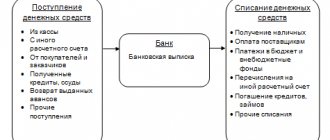
Characteristics of account 50 “Cash desk”
Consolidated account 50 in accounting is used to obtain reliable information about cash payments of a company or individual entrepreneur with individuals and legal entities. At the same time, the participants in the relationship include both third-party contractors and employees of the organization. Among typical cash transactions on accounts. 50 are listed:
- Receipts from the sale of goods and materials, works or services for cash.
- Issuance of wages, accountable and other types of payments to employees within the framework of labor relations.
- Payments for services performed with third parties.
- Various administrative and economic calculations, etc.
Typical postings to account 50 “Cash” are carried out in terms of cash receipts, disposals, circulation and internal movement. It is mandatory to prepare unified cash documentation - PKO, RKO, cash book, etc. The main registers of synthetic accounting for account 50 are given below.
Account 50 “Cashier” – subaccounts:
- 50.1 – for accounting for cash at the enterprise’s cash desk.
- 50.2 – for accounting for cash in operating cash desks.
- 50.3 – monetary documents are accounted for in account 50 “Cashier” for actual expenses for the purchase of postage stamps, prepaid air tickets, state duty stamps, bill stamps, etc. A separate sub-account is opened for each type of document.
- 50.4 – for accounting for cash in the foreign exchange office when carrying out foreign economic activity and sending personnel on business trips abroad. Additionally, sub-accounts can be opened for each type of foreign currency.
Count 50: basic information
Account 50 is the active accounting account. An increase in the resource account on it is reflected as a debit, and a decrease as a credit. For example, if funds from an accountable person are deposited at the cash register, then debit entries will be generated on the account, and if a certain amount of funds is withdrawn from the cash register for transfer somewhere, then account 50 will be involved in credit entries.
Account balance 50 is debit. It is calculated by adding debit turnover to the opening balance and subtracting credit turnover from it. The ending balance shows the balance of funds in the cash register on a specific date.
Cash resources on hand are assets. The cash balance at the reporting date is reflected in the enterprise's balance sheet in the asset category (line 1250). When preparing annual financial statements, most business accountants try to bring account balance 50 to zero.
Accounting is carried out in both national and foreign currencies.
Account 50 in accounting – postings:
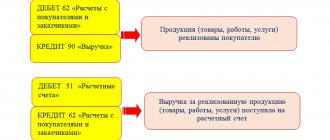
- D 50 K 90 – reflects the receipt of money from retail sales.
- D 50 K 51 (52, 55) – cash was withdrawn from a cash account (currency, special).
- D 50 K 60 – the advance payment previously issued to the supplier was returned in cash.
- D 50 K 62 – the buyer paid in cash.
- D 50 K 66 (67) – the receipt of a cash loan is reflected.
- D 50 K 71 - the accountable person returned the debt to the cashier.
- D 50 K 73 – the culprit compensates for the damage caused.
- D 50 K 75 – contribution made by the founder in cash.
- D 51, 52 K 50 – money from the cash register was deposited into a cash account (currency).
- D 70 K 50 – salaries were issued to the staff from the cash register.
- D 71 K 50 – cash was issued to the employee for reporting.
- D 66 (67) K 50 – loan or interest repaid in cash.
- D 94 K 50 - reflects the shortage of cash identified during the inventory.
Conclusion - we have examined the main entries for account 50, the typical application of which is regulated by Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Postings to account 50
| Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 50 | 51 | Withdrawing money from a current account |
| 50 | 62 | Receiving payment from the buyer in cash to the cash register |
| 50 | 75 | Contribution to the authorized capital by the founder in cash |
| 60 | 50 | Payment to the supplier in cash |
| 70 | 50 | Payment of wages to employees |
The indicated accounting entries for accounting for cash transactions are the most common standard options; you will find a complete list of entries in the Chart of Accounts ().
