346
12.05.2021
There is no mention in the Tax Code of “the main means of tax accounting.” Instead, “depreciable property” is used - assets exceeding 100,000 rubles, called “fixed assets” in accounting, where the main unit is an inventory item. The tax accounting procedure is constantly being modified; a number of innovations were also registered in 2022.
Depreciable property is not initially intended for subsequent sale; it is used by the company for other purposes. Subsequently, the object is resold, given for free use, if it is unsuitable, there is no need for further use.
Concept
In accordance with the new standard, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 257n dated December 31, 2016, fixed assets are understood as tangible assets (assets), regardless of their cost, the useful life of which is more than 12 months.
They are intended for constant repeated use in order for the organization to perform its assigned functions. Property objects may belong to an institution both by the right of operational management and by the right of ownership or use of property. According to PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”, such assets are not subject to subsequent resale and are intended to be used for the purpose of obtaining economic benefits in the future (clause 4 of PBU 6/01).
In analytics, the inventory object - IO (clause 6 of PBU 6/01) is taken as the unit of accounting for such funds. If the initial cost of the IO is below 40,000.00 rubles, then they can be taken into account as inventories. The organization determines cost boundaries independently in its policy.
Legislatively, fixed assets are regulated by the following regulations:
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 402-FZ “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011.
- PBU 6/01.
- Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets - Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n.
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia on approval of the federal standard dated December 31, 2016 No. 257n.
Registration of lease of fixed assets
In Russia, the legal aspects of leasing are regulated by Chapter 34 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Business entities can transfer various objects, including fixed assets, for temporary use on a commercial basis. In this case, the lessor remains the owner of the property, and the lessee uses the asset for the period specified in the agreement. The exception is leasing, the terms of which provide for a phased purchase.
What postings should the lessor of the fixed asset make?
As with other business transactions, in this case the relationship between the parties is reflected in accounting. Rented objects become income-generating investments, which, in accordance with the current chart of accounts, is indicated by the posting Dt01 - Kt03.
On account 03, according to PBU 6/01, profitable investments are accumulated.
Income generated by the rental of fixed assets is recorded in accounts 90 and 91 (“Sales” and “Other income and expenses”, respectively). Some features should be taken into account:
- If the rental of fixed assets constitutes the main income of the enterprise, then, based on paragraph 5 of PBU 9/99, it is considered revenue and is accounted for in account 90.
- Account 91 (“Other income”) is used if the business structure has another main source of profit (clause 7 of the same PBU).
The postings reflecting the rental of the operating system are as follows:
| Accounts | Description of action | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| If rent is your main income | ||
| 03 | 08 | Putting the facility into operation. The initial cost is carried out. |
| 03 | 03 | Transfer of OS to tenant |
| 62 | 90 (91) | Receipt of rent payments. |
| 90 | 68 | VAT calculation |
| 20 | 02 | Depreciation calculation |
| If rent is “another type of activity” | ||
| 01 | 08 | Putting the facility into operation. The initial cost is carried out |
| 20-26 | 02 | Depreciation during owner use |
| 01 | 01 | Transfer of OS to tenant |
| 76 | 91 | Rental income (“other income”) |
| 91 | 68 | VAT calculation |
| 91 | 02 | Depreciation of leased fixed assets |
Notes Depreciation of leased fixed assets accumulates on account 91, that is, it is attributed to income, through which it will be possible to restore this asset in the future. Profit tax is charged on the amount of receipts.
The leased object is still listed on account 01 as a fixed asset. It is not transferred to account 03, because the lease provides for temporary use. After the contract expires, the asset can again be used for your own needs.
OS postings from the tenant's position
Leased fixed assets are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 001. The cost of the object is indicated in accordance with the lease agreement.
Capitalization of the leased fixed assets is carried out on Dt001. When returning property, the posting ends at Kt001.
Payment of rent is taken into account as expenses, is included in the cost of the product produced by the tenant and affects the calculation of income tax.
Accounting for fixed assets in an institution
Accounting for such funds in budgetary organizations is carried out in accordance with instruction No. 157n (clause 21 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 157n dated December 1, 2010). Accounting for fixed assets is carried out through a unified chart of accounts, as well as through a special one, developed in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 162n dated December 6, 2010.
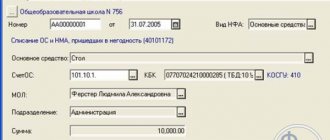
For accounting records of business transactions and movements of objects of such funds, synthetic account 010100000 “Fixed assets” is used in budget accounting. Receipts are recorded according to the synthetic account 0010600000 “Investments in non-financial assets”, disposal accounting is carried out according to the analytics of separate accounts “Fixed Assets” (ending with 410).
