Accounts receivable is one of the most significant indicators of financial statements. The write-off of accounts receivable is preceded by a lot of analytical and organizational work: identifying problematic accounts and debtors, and the possibility of debt collection. If it is impossible to collect the debt, it should be written off. At the same time, an accountant needs to know not only accounting and tax legislation, but the Civil Code and arbitration court practice.
Question: How to reflect in the accounting records of an organization that applies the simplified tax system (taxable object “income reduced by the amount of expenses”), the write-off of accounts receivable for goods sold due to the expiration of the statute of limitations? A provision for doubtful debts regarding this debt was not formed. As a result of an inventory of settlements with counterparties (based on the manager’s order), unsecured, overdue receivables were identified, for which the statute of limitations had expired. The amount of debt for the goods sold is 50,000 rubles. View answer
Definition of the concept of “bad receivables”
The amount of money that cannot be collected from counterparties (buyers) is called bad receivables; it can be classified as the illiquid assets of the enterprise. Such financial resources of an enterprise in monetary form cannot bring the income required by the enterprise, and therefore represent only a trace of being in this form.
There is also the concept of “doubtful debt” - this is somewhat different. Such debts are classified as those that are not repaid within the terms specified in the agreement and are not secured by any guarantees (clause 70 of the Accounting Regulations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance on July 29, 1998 No. 34n). An overdue debt may also be called uncollected.
Thus, it is still possible to repay doubtful debts, but not hopeless ones.
BIT.Debt management is a specialized CRM system for debt collection at all stages.
- Increases the percentage of successful collections by 30%;
- Increases employee productivity by 2 times;
- Allows you to scale quickly;
- Speeds up pre-trial collection;
- Reduces refusals in court by 2 times;
- Reduces collection costs.
More details Request a demo
Write-off of buyer's debt
Under the conditions of Example 1, the amount of accrued reserves in accounting and tax accounting differs.
In accounting, there is a bad debt in the amount of RUB 150,000.00. We will write it off completely from the reserve. In tax accounting, only 100,000.00 rubles will be written off from the reserve, and the remaining debt in the amount of 50,000.00 rubles, not covered by the reserve, will be included in non-operating expenses.
To write off bad debt using reserves, you can use the standard document of the Debt Adjustment program (Fig. 3). This document is available both from the Sales and Purchases sections.
The header of the Debt Adjustment document must be filled out by selecting the following values from the proposed lists:
table 2
| Field | Data |
| "Type of operation" | Debt write-off |
| "Write off" | Buyer's debt |
| "Buyer (debtor)" | Name of the debtor organization for which the amount of receivables recognized as bad is listed (selected from the “Counterparties” directory) |
The document is filled out automatically by clicking the Fill -> Fill in balances for mutual settlements based on accounting data. The tabular part on the Buyer's debt (accounts receivable) tab is filled in with the balances of mutual settlements as of the adjustment date as follows:
Table 3
| Field | Data |
| "Settlement amount" | Total amount of debt (RUB 150,000.00) |
| "Sum" | The amount of debt write-off in accounting. By default, this amount corresponds to the total amount owed |
| "Amount NU" | The amount of debt write-off in tax accounting. By default, this amount also corresponds to the total amount owed. Since this document will write off the debt from the reserve, it is necessary to manually correct the amount in the “Amount NU” field (RUB 100,000.00) |
| "Account" | Account on which the debt arose (62.01) |
On the Write-off account tab, you need to indicate the account where the doubtful receivables will be allocated (63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”), as well as the details of the agreement with the counterparty and the settlement document on which the doubtful receivables were generated (see Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Write-off of bad receivables using reserves
After posting the document, an accounting entry will be generated:
Debit 63 Credit 62.01 - for the amount of debt written off from the reserve created in accounting (RUB 150,000.00).
