Real estate means not only building structures, but also land plots, subsoil, and other objects closely related to the land. It is impossible to move them without damaging them. The article will discuss the tax and accounting of real estate, the peculiarities of registering transactions with them in the conditions of reorganization or liquidation of an enterprise, leasing, construction or reconstruction. In this article we will talk about accounting of real estate at cadastral value using the example of the simplified tax system tax regime.
Expenses for the purchase of real estate and acceptance for accounting under the simplified tax system
Real estate is classified as fixed assets (fixed assets) used to create goods and sell them. When the “simplified” tax is calculated, the cost of those fixed assets that are recognized as property subject to depreciation must be taken into account. Neither land nor other environmental management assets are depreciated. Therefore, the cost of the land plot cannot be taken into account when calculating the single tax.
Costs incurred when purchasing real estate from the state are taken into account as expenses for paying for the services of special organizations that prepare documents for their cadastral and technical registration. The initial cost of real estate under the simplified tax system includes:
- When purchasing – the supplier’s price plus the costs of bringing the object to condition.
- During construction - the amount paid to the contractor.
The remaining costs can be included in the expenses necessary to ensure normal activities. This occurs in the period in which the costs were incurred.
All expenses for the purchase of real estate are recognized only after the company confirms that the necessary documents have been submitted for registration. When there are no problems with determining the initial cost of the fixed assets and it has been formed, the object can be accepted for accounting. If the ownership right needs to be officially registered, then the acceptance of the OS for accounting is not affected by either the fact of submitting a package of documents or the registration process itself.
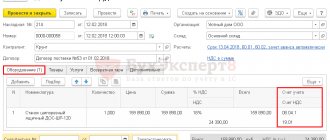
Basic wiring:
| Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| 08 | 60 | Accounting for expenses for the purchase or construction of real estate, which are included in the initial cost (with input VAT) |
| 01 | 08 | OS accepted for accounting |
Accounting for purchase and sale transactions of non-residential premises
The concept of immovable things (real estate, real estate) is given in Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Part I (1). Real estate includes things whose movement without disproportionate damage to their purpose is impossible (for example, land plots, buildings, structures, etc.).Accounting for the organization that sells the premises.
As a rule, the transfer of a property under a transfer deed occurs before the state registration of the transaction; At this point, the transfer of ownership from the seller to the buyer does not occur; therefore, the seller’s accounting does not reflect the sale of the asset. If there is a large number of fixed assets and, in particular, real estate on the seller’s balance sheet, for the convenience of analytical accounting of assets, you can open a subaccount “Fixed assets transferred under a transfer deed” to account 01 “Fixed Assets”.
For accounting purposes, until the transfer of ownership of real estate from the seller to the buyer, the seller continues to charge depreciation on this property until the asset is written off the balance sheet, that is, until it is sold (clauses 21, 22 of PBU 6/01 (33)).
For tax accounting purposes in accordance with Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2), the seller charges depreciation on a depreciable property transferred to the buyer until the transfer of ownership of the property to the buyer.
When determining the taxable base for property tax, the selling organization includes the transferred real estate at its residual value in the average annual value.
In accordance with clause 12 of PBU 9/99 (36), one of the conditions for recognizing revenue in accounting is the transfer of ownership of the property from the seller to the buyer (receipt by the buyer of a certificate of ownership).
For tax accounting purposes, real estate is a commodity (Article 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2)).
In accordance with Art. 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2) the sale of goods, work or services by an organization is recognized as the transfer on a reimbursable basis (including the exchange of goods, work or services) of ownership of goods, the results of work performed by one person for another person, the provision of services for a fee by one person to another face.
Accordingly, at the moment of transfer of ownership of real estate to the buyer, the selling organization reflects income from sales for the purposes of calculating income tax, and also charges VAT (if, for tax purposes, sales proceeds are taken into account by the seller as the goods are shipped (transferred) to the buyer ). If, for tax purposes, sales proceeds are taken into account by the seller as they are paid, the obligation to pay VAT to the budget arises at the time of payment for real estate, the ownership of which has been transferred to the buyer in accordance with the legally established procedure.
In addition, no later than 5 days from the date of sale (the date the buyer receives a certificate of ownership of the property), the seller must issue an invoice in the name of the buyer.
If payment for the property is made by the buyer before the sale of the property (transfer of ownership to it to the buyer), then the amounts received are reflected in the seller’s accounts until the moment of sale as part of advances on a separate subaccount of account 62 “Calculations for advances received.”