In the accounting of non-commercial organizations, the movement of funds is reflected in account 01 “Fixed Assets”, receipts are intermediately posted through the account. 08 “Investments in non-current assets”.
Constructed real estate objects, the rights to which must be registered, are recognized as fixed assets, regardless of whether they are registered at the time of acceptance for accounting or not. If such an object is not yet completed, then it is necessary to create a separate subaccount for it to the “Fixed Assets” account.
Upon acceptance of the fund for accounting, an act is drawn up in form OS-1. If necessary, the institution has the right to develop its own form of the document.
In order for such funds to be reflected correctly in accounting, a specialist needs to carry out a step-by-step assessment and accounting of the incoming fixed assets.
Accounting for non-depreciable fixed assets with non-zero tax value
Let's assume that the organization does not exclude the possibility of selling non-depreciable assets in the future. In this case, the tax value of the object should not be written off, otherwise it cannot be taken into account as expenses upon sale or other disposal.
Example 2
The organization KRUG LLC applies OSNO, PBU 18/02 using the balance sheet method and pays VAT. The income tax rate is 20%.
In January 2022, the organization takes into account residential premises, which are used as a service apartment for the temporary accommodation of arriving specialists. The initial cost of the apartment in accounting and tax accounting is the same and amounts to 8,000,000 rubles.
The organization has established a useful life of 400 months for the apartment. The linear method of calculating depreciation in accounting and tax accounting is used. In accounting, depreciation expenses for the apartment are taken into account on account 26.
Despite the fact that a service apartment under the conditions of Example 2 is used for production purposes, in the opinion of the Russian Ministry of Finance, such an object does not meet the criteria for depreciable property, therefore, for profit tax purposes, it does not belong to fixed assets subject to depreciation (letters dated January 24, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/3843, dated November 24, 2014 No. 03-03-06/2/59534). At the same time, there is a court decision according to which the calculation of depreciation on housing assets is legal (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated July 16, 2009 in case No. A33-14312/2006).
Regulatory authorities allow depreciation to be charged on residential premises if they clearly generate income, for example, in the form of rent. Expenses in the form of depreciation of a service apartment must be confirmed by a lease agreement drawn up in accordance with the law (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 7, 2009 No. 03-03-06/2/231, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 12, 2012 No. 16- 15/ [email protected] ).
Let's assume that the organization does not want disputes with the tax authorities and does not include a service apartment as part of the depreciable property. However, the tax value of the property is not written off, since the apartment can be rented out or sold in the future.
In this case, when preparing the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets
on the
Tax Accounting
Accrue depreciation
checkbox should be cleared (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Acceptance of non-depreciable fixed assets with non-zero cost for accounting
When posting a document, an accounting register entry is entered:
Debit 01.01 Credit 08.04.1
- for the initial cost of the fixed asset (RUB 8,000,000).
At the same time, special fields of the accounting register are filled in:
Amount Dt NU: 01.01
and
Amount Kt NU: 08.04.1
- for the tax value of the apartment (RUB 8,000,000).
Thus, at the end of January there is no difference between the book value and tax value of the fixed asset.
When performing a regulatory operation Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU 18
for January, deferred tax for the type of asset
Fixed assets
is not recognized.
Starting from February 2022, the service apartment begins to be depreciated only in accounting. When performing a routine operation Depreciation and depreciation of fixed assets
An accounting entry is generated:
Debit 26 Credit 02.01
- for the amount of depreciation of the apartment (8,000,000 rubles / 400 months = 20,000 rubles).
In tax accounting, depreciation is not calculated in accordance with the established settings. At the end of February, the book value of the apartment decreases and amounts to RUB 7,980,000. (RUB 8,000,000 – RUB 20,000). The tax value of the property does not change and remains RUB 8,000,000. The resulting difference is a deductible temporary difference, since it will lead to the formation of deferred income tax, which, with a certain degree of probability, can reduce the amount of income tax payable to the budget in subsequent reporting periods (clause 11 of PBU 18).
When performing a regulatory operation Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU 18
, a deferred tax asset is recognized by type of asset
Fixed assets
Debit 09 Credit 99.02.О
- for the amount of ONA recognition (20,000 x 20% = 4,000 rubles).
