In real life, not a single accountant lives without mistakes - this is the usual price for professionalism. First mistakes - then experience. Overpayment to the budget is a very common problem. First, let's figure out in what cases it occurs. Theoretically, there can be several options:
- an accountant's mistake, for example, an extra zero is indicated in the amount;
- the amount was transferred to the budget twice, for example, due to a bank error;
- the actual economic activity of the organization during the reporting year did not correspond to the planned one, for example, losses were received rather than income, but advance payments were transferred to the budget.
First of all, you need to decide what to do: return the amount overpaid to the budget to the organization’s account or offset it against the payment of arrears or future payments.
Possible options
The return and offset procedure is regulated by Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For convenience, we present it in the form of a diagram.
The whole procedure can be represented step by step as follows:
- We establish the fact of excessive payment to the budget.
- We check whether there is arrears on any of the taxes, penalties or fines, against which the inspectorate can offset the overpaid amounts.
- We check whether the declaration needs to be clarified at the same time.
- We determine our preferences, two options are available: refund or credit.
- We reconcile payments to the budget.
- We are preparing the necessary applications.
- We send the necessary package of documents to the inspection.
How to identify
Before you begin filling out an application for a refund or tax credit, you need to determine whether this treasured amount exists or is it just an accounting error in the records. So, how to identify the overpaid amount in taxes.
Step No. 1. Check your accounting.
Of course, first of all it is necessary to check the correctness of registration of transactions in the organization’s accounting records. It is quite possible that the error crept not in the payment order, but in the way the accountant compiled the posting. Particular attention should be paid to the procedure for registering transactions in specialized accounting programs.
Check what? Accounting accounts and analytics on them (KBK, subaccount, KOSGU, type of payment, etc.). Re-grading by BCC or type of transaction (fine, tax, fine) are the most common errors in accounting programs.
After checking, be sure to create a balance sheet and an account card for the period you are interested in. This is necessary to check whether the errors are fixed or not.
Step No. 2. Check with the bank.
If no accounting errors are found, check your bank statements. Are the transactions posted correctly in accounting, and did the bank execute payment orders correctly?
In the bank statement, you can verify the tax recipient, KBK and other payment details; it is against these indicators that you can verify the accounting data. Correct any errors found in your accounting. If the bank makes a mistake, contact your local branch to resolve the problem. It is worth noting that banking errors are isolated cases.
Step No. 3. Reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service on taxes and contributions.
So, if internal control and reconciliation with the banking organization did not produce results, then you should contact the Federal Tax Service. To do this, just contact the nearest territorial inspection office. If the institution exchanges documentation with the Federal Tax Service via secure Internet channels, then you can request an extract in electronic format. You can also obtain information in your personal account on the official website of the Federal Tax Service. For more details, see the material “Instructions: how to check tax arrears.”
Based on the results of reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service, we determine the overpaid amount for taxes. Now we decide what to choose: offset or issue a tax refund.
How to count
As a general rule, any federal tax, including income tax, can be offset against future payments for any other federal payment or fines and penalties to the federal budget. In this case, the existing arrears are repaid by the inspection itself and do not require the participation of the organization. However, the latter retains the right to submit an application for offset of overpayments on taxes; an application for this is submitted to the inspectorate at the place of registration of the organization in paper or electronic form.
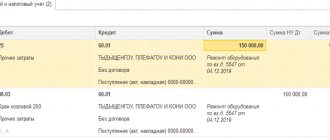
To reflect the offset operation, according to the chart of accounts approved by Order 94n, analogous accounts are used for budgetary institutions.
| The amount of profit was offset against VAT payment | 68-VAT | 68-pr | 20,000 rub. | Decision, accounting certificate |
How does an overpayment of income tax occur?
Overpayment of income tax occurs for organizations in the following cases:
- The organization pays monthly advance payments. The income tax accrued based on the results of the quarter during which these payments were made turned out to be less than the amount of advance payments. Or, based on the results of the quarter, the organization received not a profit, but a loss.
Read more about advance payments in the material “Advance payments for income tax: who pays and how to calculate?” .
- The organization submitted an updated profit declaration for the previous period with a reduction in the amount of tax accrued for payment or with the replacement of profit by loss.
Read about the specifics of creating an updated declaration in the article “Updated declaration: what does an accountant need to know?” .
- The organization made a technical error when paying taxes and transferred to the budget an amount exceeding the amount accrued according to the declaration.
How to fill
First of all, we note that applying for a credit is required separately for each type of tax, fee or contribution. It is not possible to combine fiscal payments in one document.