For tax accounting purposes for income tax, amounts are entered into special resources of the accounting register:
Amount NU Dt 63 and Amount NU Kt 62.01 - for the amount of debt written off at the expense of the reserve created in tax accounting (RUB 100,000.00). Amount PR Dt 63 and Amount PR Kt 62.01 - for a constant difference, the value of which is RUB 50,000.00.
For profit tax purposes, the remaining portion of the bad debt is written off as non-operating expenses using the Transaction document (section Transactions -> Accounting -> Transactions entered manually). In the document form, to create a new transaction, click the Add button and enter the amounts in the special resources of the accounting register (the Amount field must remain empty):
Amount NU Dt 91.02 and Amount NU Kt 62.01 - for the amount of written off debt not covered by the reserve (RUB 50,000.00). Amount PR Dt 91.02 and Amount PR Kt 62.01 - for a negative constant difference (-50,000.00 rub.). When performing the routine operation Calculation of income tax for March, which is included in the Closing of the month processing, this permanent difference leads to the recognition of a permanent tax asset in the amount of RUB 10,000.00.
Please note that in order to correctly fill out the income tax return, it is important to correctly select the item of other income and expenses - Write-off of accounts receivable (payable). Then, when automatically filling out the income tax return for the first quarter of 2022, losses from writing off bad debts in the amount of RUB 50,000.00. will be reflected on line 302 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02, as well as in the total amount on line 300 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02.
To make sure that bad debts are written off in accounting and tax accounting, you can generate a balance sheet for account 62 for March 2022, having previously made the appropriate settings on the Indicators tab. The balance sheet generated under account 63 for March 2022 will show the absence of reserves for doubtful debts.
To account for written-off debt in order to monitor the possibility of its collection (in accordance with paragraph 2 of clause 77 of the Regulations), we will also use the Operation document.
In the document form, to create a new transaction, you need to click the Add button and enter an entry in the amount of RUB 150,000.00. on the debit of off-balance sheet account 007 indicating the corresponding analytics (sub-account Counterparties and Agreements).
What debts are considered bad
Bad debts, according to clause 2 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, include the following monetary amounts:
- termination of obligations due to liquidation of the enterprise or on the basis of an act of a government body;
- the statute of limitations has expired (according to Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is equal to 3 years, but in some cases it can be extended);
- debtor is an individual who has undergone bankruptcy proceedings, which releases him from obligations to the creditor;
- suspension of enforcement proceedings by bailiffs due to the impossibility of collection: lack of property, funds or impossibility of obtaining information about the debtor.
Documents for writing off accounts receivable in tax and accounting
Unlike accounting, in which a company can only create a reserve for doubtful debts and then use it to pay off bad debts, there is a simpler method in tax accounting. Write off bad receivables immediately to losses.
But there are exceptions when, for example, a debtor company is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities at the initiative of the tax service due to lack of movement in bank accounts and failure to submit reports. In this situation, it is impossible to write off the debt in tax accounting. The Ministry of Finance claims that in these circumstances there is no reason to write off receivables. You will have to wait 3 years for the statute of limitations to expire.
So, to pay off bad receivables, the company conducts an inventory. Experienced accountants do this before reconciling the balance at the end of the year, but according to the approved guidelines. by order of the Ministry of Finance dated June 13, 1995 No. 49, this can be done in another period - based on the results of any of the quarters.
We prepare the following documents, in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49 and Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of August 18, 1998 No. 88:
- Form No. INV-22 (Order to conduct an inventory).
- Form No. INV-17 (act of settlements with debtors);
- Appendix to form No. INV-17 (information about buyers: name of organization or full name of individual, amount of debt, date of debt, etc.).
However, the enterprise has the right to replace the unified forms with its own and reflect the inventory results in them.
After completing the inventory, an order from the director and an accounting certificate are issued where all calculations are detailed. These documents are accompanied by payment orders, invoices and agreements on transactions with debtors. If there was an interruption of the limitation period, it is also necessary to attach supporting papers: letters, reconciliation acts, court acts. Only after completing the entire procedure does the accountant write off the required amount.