In the event that, under a transaction from the sale of a real estate property that is depreciable property, the selling organization receives a loss, then in accordance with clause 3 of Art. 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2), the loss received under the transaction is included in other expenses in equal shares during the period defined as the difference between the useful life of this property and the actual period of its operation until the moment of sale.
In the accounting records of the selling organization, the transaction for the transfer and sale of real estate will be reflected in the following accounting entries:
Item No.
| Contents of a business transaction | Account correspondence | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The real estate was transferred to the buyer under a transfer deed | 01 s/s “Fixed assets transferred under a transfer deed” | 01 s/s “Fixed assets in operation” |
| 2 | The initial cost of fixed assets is written off upon their disposal (transfer of ownership) | 01 s/s “Disposal of fixed assets | 01 s/s “Fixed assets transferred under a transfer deed” |
| 3 | The amount of accrued depreciation is written off | 02 | 01 s/s “Disposal of fixed assets |
| 4 | The sale of real estate is reflected at the time of transfer of ownership to the buyer | 62 | 91/1 |
| 5 | The residual value of the fixed asset is written off | 91-2 | 01 s/s “Disposal of fixed assets” |
| 6 | VAT charged on sales | 91-2 | 68 (76) |
If the seller organization incurred certain expenses (state duty, commission fees, etc.) associated with the sale of premises, then they must be taken into account in account 44 “Sale expenses”.
The balance formed on this account is written off to the debit
of account 91 “Other income and expenses”
on the date the transaction for the sale of premises is reflected in the accounting records.
Buyer's accounting
, when the premises are purchased to house an office or production workshop. In this case, two accounting options are possible.
First option: the act of acceptance and transfer of the building is executed after state registration of ownership of the property. In this case, the accounting records of the buyer of the premises are as follows:
| No. | Contents of a business transaction | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The purchase price of real estate is reflected without VAT on the date of transfer of ownership | 08 “Investments in non-current assets” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” |
| 2 | The amount of “input” VAT on the transaction is reflected | 19 “VAT on purchased assets” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” |
| 3 | The value of real estate is taken into account as part of fixed assets on the date of the acceptance certificate | 01 "Fixed assets" | 08 “Investments in non-current assets” |
Organizations themselves choose in which account to record fixed assets, the rights to which are subject to state registration. The decision made will not affect the calculation of depreciation, but the amount of property tax depends on it.
According to clause 52 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 91n (46), organizations are given the right to choose their own accounting option. Thus, “it is allowed to accept for accounting as fixed assets” real estate objects for which capital investments have been completed, the corresponding primary documents for acceptance and transfer have been drawn up, the objects are actually in operation, and the documents have been submitted for state registration (clause 52). Such fixed assets are accounted for in a separate subaccount to account 01 “Fixed Assets”.
On this basis, organizations decide to either “hold” such objects on
account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”
or transfer them to account 01 “Fixed Assets”. The chosen option must be fixed in the accounting policies. The amount of property tax and the moment of applying the VAT deduction directly depend on the decision made.
Second option: the acceptance and transfer certificate of the fixed asset is signed before the date of state registration of ownership of the property.
In the case of the acquisition or creation of real estate by contract or economic means, the ownership of the real estate passes to the buyer (customer-developer) from the moment of state registration of this right (Clause 1 of Article 564 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Part II (1)).
Fixed assets include land plots owned by the organization, environmental management facilities, real estate, etc.
Before an object is accepted for accounting as a fixed asset (to account 01 “Fixed Assets”), depreciation on objects that have not passed state registration is not reflected in accounting.
The acquisition of real estate has its own characteristics for a number of taxes.
Income tax.
For tax accounting purposes, in accordance with clause 8 of Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2), fixed assets, the rights to which are subject to state registration in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, are included in the corresponding depreciation group from the moment of the documented fact of filing documents for registration of these rights. Accordingly, the calculation of depreciation for tax accounting purposes begins on the 1st day of the month following the month in which this object was put into operation (inclusion in the corresponding depreciation group).
Value added tax.
Acceptance of the presented (calculated) value added tax for deduction to the budget depends on the basis on which the real estate “appears” on the balance sheet of the organization, namely: when purchasing a ready-to-use object under a sales contract; when purchasing an unfinished capital construction project; during the construction of an object by contract or economic method.
The buyer has the right to deduct the amount of VAT submitted to the budget, taking into account the following features:
- in case of acquisition of real estate under a purchase and sale agreement.
