Inventory of goods in a warehouse is a check to clarify data about the inventory and material assets stored in it. The research results are compared with the information specified in accounting and financial documents. Such an audit allows you to timely identify surpluses and theft in production.
When is it necessary to conduct a warehouse inventory?
There are scheduled and unscheduled inspections. The first type of procedure is carried out once a year according to the approved schedule. The second type of audit is appointed by the company's management or regulatory authorities in the presence of special circumstances.
The list of special cases is prescribed in Federal Law No. 402 of 2011. Such situations include:
- change of management or transfer of ownership and management of the company;
- reduction of more than 50% of the workforce;
- transfer of the organization to another form of ownership;
- fact of theft, illegal use of property, damage;
- complete or partial destruction of stocks as a result of an emergency.
Emergency situations mean events related to force majeure. These include floods, fires, hurricanes and other disasters not related to human factors. Below we will look at how inventory is carried out correctly in a warehouse and what documents are drawn up at the end of the event.
Documents for download.
- – a decision by the manager about all the steps that need to be taken regarding the event. At large enterprises, several copies of the form are allowed for different types of warehouse inventory. Most often, a large number of orders are created when it is necessary to conduct an audit of several premises within one company.
- – required in 2 copies to record the total upon counting of products. The documents are kept by the employee being inspected and in the accounting department.
- previously issued (INV-4 form) - filled out for items received for which there is no payment. For such positions there are special conditions for the transfer of ownership rights. The form classifies them into two categories: revenue not received due to delays and due to non-arrival of the payment date.
- , which is kept by the employee responsible for savings (INV-5 form) - all inventories are taken into account. The receipt for the form indicates which items need to be capitalized or written off. Facts of disagreement with accounting data in the accounting department are recorded in the statement (form INV-19).
- not arrived at the warehouse (INV-6) - appropriate for accounting for products that were not delivered due to long-term transportation, are delivered, they are declared with the appropriate notes during the inventory of goods in the warehouse; we will consider in more detail below how to correctly carry out such a check.
How to properly organize inventory in a company?
Inventory can be carried out in two ways: manually counting goods and then checking them against the data of the accounting system, or automating the process. Let's look at each approach in more detail; the comparison is presented in Table 1.
Warehouse inventory “manually”
To carry out an inventory of the balances in a warehouse manually, without using special equipment for counting, you need to literally close the warehouse, stop the operation of the outlet (it is important that the warehouse is not replenished with goods at this time and nothing is taken from there) and recalculate all the contents. Then reconcile with the data in the accounting system and correct discrepancies
Inventory automation
Automation is the first step towards eliminating the influence of the human factor and speeding up any processes in the company. Inventory automation implies, first of all, the recalculation of balances using special equipment (data collection terminal, hereinafter referred to as TSD), as well as the rapid exchange of data from the accounting system and the terminal.
However, the implementation of TSD itself is not enough; it is important to approach the issue of automation comprehensively. As a result of inventory automation, the process speeds up, becomes cheaper, and at the same time reduces the risk of mechanical errors by personnel.
Table 1 - Comparison of manual and automated inventory processes
| Process characteristics | Manual inventory | Automated inventory |
| Who is it suitable for? | For companies where all goods in the warehouse can be counted overnight or over the weekend when the warehouse is closed. | For companies that have places to store manufactured and sold goods, and for owners who want to do inventory quickly, without errors and downtime. |
| Influence of the human factor | High. There is a risk of errors in counting goods, distortion of data to the required quantity when reconciling with data in the accounting system in the case where in fact there are more goods. | Minimized. Essentially, everything is calculated and compiled by TSD, integrated with the accounting system. A person's ability to influence the process is minimal. |
| Dependence on company work schedule | High dependency. It is difficult to plan the timing; in the absence of holidays or weekends, inventory may be delayed, and the company will continue to incur losses. | Absent. Inventory can be carried out at any time without downtime in production or trade. |
| Possible difficulties | It is difficult to calculate the time; the process may drag on and take longer than planned. | If the movement of goods is not recorded, then shortages and inconsistencies are possible. |
| Process steps |
|
|
Ready-made solutions for all areas
Stores
Mobility, accuracy and speed of counting goods on the sales floor and in the warehouse will allow you not to lose days of sales during inventory and when receiving goods.