Typical transactions for account 51
| Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 51 | 62 | Receipt of payment or advance from the buyer |
| 51 | 50 | Cash deposit to the bank from the company's cash desk |
| <51 | 75 | Contribution to the Authorized Capital by non-cash means |
| 51 | 66 (67) | Obtaining a short-term (long-term) loan |
| 60 | 51 | Payment to the supplier by bank transfer |
| 50 | 51 | Withdrawing money from an account |
| 75 | 51 | Payment of dividends by bank transfer |
| 66 (67) | 51 | Repayment of credit (loan) |
Summarize:
An organization can use both cash and non-cash money for mutual settlements. To account for the former, a cash register is used, and for the latter, a current account is used. Each cash accounting operation must be documented in primary documents, and the corresponding entry is reflected in the accounting records.
Lesson 9 Summary
Main conclusions on the topic:
- any transactions with cash are considered cash transactions;
- the receipt of funds is accompanied by the execution of a receipt order, the issue - by filling out an expenditure order;
- To perform cash transactions, a cash register is required;
- organizations are set a cash limit depending on the volume of cash payments;
- For each transaction, the accounting department makes a record or entry to account 50.
The "Cash" account is reflected in the asset balance sheet of the enterprise.
Receipt of money to the cash register: posting Dt 50 Kt 51 and others
According to the Chart of Accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 34n, account 50 “Cash” is active. In this case, cash receipts are reflected in the debit of account 50.
There may be several sources of replenishing the organization's cash register with funds. One of them is withdrawing money from a current bank account. In such cases, the transaction is traditionally recorded by the following entry: Debit 50 Credit 51.
But there are often situations where time gaps arise between the debiting of cash from one cash source of the company and its capitalization on another. For example, if the collector received funds from the bank at the end of the working day, it may not be possible to post the necessary amounts to the organization's cash desk to account 50 on the same day. In such cases, it is possible to use account 57 “Transfers in transit”:
- Dt 57 Kt 51 - receipt of funds based on a bank receipt to the responsible person (as of the date the cash collector received the cash);
- Dt 50 Kt 57 - posting of received cash to the cash desk (on the date of receipt of cash at the cash desk).
If the operation of withdrawing cash and crediting it to the cash register can be completed within 1 business day, then in accounting it will find a reflection that is already familiar to us: Dt 50 Kt 51.
The return of unused funds to the cash desk by accountable persons is accompanied by the following posting: Debit 50 Credit 71 - recording of unused amounts, balances of funds after the accountant purchases materials and pays for services.
From November 30, 2020, the organization can set the deadline for the reporting person to submit the advance report independently, reflecting it in internal local acts, for example, in its accounting policies or regulations on business trips. The requirement that the JSC must be submitted no later than 3 working days after the date of expiration , for which reports were issued, or from the date of return to work, cancelled. The exception is a business trip. Seconded accountants are also required to report expenses within 3 days upon return.
In the guide from ConsultantPlus you will find nuances and step-by-step algorithms for issuing funds against an advance report, as well as for processing settlements with accountable persons. Study the material for free by getting trial online access to the K+ system.
You will find other information about the actions of accountable persons, including when returning funds, in the article “Features of advance reports in accounting.”
If cash comes from customers, then the replenishment of the organization’s cash desk is as follows: Dt 50 Kt 62.
Postings from cash documents
An organization's cash register is a record of not only cash, but also other financial documents.
The following subaccounts can be opened for account 50:
- 50.1 - the main cash register used;
- 50.2 - operational cash desk, if the institution has several facilities for accepting money;
- 50.3 - purchased financial documents for a specific purpose (vouchers, tickets, coupons, etc.).
To reflect the receipt of monetary documents in correspondence with account 50, account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” can be used: Debit 50 Credit 76.
After this, the received documents can be issued, for example, for reporting to employees sent on a business trip: Debit 71 Credit 50.
List of basic documents for working with cash
It should be remembered that any operation on an account. 50 occurs with documentary support. Every action related to cash is confirmed by primary documents. Such forms are called cash forms; they have an approved form and rules for filling out.
There are only five main ones:
- A PKO or receipt order is issued upon receipt of any amount of cash. His task is to confirm the receipt of money at the enterprise’s cash desk. Form KO-1 contains all the necessary details - number, date of statement, amount, basis for receipt of funds.