A detailed calculation of IT is presented in the Help-calculation of deferred tax
for January 2022 (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Help-calculation ONA
As the apartment is depreciated in accounting, a temporary difference by type of asset Fixed assets
will increase monthly by 20,000 rubles.
Accordingly, the amount of recognition of ONA will increase. By the end of 2022, BP by type Fixed assets
is 220,000 rubles, and IT is recognized in the amount of 44,000 rubles. (RUB 220,000 x 20%).
If the apartment is not sold during its useful life, then after 400 months the object will be fully depreciated and the book value will become zero. The tax value will not change and will be 8,000,000 rubles, therefore, IT will be recognized in the amount of 1,600,000 rubles.
Now let’s assume that from October 2022, the service apartment begins to generate income in the form of rental payments. From this moment on, the fixed asset can be depreciated in tax accounting. Then in September 2022 you will need to create a special document Changing the state of the OS
(section
OS and intangible assets
-
OS depreciation parameters
), which is intended to suspend or resume the calculation of depreciation on fixed assets.
Document header Changing the OS state
should be filled in as follows (Fig. 7):
- in field Event
– indicate the name of the event in the life of the fixed asset, which is reflected in the document.
Events that happen to fixed assets are stored in the OS Events
, which is filled in independently by the user; - don't set flag Reflect in accounting
, since nothing changes in accounting;
- set flag Reflect in tax accounting
, since a change in state affects tax accounting;
- set flag Affects the calculation of depreciation (wear and tear)
, since the document will affect the calculation of depreciation;
- set flag Calculate depreciation (wear and tear)
to resume accrual of fixed assets depreciation. This change will apply starting next month.
In the Fixed Assets
indicate the name of the service apartment for which depreciation is included in tax accounting.
Rice. 7. Changing the OS state
When posting a document Change of OS state
accounting entries are not generated, but entries are entered into the registers of the OS accounting subsystem:
- Calculation of depreciation of fixed assets (tax accounting)
;
- OS Events
.
By the end of September 2022, the taxable difference by type of fixed assets
is 160,000 rubles, and IT is recognized in the amount of 32,000 rubles. (RUB 160,000 x 20%).
From October 2022, the apartment begins to be depreciated also in tax accounting, therefore the resulting amounts of VR and ONA by type of assets and liabilities Fixed assets
don't change.
The further “fate” of BP and ONA will depend on many factors. For example, on whether the accrual of depreciation in accounting and (or) tax accounting will be continued or suspended.
What applies to fixed assets
Such funds are understood as the property of an organization used for the production of goods, works or services or for the direct functioning of the institution for a period exceeding 12 months, or a production or operational cycle exceeding 1 year.
Fixed assets include:
- buildings and constructions;
- cars and equipment;
- instruments, devices and tools;
- computer technology;
- vehicles;
- inventory and household supplies;
- breeding and working cattle;
- perennial plantings;
- roads.
Fixed assets are also various capital investments - investments for the purpose of radical land improvement and leasehold funds, plots of land, environmental management facilities.
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting only if certain criteria are simultaneously met:
- The fund is intended for the production of goods, works, services, as well as for the functioning of an institution or for the sale of funds for monetary compensation for temporary use and possession.
- The use of the product should occur over a long period, the duration of which exceeds 12 months.
- The company does not plan to further resell the fund.
- In the future, the tool may bring profit or economic benefit to the organization.
Fixed assets do not include objects recorded as finished products in the warehouses of the manufacturer or products in the warehouses of distributors. These goods will be resold, which is a failure to comply with one of the criteria for classifying products as fixed assets.
Objects that are in transit or transferred for installation are not included in this category. Capital and financial investments, with the exception of investments in leased assets and land improvement, also do not qualify as fixed assets.
How to determine the useful life of fixed assets
When accounting for such an asset, it is necessary to determine its useful life and depreciation group. When objects are used, their cost is transferred to the cost of manufactured products using depreciation.
The useful life is understood as the period of profit and economic benefits from the operation of a fixed asset. The institution determines the useful life independently, guided by its industry and organizational characteristics. For some objects, the SPI is established on the basis of a quantitative factor, that is, by the number of manufactured products or work performed, services in kind that the enterprise plans to receive from the use of one or another fixed asset.
When determining the SPI, specialists should be guided by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1 of 01.01.2002. It establishes a classification of objects, in which fixed assets are grouped by useful life - for each classification group, upper and lower time limits are defined.
If a property object consists of several components, then situations are possible when a different useful life is established for each of its components. Such components are reflected in accounting as separate fixed assets.
