Account 80 Authorized capital is used to account for the authorized capital that is created in joint stock companies (JSC) and limited liability companies (LLC).
Account 80 also takes into account the share capital created in general partnerships and limited partnerships, the authorized capital formed during the creation of a state or municipal unitary enterprise based on the right of economic management and contributions of partners, if the organization is a party to a simple partnership agreement (joint activity) and she is entrusted with keeping accounting records under the agreement (only in this case, account 80 will be called “Deposits of partners”).
Account 80 Authorized capital
The authorized capital of a joint stock company (JSC) being established is the sum of the par value of the shares of this company distributed among its shareholders.
The authorized capital of a limited liability company (LLC) is the sum of the nominal value of shares distributed among the company's participants.
The amount of the organization's authorized capital must be specified in the agreement on the establishment of the company and in the charter.
On the date of state registration, the organization makes an entry about the amount of its authorized capital:
Debit 75 Credit 80 – reflects the amount of the authorized capital and the debt of the founders to pay it.
To account for settlements with the founders for the formation of the authorized capital, a special sub-account 75-1 “Settlements on contributions to the authorized (share) capital” is provided. When shareholders (participants) make contributions to the authorized capital of the company, they make an entry:
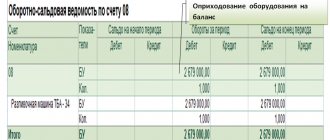
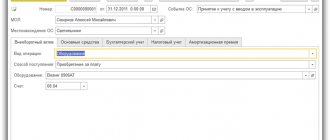
Debit 51 (50, 52, 08, 10, 58, ...) Credit 75 – contribution to the authorized capital was made.
Accounting and audit of settlements with founders
Accounting involves performing an assessment of deposits. This is not always easy to do. For example, it is difficult to value an intangible asset. The evaluation is carried out on the basis of mutual consent of the creators. The corresponding agreement is recorded in the constituent documents. If the asset is not in cash form, the valuation is carried out by an independent appraiser. The amount received as a result of a professional assessment may be reduced by the founders. However, it cannot be increased on the basis of paragraph 2 of Article 66 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The founders of a unitary entity can be state or municipal structures. To record settlements, you need to open subaccount 1 to account 75. Replenishment of the fund is recorded with this posting: DT75/1 KT80. Formation of a fund of a unitary structure.
Please note => Payment of sick leave for interrupted service
Instructions 80 count
Instructions for using the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations in accordance with Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000:
Account 80 “Authorized capital” is intended to summarize information about the state and movement of the authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital) of the organization.
The balance in account 80 “Authorized capital” must correspond to the amount of the authorized capital recorded in the constituent documents of the organization. Entries in account 80 “Authorized capital” are made when forming the authorized capital, as well as in cases of increasing and decreasing capital, only after making appropriate changes to the constituent documents of the organization.
After the state registration of an organization, its authorized capital in the amount of contributions of the founders (participants) provided for by the constituent documents is reflected in the credit of account 80 “Authorized capital” in correspondence with account 75 “Settlements with founders”.
The actual receipt of deposits of the founders is carried out on the credit of account 75 “Settlements with founders” in correspondence with the accounts for accounting for cash and other valuables.
Analytical accounting for account 80 “Authorized capital” is organized in such a way as to ensure the formation of information on the founders of the organization, stages of capital formation and types of shares.
Account 80 is also used to summarize information about the status and movement of contributions to common property under a simple partnership agreement. In this case, account 80 is called “Comrades’ Deposits”. The property contributed by the partners to the simple partnership on account of their contributions is accounted for as a debit in the property accounting accounts (“Current accounts”, “Fixed assets”, 41 “Goods”, etc.) and a credit in account 80 “Deposits of partners”. When property is returned to partners upon termination of a simple partnership agreement, reverse entries are made in accounting.
Analytical accounting for account 80 “Deposits of partners” is maintained for each simple partnership agreement and each participant in the agreement.
Account 81 in accounting
A decrease in the size of the authorized capital must be reflected in the organization’s constituent documents (read more about amending the Charter using the example of an LLC). Adjustments to constituent documents must also be registered with the Federal Tax Service (the information will be reflected in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities). The use of account 81 to display information on activities with purchased own shares of joint-stock companies (shares of participants in other companies and partnerships) is carried out in accordance with the current Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94 and other legally approved documents (for example, Federal Law 208 dated December 26, 1995 as amended on July 29, 2019 for JSC).