Inventory of calculations
To check the amounts of receivables, as well as compare the reserves for doubtful debts accrued in accounting and tax accounting, we will use the Subconto Analysis report (Reports section).
In the command panel of this report, you need to set the period for generating the report, and from the presented list of subconto types, select the value Contracts. In the settings panel (Show settings button) on the Indicators tab, set the BU (accounting data) and NU (tax accounting data) flags.
On the Selection tab, you can set selection for a specific agreement with the debtor.
The generated report allows you to analyze accounting and tax accounting data for the selected agreement at the time of expiration of the limitation period with details of the accounts (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Analysis of the subconto under the agreement with the debtor
Before performing an operation to write off a bad debt, it is necessary to draw up an inventory of settlements. The program uses the document Inventory of Payments document for this purpose, which can be accessed via the hyperlink of the same name from the Sales and Purchases sections.
The document is filled out automatically by clicking the Fill button based on accounting data. The tabular part on the Accounts Receivable tab (Fig. 2) is filled in with the balances of accounts receivable as of the inventory date as follows:
Table 1
| Field | Data |
| "Counterparty" | Names of debtors |
| "Settlement account" | Accounts for which accounts receivable are recorded |
| "Total" | Accounts receivable amount |
| "Confirmed" | The amount for which there is documentary evidence. By default, all debt is considered confirmed |
| "Not confirmed" | An amount for which there is no documentary evidence. This field must be filled in manually |
| “Incl. the statute of limitations has expired" | The amount of overdue receivables for which the statute of limitations has expired. This field must be filled in manually |
Rice. 2. Inventory report of settlements
The tabular part on the Accounts Payable tab is filled out in the same way as filling out the Accounts Receivable tab. Under the terms of Example 1, there are no accounts payable.
The Settlement Accounts tab displays a list of accounts for settlements with counterparties for which an inventory of settlements is performed.
By default, the following accounts are included in this list:
- 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”;
- 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”;
- 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”;
- 67 “Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings”;
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, including accounts 76.07 “Settlements for rent”, 76.27 “Settlements for rent (in foreign currency)” and 76.37 “Settlements for rent (in cu)”;
- 58 “Financial investments”.
The user can manage the list of accounts by adding other accounts or disabling accounts suggested by the program.
On the Inventory bookmark, in the appropriate fields, you should indicate the timing of the inventory, details of the basis document, as well as the reason for conducting the inventory of calculations.
On the Inventory Commission tab, you need to fill out the list of commission members by selecting them from the Individuals directory.
The chairman of the commission is indicated using a flag in the Chairman field.
The document Calculation Inventory Act does not generate transactions, but allows you to generate the following printed forms of documents (Print button):
- Order to conduct an inventory (INV-22);
- Inventory report of settlements (INV-17).
Features of writing off bad receivables in tax accounting
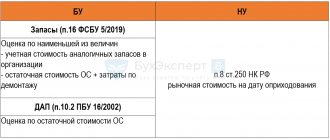
If an enterprise has chosen the method of creating a reserve for doubtful debts and then paying off debts, then this method is only possible for those organizations that pay income tax and use the accrual method. Since with the cash method it is not possible to create a reserve. (clause 7, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
Let's consider the procedure.
We identify doubtful debts: amounts of money arising from the sale of goods (services or work), not repaid within the terms established by the contract and not secured by collateral, a bank guarantee or guarantors (clause 1 of Article 266, Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The exceptions are (what cannot be included in the reserve):
- advance payment transferred to the seller (delivery may not have taken place);
- fines;
- sanctions and prepayment.
Doubtful debts are divided into 3 groups, according to paragraph 4 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- First group. This includes those debts whose duration exceeds 90 calendar days. The reserve must include 100% of the debt.
- Second group. The term of debts is from 45 to 90 calendar days. The reserve includes 50% of the debt.
Third group. The debt term is less than 45 calendar days. No reserve possible.
