The procedure for purchasing food or industrial products between the seller and the buyer is regulated by the provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Chapter 30).
The participants enter into an agreement under which one of the parties undertakes to supply a certain quantity of goods (services), and the other party undertakes to pay for it. Failure to comply with the provisions of the agreement serves as grounds for its termination and return of the goods, the grounds for which are defined by law.
Question: The buyer resells to the seller goods previously purchased from him and accepted for registration. In this case, the buyer, as a new seller, issues an invoice to the seller, as a new buyer. In this case, the former seller accepts VAT for deduction in the general manner as an ordinary buyer. How to reflect this option of returning goods in accounting? View answer
Basic Concepts
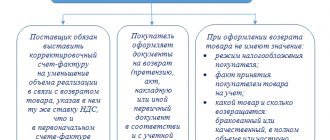
When purchasing a product for further sale (wholesale), the seller is called the supplier, and the buyer is called the counterparty. The role of the supplier can be directly from the manufacturer (manufacturer) of the product, a legal organization or an individual. In relation to the buyer, the supplier is obliged to:
- provide a certain number of purchased products of appropriate quality;
- fully satisfy legal claims regarding the acquisition from the counterparty;
- make deliveries within the terms specified in the contract, without delays.
The counterparty is obliged to accept the supplied objects and pay for everything provided to him in the manner specified in the contract: advance (preliminary) payment, upon receipt, upon sale (according to schedule).
If payment terms are violated, the seller has the right to file a payment claim against the consumer.
How to reflect the return of goods in tax accounting for income tax ?
If the supplier fails to comply with the terms of the agreement, the buyer has the right to return the goods in whole or in part. Problems with return transfer often arise due to a lack of completeness of the delivery or non-compliance with quality parameters. The supplier and counterparty document the transaction by making the necessary accounting entries.
By the way! By agreement, it is possible to replace the purchase or eliminate violations within a specified time frame. If the seller evades fulfillment of claims, the counterparty has the right to send a statement of claim to the judicial authorities.
Legal basis for returning goods
The transfer of the purchase between the parties to the transaction is regulated by the supply agreement (Article 506 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). It is allowed to transfer at the place of purchase the products that were actually delivered to the counterparty. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the reasons may include the following:
- what was purchased does not correspond to the declared quality (Article 475);
- the supplied assortment does not correspond to the documents (Article 468);
- the quantity (volume) of the delivered object turned out to be less than the value indicated in the documents (Article 466);
- the counterparty was not provided with the necessary documents for the delivered object (Article 464);
- packaging of products is not carried out according to established requirements or the necessary containers are missing (Article 482).
The recipient who discovers non-fulfillment (performance of inadequate quality or volume) by the supplier of the terms of the agreement in terms of delivery time, completeness, quality characteristics of the supplied products, has the right to refuse to fulfill contractual requirements in relation to products for which the relevant requirements are violated. Such a refusal may be grounds for returning the product.
Is the return of goods to a seller who does not pay VAT subject to VAT?
The fact that the product does not comply with the terms of the agreement may be revealed during its acceptance or later as a result of the discovery of hidden defects. Therefore, in consumer accounting, goods can be either capitalized or not. The seller is sent a document regarding discrepancies (act) with a claim for the return of what was received attached.
Among the conditions for return, there may be the right of the counterparty, specified in the contract, to return what was purchased but not sold by him within the agreed period after delivery, or the right to return transfer by mutual agreement of the parties to the transaction.
In such situations, the supply agreement applies a reverse sale of what was received, but now the supplier acts as the buyer, and the previous buyer acts as the supplier.
How to return in the absence of grounds, but with the consent of the other party?
What documents should I fill out?
Regardless of whether a return is provided for in the contract or not, the required documents for a return are :
- waybill (unified form TORG-12 or a self-developed document);
- invoice (you can find out how to issue an invoice for returning goods to a supplier, and also see a sample document here).
The important aspect is that in these documents the supplier will become the buyer and the buyer the supplier.
Packing list
The supplier of the goods is the former buyer . Accordingly, its data is indicated in the columns “name, address, details”.