Depreciation group and useful life of fixed assets
In tax accounting, determine the useful life (USI) of the fixed asset according to the Classification. In accounting, the same SPI is usually used, although the classification of OS for these purposes is optional (clause 1 of article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 20 of PBU 6/01).
Look for the OS in the Classification by name. Don't stop at the first item you find - look through all the results. Be sure to read the notes, there may be additions, clarifications or exceptions to the OS name.
Use synonyms and keywords. So, you will not find a laser printer under the name “printer”. And regarding the key phrase “printing devices” - yes, it has a second depreciation group.
For OKOF, look for the depreciation group in the Classification if you can’t find it by name and keywords. To do this, first find its code for the OS in OKOF. If it is 9-digit, discard the last digit and look in the Classification for the combination XXX.XX.XX.X. If unsuccessful, discard the last digit again and repeat the search. If it fails again, it means your OS is not in the Classification.
How to determine a depreciation group and choose a depreciation method
Fixed assets must be depreciated monthly - deduct a certain amount from the value of the fund for current costs. Land plots and natural resources (subsoil, water resources, etc.) are not subject to depreciation in accounting, since they do not wear out and do not lose their consumer properties.
According to the general accounting rules, a specialist can use the following depreciation methods:
- Linear - the same amount of deductions is written off every month.
- Declining balance method - the amount of deductions is established according to the residual value at the beginning of the reporting year and depreciation standards obtained by applying the acceleration factor. The index value in accounting for fixed assets cannot exceed 3.0.
- The method of writing off the cost by the sum of the numbers of years of the useful life - depreciation charges are calculated annually, based on the total number of years of operation of the fixed asset and the number of remaining years until the end of the period.
- The method of writing off the cost is proportional to the volume of products, work - the monthly write-off amount is determined in the accounting of fixed assets by the number of units of goods produced each month, as well as the total planned volume for the entire period of operation.
Depreciation methods are selected by the accountant for each group of fixed assets in the institution and are applied throughout the entire operational period, that is, the useful life.
For tax accounting, only linear and non-linear depreciation methods apply, which are used for all main objects registered in the organization. In this case, the selected methodology for depreciation can be changed during operation.
Accounting records for writing off depreciation charges are prepared monthly in the amount of annual depreciation write-offs divided by 12 months.
To carry out depreciation charges in non-profit organizations, account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” is used. The following accounts are used in budget accounting:
- 0 106 00 000 - for fixed assets involved in capital construction;
- 0 109 00 000 - if depreciation charges for fixed assets participate in the formation of the cost of goods, work, services or are taken into account in distribution costs;
- 0 401 00 000 - if depreciation is not taken into account in distribution costs.
Depreciation deductions must be made starting from the first day of the period (month) following the month the fixed asset was accepted for accounting. The write-off ends upon disposal or full repayment of the fund's value.
In cases of conservation for a period exceeding 3 months, as well as during repairs, modernization, reconstruction of fixed assets lasting more than a year, depreciation deductions are suspended. In other situations, suspension of depreciation is not possible.
Every month, after depreciation is calculated, the residual value of the fixed asset is updated - the difference between the original cost and depreciation charges.
OS accounting: PBU and FSBU - let's look at the differences
In 2022, PBU 6/01 is still in effect. However, starting from January 1, 2022, FSB 06/2020 “Fixed assets” and 26/2020 “Capital investments” are mandatory for use.
Important! It is allowed to apply new Federal Accounting Standards already in 2022 - organizations are given the right to choose, but this must be indicated in the accounting policies. The main provisions of accounting according to the new standards must also be spelled out.
The table summarizes the differences in accounting for fixed assets when applying PBU 6/01 and FSBU 6/2020.