- Taking into account the entire amount of receivables, a reserve is formed, VAT must be included. (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated June 11, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/21726).
- It is necessary to check the amount of the reserve, which should not exceed 10% of revenue. For the calculation, income from sales for the tax period is taken, after summing up the results of which a reserve is created. For example, if an accountant creates a reserve based on the results of the reporting period, then the reserve must meet a limit commensurate with the larger value: 10% of revenue for the current or previous reporting period.
- The amount of the reserve is allocated to non-operating expenses.
Let's give a few examples.
First example.
Solnyshko LLC performs an operation in tax accounting to create a reserve for doubtful debts. On June 30, an inventory was carried out, which revealed an overdue debit debt of 600,000 rubles. The period of its occurrence is 50 days, i.e. belongs to the second group (the reserve includes 50% - 300,000 rubles).
Sales income (revenue) according to tax accounting data for 6 months is 2,800,000 rubles. Thus, the reserve cannot be higher than 280,000 rubles (10% of the revenue).
At Solnyshko LLC, the accountant writes off 280 thousand rubles for non-operating expenses.
Further, as soon as the receivables go from doubtful to uncollectible, they will need to be repaid using the reserve. In this case, new expenses will not arise, and the size of the reserve will decrease.
Second example.
At Solnyshko LLC, the reserve for doubtful debts as of June 30 amounted to 280,000 rubles.
The next month (July), 50,000 rubles from the debt became uncollectible (as a result of the liquidation of the debtor's enterprise). Thus, the amount of the reserve decreased and amounted to 230,000 rubles. NU does not incur any expenses in connection with this operation.
On the last date of each tax period, an adjustment is made; for this, 2 values are compared:
- newly created reserve.
- unused portion of the reserve for previous periods.
The difference between these values is included in non-operating income of the current period if the second value is greater than the first. If on the contrary, then according to clause 5, article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the difference is included in expenses. But, as in the first example, the limit of 10% must be strictly observed.
Example three.
As of September 30, the accounts receivable of Solnyshko LLC amounted to 550,000 rubles (600,000 rubles as of June 30 – 50,000 written off in July).
Now the receivables move to the third group (their period of occurrence is more than 90 days), so they are included in the reserve in the amount of 100%. Income from sales according to tax accounting data for 9 months amounted to 5,000,000 rubles. The reserve cannot be higher than 500,000 rubles (10% of 5,000,000 rubles).
We compare 500,000 rubles with the unused reserve created based on the results of the previous period, which was equal to 230,000 rubles. The first value is greater than the second, which means that in the tax accounting of Solnyshko LLC it is necessary to reflect expenses of 270,000 rubles.
But in tax accounting there is another option for writing off, without creating a reserve for doubtful debts. It's very simple. With this option, based on the inventory results, the company writes off bad debts as non-operating expenses.
However, under the simplified tax system, organizations cannot include doubtful debts as expenses.
However, this method is only possible in tax accounting; it is impossible to refuse the provision for doubtful debts in accounting.
And in practice, an enterprise usually chooses one way to write off such debt in both tax and accounting.
Accounting entries for debt recovery
When funds are received to repay doubtful debts, the amounts are written off from off-balance sheet accounting and taken into account in the corresponding balance sheet accounts for accounting for settlements. The balance sheet records entries that are “reverse” to those entries that were used when writing off receivables from the balance sheet (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 11, 2016 No. 02-07-10/7306).
More on the topic: Budget classification when paying the costs of legal proceedings
Example. The institution's commission decided to write off doubtful receivables for prepayment for materials from the balance sheet to the off-balance sheet to monitor the possibility of collection. The debtor's property status has changed and funds to repay receivables have been transferred to the personal account.
Decrease in off-balance sheet account 04 – debt is written off from off-balance sheet accounting;
Debit KRB 2,206 34,564 Credit KRB 2,401 20,273 – the debt was accepted onto the balance sheet.