The amount of VAT presented by the seller, the organization on the basis of paragraph 1, paragraph 2 of Art. 171 and paragraph 1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2) has the right to accept for deduction if there is an invoice and documents confirming the actual payment to the seller, after the asset has been registered. That is, from the moment the property is accepted into account 01 “Fixed assets” upon receipt of a certificate confirming state registration of ownership. - in the case of purchasing the work of contractors during their capital construction, assembly (installation) of fixed assets;
goods (works, services) for construction and installation work; objects of unfinished capital construction. The VAT amounts presented by the sellers, the buyer on the basis of clause 6 of Art. 171 and paragraph 5 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2) has the right to accept for deduction to the budget in the presence of invoices and documents confirming actual payment to sellers, as the relevant objects are registered for tax purposes as depreciable property, from the first month of depreciation on the corresponding object for tax purposes accounting. That is, from the next month after submitting documents for state registration of ownership of real estate. - in the case of carrying out construction and installation work for one’s own consumption, the cost of which is included in expenses taken for deduction when calculating income tax.
The right to a deduction in the form of tax amounts calculated by the taxpayer in accordance with Art. 166 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2) when carrying out construction and installation work for one’s own consumption, arises in the tax period in which he paid the tax amounts calculated in accordance with Art. 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2) for construction and installation work performed for own consumption.
When performing construction and installation work for one's own consumption, the tax base is determined as the cost of the work performed, calculated on the basis of all actual expenses of the taxpayer for their implementation.
The date of completion of construction and installation work for own consumption is determined as the day of registration of the corresponding object completed by capital construction. That is, from the moment the property is accepted into account 01 “Fixed assets” upon receipt of a certificate confirming state registration of ownership.
Property tax.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2) the object of taxation for Russian organizations is movable and immovable property (including property transferred for temporary possession, use, disposal or trust management contributed to joint activities), accounted for on the balance sheet as fixed assets
in accordance with the established accounting procedures. Thus, if the acquired real estate is accounted for as a debit to account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” in accordance with the accounting policy of the organization, its value is not included in the taxable base for property tax.
Now let's consider the situation when the premises are purchased for further resale. In this case, real estate does not qualify as fixed assets on the basis of paragraphs. “c” clause 4 of PBU 6/01 (33) (an asset is not a fixed asset if it is intended to be resold) and its accounting procedure is regulated by PBU 5/01 (32). This document does not define the moment of recognition of current assets in the accounting of an organization, therefore, one can be guided by the general rule: one of the main criteria for recognizing a current asset in accounting is the moment of transfer of ownership on the basis of Art. 223 Civil Code of the Russian Federation, part I (1). The premises intended for sale will be accounted for in account 41 “Goods”.
The following entries must be made in accounting:
| No. | Contents of a business transaction | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The purchase price of the premises excluding VAT is reflected on the date of state registration of the transfer of ownership | 41 "Products" | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” |
| 2 | The amount of “input” VAT on the transaction is reflected | 19 “VAT on purchased assets” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” |
| 3 | Payment to the seller for the purchased premises | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | 51 “Current account” |
| 4 | The amount of “input” VAT is taken into account as deductions | 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” s/s “Calculations for VAT” | 19 “VAT on purchased assets” |
| 5 | The sales value of the premises purchased for resale is reflected on the date of state registration of ownership by the new owner, regardless of the date of the acceptance certificate | 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” | 90-1 “Revenue” |
| 6 | VAT charged | 90-3 "VAT" | 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” s/s “Calculations for VAT” |
| 7 | The purchase price of the premises has been written off | 90-2 “Cost of sales” | 41 "Products" |
| 8 | The financial result of the transaction is written off to the profit and loss account with the last turnover of the month | 90-9 “Profit and loss from sales” | 99 "Profits and losses" |
| 9 | Received funds from the buyer of the building | 51 “Current account” | 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” |
Typically, a property purchased for resale requires renovation or even reconstruction. In this case, the actual cost of the building based on clause 6 of PBU 5/01 (32) includes the costs of bringing assets to a state in which they are suitable for use for the intended purposes, as well as costs associated with improving the technical characteristics of the received assets.
To reflect in the accounting accounts the purchase price of premises that will be repaired or reconstructed before sale, it is necessary, in our opinion, to use subaccount 10-2 “Purchased semi-finished products and components, structures and parts.”
This subaccount takes into account the availability and movement of purchased semi-finished products, finished components (including building structures and parts from contractors) purchased to complete manufactured products (construction), which require costs for their processing or assembly.