To learn more
Warehouses
Speed up your warehouse employees' work with mobile automation. Eliminate errors in receiving, shipping, inventory and movement of goods forever.
To learn more
Marking
Mandatory labeling of goods is an opportunity for each organization to 100% exclude the acceptance of counterfeit goods into its warehouse and track the supply chain from the manufacturer.
To learn more
E-commerce
Speed, accuracy of acceptance and shipment of goods in the warehouse is the cornerstone in the E-commerce business. Start using modern, more efficient mobile tools.
To learn more
Institutions
Increase the accuracy of accounting for the organization’s property, the level of control over the safety and movement of each item. Mobile accounting will reduce the likelihood of theft and natural losses.
To learn more
Production
Increase the efficiency of your manufacturing enterprise by introducing mobile automation for inventory accounting.
To learn more
RFID
The first ready-made solution in Russia for tracking goods using RFID tags at each stage of the supply chain.
To learn more
EGAIS
Eliminate errors in comparing and reading excise duty stamps for alcoholic beverages using mobile accounting tools.
To learn more
Certification for partners
Obtaining certified Cleverence partner status will allow your company to reach a new level of problem solving at your clients’ enterprises.
To learn more
Inventory
Use modern mobile tools to carry out product inventory. Increase the speed and accuracy of your business process.
To learn more
Mobile automation
Use modern mobile tools to account for goods and fixed assets in your enterprise. Completely abandon accounting “on paper”.
Learn more Show all automation solutions
Formation of the commission
To take inventory of a warehouse, the head of the company must issue an order. It contains deadlines and names the reasons for the event. One of the paragraphs of this administrative document is devoted to the approval of the personnel of the upcoming inventory commission.
The numerical minimum of this body is not mentioned in regulations. The guidelines of the Ministry of Finance provide only for the positions of commission members. Its composition includes the following officials:
- a representative of the company's management in the status of chairman;
- accounting representative;
- employees of the supply, sales, and logistics departments.
Representatives of the company’s internal audit bodies can also work on the commission; it is possible to invite an auditor from a third-party audit organization.
Carrying out an inventory of the warehouse as a whole, the details of the event are formalized by order of the director of the company using the standard form INV 22. This form, like a number of samples of other documents for inventory of the warehouse, was developed by the State Statistics Committee.
Who conducts the warehouse inventory?
Control of balances is carried out at the initiative of the head of the company to compare the actual amount of inventory with the total data specified in the documents. The event makes it possible to establish natural loss that occurs in the process of spoilage and other reasons not related to the human factor, arithmetic and technical errors in primary documentation, misgrading, deficiencies and excesses.
The procedure for conducting inventory in a warehouse is regulated by the provisions of the Methodological Instructions approved by Order No. 49 of the Ministry of Finance of June 13, 1995; if a theft or suspicion of theft is detected, third-party services are involved. These include independent expert commissions, auditors, representatives of law enforcement agencies and the tax service. Representatives of each type of inspection are included in the firm’s commission and approved by issuing a special order.
Composition of the commission
The recount is carried out in the presence of the employee responsible for storage, but he is not included in the commission. This is approved by an order issued by the manager. In a small company, at least three people are appointed, in a large enterprise - from 6 people. It is recommended to appoint the following specialists:
- chief accountant or his deputy;
- director or deputy of the company;
- head of the department;
- representative of the logistics department;
- security or security officer of the company;
- employee responsible for compliance with labor rights.
The composition of the commission when conducting inventory in a warehouse is selected at the discretion of the manager. The goal is to ensure an efficient recount. The inspection must include the equipment necessary for weighing and counting, as well as the appropriate equipment for counting and transportation. If the number of employees in the commission is approved less than the minimum allowable number, the results of the event will be considered invalid.
Composition of the inventory commission
The assessment of balances is carried out at the initiative of the manager in order to recalculate actual values and compare them with the balances indicated in the reports. The audit makes it possible to identify natural losses associated with damage and other reasons not related to the human factor, as well as to identify errors of an arithmetic or technical nature. In addition, high-quality re-registration allows you to restore order in the original documentation and correct inaccuracies.
The procedure is regulated by the Methodological Instructions of the Order of the Ministry of Finance (dated June 13, 1995). In case of suspicion of theft, independent experts, auditors, law enforcement agencies, and tax inspectors are involved in the procedure.
Representatives of each of the above authorities are included in the commission, which is prescribed in the relevant order.
Directly during the recalculation, there is an employee responsible for storage, but not included in the commission composition. This is stated in the manager’s order.
Number of representatives of the inventory commission:
- For small businesses – from 3 people;
- For large organizations – 6 or more people.
As a rule, the commission includes:
- Chief accountant (or his deputy);
- Head of the company (or deputy);
- Logistics department employee;
- Security representative;
- The person responsible for compliance with labor law rights.
The final list of warehouse audit participants is approved at the discretion of the manager. The main task is to ensure high-quality recounting.
The event is carried out using appropriate equipment, scales, scanners and other specialized equipment for effective assessment and movement.
Important! If the commission consists of fewer people than established by law, the results of the audit are considered unreliable.
Types of inventory
Full inventory control involves recalculation and comparison of all property in the enterprise. Objects that the company rents are also subject to inspection.
Partial audit is a study of only some goods and values. If a shortage is identified during the event, the scope of inspection expands.
Selective - implies the recalculation of only certain types of stocks or values.
Scheduled – assigned according to the approved schedule. The list of objects to be studied is determined by the director.
Regularity of warehouse inventory
Taking inventory of material assets in a warehouse is not an easy task. The main problem is to carry out an inspection without stopping its activities, without violating the regime of acceptance and dispatch of goods. Therefore, entrepreneurs are primarily concerned with the question: how often should inventory be taken at the central warehouse?
The accounting law states that the timing and procedure for checking the safety of property is determined by the enterprise itself (Article 11). The decision can be made by the owner, the board of directors, or formalized by order of the general director.
At the same time, the law emphasizes the need for mandatory inspections in cases established by legislative acts. These cases are spelled out in paragraph 27 of the accounting regulations:
- annually before the formation of the annual report;
- when changing the warehouse manager or storekeeper;
- when a storage facility with its contents is transferred to another owner, transferred for rent, or reorganized as a unitary enterprise;
- after discovering a damaged object or theft of products;
- before the liquidation of an economic entity.
Thus, at least one complete audit of the warehouse must be carried out by the owner every year.
Typically, enterprises develop inventory regulations. It is included in the list of documents on accounting policies and approved by order of the director. So, if an audit of a warehouse involves its complete implementation of the entire amount of material, with the involvement of an audit commission, then it is recommended to carry out an inventory by individual categories of goods, groups of storekeepers, by teams, etc. Such inspections are carried out monthly, and sometimes weekly.
The regulations describe how inventory is carried out in the warehouse, who participates in it, and what documents are drawn up.
Preparatory work
The warehouse is being put in order. Many people have a question: where to start, how to carry out inventory in a warehouse effectively. Initially, documents are prepared for the commission related to receipts, write-offs, movements and other operations (damage, loss, expenses) for the period under review.
In papers relating to the previous reporting period, o. Preparing them allows you to speed up the audit process and promptly detect discrepancies between facts and the source document.
