (menu: “Operations”). In this case, the program itself will “determine” which routine operations are necessary and carry out them in the correct sequence. Execution occurs by clicking the “Perform monthly closing” button.
When carrying out the routine operation “Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26”, several stages are performed: distribution of indirect costs (according to the established “Distribution Methods”), calculation of direct costs for each product and for each division, cost adjustment.
Let us give an example of the operation “Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26” (the organization uses the “direct costing” method). There are entries for closing account 26 (not all are visible in the figure), adjusting product output, and adjusting the cost of goods sold. (Adjustment amounts can also be negative if the actual cost is less than planned).
After closing cost accounts, you can generate calculation certificates (available from the “Month Closing” processing or through the menu: “Reports – Calculation certificates”).
Help-calculation “Calculation”:
Help calculation “Product cost”: