How to prepare an accounting statement
If an error was made when recording business transactions in the accounting accounts, the specialist must issue an accounting certificate, which indicates that the entries have been corrected. The reason for this action is that all data that is reflected in the accounting registers is produced on the basis of primary accounting documents. This fact is recorded in the Federal Law “On Accounting”.
Such a certificate is necessary for the implementation of data correction, as well as the facts of an error. After this, based on her information, the correct option is transferred to the accounting registers. It is worth noting that the accounting certificate is transferred to them separately from other documents.
It is drawn up in free form, but a mandatory criterion is to write down all the details that are enshrined in the federal law “On Accounting”.
However, in budgetary organizations the document has a special form - f. 433.
You also need to write:
- Description of the error made when registering a business transaction;
- The full name, as well as the location of the document in which the data needs to be corrected;
- Detailed contents of the error;
- An explanation of the reason why it was admitted;
- Method for correcting incorrectly entered information.
Legal liability
If a specialist from the accounting department missed an error and entered it into accounting, after which it was discovered by Tax Service employees during an audit, then this situation could lead to penalties.
Thus, according to Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, their amount ranges from 10,000 to 30,000 rubles, and it may also be a fine of 20% of the amount of unpaid tax or insurance premiums. Moreover, its amount must be more than 40,000 rubles.
Documents with errors are often mistaken for fake papers. Therefore, they are brought to justice under this article.
For using a forged document, a person or organization is subject to criminal liability under Article 327 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. For such a crime, a person or organization may receive:
- Fine up to 80,000 rubles;
- A fine in the amount of salary for a period of up to six months;
- Correctional labor for up to 2 years or compulsory labor for up to 480 hours;
- Arrest up to 6 months.
If the court proves that an accounting employee knowingly falsified a document, he will face either administrative or criminal liability.
For example, a company that produced counterfeit forms or seals will be held administratively liable under Article 19.23 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The punishment will be a fine in the amount of 30,000 to 40,000 rubles and confiscation of counterfeits.
Which primary documents are not allowed to be corrected?
Instructions of the Central Bank dated March 11, 2014, No. 3210-U, established that the entered data cannot be corrected in cash documents (clause 4.7). Such forms include expenditure and receipt orders. But the cash book with payroll is included in the category of documentation for which adjustments are allowed. In the case of a cash book, the procedure for making changes is as follows:
- Correction of errors in primary accounting documents drawn up on paper must be accompanied by an indication of the date of the changes, signatures with transcripts of the persons responsible for filling out this form.
- Electronic documents that have already been signed cannot be modified.
If an error was made several days ago, and was noticed only now, when it distorts the data in subsequent days, all sheets with incorrect information must be corrected. If the error consists of missing a blank sheet of the cash book, this blank form is crossed out and subject to cancellation.
Which primary documents are not allowed to be corrected? In addition to cash registers, it is not allowed to make adjustments to payment forms (clause 2.4 of the Regulations dated June 19, 2012 No. 383-P). Corrections to strict reporting forms that are used when making cash payments are also prohibited.
If an erroneous entry was made in one of these documents when filling out, the accountant cannot cover up the numbers or inscriptions with a proofreader, write in with a pen or cross out the data reflected in the form.
In this case, only the execution of a new copy of the order or instruction is allowed. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
An error was discovered by the Federal Tax Service during an inspection.
If the tax office identifies an error in accounting data, it may apply penalties to the business entity and its officials. This is possible if two conditions coincide - the distortion of accounting information occurs systematically (two or more times in one reporting period) and entails an understatement of the tax base.
When conducting an audit, tax officials pay attention to documents with corrections.
If such a document does not allow unambiguous identification:
- parties to the transaction;
- name of the product or service;
- the value of the subject of the transaction;
- tax rate;
- tax amount.
It is not accepted by the tax authorities and may become a basis for refusal of a tax deduction.
In addition, such documents may raise doubts among tax authorities about the actual implementation of the transaction. If the tax office recognizes the information in the documents as incorrect or contradictory, then it may consider the transaction to be a sham, concluded for the purpose of obtaining a tax benefit.
Making an error when preparing primary accounting documents, as a rule, does not entail negative consequences for the enterprise if it is corrected. The specific method by which changes are made to accounting documentation must be prescribed in the accounting policies of the enterprise or organization. It should be remembered that corrections are not made to cash and bank orders and payment orders; they can only be replaced with new ones.
Quite often questions arise about how to correctly make corrections to primary documents, and how such corrections are reflected in accounting and reporting. We will talk about this in this article.
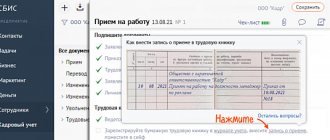
In accordance with clause 7 of Article 9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 402-FZ), corrections are allowed in the primary accounting document, unless otherwise established by federal laws or regulations acts of state accounting regulatory bodies. The correction in the primary accounting document must contain the date of the correction, as well as the signatures of the persons who compiled the document in which the correction was made, indicating their surnames and initials or other details necessary to identify these persons.
Errors in primary accounting documents are corrected as follows: the incorrect text or amounts are crossed out and the corrected text or amounts are written above the crossed out. Crossing out is done with one line so that the correction can be read. In this case, the correction of an error in the primary document must be indicated by the inscription “corrected” (clause 4 of the Regulations on Documents and Document Flow in Accounting, approved by the Ministry of Finance of the USSR on July 29, 1983 No. 105).