The financially responsible person gives the sorted package of papers to the commission for signature. Documents on inventories written off as expenses are attached to all inventories. The write-off is certified by a signature.
Warehouse inventory procedure
Algorithm for conducting general warehouse inventory:
- Before making an inventory of a warehouse, it is necessary to appoint an inventory commission.
- Suspension of shipment and acceptance of goods.
- Preparation of inventory sheets with data on goods (name, article, quantity, storage address).
- Reconciliation of actual availability of goods and availability according to the statement.
- If a discrepancy or defect is detected, a pallet is placed for recalculation of the goods.
Partial inventory can be carried out when discrepancies in accounting data are identified, without stopping warehouse processes.
Algorithm for conducting a partial inventory:
- Preparation of a statement with the addresses of goods.
- Checking the actual availability of goods at addresses.
- The data is verified against the accounting system.
- Reconciliation with accounting system data.
It is advisable to keep records of warehouse balances, observing expiration dates, storage conditions, quality of goods, and also carry out control measurements and weighings.
The main effects of implementing WMS in a warehouse are inventory of the warehouse without stopping warehouse operations, processing of inspection results automatically. Read more about how warehouse efficiency has increased by 30% in the news section on the ABM Cloud website.
Warehouse inventory procedure
According to the rules for conducting inventory, matching statements are prepared at the warehouse. During the recalculation process, they will be updated with current information related to the discrepancy in fact with the information in the documents. The data is entered into a single register in which all statements and inventories are recorded. At the end of the procedure, a conclusion is drawn up according to the information in the register.
Goods that are temporarily in the warehouse are recorded in a separate statement. All facts of discrepancy, including absence, must be recorded. The financially responsible person must be at the workplace during the registration of such a disagreement. If ambiguous situations are detected, the copies are re-compared with the information from the generated report.
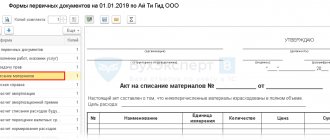
Step 1. Issue an order to conduct an inventory
The issuance of an order is the beginning of the inventory process. The order is drawn up in any form or on a form (INV-22). It states the reason for the inspection, the composition of the commission, the list of stocks or objects being inspected, the date and deadline for completion.
Sample document
The order is drawn up in accordance with the norms of office work in a printed version according to the sample. This order is given for familiarization to all members of the inventory commission against signature on the document.
Step 2. Property audit
A warehouse audit is the identification of the actual availability of stocks and balances. The information is recorded in the inventory in sections: type of product, grade, article and other important identification data in accordance with paragraph 3.15 of the Methodological Instructions. Comparison is carried out through reweighing and re-measuring. information is entered into the statement only upon the fact of recount; recording from the words of, including the interested person, is not allowed. The following are subject to mandatory audit:
- names on the way;
- goods issued for which payment has not been received;
- company assets stored on the premises of other companies;
- materials transferred for processing to other organizations.
The container is examined by the commission according to its type, condition and purpose of use in accordance with paragraph 3.26 of the Guidelines. If during the procedure it is necessary to receive new goods, they are accepted in the presence of the commission and placed in the receipt at the end of the inventory check. The fact of receipt is recorded in a separate statement.
If the inventory regulations in the warehouse are violated, the inspection period is delayed, the release of products is allowed after written permission from management. The released goods are recorded in a separate statement, and the issue is carried out in the presence of the commission. If the financially responsible person has several storage facilities at his disposal, the inspection is carried out gradually. After completing the inspection of the premises, they seal it with a sealer and proceed to inspect the next one.
Step 3. Registration of warehouse inventory results
The results of the inventory audit are documented in a package of documents:
- inventory (INV-3);
- document on verification of shipped goods (INV-4);
- act of settlement for positions en route (INV-6);
- matching statement (INV-19).
Papers are generated confirming the facts of the shortage. If the culprit is not identified, such a discrepancy is recorded by postings:
- DT2 CT1;
- DT94 KT1;
- DT91/2 KT64.