Although the purchased building can be classified as a “semi-finished building” with a big stretch, in our opinion, it is not possible to choose other accounts. If an organization wants to introduce a new synthetic account to reflect the purchase price of real estate, then this can be done, but with the permission of the Russian Ministry of Finance.
When purchasing, renovating and selling premises, the following records are made:
| No. | Contents of a business transaction | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The purchase price of the premises excluding VAT is reflected on the date of state registration of the transfer of ownership | 10-2 “Purchased semi-finished products and components, structures and parts” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” |
| 2 | The amount of “input” VAT on the transaction is reflected | 19 “VAT on purchased assets” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” |
| 3 | Payment to the seller for the purchased premises | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | 51 “Current account” |
| 4 | The amount of “input” VAT is taken into account as deductions | 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” s/s “Calculations for VAT” | 19 “VAT on purchased assets” |
| 5 | The cost of repairs to the premises carried out by a contractor is reflected, excluding VAT | 20 "Main production" | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” |
| 6 | The amount of “input” VAT on contract work is reflected | 19 “VAT on purchased assets” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” |
| 7 | The cost of repairs is included in the purchase price of the premises | 10-2 “Purchased semi-finished products and components, structures and parts” | 20 "Main production" |
| 8 | Payment to the contractor for repairs | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | 51 “Current account” |
| 9 | The amount of “input” VAT on contract work is taken into account as deductions is taken into account as deductions | 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” s/s “Calculations for VAT” | 19 “VAT on purchased assets” |
| 10 | The sales price of the purchased and renovated premises is reflected on the date of state registration of ownership by the new owner, regardless of the date of the acceptance certificate | 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” | 91-1 “Other income” |
| 11 | VAT charged on the sales price | 91-2 “Other expenses” | 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” s/s “Calculations for VAT” |
| 12 | The actual cost of the premises has been written off | 91-2 “Other expenses” | 10-2 “Purchased semi-finished products and components, structures and parts” |
| 13 | The financial result of the transaction is written off to the profit and loss account with the last turnover of the month | 91-9 “Balance of other income and expenses” | 99 "Profits and losses" |
| 14 | Received funds from the buyer of the premises | 51 “Current account” | 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” |
The act of acceptance and transfer of a building (structure) No. OS-1a, approved by Resolution of the State Civil Code of the Russian Federation No. 7 (24), is used as a single primary document in all cases of alienation of real estate.
To avoid unintentional distortions in the balance sheets of non-current assets, as well as double taxation of the acquired building, you can enter into a lease agreement for the acquired property for a period of less than one year from the date of the acceptance certificate. In this case, you can do without state registration of the lease agreement on the basis of Article 651 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Part II (1).
In this agreement, the buyer of the property will be the tenant, and the seller will be the lessor. When the justice authorities register the ownership of the buyer, the lease agreement on the basis of Article 413 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Part I (1) is automatically terminated, since the debtor-tenant becomes the owner of the building.
With this option, the following accounting entries will be made:
| No. | Contents of a business transaction | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The cost of the received fixed assets in the valuation specified in the lease agreement as of the date of the acceptance certificate is capitalized on the balance sheet | 001 | — |
| 2 | Fixed assets written off from the account on the date of state registration of ownership rights | — | 001 |
| 3 | The purchase price of the building is reflected without VAT on the date of state registration of ownership | 08 | 60 |
| 4 | The amount of “input” VAT on the transaction is reflected | 19 | 60 |
| 5 | The cost of the building is taken into account as part of fixed assets on the date of state registration of ownership | 01 | 08 |
Accounting for real estate reconstruction under the simplified tax system
Reconstruction of a property means improving its quality characteristics. The costs of its implementation under the simplified tax system are taken into account in expenses. They are recognized as such from the moment the facility is put into operation. Expenses are written off evenly until the end of the year, which marks the completion of reconstruction or repair of the property. Paid expenses are taken into account.
Example No. 1. (income minus expenses), reconstructed the workshop building and launched it in June. In total, the work cost 120 thousand rubles. The money was transferred to the account of the company that did the reconstruction.
Expenses will be taken into account at 40 thousand rubles. (120 thousand/3):
- the thirtieth of June;
- the thirtieth of September;
- thirty first December.
The costs of design documentation are also expenses that increase the cost of the operating system (initial).
Initial cost of real estate for enterprises with OSNO
When an organization uses OSN, the cost of OS should include:
- The cost of a property built or purchased.
- Interest on a loan (loan) that is attracted to the acquisition of fixed assets and is recognized as an investment asset.