If an organization is registered with several Federal Tax Service Inspectors at once, for example, it has several branches or separate divisions, then the document should be submitted exactly to the inspection department where the overpayment of taxes occurred.
Instructions for filling:
- In the header of the document we indicate the TIN and KPP of the taxpayer-applicant.
- The application number is a serial number for the current year.
- Payer status: for an organization it is either “1” - taxpayer, or “4” - tax agent.
- Enter the article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in accordance with which we carry out the offset. Indicate the article number in the field: “176” - for VAT credit, “203” - for excise tax and “78” - for other fiscal payments (taxes, fees, contributions).
- Select the type of payment from the list provided. For example, to offset income tax, select “1”, to offset VAT penalties, select “4”.
- Then we determine the period or specific date for which the overpaid amount was generated. For example, for January 2022 - MS.01.2019, for the 1st quarter of 2022 - KV.01.2019, for the 1st half of the year - PL.01.2019, for the year - GD.00.2019. We indicate a specific date if the law establishes the exact date for filing a declaration or paying a tax. For example, 03/28/2019 to pay income tax.
- OKTMO - the code corresponds to the code of the place where the taxpayer is registered.
- Indicate the BCC corresponding to the tax, fee, contribution for which the overpayment was detected.
- On the second sheet of the document, indicate the overpaid amount in rubles and kopecks. Then determine what the payment should be redirected to: “1” - for arrears, “2” - for future periods. Specify the tax period to be offset against future payments.
- Enter OKTMO at the place where the payment was made.
- BCC of the tax, fee, contribution against which the offset is made.
- The last page (section “Information about an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur”) is not filled out by institutions.
What will change from October 1, 2022
From October 1, 2022, para. 2 p. 1 art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and from this date, when offsetting taxes, it will not matter what type of tax this or that tax belongs to. That is, for example, an overpayment of VAT can be offset against the arrears of corporate property tax. The same applies to penalties and fines: since the “link” to the type of taxes has been canceled, the same overpayment of value added tax can be offset not only against property tax, but also against arrears of penalties and (or) property tax fine.
The rules for the return of overpayments will also change: it will be possible to return the overpayment only on the condition that the payer does not have arrears for any taxes, penalties, fines, and not just for taxes of the same type. We can say that if it becomes easier to offset the overpayment, then it will become more difficult to return it.
Attention: the rules of offset and return for insurance premiums will not change.
Since no transition periods are provided, offsets and refunds under the new rules will also apply to amounts paid before October 1, 2022. It does not matter when exactly the overpayment occurred. It is important that the offset or refund itself occurs after the specified date (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 10, 2020 No. 03-02-07/1/72100).
Online accounting from Kontur.Bukhgalteriya or My Business will help you to keep your books competently and monitor the status of your tax and contribution payments. Automated accounting (including for employees, goods, materials). 24/7 support and expert advice. More than 2000 forms of primary and personnel documents.
How to return
It makes sense to return funds when you are sure that the organization has no debts to pay taxes, penalties and fines. Ideally, you need to obtain a reconciliation report from the tax office. Please keep in mind that the refund will be made only after the existing arrears have been repaid. Otherwise, the return application will be rejected.
If the head of the organization has decided that the overpaid amount needs to be returned, it is necessary to fill out an application for a refund of the overpayment of taxes; the terms of transfer to the organization's current account are calculated from the date of filing the application and amount to no more than one calendar month.
The return of the overpaid amount must be reflected in standard posting.
| Wiring | Operation |
| Dt 51 Kt 68 | Overpaid income tax refunded |
Please note that applying for a refund from the budget should take into account the current circumstances. For example, for monthly payments, such as insurance premiums or personal income tax, it makes no sense to return overpaid amounts, because next month the organization will again calculate wages and calculate payments towards insurance coverage. However, if we are talking about a company being reorganized or liquidated, then the return is justified.
You should also take into account the company's planned performance indicators. For example, if a budget institution previously provided paid services. Based on the results of the reporting provided to the Federal Tax Service, an overpaid amount of VAT was identified. However, business activity was terminated by the decision of the founder. Let us remind you that public sector employees are exempt from paying VAT on activities financed by subsidies. Consequently, the institution has no obligation to calculate and pay VAT in the current period. And it will not be possible to offset the overpayment against future VAT charges (paid services have been discontinued). It is in this case that you need to fill out an application for a refund of the overpaid tax.
But even in such a situation, the institution has the right to transfer the overpaid money to other payments. For example, to pay off debts on transport, land tax or property tax. Therefore, the decision must comply with the provisions of the law and satisfy the needs of the taxpayer.