There are limits to shortages that can be attributed to production costs. If the quantity of missing goods exceeds acceptable standards, additional investigations are ordered to identify the culprits and the reasons for the discrepancy. If the commission has identified the culprit of the shortage, the information is marked with the following entries:
- DT73 KT94;
- DT50 KT73.
The surplus is registered with the wiring DT1 KT91/1. Many people have difficulties with preparing the final documents for the audit in the warehouse; we will consider how the final stage is carried out below.
Why do you need an inventory?
There are different types of inventories - full and partial. In a partial inventory, you can check only the necessary items of goods. For example, conduct a scheduled or unscheduled inspection to control products stored in warehouses and stores.
The timing of the inventory is set by the head of the organization, if the inventory is not included in mandatory cases (according to Article 12 of the Law “On Accounting”), such as:
- when selling property or transferring property for rent;
- when transforming a state or municipal unitary enterprise;
- when changing the financially responsible person;
- before preparing the annual financial statements;
- upon liquidation or reorganization of an enterprise;
- when cases of theft are detected or in the event of natural disasters, fire or an emergency caused by extreme conditions.
When preparing and conducting an inventory, be guided by the following documents:
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n “On approval of the Guidelines for accounting of inventories.”
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 13, 1995 No. 49 “On approval of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory of Property and Financial Liabilities.”
- Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.
- Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated March 27, 2000 No. 26.
The inventory is carried out to:
- Identify the actual presence of property in the organization to ensure its safety, as well as identify unaccounted for property and goods.
- Check the contents and rules of operation of the organization’s fixed assets, as well as the correct conditions for storing inventory and the use of intangible assets.
- Determine the actual use of inventory in the production process and production of products.
- Identify the presence of surpluses and shortages of goods and products from the organization in the warehouse and store.
- Check the complete and correct reflection in accounting, evaluate inventory resources taking into account their market value and actual condition.
End of the event
After drawing up the final documentation based on the results of the inspection, a protocol on the work of the commission is formed and discrepancies are calculated in monetary terms. This indicator can confirm losses or savings in production. The cause of the shortage is improper storage, theft, or negligence of the person responsible for the valuables. Excesses (savings) on a large scale appear as a result of dishonest work by employees or fraudulent actions with primary documents or accounting programs.
Persons found guilty of discrepancies between facts and accounting data are subject to financial liability. They compensate for losses by reimbursing the required amounts from earnings in the amount in accordance with the provisions of the liability agreement and the contract. The manager has the right to demote the guilty party in position, and in case of theft on a large scale, dismiss from the enterprise under the relevant article of the Labor Code or transfer the case to law enforcement agencies.
Characteristics
A characteristic feature of filling out these types of forms is that for their correctness and further legal force, it is necessary to form a special commission. It must consist of at least three people, in addition to the main person financially responsible for warehousing of inventory items.
A chairman must be elected in the commission, the remaining representatives are appointed by members of the commission. The entire document is based on a listing of the facts established by the commission.
Who exactly will fill out the form is not particularly important. Moreover, all members of the commission must sign their signature, even if they do not agree with the results of its conduct. In addition to signatures, in this case they simply make a note stating that it is in the final indicators that they are not satisfied or do not correspond to the facts they have established.
It is important to know that not all fields need to be completed by the end of the inventory process. Some of them are deliberately left blank, since the INV-5 form, after filling out, goes to the accounting department and the rest of the necessary data is entered into it there.
Inventory automation
Used to replace manual comparison with information collection using equipment. Such an audit helps reduce the likelihood of inaccuracies associated with the human factor. The labeling process is labor intensive. offers updated programs, for example, Warehouse 15 - for working under new reporting conditions, as well as projects for labeling different product groups.