Thus, the mechanism for making corrections to primary accounting documents, set out in paragraph 7 of Art. 9 of Law No. 402-FZ is not strictly regulated. These provisions of Law No. 402-FZ establish only the minimum requirements for the content of the corrected primary accounting document: mandatory indication of the date the corrections were made, as well as identifying information about the persons who made the correction.
However, in practice, correction of incorrectly completed primary documents is also used by completely replacing them with new documents with the same details, indicating the date of the corrections.
It should be noted that current legislation and regulations do not prohibit the use of such a correction procedure. At the same time, the legality of such a procedure for correcting primary accounting documents, including for tax purposes, is also confirmed in private clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, for example, based on Letter No. 07-01-09/2235 dated January 22, 2016, it follows that, on the one hand On the other hand, Law No. 402-FZ does not provide for the replacement of a primary accounting document previously accepted for accounting with a new document if errors are detected in it. On the other hand, taking into account parts 2 - 4 art. 8 of Law No. 402-FZ, as well as the Accounting Regulations PBU 1/2008 “Accounting Policy of the Organization”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 6, 2008 No. 106n, the organization has the right to independently develop ways of making corrections to the primary accounting documents compiled on on paper and in the form of an electronic document, based on the requirements established by Law No. 402-FZ, regulatory legal acts on accounting, and taking into account the peculiarities of document flow.
Currently, arbitration practice has developed in similar situations, according to which the legislation of the Russian Federation does not prohibit making changes to primary accounting documents, including by replacing them with properly executed ones, without changing indicators affecting the volume and content of business transactions (for example, Resolution FAS Moscow District dated May 21, 2008 N KA-A41/4238-08 in case No. A41-K2-14877/07, Resolution of the Ninth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated October 7, 2009 in case No. A40-51820/08-14-203 (FAS Resolution Moscow District dated January 15, 2010, this Resolution was left unchanged), the Resolution of the Fourteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated March 28, 2013 in case No. A13-9242/2012, which stated that, as well as the Resolution of the Nineteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated February 21, 2013 in case No. A64-3569/2012).
Taking into account the above, as well as the established arbitration practice, it seems possible to draw the following conclusion.
Correction of primary accounting documents is allowed both by making changes to existing documents and by issuing new ones in the above order - i.e. with the same date under the same number, indicating in the source document (or in the accompanying letter) the date of the correction. At the same time, the implementation of the first of these correction methods is associated with lower tax risks.
It is not allowed to make unilateral changes to primary accounting documents. In this case, one should take into account the established arbitration practice, for example, Resolution of the Tenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated January 16, 2015 No. 10AP-14763/2014 in case No. A41-53651/14, according to which unilateral change of information in primary documents without the mutual will of the parties is contrary to the law and does not entail legal consequences, as well as the Resolution of the First Arbitration Court of Appeal dated June 30, 2015 in case No. A43-27322/2014.
The procedure for correcting errors in accounting and reporting is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 28, 2010 No. 63n “On approval of the Accounting Regulations “Correcting Errors in Accounting and Reporting” (PBU 22/2010)” (hereinafter referred to as PBU 22/2010) and depends on the significance of the error and the moment it was discovered.
The organization determines the criteria for the materiality of an error independently, taking into account clause 3 of PBU 22/2010.
We will consider the most difficult case from the point of view of making corrections - the discovery of an error after the presentation of financial statements and after their approval.
In accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 9 PBU 22/2010 a significant error of the previous reporting year, identified after the approval of the financial statements for this year, is corrected by entries in the corresponding accounting accounts in the current reporting period. In this case, the corresponding account in the records is the account for retained earnings (uncovered loss).
According to paragraphs. 2 clause 9 PBU 22/2010, when correcting a significant error of the previous reporting year, identified after the approval of the financial statements for this year, in addition to making corrections to the accounting, the comparative indicators of the financial statements for the reporting periods reflected in the financial statements of the organization for the current reporting year are adjusted. Restatement of comparative financial statements is carried out by correcting the financial statements as if the error of the previous reporting period had never been made (retrospective restatement). Retrospective restatement is carried out in relation to comparative indicators starting from the previous reporting period presented in the financial statements for the current reporting year in which the corresponding error was made.
At the same time, clause 10 of PBU 22/2010 provides that in the event of correction of a significant error of the previous reporting year, identified after the approval of the financial statements, the approved financial statements for the previous reporting periods are not subject to revision, replacement and re-presentation to users of the financial statements.
In accordance with paragraph 14 of PBU 22/2010, an error of the previous reporting year that is not significant, discovered after the date of signing the financial statements for this year, is corrected by entries in the corresponding accounting accounts in the month of the reporting year in which the error was identified. Profit or loss arising as a result of correcting this error is reflected as part of other income or expenses of the current reporting period.
Tax audits are becoming tougher. Learn to protect yourself in the Clerk's online course - Tax Audits. Defense tactics."
Watch the story about the course from its author Ivan Kuznetsov, a tax expert who previously worked in the Department of Economic Crimes.
Come in, register and learn. Training is completely remote, we issue a certificate.
Answers to common questions
Question: If the person responsible for maintaining the document is absent, can an employee make corrections by proxy?
Answer: The fact is that a power of attorney is an instrument of civil law relations. According to labor legislation, the labor function must be performed by the employee personally, and in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation such a term as “power of attorney” is not used at all. When drawing up a power of attorney, it must indicate a specific person, but if the employment contract with the employee is terminated, this cannot be done. The procedure by which accounting is kept in the company is approved by the manager, so only he can decide who will sign the corrections in the event of the absence of the required employee.