The buyer will also be the shipper. It is not necessary to fill in the fields regarding the shipper (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 25, 2014 No. ED-4-15/ [email protected] ).
The consignee is the former seller (supplier) . His details are indicated in the “consignee” column.
The “Payer” column is filled in only if the former buyer receives money upon return.
The “Base” column is the most important point . This indicates “return of goods”. The details of the invoices on which the returned products were accepted, the details of the contract and other documents regarding the return are also listed.
Items about the product. Here it is necessary to clearly describe the products, quantity, packaging and other conditions, on the basis of which complete agreement with previously accepted products will be seen.
The document is signed by the manager, chief accountant, financially responsible person and recipient.
also indicate in the delivery note the documents on the basis of which the return agreement was concluded - letters, additional agreement.
Invoice
If the organization that previously acted as the buyer is on the general taxation system, then an invoice is issued. It is reflected in the sales book, and for the supplier - in the purchase book.
If the organization that previously acted as the buyer is under a simplified taxation regime, then an invoice is not issued, because this organization does not pay VAT and is not entitled to a tax deduction (you can learn about the nuances of returning goods to a supplier under different taxation systems, and also see how to correctly fill out a profit declaration here).
Differences in Concepts
Some accountants do not share the concepts of “return of goods” and “reverse sales,” resulting in numerous problems with the preparation of documentation and with the reflection of transactions performed in accounting (tax, accounting).
If, some time after shipment of the purchased shipment, the purchaser returns what he received (in whole or in part) to the seller, it is important to find out the exact reason for this.
When the reason for the return movement of products is the non-compliance of the supply with the terms of the agreement (specification) in terms of configuration, color, quality or size, then the procedure should be interpreted as a return.
This situation arose as a result of the seller’s failure to properly fulfill its obligations to deliver what was ordered.
If the contract is terminated for the reason specified in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the obligations of the parties are not fulfilled, and there is no fact of implementation. With such a transfer, a waiver of the owner’s rights to the acquisition received is obtained, and not a restoration of the transferred right of ownership. The buyer, who has already recorded the receipt in accounting, must make reversing entries to correct it.
In cases where the purchaser does not have any claims to the received product, and its movement to the place of sale is carried out by agreement with the seller (for example, a part that was not sold on time), then the process is a reverse sale. In fact, 2 transactions take place: in the first transaction, the supplier sold goods to the buyer, and then in the second transaction, the buyer sold the same objects or part of them to the supplier. Both parties formalize and record the transaction as a regular purchase or sale of products.
By the way ! A product received under an agreement that meets the quality requirements is returned to the seller only by decision of the parties to the transaction or if the situation is stipulated by the terms of the current agreement (Article 450, Article 453 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Upon receipt, ownership of the product is transferred to the acquirer (Article 223 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), and upon reverse sale, carried out at the same cost at which the product was purchased, ownership changes to its original state (before sale).
How to avoid overpaying taxes
An option to solve this problem, in our opinion, is a delayed transfer of ownership. What explains this conclusion?
As a general rule, ownership of the goods passes to the buyer from the moment he receives it (Article 224 of the Civil Code). An exception to the general rule is Article 461 of the Civil Code. It provides for this possibility: the seller retains ownership of the goods - even if it has been shipped to the buyer - until certain circumstances occur.
And if such circumstances do not occur within a certain period of time, the seller, as the owner who has the right to determine the fate of this product, has the right to demand that the buyer return the product to him.
Photo from the site megapolis-real.by
But, as we have repeatedly repeated, the procedure for transferring ownership, which differs from that established by the general rule, must be determined in the contract itself!
Consequently, the return of even high-quality goods, without negative consequences, under a sales contract is possible. But only on condition that in this agreement:
1. Circumstances are provided for until the occurrence of which ownership rights remain with the seller (clause of deferred transfer of ownership rights).
2. At the time of returning the goods, such circumstances had not occurred.
Thus, the parties can be guided by the procedure for transferring ownership rights expressly agreed upon by the parties in the contract. For example, the transfer of ownership when certain conditions are met - when selling goods to third parties, paying for goods.