Refund of overpayment
To return money to the current account, the organization submits an application in the KND form 1150058 within three years from the date of the overpayment. To make a decision, inspectors have 10 working days from the moment they receive the application or sign the reconciliation report. After 5 working days, tax authorities are required to inform the organization or individual entrepreneur about the decision made (clause 9 of Article 78 of the Tax Code). After a month, return the overpayment to your bank account. If the taxpayer made a mistake and provided incorrect details, the refund will be processed after clarification.
Refund of overpaid taxes is a right, not an obligation, of the taxpayer. An organization or individual entrepreneur can waive their right, which does not contradict paragraph 6 of Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-07-11/63803 dated December 11, 2014).
How to fill out a tax refund application
The tax refund application is filled out according to similar rules. Please note that the updated KND form 1150058 itself already contains detailed instructions and tips for filling out.
The document can only be issued in relation to a specific fiscal payment. You cannot combine several types of overpayments in one refund application. Even if the taxpayer returns overpaid penalties and fines for one fee, he will have to prepare two refund applications. One is for a tax penalty, the second application is for a refund of the fine. Since for each payment the corresponding budget classification code is determined - KBK.
Submit an application for a tax refund to the exact branch of the Federal Tax Service where the taxpayer is registered. If the overpaid amount is identified in a separate division, report it to the Federal Tax Service at the place where the OP is registered.
Instructions for filling out a tax refund application, key aspects:
- The checkpoint should indicate the code assigned to the organization or separate division in the tax authority to which you are submitting an application for a tax refund.
- Correctly indicate the reason for the overpayment. There are several options available to choose from. For example, if you overpaid, indicate code “1” in your tax refund application. If the taxpayer is claiming a refund of VAT or excise taxes from the budget, then enter “3”.
- Detail the type of payment for which you are processing a refund from the budget. If you are returning the amount for the main obligation, write “1” in the return application, “4” for compensation of overpaid penalties, “5” for fines.
- In the “Account Information” section of the tax refund application, enter the necessary information about the banking organization in which the corresponding current account is opened. Then indicate the type of account, according to the decoding indicated in paragraph 6 of the filling rules (see the KND 1150058 form itself). The recipient is the applicant organization.
Please note that there are exceptional filling rules for public sector institutions. So, for example, a budgetary institution in the “Name of the bank” paragraph must indicate the name of the Federal Treasury body in which the personal account is opened. The account number is the standard 20 characters. But the recipient of the payment for public sector employees is not the name of the organization, as, for example, NPOs or commercial firms must register. In this paragraph, you must indicate code “3” and enter the name of the body that opens and maintains personal accounts. In most cases, this is a territorial branch of the Federal Treasury.
NPOs and commercial firms do not indicate the personal account number and BCC for enrollment. But public sector institutions are required to fill out the fields. The personal account number is a unique number (can contain not only numbers, but also Latin letters). But the BCC is determined for each type of institution individually:
- autonomous ones enter zeros in the budget classification code;
- budgetary - indicate KBK 000000000000000000130;
- government - fill out the KBK in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 132n.
The last section of the tax refund application does not need to be completed. It is intended for individuals.
Special cases
Sometimes there is an overpayment of federal taxes and an underpayment of those regulated by the subject, that is, payments are made to different levels of the budget system. This is called a violation of interbudgetary regulation, and such cases are regulated not by Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 12, 2013 No. 107n and the Budget Code.
First of all, in such a situation, it is necessary to clarify the tax payment that caused the problem. And then, to correct the situation, write and send a letter to the tax office to clarify the details of the payment order regarding the budget classification code. It is compiled in free form and submitted in written or electronic form.
How to find out about an overpayment
Both the taxpayer himself and tax inspectors can find overpayments of taxes. You can order a reconciliation report from the tax office or check your transfers in your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website. Within five working days after submitting the documents, tax officials must issue a reconciliation report and send it to the taxpayer.
If the tax authorities were the first to discover the overpayment, they are obliged to notify the organization - within 10 working days they must send a written message and indicate the date the overpayment was discovered (clause 3 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The date of discovery of the overpayment is the day when the inspector discovered the excess for a particular tax. Regardless of whether the tax inspectorate informed the taxpayer about the fact of an overpayment or not, the overpayment can be disposed of within three years from the date of occurrence.
Taxes to the budget for the taxpayer can be transferred by any other person - an organization, an entrepreneur or a citizen without the status of an individual entrepreneur (paragraph 4, paragraph 1, article 45 of the Tax Code). But only the taxpayer himself has the right to return the excess or offset the payment. Third parties cannot do this (paragraph 5, paragraph 1, article 45 of the Tax Code).