| No. | Provisions of PBU (main points) | FSBU provisions (main points) |
| Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting | ||
| 1 | The definition of fixed assets is an asset that is used in the current activities of the company, is not intended for sale, has been in use for more than 12 months and generates (or is capable of generating) income for the company | The condition that the asset is not intended for sale has been removed (that is, the asset can now be sold if it has become unnecessary). Property used for environmental protection can now be taken into account as fixed assets |
| 2 | If the asset no longer meets the criteria, assign it to other assets (for example, materials). It is not spelled out in the PBU, but the rule is unspokenly applied. FSBU: this rule is spelled out | |
| 3 | A list of costs that form the initial cost of an object has been approved (although this list is open) | We also accept fixed assets for accounting at their original cost, but the list of costs has not been approved |
| 4 | The minimum threshold for determining the initial cost is 40 thousand rubles. Cheaper property is included in materials or included in fixed assets (if a different limit is specified in the accounting policy) | The company sets the minimum cost of classification as an operating system independently |
| 5 | It is not necessary to distribute the operating system into types and groups | Companies must distribute all fixed assets into types and groups based on similar uses (for example, buildings, transport, office equipment, etc.). For each group, a single method of subsequent valuation is established: at original cost or taking into account revaluation |
| 6 | Each inventory item is accounted for separately. If the fixed asset contains parts with different useful lives, consider them separately | The disclosure of the accounting unit has been preserved as in the PBU, but has been supplemented by the fact that as a separate asset it is now possible to take into account the costs of repair, maintenance and technical inspection of the asset with a frequency of more than 12 months |
| Use and depreciation | ||
| 7 | The procedure for determining the useful life (SPI) has been approved (clause 20), can be changed based on the results of reconstruction or modernization | A similar procedure for determining PPI, however, is revised annually if the conditions for using the OS have changed. There are no conditions for modernization or reconstruction of the facility |
| 8 | It is allowed to accrue depreciation of fixed assets in four ways: linear, reducing balance, proportional to the volume of production and by the sum of the numbers of years of SPI | There are three methods left in the list (the method of calculating the sum of the number of years of SPI has been excluded). When choosing a reducing balance method, the company must independently approve the calculation formula. Important! With any chosen depreciation method, the residual value of the asset must correspond to its liquidation value. Install it for each object and approve it on the date of acceptance for accounting of fixed assets |
| 9 | Start calculating depreciation from the next month after the asset is accepted for accounting | Depreciation begins to accrue from the date the asset is accepted for accounting. If a company decides to use the old accrual procedure, this must be stated in the accounting policy. Investment properties that are overvalued are not depreciated |
| 10 | Conservation for more than 1 quarter: depreciation is suspended | There is no suspension of depreciation for a mothballed asset (exception is when the established liquidation value is reached) |
| 11 | There is no need to check any OS data. Exception for fixed assets revalued annually | At the end of each year, the SPI, liquidation value and method of calculating depreciation are checked. If conditions change, the company has the right to change these data, and all adjustments are reflected as a change in estimated values |
| Change in the initial cost of the OS | ||
| The cost of an asset can only change after revaluation, modernization or reconstruction | FSB allows changes in the cost of fixed assets if its initial cost took into account the costs of dismantling and disposal, which increased/changed in subsequent periods | |
| If you decide to re-evaluate some groups of operating systems, remember that you will have to do this annually. In this case, the increase in the cost of fixed assets (revaluation) is included in additional capital (account 83), the markdown (decrease in value) is reflected as other expenses. However, only if the revaluation amounts for previous periods are exceeded | Revaluation is carried out according to the rules of IFRS at fair value (IFRS 13 “Fair value measurement”). If desired, this can be done more than once a year. The markdown is reflected in the losses of the current period, the additional assessment is attributed to the total financial result, without being included in the profit or loss of the current period | |
| Are existing OS assets depreciating? PBU does not take this into account | Impairment of fixed assets is accounted for according to the rules of IFRS 36 “Impairment of Assets” | |
| Decommissioning of OS objects | ||
| Deregistered upon disposal or when they cease to provide economic benefit | The general write-off procedure has been preserved. However, if the asset is impaired, these amounts reduce its residual value. | |
How to form the initial cost of fixed assets
Cost is the cost of purchasing or producing a fixed asset. The initial cost consists of the following quantities:
- amounts transferred to the seller;
- price of delivery, installation and commissioning;
- costs of construction work;
- costs of information services when purchasing a fixed asset;
- customs duties and fees paid when importing an object, state duty for the purchase;
- other costs.
At the same time, general business expenses are not taken into account as part of the initial cost, with the exception of costs associated with a specific object and VAT.
The initial cost is reflected in the accounting of the fixed asset and does not change during its operation, except in cases of modernization, reconstruction, revaluation, completion or partial liquidation of the inventory item.
Taxation of fixed assets
The article has already talked about how to capitalize a fixed asset and how to sell it, but one more important issue remains - taxation.
We should start with one of the main fiscal obligations of any commercial entity - VAT.
Value added tax is levied on all transactions involving the acquisition, sale, repair and rental of fixed assets without exception. It is accrued if three necessary conditions are simultaneously met:
- OS was acquired for activities subject to VAT.