Special mobile readers are used to read stickers and barcodes. Balances are recalculated through the database terminal. Information is entered into the database automatically for each item of goods. The advantages of the Cleverens automated check include:
- reducing the time for collecting and processing information by 2 times;
- there is no requirement to close the warehouse during the audit period;
- there are no errors due to human factors;
- the costs of introducing automation will pay off within 2 years;
- the risk of information distortion is minimized.
The implementation of automation is carried out in stages. Initially, a database is formed, in the appropriate sections of which information on property, goods, inventories and other material assets in the enterprise is entered. Each reporting unit is marked with a sticker or barcode, allowing you to find the position in the database. A scanner is used to read data from such stickers. The information is processed and stored in the database.
Matches are recorded immediately, and information about missing copies or missing items becomes available after the verification is completed. The terminal automatically notifies you of a shortage. The obtained data is recorded in electronic format and used for calculations and analysis. The Cleverence company offers software for automating business processes that allows you to label products and track statistics on which brands for a given item are delivered to the warehouse complex.
Stages of implementation of automated solutions for warehouse inventory
- Database creation. All property is included in it.
- Marking. Each product item is labeled with a barcode.
- Scanning markings. Information from the barcode is read using a scanner, the received data is processed and stored in a database.
- Recording the results. Coincidences between the information received and the information previously entered into the database are recorded.
- The final stage. Transferring the received information into an electronic system, from where it can be retrieved for subsequent analysis and processing.
All these steps are also suitable for store inventory.
The advantages of automated inventory are
- Double reduction in time for all operations.
- There is no need to close or stop the enterprise warehouse.
- The influence of the “human factor” is excluded.
- The payback period for implementing automated solutions is up to two years.
- The objectivity, reliability and completeness of property inspection results are ensured.
What is not allowed to be done during an audit of a warehouse with products
- Mix items, change storage locations of goods.
- Send products and consumables to production shops. The exception is situations when these operations are approved by written order of the manager.
- Allow employees and department heads to enter the warehouse without being accompanied by members of the commission. The rule applies to revisions with a long execution time.
If the working day has ended, but the work has not yet been completed, then the object must be sealed, indicating the exact closing time on the seal.
Ready-made solutions for all areas
Stores
Mobility, accuracy and speed of counting goods on the sales floor and in the warehouse will allow you not to lose days of sales during inventory and when receiving goods.
To learn more
Warehouses
Speed up your warehouse employees' work with mobile automation. Eliminate errors in receiving, shipping, inventory and movement of goods forever.
To learn more
Marking
Mandatory labeling of goods is an opportunity for each organization to 100% exclude the acceptance of counterfeit goods into its warehouse and track the supply chain from the manufacturer.
To learn more
E-commerce
Speed, accuracy of acceptance and shipment of goods in the warehouse is the cornerstone in the E-commerce business. Start using modern, more efficient mobile tools.
To learn more
Institutions
Increase the accuracy of accounting for the organization’s property, the level of control over the safety and movement of each item. Mobile accounting will reduce the likelihood of theft and natural losses.
To learn more
Production
Increase the efficiency of your manufacturing enterprise by introducing mobile automation for inventory accounting.
To learn more
RFID
The first ready-made solution in Russia for tracking goods using RFID tags at each stage of the supply chain.
To learn more
EGAIS
Eliminate errors in comparing and reading excise duty stamps for alcoholic beverages using mobile accounting tools.
To learn more
Certification for partners
Obtaining certified Cleverence partner status will allow your company to reach a new level of problem solving at your clients’ enterprises.
To learn more
Inventory
Use modern mobile tools to carry out product inventory. Increase the speed and accuracy of your business process.
To learn more
Mobile automation
Use modern mobile tools to account for goods and fixed assets in your enterprise. Completely abandon accounting “on paper”.
Learn more Show all automation solutions
What not to do when taking inventory of inventories
During the audit, it is not allowed to mix items or transfer them for storage to other sections or premises. During the inspection period, the release of inventories and consumables to production is prohibited, except in situations where the need for release is confirmed by written permission from the manager.