The seller can and must determine the conditions for the possible return of the goods transferred to the buyer. For example, usually the seller explicitly states in the contract that he allows the sale of such goods to third parties. In addition, the parties agree on the procedure for action when the seller makes a request to return the goods. It is advisable to directly indicate in the contract the right of the owner (seller) to demand the return of the goods, as well as the buyer’s obligation to return the goods within a certain time frame.
Registration of reverse sales
The reverse sale procedure does not require the execution of an act (form TORG-1). The buyer sends the supplier an invoice for the amount of the goods being transferred back. The specified document is registered in the sales book (letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-09/17 (03/02/2012), 03-07-11/79 (03/23/2012)).
According to the accounting records of the seller, proceeds from the sale are recognized as receipts from ordinary types of activities, and expenses (in the form of cost) are recognized as expenses for ordinary types of activities (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 32N, 33N, 05/06/1999).
The counterparty completes the sale in a standard manner, and the supplier makes the following transactions (debit/credit):
- 62 / 90.1 – reflection of revenue from sales (Settlements with buyers and customers/Sales (revenue));
- 90.3 / 68 – calculation of VAT on sales (Sales (VAT)/Calculations for taxes and duties (VAT));
- 90.2 / 41 – write-off of production costs (Sales (cost of sales)/Goods);
- 41 / 60 – transfer of the object to the warehouse (return);
- 19 / 60 – allocation of VAT on the product;
- 68 / 19 – direction of VAT for deduction;
- 60/62 – mutual settlement of the parties (with the drawing up of an act).
By the way! When returning, the seller can set off the VAT accrued upon sale as a deduction (Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which can be applied in full after all adjustments have been made in the accounting, but no later than 12 months from the date of return (Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Registration in the case when the buyer is not a VAT payer
During the reverse sale, the original buyer, and now the seller, who is not registered as a VAT payer due to working under the simplified taxation system, can nevertheless deduct VAT on returned goods (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-15-29, 07.03 .2007).
The original seller makes adjustments to the invoice it previously issued to the purchaser. The specified document is subject to registration in the purchase log (for the amount of the amount to be returned). Therefore, it turns out that the failed seller will be able to offset VAT on the returned items. The reason for the return of the product and the fact that it was accepted or not registered by the counterparty who did not pay VAT at the time of return do not matter.
If the purchased item is returned by an individual, when transferring money from the cash register, it is recommended to register the details of the issued cash order (expenditure) in the purchase log. After the newly received object is capitalized, the seller has the opportunity to accept VAT (deductible).
By the way! Some accountants believe that upon return, the former acquirer must transfer VAT to the seller through a payment order, since this transaction is identical to the offset of claims and commodity exchange transactions, when the amount of tax is transferred to the partner in money (Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But according to the clarification of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation (letter No. 03-07-11/128, 04/27/2007), if the purchase is returned to the supplier, then the amount of tax must be deducted and cannot be compensated at the expense of the purchaser. Therefore, when transferring back, the buyer does not have to send the tax amount separately.
Return of goods upon shipment without transfer of ownership in "1C: Accounting 8"
We will consider the procedure for the seller to reflect the return of goods under a contract with a special condition for the transfer of ownership in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0, using the following example.
Example
The organization Trading House LLC (seller) shipped a consignment of goods (10 pieces) worth RUB 150,000.00 to Modny Gorod LLC (buyer). (including VAT 20% - RUB 25,000.00). The goods are delivered by the seller using a transport company. Ownership of the goods passes to the buyer upon acceptance of the goods at the buyer's warehouse. Due to the discovery of a defect, the buyer returned some of the goods to the seller:
- 1 PC. — upon acceptance (before the transfer of ownership to the buyer);
- 2 pcs. - after acceptance (after the transfer of ownership to the buyer). The sequence of operations is given in the table.
Shipment of goods to the buyer
To enable the mechanism for calculating VAT on shipment transactions without transfer of ownership, you must set the flag for the value Accrue VAT on shipment without transfer of ownership on the VAT tab of the Taxes and Reports Settings form (Main section - subsection Settings - Taxes and Reports).