- The main facility has been put into operation.
- The purchase of the OS is confirmed by a correctly executed invoice.
If a fixed asset is purchased free of charge, then its cost is included in the income portion. Profit tax is charged on this amount, as well as on the sale of products produced through this operating system.
The sale of a fixed asset in accounting is treated as a sale; 20% VAT is deducted from the proceeds if the seller accepted the tax as a deduction at the time of its acquisition. Otherwise, if the cost of the fixed assets “hangs” on account 01 along with incoming VAT, then the tax should be calculated differently:
Where: S – the sum of the residual value with commissioning costs
Property tax is calculated on the basis of accounts 01 (“Fixed Assets”) and 03 (“Income Investments”), based on articles of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and other regulatory documents.
The tax base is the residual value of the object, equal to the original cost plus the costs of putting it into operation minus depreciation made by the actual owner (not the former).
Since the beginning of 2013, accounting for property taxes involves accrual exclusively on real estate items related to fixed assets.
How to revaluate fixed assets
The institution has the right to organize a revaluation of fixed assets if necessary. Revaluation is carried out every year as of December 31 for all fixed assets grouped on a homogeneous basis.
Upon revaluation, the value of assets is revalued, that is, increased, or decreased - discounted. This cost is called replacement cost.
For revalued objects, depreciation charges are formed from the replacement cost.
Important changes for 2022
On January 1, 2018, a new federal standard for fixed assets came into force. Now accounting for fixed assets in accounting must be done differently. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the key innovations shown in the table:
| Name | Content |
| Changing the grouping of fixed assets | Non-residential premises join the “Buildings and structures” group. There is no separate group for the library collection. The new grouping of objects does not directly coincide with OKOF, as before. |
| Investment property concept | This is a type of real estate that is owned by an organization and is either rented out by the owner or acts as an investment, resulting in an increase in the value of the real estate. This is a completely new group. |
| Recalculation of depreciation of some fixed assets | The limits of the initial cost of funds when calculating depreciation have been increased. Low-value property - up to 10,000 rubles. (write-off from the balance to 21 off-balance accounts). Funds from 10,000 to 100,000 rubles. upon commissioning they are depreciated at 100%. With an initial cost of over 100,000 rubles. The organization independently decides on the depreciation method. Library collection worth up to 100,000 rubles. — depreciation is charged at 100%. |
| Choosing a depreciation method | If the initial cost of the AI is 100,000 rubles. and above, then the depreciation method is selected by the institution based on the functional use of the object, that is, the method must be based on the method of obtaining economic benefits (utility potential). In 2022, the choice of institution will be made between the linear method, the method of proportional to production volume or the declining balance method. |
Also, organizations now have the right to change the method of calculating depreciation, but only from January 1. To take into account different groupings of fixed assets, you can use all 3 depreciation methods, prescribing this in your accounting policy.
Important changes also affected reporting on funds. Reports will become more detailed and transparent.
Tax accounting of fixed assets in 2022 will remain unchanged. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depreciable property is considered to be the property the owner of which is an institution and which is used to generate income. The useful life of such inventory items is more than 12 months.
From 01/01/2016, the initial cost value of the material value, at which the object is recognized as a fixed asset, increased to 100,000 rubles. This rule applies to those inventory objects that the organization puts into operation starting from 01/01/2016 (clause 7 of article 5 of the Federal Law “On Amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” dated 06/08/2015 No. 150).
On January 1, 2017, the new OKOF classifier came into force, thanks to which a new classification of fixed assets was approved (RF PP No. 640 dated July 7, 2016, Rosstandart Order No. 2020-st dated December 12, 2014). When registering an object for both accounting and tax purposes, each organization must use updated classifiers.
Accounting for fixed assets with zero tax value
By the tax value of a fixed asset we mean the cost of the object, which can subsequently be taken into account as expenses for profit tax purposes through depreciation, upon sale or other disposal.
The criteria for recognizing property as depreciable are named in Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and the procedure for determining its value is in Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, property that is not used to generate income is not recognized as depreciable. According to the official position of the regulatory authorities, expenses for office decoration (for example, flowers and paintings) cannot be taken into account when calculating income tax, since such expenses are not aimed at generating income and are not related to the organization’s activities (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 25, 2007 No. 03-03-06/1/311). For the same reason, when calculating income tax, it is impossible to take into account the costs of landscaping the territory (clause 49 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 10, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/96105, dated April 1, 2016 No. 03- 03-06/1/18575).