Typical transactions for account 80
By debit of the account
| Contents of a business transaction | Debit | Credit |
| An object of fixed assets was transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of an agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 01 |
| Property intended for rental is transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 03 |
| An intangible asset was transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of an agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 04 |
| Upon termination of the agreement on joint activity, the equipment is transferred to the participant of the simple partnership (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 07 |
| Investments in non-current assets were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 08 |
| Materials were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 10 |
| Animals are transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 11 |
| The costs of acquiring material assets upon termination of the agreement on joint activity were transferred to the participant in a simple partnership (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 15 |
| The amount of deviations in the value of inventories transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity was written off (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 16 |
| Work in progress was transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 20 |
| Semi-finished products were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 21 |
| Ancillary proceedings were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 23 |
| The servicing production was transferred to the participant of the simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 29 |
| Goods were transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 41 |
| Finished products were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 43 |
| Cash was transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 50 |
| Non-cash funds were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 51 |
| Funds in foreign currency were transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 52 |
| Funds were transferred from a special bank account upon termination of a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 55 |
| Shares and debt securities were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 58-2 |
| The debt for the return of deposits to the founders of the organization is reflected when the authorized capital is reduced (after amendments are made to the constituent documents) | 80 | 75-2 |
| Own shares purchased from shareholders were canceled (after amendments were made to the constituent documents) | 80 | 81 |
| The authorized capital was reduced to the amount of net assets (after amendments were made to the constituent documents) | 80 | 84 |
By account credit
| Contents of a business transaction | Debit | Credit |
| An object of fixed assets received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 01 | 80 |
| Property intended for rental, received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement, was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 03 | 80 |
| An intangible asset received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 04 | 80 |
| Equipment requiring installation received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 07 | 80 |
| Current assets received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement are taken into account (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 08 | 80 |
| Materials received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement were capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 10 | 80 |
| Animals received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement have been capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 11 | 80 |
| Inventory received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 15 | 80 |
| The amount of deviations in the cost of inventories received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement is taken into account (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 16 | 80 |
| An item of work in progress was received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 20 | 80 |
| Semi-finished products received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement were capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 21 | 80 |
| Part of the costs of auxiliary production paid by a participant in a simple partnership is counted towards the contribution to the joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 23 | 80 |
| Part of the costs of service production paid by a participant in a simple partnership is counted towards the contribution to the joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 29 | 80 |
| Goods received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement were capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 41 | 80 |
| Cash received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 50 | 80 |
| The funds deposited as a contribution under the joint activity agreement have been credited to the current account (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 51 | 80 |
| Funds in foreign currency deposited as a contribution under a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) have been credited to a foreign currency account. | 52 | 80 |
| A contribution was made to a special account under a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 55 | 80 |
| Shares and debt securities received as a contribution under a joint venture agreement were capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint venture) | 58-1 | 80 |
| The debt of the founders (participants) for contributions to the authorized capital is reflected (after state registration of the organization) | 75-1 | 80 |
| The authorized capital was increased due to additional capital (after amendments were made to the constituent documents) | 83 | 80 |
| The authorized capital was increased (after amendments were made to the constituent documents) | 84 | 80 |
Typical accounting entries for account 75
Since the list of transactions carried out on account 75 is very wide, we will highlight only the most significant and frequently used by the accountant. We are talking about the following wiring:
| Debit correspondence | Loan correspondence | the name of the operation |
| 75 | Calculations of contributions to the company's management company | |
| , , | 75 | Contributions from founders, including contributions to temporary savings accounts |
| 75 | Fixing the cost of fixed assets or intangible assets on the balance sheet of the enterprise | |
| , | 08 | Arrival of OS and intangible assets |
| 10, 41 | 75 | Goods contributed as a contribution to the management company are capitalized |
| 75 | Reflection of financial investments, including shares | |
| 66 | 75 | The loan debt is offset against the share of the company's management company |
| 75 | 50, 51 | The founders were paid the difference by which the authorized capital was reduced |
| 81 | 75 | Debt to the founder who left the organization, and distribution of the remaining amount among the remaining founders |
There are many other transactions associated with the provision of loans to founders, as well as the sale or purchase of shares. Their use is independently regulated by the company’s management and is prescribed in the accounting policies.
Accounting 75: active or passive?
To correctly reflect the data, you need to know whether the account is active or passive 75 . The answer to this question depends on the type of debt that is reflected in this account. For example, the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital is displayed as a debit to account 75, and the debt of the enterprise for the payment of dividends is shown as a credit. Debt can be reflected both as a debit and as a credit, respectively, account 75 is active-passive.
Thus, in the balance sheet, the first case will be reflected as a debit balance in the asset line on line 1230 “Accounts receivable”, and the second - as a credit balance of account 75 in the liability line on line 1520 “Accounts payable” or on line 1450 “Other liabilities”, if the debt is long-term (according to the order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n).
Transactions with dividends
Dividends are one of the types of income of the founder. It is formed from the company's profit, which remains after paying all taxes due and is called net. This part is distributed among the founders in proportion to their share of shares. Payment of dividends is an indicator of the successful operation of the enterprise.
The source for accrual of dividends is data from the financial statements (balance sheet). Settlements with founders are regulated by legislative acts.
You can distribute not only the profit of the current year to pay dividends, but also take the undistributed balance of previous reporting years. In order to correctly carry out the calculation, the accounting department will need a protocol of the decision of the general meeting of participants or shareholders.
Payment is made in accordance with the share of participants in the authorized capital of the company. The payment procedure is based on Federal Law No. 14 dated April 23, 2018, and reflected in accounting - on the basis of PBU 7/98.
Accrued amounts are paid within 60 days after the decision is made. The classic payment option is cash payment. This can be non-cash or cash. It is also possible to repay the debt with property, but this option is considered more complex from a tax point of view.
Which line in the balance sheet shows account 75?
Settlements with founders should also be reflected in the company's financial statements.
In the balance sheet, settlements with participants can be included in accounts receivable and payable, since accounting account 75 is active-passive.
The amount is entered in asset line 1230 “Accounts receivable” of the report form when the balance on account 75 is debit. If the company has a credit balance on this account, the accountant reflects this amount in liability line 1450 “Other liabilities” or 1520 “Accounts payable” on the balance sheet, depending on the duration of the obligation.
That is, in accounting, account 75 “Settlements with founders” in the balance sheet is displayed in an active or passive line, depending on the final balance of the account.
When drawing up a balance sheet, it is imperative to take into account the final balances of subaccounts. It is unacceptable to generalize information in this case, since the full picture of settlements with the founders of the enterprise is not displayed (clause 34 of PBU 4/99).