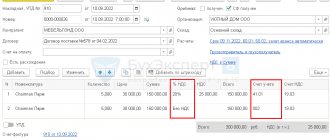
To perform operations 1.1 “Reflection of the shipment of goods without transfer of ownership”; 1.2 “Calculation of VAT on shipment without transfer of ownership”, you must create a Sales document (act, invoice) with the transaction type Shipment without transfer of ownership (section Sales - subsection Sales), fig. 1.
Rice. 1. Shipment of goods to the buyer
After posting the document, the following accounting entries are entered into the accounting register:
Debit 45.01 Credit 41.01
— for the cost of goods shipped in the amount of RUB 100,000.00. (10 pcs x 10,000.00 rub.);
Debit 76.OT Credit 68.02
— for the amount of accrued VAT in the amount of RUB 25,000.00. (10 pcs. x RUB 12,500.00 x 20%).
A registration entry is made in the Sales VAT accumulation register to create a sales book for the tax period of shipment of goods.
To issue an invoice for shipped goods (operation 1.3 “Issuing an invoice for shipped goods”), you must click on the Issue an invoice button at the bottom of the Sales document (act, invoice), Fig. 1. In this case, the document Invoice issued is automatically created, and a hyperlink to the created invoice appears in the form of the basis document.
In the new posted document Invoice issued, which can be opened via a hyperlink, all fields will be filled in automatically based on the data in the Sales document (act, invoice).
Besides:
- in the line Basis documents there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding implementation document;
- in the Operation type code field the value 01 will be reflected, which corresponds to the shipment (transfer) of goods (work, services), property rights (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] );
- The Receipt Method switch will be set to Hard copy if there is no valid agreement with the seller to exchange invoices electronically. If there is an agreement, then the switch will be in the Electronic position;
- in the line Issued (transferred to the counterparty), a flag will be placed and the date of registration of the Sales document (act, invoice) will be indicated, which, if necessary, should be replaced with the date of actual issuance of the invoice. If an agreement has been concluded with the buyer on the exchange of invoices in electronic form, then the date of sending the electronic invoice file to the EDF operator, indicated in its confirmation, will be entered in the field.
As a result of posting the issued Invoice document, a registration entry is made in the Invoice Journal register to store the necessary information about the issued invoice.
Using the Print document Invoice issued button, you can view and print the invoice.
Thus, in the sales book for the third quarter of 2022 (approved by Resolution No. 1137) - section Reports - subsection VAT - the registration entry for invoice No. 5 dated 07/01/2020 will be reflected for the amount of VAT accrued upon shipment of goods in the amount RUB 25,000.00 with KVO 01.
Return of goods from the buyer before sale
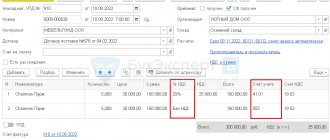
Return of goods made before the transfer of ownership of the goods to the buyer in accordance with the terms of the contract (operations 2.1 “Reversal of shipment of goods without transfer of ownership”; 2.2 “Adjustment of accrued VAT”; 2.3 “Reflection of tax deduction”) is registered using the document Return of goods from the buyer (Fig. 2), which can be generated from the Sales document (act, invoice) with the operation type Shipment without transfer of ownership by clicking the Create based button (Fig. 1).
Rice. 2. Return of shipped goods from the buyer
In a new document filled with information from the Sales document (act, invoice), it is necessary to indicate in the Quantity column of the tabular part of the document the quantity of goods returned to the seller before the moment of its sale to the buyer.
After posting the document, the following accounting entries are entered into the accounting register:
Debit 45.01 Credit 41.01
— REVERSE for the cost of returned goods in the amount of RUB 10,000.00. (1 piece x 10,000.00 rub.);
Debit 76.OT Credit 19.03
— REVERSE for the amount of VAT accrued upon shipment of returned goods in the amount of RUB 2,500.00. (1 piece x RUB 12,500.00 x 20%);
Debit 68.02 Credit 19.03
- for the amount of VAT claimed for tax deduction in respect of returned shipped goods in the amount of RUB 2,500.00.
As a result of posting the document, entries are made in the VAT accumulation register presented with the type of movement Income and Expense.