- RKO or expenditure order is issued for the issuance of funds from the cash register. Form KO-2 also has standard details for filling out - date, number, amount. Additionally, the recipient's passport details are indicated in a separate column.
- Cash book. An entry is made in the book for each order, both incoming and outgoing. If no transactions were performed on any day, there will be no records. Form KO-4 is maintained on the basis of completed primary cash documents. Individual entrepreneurs have the right not to keep a cash book.
- Settlement and payment statement. This document is drawn up when issuing salaries to employees of the organization. One RKO is issued for the full amount of the statement. Basic details - period of salary payment, date and number, data on employees, amount of accruals, deductions and payout.
- Journal of cash documents. It keeps a record of all issued orders. Form KO-3 is filled out at any enterprise.
The first three documents are considered the most mandatory. They are issued constantly, during any cash transaction.
There is also another cash document - a book of accounting for cash received and issued by the cashier. Form KO-5 is maintained if the company has a division of the cash register into departments.
Important! Any corrections in the documents are prohibited.
Balance at the beginning of the period on account 50 “Cash” -100,000.00
Transactions for the month:
1) Cash received from customers in the amount of -35,000.00
2) Issued from the cash register to report to I.I. Ivanov - 500.00
3) They paid wages to workers from the cash register -125,000.00
Display the balance of account 50 “Cash” at the end of the period.
Solution:
Account 50 Active, active account balance for Dt. This is a synthetic account. It is expressed in monetary terms, i.e. in rubles.
Operations:
1) Dt 50 Kt 62 35,000.00
2) Dt 71 Kt 50,500.00
3) Dt 70 Kt 50 125000.00
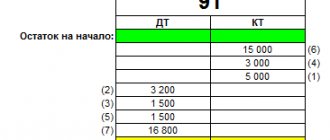
Let's make an airplane according to count. 50 “Cashier”, account Active
| Dt 50 “Cash desk” Kt | |
| Initial balance 100,000.00 | |
| 35 000,00 | 500,00 125 000,00 |
| Turnover for diesel fuel – 35,000.00 | Turnover by Kt - 125,500.00 |
| Sk= 9,500.00 | |
The balance at the end of the period for account 50 “Cash” is 9,500.00 rubles.
Indicates the availability of funds in the company's cash register at the end of the period.
The analytical account for the account will reveal more detailed information to us. 50 "Cashier".
Let's consider an example of an analytical account using the same conditions for account 50 “Cash”,
For correct accounting, sub-accounts are opened, which are assigned to each of the branches.
Balance at the beginning of the period on account 50 “Cash” -100,000.00, incl.
Balance at the cash desk of branch No. 1-30,000.00 50.1.1
Balance at the cash desk of branch No. 2-50,000.00 50.1.2
Balance at the cash desk of branch No. 3-20,000.00 50.1.3
Transactions for the month:
1) Cash received at the cash desk from customers in the amount of 35,000.00 , including
To the cash desk of branch No. 1-10,000.00
To the cash desk of branch No. 2-15,000.00
To the cash desk of branch No. 3-10,000.00
2) Issued from the cash register for reporting - 500.00 including
From the cash desk of branch No. 2 to Ivanov I.I. - 500.00
3) They gave out wages to workers from the cash register - 125,000.00 , including
From the cash desk of branch No. 1 - 40,000.00
From the cash desk of branch No. 2 - 55,500.00
From the cash desk of branch No. 3 - 29,500.00
Let's make airplanes based on numbers. 50 “Cash” for each branch separately in analytical accounting and compare with synthetic accounting account 50 “Cash”.