- Expenses to bring the property to a usable condition (repair work, reconstruction).
- Other costs that are directly related to the purchase (intermediary commissions, travel expenses).
For companies used by OSNO, there is no need to submit documents for state registration in order to begin calculating depreciation.
What documents are required for admission?
An object is purchased from a supplier for a certain, pre-agreed fee. The price of the asset is specified in the supply or purchase and sale agreement. At the time of transfer of property value to the buyer, a transfer and acceptance certificate is drawn up. As a rule, the parties form the deed form according to the standard form:
- OS-1 – for single objects other than real estate;
- OS-1a - exclusively for transferred structures;
- OS-1b – if several assets of an identical type are purchased for a fee.
If equipment is accepted at a warehouse without being used as OS, then the receipt certificate OS-14 is used.
The transfer deed completed by both parties serves as the main document on the basis of which it is possible to capitalize the object as a fixed asset.
Accounting for such costs is carried out on the basis of documents:
- invoices;
- acts of provision of services and works.
The purchase of OS includes the costs of paying the cost under the contract, as well as other related expenses - transport, installation and others.
An OS-6 inventory card is created for the received object.
Filling OS-1
The transfer deed is drawn up for each party. The OS-1 form contains several sections, the design of which depends on whether the object was previously in operation or not. For new fixed assets, you do not need to fill out the first section; only data on used assets is provided here - period of use, initial cost.
The second section is filled out in the copy of the receiving party, data is provided on the day of acceptance for accounting - cost, useful life, taking into account the indicators of the first section.
The completed form of the OS-1 act is signed by both parties.
An example of filling out a transfer and acceptance certificate for a fixed asset:
An example of OS-1 design in excel - .
Features of real estate accounting
Real estate is a special commodity. This can be said because:
- Ownership and other real rights must be registered in a unified state register. Only then are they recognized as legal.
- When a company initially intends to sell a property, it is not accounted for as fixed assets. This applies to those enterprises that are engaged specifically in the purchase of real estate and its sale. Therefore, such objects for them are not OS, but goods (count 41).
- For tax purposes, it does not matter how exactly the property is recorded in accounting. It is always reflected as property subject to depreciation.
Real estate accounting for the seller
When selling or disposing of a property, its value must be written off from accounting. Revenue may be recognized if the following conditions are met:
- The company has the right to it. It is confirmed by specific agreements.
- The amount of revenue is designated and calculated.
- There is evidence that the entity will increase its economic benefits by carrying out the sale transaction.
- The ownership of the property was transferred to the buyer.
- The costs of the sales transaction are determined unambiguously.
Income and expenses from writing off fixed assets from accounting are credited to profit and loss as other income and expenses.
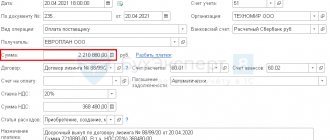
Example No. 2. Company A sold a building to company B for 2 million rubles. (VAT – RUB 305,084). The object was transferred on March 1, 2016. The right to property was registered on April 30. 2016 Initial cost of the structure - 4.5 million; depreciation amount - 3 million.
The selling company made accounting entries:
| date | Debit | Credit | Sum | Operations |
| 01.03.2016 | 02 | 01 | 3 000 000 | Write-off of depreciation accrued on the structure |
| 45 | 01 | 1 500 000 | Write-off of residual value | |
| 01.04.2016 | No entries available | |||
| 25.04.2016 | 62 | 91.1 | 2 000 000 | Sales revenue in the amount of other income |
| 91.2 | 68 | 305 084 | VAT charged | |
| 91.2 | 45 | 1 500 000 | Write-off of residual value | |
| 91.9 | 99 | 194 196 | Profit reflected | |
The tax documents of company A (seller) reflect (rub.):
- Sales income 1,694,916 (2,000,000 – 305,084)
- Expenses 1,500,000
- Profit from sales 194,916
How to reflect the acquisition of a building in transactions
The purchase of a building by a non-profit organization can be carried out if it is intended for use in work, as well as in the expansion of the enterprise, in particular the implementation of business activities, and also if the conditions of subparagraphs “b” and “c” of PBU 6/01 are met.
The transactions made when purchasing a building are as follows:
| Debit | Credit | Operation name | A document base |
| 08.04 | 60.01 | Arrival of OS | Clauses of PBU 6/01 |
| 60.01 | Payment for the building | Clauses of PBU 6/01 | |
| 01.01 | 08.04 | OS commissioning | Clauses of PBU 6/01 |
Accounting when purchasing real estate. Depreciation calculation
The organization that purchased the property accepts it for registration regardless of the fact of registration of the right to the property. The property is one of the types of fixed assets, therefore it is subject to inclusion in a separate depreciation group. From the beginning of the month following the purchase, the amount of depreciation is calculated. Read also the article: → Depreciation of fixed assets: types, calculation features, use in management.