An income in this register is a potential entry in the purchase book, an expense is a VAT claim for deduction or a write-off for other reasons. For example, the tax amount can be included in the cost of goods, written off against the organization’s net profit, etc.
To create a purchase book, an entry is made in the Purchase VAT accumulation register.
According to paragraph 1.4 of the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected], when returning from January 1, 2019 the entire batch (or part) of goods, both accepted and not accepted for registration by buyers, the seller is recommended to issue adjustment notes invoices for the cost of goods returned by the buyer.
Thus, when returning the entire consignment of goods or part of the goods, the seller makes a tax deduction for the VAT amounts calculated and presented to the buyer upon shipment of the returned goods, based on the adjustment invoice issued by him.
To issue a correction invoice for shipped goods (operation 2.4 “Issuing a correction invoice”), you must click on the Issue a correction invoice button at the bottom of the Return of goods from buyer document (Fig. 2). In this case, the document Adjustment invoice issued is automatically created, and a hyperlink to the created invoice appears in the form of the basis document.
In the new posted document Adjustment invoice issued (Fig. 3), which can be opened via a hyperlink, all fields will be filled in automatically based on the data in the document Return of goods from the buyer.
Rice. 3. Corrective invoice when returning shipped goods
Besides:
- in the line Documents-basis there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding document for the return of goods;
- in the Transaction type code field, the value 18 will be reflected, which corresponds to the preparation of an adjustment invoice due to a decrease in the cost of goods (work, services) shipped, transferred property rights, including in the case of a decrease in the quantity (volume) of goods shipped ( works, services), transferred property rights (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] );
- The Receipt Method switch will be set to Hard copy if there is no valid agreement with the seller to exchange invoices electronically. If there is an agreement, then the switch will be in the Electronic position;
- in the line Issued (transferred to the counterparty), a flag will be placed and the date of registration of the Sales Adjustment document will be indicated, which, if necessary, should be replaced with the date of actual issuance of the adjustment invoice. If an agreement has been concluded with the buyer on the exchange of invoices in electronic form, then the date of sending the electronic invoice file to the EDF operator, indicated in its confirmation, will be entered in the field.
As a result of posting the document Adjustment Invoice issued, a registration entry is made in the Register of Invoices to store the necessary information about the adjustment invoice issued to the buyer.
Using the Print document Adjustment invoice issued button (Fig. 3), you can view and print the adjustment invoice.
As a result of the operation to return shipped but not sold goods, a registration entry will be made in the purchase book for the third quarter of 2022 (section Reports - VAT subsection) for adjustment invoice No. 6 dated 07/07/2020, issued to invoice No. 5 dated 07/01/2020, with transaction type code 18, which corresponds to the preparation of an adjustment invoice due to a decrease in the cost of goods (work, services) shipped, transferred property rights, including in the case of a decrease in prices (tariffs) and ( or) reducing the quantity (volume) of shipped goods (works, services), transferred property rights (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ).
Sales of shipped goods
To perform operations 3.1 “Accounting for revenue from the sale of goods”; 3.2 “Reflection of VAT on the sale of goods”; 3.3 “Write-off of the cost of goods sold”, you need to create a document Sales of shipped goods (Fig. 4) based on the document Sales (act, invoice) (Fig. 1) by clicking the Create based button.
Rice. 4. Sales of shipped goods
Since before the transfer of ownership of the goods to the buyer, some of the goods were returned to the seller, as a result of posting the document Sales of shipped goods, accounting entries are generated taking into account the return of goods made before the sale:
Debit 90.02.1 Credit 45.01
- for the cost of goods sold in the amount of RUB 90,000.00. (9 pieces x 10,000.00 rub.);
Debit 62.01 Credit 90.01.1
- for the amount of proceeds from the sale including VAT in the amount of RUB 135,000.00. (9 pieces x 15,000.00 rub.);
Debit 90.03 Credit 76.OT
— on the amount of VAT accrued on the sale of goods in the amount of RUB 22,500.00. (9 pieces x RUB 12,500.00 x 20%).
Reflecting the sale of previously shipped goods under a contract with a special condition for the transfer of ownership does not lead to a change in the amount of VAT accrued upon the shipment of these goods.