If the inventory is being carried out over a long period of time, employees, including the head of the department, are not allowed to enter the territory without the presence of a commission. At the end of the working day, the object is sealed with the exact time indicated on the seal.
The inventory commission is carried out before drawing up the annual final documentation.
The results of the event are subject to mandatory documentation. At the end of the inspection, a protocol is drawn up, which is endorsed by the signature of the manager and the company’s seal. Inventory of goods in a warehouse is the only way to confirm the integrity of the storage of material assets in the company’s warehouse. Number of impressions: 47147
Components of the form
The inventory has several pages. The first is introductory, it contains a part with a receipt, the second and subsequent elements are presented in the form of a table. At the conclusion, the signatures of the responsible persons are affixed.
First part of the form
Fundamentally important points are indicated at the beginning. In the form of a small table on the far right side of the sheet, the form numbers according to OKUD, OKPO, the code of the type of activity of the organization, the document number and the date of its preparation, two dates: the beginning and end of the inventory are listed (even if it was carried out on one day, indicating both identical ones is mandatory), type of transaction performed and accounting account number. The last two columns are filled in by the accountant after the signatures of the commission members and consideration by the manager.
Also, separate lines are left for the full name of the organization (abbreviations to LLC, OJSC, individual entrepreneur, etc.) and the name of the division are acceptable. The latter, in the vast majority of cases, is a warehouse under some serial number, since the INV-5 form is the most common in warehouse policy.
Important point! At the top, the basis for the inventory must be indicated. This may be an order, notification or order from the head of the company as a whole or its division.
In any case, the inventory process must be carried out under the guidance and knowledge of the persons concerned. This fact must have documentary evidence.
Part with receipt
On the first sheet of the document there is a receipt from the financially responsible person stating that by the time the inventory began, all the primary reporting documents necessary for this had been submitted to the accounting department, and goods and materials (inventory assets) had been capitalized and accepted for safekeeping.
Also, at the beginning of the verification process, all material resources written off from accounts must be indicated in the disposal papers. It is undesirable for them to actually be in the warehouse itself to avoid misunderstandings.
The receipt must also indicate the date of its signature and the deadline for removing the remaining material assets.
The second part of the form is tabular
The information is very compactly placed in the table. Using the latter is extremely convenient. The form was formed in the 90s, but still remains relevant. The rows of the table are filled in as the actual availability of inventory items in the warehouse is compared with the data in existing documents. The columns should contain the following information:
- The sequence number of the line.
- Name and OKPO code of the supplier or recipient.
- Nomenclature number of the product, its grade, type or group, full name.
- Storage location (usually the cell or location number is indicated).
- The date when the goods were accepted for responsible warehousing.
- Name, number and date of the document that indicates the receipt of goods and materials at the warehouse (for example, invoice 25 dated August 23, 2019).
- The unit of measurement of the purchased goods and the code of this unit according to OKEI (g, kg, l, pcs., etc.).
- How much inventory material actually exists, total quantity and cost.
- How much goods are available according to currently maintained accounting records.
If the last two columns of the same column are not identical, then this is a defect of the accountant or storekeeper (or other person financially responsible for the product being described). The INV-5 form is convenient precisely because it is possible to illustrate this kind of discrepancy.
Final part
When the inventory is nearing completion, the chairman of the commission and all its members must review the compiled table and put their signatures at the end of the inventory list of inventory items accepted for safekeeping. The signatures will indicate that the availability of goods, their actual quantity and cost have been verified.
Important! Separately at the end, the total amount of all inventory items is indicated in numbers and words.
The financially responsible person puts his signature after all members of the commission as a sign that he has no complaints about their work and agrees with the data provided. The form leaves space for the signatures of two such MOLs, but there may be more. Below the signature of the responsible person is usually the signature of the accountant who verifies the calculations made in the document.