Branch No. 1
| Dt 50.1.1 “Cash desk” Kt | |
| Initial balance 30,000.00 | |
| 10 000,00 | 40 000,00 |
| Turnover for Dt – 10,000.00 | Turnover according to Kt - 40,000.00 |
| Sk= 0 | |
Branch No. 2
| Dt 50.1.2 “Cash desk” Kt | |
| Initial balance 50,000.00 | |
| 15 000,00 | 500,00 55 500,00 |
| Turnover for Dt – 15,000.00 | Turnover by Kt - 56,000.00 |
| Sk= 9000.00 | |
Branch No. 3
| Dt 50.1.3 “Cash desk” Kt | |
| Initial balance 20,000.00 | |
| 10 000,00 | 29 500,00 |
| Turnover for Dt – 10,000.00 | Turnover by Kt - 29,500.00 |
| Sk= 500.00 | |
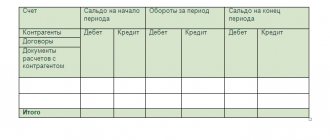
Balance sheet for account 50 Cash desk
| Branch number | Initial balance | Revolutions | Balance end | ||
| Dt | CT | Dt | CT | Dt | CT |
| 50.1.1 | 30 000 | 10 000 | 40 000 | — | |
| 50.1.2 | 50 000 | 15 000 | 56 000 | 9 000 | |
| 50.1.3 | 20 000 | 10 000 | 29500 | 500 | |
| TOTAL | 100 000 | 35 000 | 125 500 | 9 500 |
Thus,
1) Opening balance of synthetic active account 50 “Cash” = Opening balance of analytical accounts 50 “Cash” by branches
30 000+50 000+20 000=100 000
2) Turnovers per Dt of synthetic account 50 “Cash” = Turnovers per Dt of analytical accounts 50 “Cash” by branches
10 000+15 000+10 000=35000
3) Turnovers per CT synthetic account 50 “Cash” = Turnovers per CT of analytical accounts 50 “Cash” by branches
40 000+56000+29500=125 500
4) Final balance of synthetic active account 50 “Cash” = Final balance of analytical accounts 50 “Cash” by branches = 9500
The same analogy is in passive accounting accounts.
Example 2:
Balance on account 70 Settlements with personnel for wages at the beginning of the period - 150,000.00
Operations:
1) The wages of workers are added to the costs of main production 150,000.00
2) Personal income tax is withheld from the salaries of employees, ______
3) The salary was transferred from the organization’s current account to the employees’ cards, close account 70 so that the final balance is equal to “0”
Solution:
1) Dt 20 Kt 70 150 000,00
2) Dt 70 Kt 68 Personal income tax 150,000*13%= 19 500,00
3) Dt 70 Kt 51 150 000+(150000-19500) = 280 500,00
Let's make an airplane account 70 Settlements with personnel for wages,
Passive
| Dt 70 Kt | |
| Initial balance 150,000.00 | |
| 19 500,00 280 500,00 | 150 000,00 |
| Turnover for diesel fuel – 300,000.00 | Turnover by Kt - 150,000.00 |
| Sk= 0.00 | |
The account is closed, i.e. has no balance, the company has paid off its salary arrears in full.
This is a synthetic account expressed in monetary terms, rubles.
We will see more detailed information in the analytical account 70, having examined the analytics of this account using the same example of account 70.
Fill out the balance sheet according to account 70
Balance sheet according to account 70
| Full name | Initial balance | Revolutions | Final balance | ||
| Dt | CT | Dt | CT | Dt | CT |
| — | — |
Balance on account 70 Settlements with personnel for wages at the beginning of the period - 150,000.00, including
Ivanov I.I.-50,000.00
Petrov P.P.-50,000.00
Sidorov S.S.-25000.00
Kiselev A.V.-25000.00
Operations:
Dt 20 Kt 70
Salary accrued to employees - 150,000.00, including
A) Ivanov I.I. -50,000.00
B) Petrov P.P. -50,000.00
B) Sidorov S.S. - 25000.00
D) Kiselev A.V. - 25000.00
2.Personal income tax-19,500.00 was withheld from the salaries of employees, including Dt 70 Kt 68
A) Ivanov I.I. —
B) Petrov P.P. —
B) Sidorov S.S. -
D) Kiselev A.V.-
The salary was transferred from the organization's current account to the employees' cards, close the account 70 so that the final balance is equal to “0” Dt 70 Kt51