At the same time, there are court decisions according to which the costs of aquariums and other interior items can be included in expenses that reduce the tax base for income tax (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated June 16, 2009 No. KA-A40/5111-09, dated 05/23/2011 No. KA-A40/4090-11). Read more in the material “Office improvement expenses: justification features, court opinion.”
The costs of landscaping a production facility, as a result of which perennial plantings are created, according to the courts, can be taken into account in income tax expenses through depreciation (resolution of the Moscow District Arbitration Court dated February 24, 2015 No. F05-413/2015 in case No. A40-59510/ 13).
Let’s assume that the organization does not want claims from the tax authorities and does not include the “disputed” fixed asset in the depreciable property as not meeting the criteria of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Let's look at an example of how this situation can be reflected in “1C: Accounting 8” (rev. 3.0).
Example 1
The organization TREAGOLNIK LLC applies OSNO, PBU 18/02 (accounting in the program is carried out using the balance sheet method without reflecting PR and BP), and pays VAT. The income tax rate is 20%.
In February 2022, the organization purchased an aquarium worth RUB 144,000.00. (including VAT 20%) and installed it in the director’s reception area.
Revenue from sales of services in February amounted to RUB 240,000.00. (including VAT 20%), there were no other income and expenses in January-February 2020.
Since the organization will never be able to recoup the cost of the aquarium in tax expenses, its tax value will be zero (it is unlikely that the organization plans to sell such an object in the future). To account for fixed assets that are not recognized as depreciable under Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following actions can be used in the program:
- reflect the receipt of a non-current asset;
- reflect the acceptance of the fixed asset only in accounting, and write off the tax value of the fixed asset.
The receipt of equipment is reflected in the standard accounting system document Receipt (act, invoice)
with the type of operation
Equipment (section OS and intangible assets).
When posting the document, accounting entries will be generated:
Debit 08.04.1 Credit 60.01
— for the cost of the aquarium received by the organization (RUB 120,000.00);
Debit 19.01 Credit 60.01
— for the amount of VAT (RUB 24,000.00).
For tax accounting purposes for income tax, the corresponding amounts are also recorded in the resources Amount NU Dt
and
Amount NU Kt
for accounts where tax accounting is maintained (except for account 19 “VAT on acquired values”).
Acceptance for registration and commissioning of the aquarium is registered with the document Acceptance for registration of OS
from the section
OS and intangible assets
.
On the Tax Accounting
in the field
Procedure for including costs in expenses
, select the value
Inclusion in expenses when accepted for accounting
.
In this case, in the Expense Reflection
, you can select one of two values:
- Similar to depreciation
- in this case, the cost of fixed assets in tax accounting will be written off to the account and cost item specified to reflect depreciation expenses in accounting.
The method of reflecting expenses
is selected from the directory of the same name and is indicated in the
Method of reflecting depreciation expenses
on
the Accounting
.
In order for the cost of fixed assets not to be taken into account in tax accounting, in the Method of reflecting expenses
, you must indicate an item of costs (or an item of other income and expenses) not taken into account for profit tax purposes; - Another way
- in this case, in the
Method
, you should indicate a separate
Method for reflecting expenses
, used only in tax accounting (Fig. 1).
In this Method of reflecting expenses
, you should indicate a separate account and analysis of expenses that are not taken into account in tax accounting (for example, account 91.02 “Other expenses”), and an item of other income and expenses with the Accepted
for tax accounting
.
Rice. 1. Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets with zero tax value
When posting a document, accounting register entries are generated:
Debit 01.01 Credit 08.04.1
— for the initial cost of the fixed asset (RUB 120,000.00);
Debit 91.02 Credit 01.01
- with an unfilled amount in accounting.
For tax accounting purposes, the cost of an aquarium accepted for accounting and immediately written off is 120,000.00 rubles. reflected in special fields of the accounting register:
Amount Dt NU: 01.01
and
Amount Kt NU: 08.04.1
;
Amount Kt NU: 01.01
.
We will generate a report : Turnover balance sheet
on account 01.01 to obtain information about the initial cost of the fixed asset item. Using the report settings panel, we will simultaneously display accounting and tax accounting data (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. SALT for account 01
As you can see, the difference between the book value and tax value of the aquarium is 120,000.00 rubles, and it is temporary due to the requirements of IAS 12, paragraph 8 of the new edition of PBU 18/02, as well as Recommendation No. R-102/2019- KpR.