For tax accounting, it is important to comply with the following requirements:
- The company prepared and submitted documents for state registration.
- The facility has already been put into operation.
Most often, a company that has purchased real estate uses the straight-line depreciation method (see → methods for calculating depreciation of fixed assets in accounting). The rate is determined based on the period of useful use. It is reduced by the number of years (months) of work at the previous enterprise.
The useful life of the OS is determined by one of the following methods:
- Taking into account the useful life of the total.
- Based on its remainder.
Important! When choosing the second option, you should have a document confirming the period of use of the OS by the previous owner. If this is not possible, then you need to go with the first option. The organization can set this period independently.
Example No. 3. (Following the data of example No. 2). The buyer records in his accounting:
| date | Debit | Credit | Sum | Operations |
| 01.03.2016 | 08 | 60 | 1 694 916 | The construction has arrived |
| 01 | 08 | 1 694 916 | The structure is accepted for accounting as fixed assets | |
| 25.04.2016 | 19 | 60 | 305 084 | VAT amount allocated |
| 68 | 19 | 305 084 | VAT is accepted for deduction |
Transactions for the acquisition of OS costing over 40 thousand rubles
There is a category of property that falls into the category of value more than 40,000 rubles. Subject to the necessary selections, which are established in paragraphs 4 and 5 of PBU 6/01 (Use period is more than a year, property is necessary for work in the management field, not for resale), it should be taken into account as part of the OC, and not in the MTZ.
The transactions for purchasing such funds are similar to the previous ones:
| Debit | Credit | Operation name | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 08.04 | 60.01 | The cost of the purchased OS is taken into account (excluding VAT) | price without VAT | Clauses 4-5 PBU 6/01 |
| 08.04 | 60.01 (76.05) | The costs of transportation and installation of the OS are taken into account | price without VAT | Clauses 4-5 PBU 6/01 |
| 19.01 | 60.01 (76.05) | VAT on fixed assets allocated | VAT | Clauses 4-5 PBU 6/01 |
| 01.01 | 08.04 | OS commissioning | price without VAT | Clauses 4-5 PBU 6/01 |
Technical inventory of real estate objects
Real estate objects are individually defined things. They are subject to a single accounting and registration procedure - starting with cadastral registration and ending with the preparation of documents for ownership. Accounting involves assigning a specific number, called a cadastral number. It is unique and not repeated throughout the country over time.
This happens in the process of cadastral and technical accounting, in the manner prescribed by law. Inventory of real estate - capital construction projects, and cadastral registration of land are needed for the official registration of rights. This ensures the participation of resources in circulation.
The procedure for conducting them is regulated by regulations of the executive branch, but not by federal laws. Failure to assign a cadastral number to an OS object during technical registration cannot prevent its state registration.
| (62 pages) Contents: 1. Separate accounting when combining the simplified tax system and UTII: features and rules for accounting 2. Deadlines for submitting a declaration under the simplified tax system 3. The procedure for calculating and paying income tax under the simplified tax system 4. Real estate accounting under the simplified tax system 5. Application features tax regime of the simplified tax system for legal entities in the form of a closed joint-stock company 6. Peculiarities of maintaining the accounting policy of the simplified tax system 7. Advantages of applying the tax regime of the simplified tax system for LLCs and individual entrepreneurs 8. Peculiarities of selling an LLC using the simplified tax system 9. Combining the simplified tax system and PSN 10. How to keep accounting for an LLC using the simplified tax system? |
Real estate accounting in SNT - features
SNTs are non-profit organizations, which means they must maintain full accounting records - from developing accounting policies to submitting reports to tax and statistical authorities. The statutory activities of SNT are not subject to taxes. Therefore, VAT on purchased fixed assets is included in their cost.
Real estate built on its own must be reflected in accounting at the amount of actual expenses.
For detailed accounting of land areas and other real estate received by SNT as a property share, you need to keep an appropriate book. It consists of three sections, taking into account:
- area of land plots;
- implicit OS;
- inventory data.
When SNT receives from local authorities, for example, a land ownership deed or a lease agreement, an entry must be made about this in the property accounting book.
⊕ accounting of property, land and electricity in SNT