Features of writing off bad receivables in accounting
But in accounting, the company has no choice about how to write off bad receivables; according to clause 70 of the Regulations on maintaining accounting records, it is necessary to use the method of forming a reserve for doubtful debts. The procedure for its formation is not established by law, therefore each enterprise develops this procedure independently and reflects it in its accounting policies.
Unlike tax accounting, in accounting, the reserve for doubtful debts includes any overdue debt, and not just those associated with the sale of services, goods and work.
The formation of the reserve is reflected by the following posting:
credit account 63 “Provision for doubtful debts”
debit account 91 “Other expenses and income”
Write-off from the debt reserve is reflected by the following entry:
debit account 63
credit account 62 (or 76, 60)
An example of how to reflect in accounting the write-off of bad receivables at Solnyshko LLC
At Solnyshko LLC, the reserve for doubtful debts as of June 30 amounted to 280,000 rubles.
debit account 91 credit account 63
With this posting, overdue accounts payable to customers are included in the reserve.
The next month (July), 50,000 rubles from the debt became uncollectible (as a result of the liquidation of the debtor's enterprise). The wiring is completed:
debit account 63
loan account 62
Using this entry, the debt in accounting is written off against the reserve.
Important information!!! The company always has a chance that even after the statute of limitations has expired, the buyer (counterparty) will return the money to the company for the goods or services provided. Therefore, written-off debts are recorded in an off-balance sheet account for 5 years from the date of the write-off operation. Only in the case when the debtor organization is liquidated or an individual. the person is declared bankrupt, the accounting of such debt can be suspended.
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter
Accounting records for writing off unrealistic (uncollectible) and doubtful debts
Write-off of unrealistic (uncollectible) and doubtful receivables (for income, sources of financing the budget deficit, granted loans, advances) relates to subarticle 173 “Extraordinary income from transactions with assets” of the KOSGU (clause 9.7.3 of the procedure, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance Russia dated November 29, 2017 No. 209n, hereinafter referred to as Procedure No. 209n).
More on the topic: Reporting for 9 months: preparation (video materials)
Unrealistic (unreliable) for collection, doubtful receivables for expenses (for advance payments made, for state and municipal guarantees for which equivalent claims do not arise on the part of the guarantor to the debtor) are written off to subarticle 273 “Extraordinary expenses for transactions with assets” of KOSGU ( clause 10.7.3 of Order No. 209n).
Transactions are reflected in accordance with paragraphs. 78, 80, 82, 84 instructions, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 6, 2010 No. 162n (for government institutions), paragraphs. 94, 98, 102, 106, 152 instructions, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n (for budgetary institutions), paragraphs. 97, 101, 105, 109, 180 instructions, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 23, 2010 No. 183n (for autonomous institutions).
Accounting entries are reflected in correspondence with accounts 040110173 “Extraordinary income from transactions with assets”, 040120273 “Extraordinary expenses on transactions with assets”. In 1 – 17 digits of accounts the same code is indicated as that of the settlement account corresponding to them.
Doubtful debts written off from the balance sheet are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 04 (clause 339 of Instruction No. 157n).
Example 1. A budgetary educational institution provides paid educational services. The accounts include doubtful accounts receivable for the education of children who graduated from school. The institution's commission decided to write off the debt from the balance sheet to the off-balance sheet to monitor the possibility of collection.
Debit KDB 2,401 10,173 Credit KDB 2,205 31,667 – doubtful debts are written off from the balance sheet;
Increase in off-balance sheet account 04 – debt accepted on off-balance sheet.
Example 2. A budgetary educational institution has accounts receivable for advance payment for materials. The counterparty is declared insolvent. The institution's commission decided to write off doubtful debts from the balance sheet to the off-balance sheet to monitor the possibility of collection.
Debit KRB 2,401 20,273 Credit KRB 2,206 34,664 – doubtful debts are written off from the balance sheet;
Increase in off-balance sheet account 04 – debt accepted on off-balance sheet.