In February 2022, when performing a regulatory operation, Calculation of income tax
accounting entries will be generated with simultaneous distribution among budgets:
Debit 99.02.T Credit 68.04.1
— for the amount of current tax RUB 40,000.00. (200,000.00 x 20%).
When performing a regulatory operation Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU 18
for January, included in the
month-end
a deferred tax liability (DTL) is recognized for the asset type
Fixed assets
Debit 99.02.О Credit 77
— in the amount of RUB 24,000.00. (RUB 120,000.00 x 20%).
A detailed calculation of IT is presented in the Deferred Tax Calculation Certificate
for January 2022 (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. IT calculation
As of 01/01/2020:
- the tax rate is set at 20%;
- no deductible and taxable temporary differences were identified according to accounting data;
- deferred taxes are not recognized.
At the end of February (as of 03/01/2020):
- the book value of assets is 120,000 rubles. (column A), the tax value of assets is zero (column B). This means that in the future the organization will not be able to take into account the cost of the fixed asset;
- the difference between the book value and tax value of the fixed asset is 120,000 rubles. (120,000 rubles - 0 rubles) and is reflected in column 7. This is a taxable temporary difference, since it will lead to the formation of deferred income tax, which should increase the amount of income tax payable to the budget in the next reporting period or subsequent ones reporting periods (clause 11 of PBU 18);
- IT was recognized in the amount of 24,000 rubles. (RUB 120,000 x 20%), which is reflected in column 9.
In February 2022:
- there was an increase in the taxable temporary difference by 120,000 rubles. (120,000 rubles – 0 rubles), which is reflected in column 11;
- IT was recognized in the amount of 24,000 rubles. (column 11a).
Accordingly, the income tax expense for January-February 2020 is RUB 64,000.00. (RUB 24,000.00 + RUB 40,000.00). In this case, the conditional income tax (tax calculated according to accounting data) for the specified period is 40,000 rubles. (RUB 200,000 x 20%).
These indicators are reflected in the reference calculation Income tax expense
, formed in January (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Income tax expense for January 2020
At the same time, the calculation certificate reflects a constant tax expense in the amount of 24,000.00 rubles, which, in accordance with paragraph 9 of Recommendation No. R-109/2019-KpR, is defined as a numerical reconciliation between income tax expense and conditional tax expense on profit (RUB 64,000.00 - RUB 40,000.00).
Thus, the difference of 120,000.00 rubles, formed under the conditions of Example 1, represents both a temporary and permanent (“complex”) difference.
In March 2022, the aquarium begins to be depreciated on the books. As the fixed asset is depreciated, IT will be repaid.
How in “1C: Accounting 8” edition 3.0, in accordance with the new edition of PBU 18/02, take into account fixed assets that are not used to generate income (for example, an aquarium or a music center)
Postings
1. Accounting for the receipt of fixed assets.
Accounting for the receipt of fixed assets and the commissioning of inventory objects is carried out at the original price (purchase cost) of the object. IO is accepted for accounting on the date when the initial cost is fully formed, and for tax purposes - at the time the fund is put into operation:
- Dt 08 Kt 60/10/70/69) - taking into account expenses for the acquisition or creation of fixed assets;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 - carrying out incoming VAT;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - formation of the initial cost of the inventory item.
For budget accounting, the postings will be as follows:
- Dt 110631310 Kt 130231730 - equipment has arrived;
- Dt 110434310 Kt 110631410 - commissioning of equipment;
- Dt 130404310 Kt 110404410 - depreciation calculation.
2. Accounting for the disposal of fixed assets.
Let's consider options for the sale and liquidation of the property. Accounting for the disposal of fixed assets reflects the sale price and the residual value of the investment:
- Dt 62 Kt 91 - income from sales;
- Dt 91 Kt 68 - VAT;
- Dt 02 Kt 01 - write-off of depreciation;
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - write-off of residual value.
Entries for budget accounting:
- Dt 110434 410 Kt 110134410 - depreciation write-off;
- Dt 140110172 Kt 110134410 - write-off of residual value.
Liquidation accounting:
- Dt 02 Kt 01 - write-off of depreciation;
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - the residual value is written off.
Dt 0 401 10 000 (analytics - 401 10 172) Kt 0 101 00 000 (required analytical account) - posting for partial liquidation of a fixed asset in a budget institution.
3. Off-balance sheet accounting.
Off-balance sheet accounting of fixed assets is maintained in accounts 001 and 011 (transfer or rental of inventory items), 005 (installation equipment), 010 (depreciation of some objects is reflected).