Accounting for construction costs of fixed assets
The management company is going to improve the territory of the village that it serves. They also need to build a playground, or a winter shed to store equipment for work.
To do this, the management company hired a contractor to carry out the work and purchased all the necessary materials. In this case, the organization’s accountants may have reasonable questions: how is the accounting of trade and material assets organized? Do you need documents from the contractor? If necessary, what documents should be required from him? How is an object registered? We decided to show you, using the example of the 1C: Accounting program, how all this is formalized and done officially and correctly.
For example, you have an agreement, the clause of which sounds something like this:
In this case, the customer takes into account not only his own costs for the material, but also the cost of the contractor’s work, which is why the total cost will be the sum of these two factors and will be much higher, which is not always profitable.
The next step is the purchase of trade and material assets that may be needed for construction, as well as their further transfer to the contractor. To reflect this operation in the 1C: Accounting program there are two methods:
- through a system for recording trade and material assets, which are transferred to the contractor through a separate warehouse;
- through a special document “Transfer of raw materials for processing”, which is generated in the program.
We will now talk about the advantages and disadvantages of both methods using examples.
Accounting of the object
The initial cost of the operating system will be formed by other expenses different from those that are present in the economic method:
- payment for contractor services minus VAT;
- payment of state duty for registration of rights to built real estate.
VAT can be deducted if the contractor provides a correctly executed invoice.
Important! For the purposes of accounting for objects, costs will still be collected on the debit of account 08 (08.3, if we are talking about construction) in correspondence with the accounts for accounting for these expenses - account 60 for the contractor.
Paperwork
To reflect in the accounting records the entries for accounting for the costs of construction or manufacturing of an OS object by contractors, the following document is used - the acceptance certificate for the work performed.
This act serves as the basis for accounting for the costs of paying for contract work. The acceptance certificate is attached to the contract concluded at the initial stage of concluding the contractual relationship.
Posting table
Accounting entries during the construction (creation) of an operating system by contract are summarized in the table below:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Accounting for labor costs of contractors is reflected | 08 | 60 |
| Input VAT on payments for contractors' services has been taken into account | 19 | 60 |
| The constructed (created, manufactured) object is accepted for accounting at its original cost as a fixed asset | 01 | 08 |
Important! Until the rights to the constructed object are registered, it must be accounted for in a separate subaccount of account 01.
After receiving confirmation of state registration, the object is transferred to another subaccount of account 01, where records of all available real estate are kept.
Accounting for fixed assets upon receipt as a result of:
- contribution to the authorized capital;
- free receipt;
- purchase for a fee.
Example
Example conditions:
The company entered into a contractual agreement with a contracting company for the construction of an office building. Construction of the property will be completed in 2022.
The total cost of the work performed by the contracting company is 1,770,000 (VAT is included in this cost in the amount of 270,000).
Upon completion of the work, a certificate of completion of construction work was drawn up.
The object was registered under state law, for which a fee of 15,000 rubles was paid.
Accounting entries for this example:
| Sum | Business transaction | Debit | Credit |
| 1500000 | Contractor labor cost accounting shown | 08.3 | 60 |
| 270000 | VAT allocated on the cost of contractor services | 19 | 60 |
| 270000 | VAT transferred for deduction | 68.VAT | 19 |
| 1770000 | Contractor's work paid | 60 | 51 |
| 15 000 | The amount of duty paid is reflected as part of construction costs | 08.3 | 96 |
| 1515000 (1500000+15000) | The erected construction project is accepted for accounting as a fixed asset in an independent subaccount | 01.Buildings without registration | 08.3 |
| 15000 | The state duty for state registration of rights to the building has been transferred | 68. State duties | 51 |
| 15000 | State registration of rights to the constructed OS object is reflected | 96 | 68. State duties |
| 1515000 | The constructed building is included in the fixed assets | 01.Buildings | 01.Buildings without registration |
Through inventory accounting
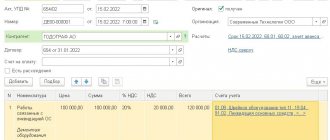
So, let’s say the customer buys the necessary materials and checks in at his warehouse.
Now he needs to display the transfer of valuables to the Contractor, which means he needs to create a warehouse for this, which you will call “Contractor”.
The transfer of materials itself will be formalized through a special document called “Transfer of Goods.”
The only disadvantage of this method is that documents are not issued in printed M-15 form and if you need it, you will have to create it manually. When your counterparty reports on where and how much material he used, you will need to collect all the costs in the “Request Invoice” document.
If your counterparty still has some unspent valuables, then they need to be processed back to your warehouse through a document called “Transfer of Goods.”
This method is quite good for those who do not want to do manual adjustments, but most often they use the second method, which we will write about below.
Documenting
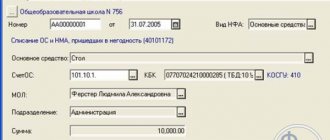
After examining the object, the commission must give an opinion on the possibility of its use. To do this, you need to draw up a primary document, which must contain the mandatory details provided for in Part 2 of Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ. Such a document may be an act in form No. OS-1a or in form No. OS-1.
Apply the act in form No. OS-1a during the construction of buildings (structures). Draw it up at the time the object is included in the fixed assets (at the time its value is reflected in account 01 “Fixed assets” or 03 “Income-generating investments in tangible assets”) (paragraph 2 of the instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7). Draw up an act based on primary accounting documents confirming the expenses incurred. Do not fill out the details of the donating organization, which are provided at the beginning of the act, as well as the sections “Information on the condition of the fixed asset object on the date of transfer” and “Passed over”.
In the act in form No. OS-1a, indicate:
- number and date of its compilation;
- full name of the fixed asset;
- place of acceptance of the fixed asset;
- factory and assigned inventory numbers of the fixed asset;
- depreciation group number and useful life of the fixed asset;
- information about the content of precious metals and stones;
- other characteristics of the fixed asset (total area, number of floors, etc.).
In addition, put a note on the conclusion of the acceptance committee (for example, the entry “Can be used”). The executed act is approved by the head of the organization.
When producing other fixed assets (except buildings and structures) on your own, use the form of act No. OS-1. When filling it out, apply the same rules as when drawing up form No. OS-1a.
This procedure follows from the instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7.
Simultaneously with drawing up the act in form No. OS-1a (OS-1), fill out the inventory card in form No. OS-6a (OS-6) in one copy. Draw up an inventory card on the basis of the act and primary documents. In the future, enter into the card information about all changes that affect the accounting of fixed assets (revaluation, modernization, internal movement, disposal). Reflect this information on the basis of primary documents (for example, on the basis of the acceptance certificate for modernized fixed assets in form No. OS-3).
This procedure is provided for by the instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7.
Attention: the absence (failure to submit) primary documents for accounting for fixed assets is an offense (Article 106 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 2.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation), for which tax and administrative liability is provided.
Through a special document “Transfer of raw materials for processing”
The customer purchases materials and delivers the material to his warehouse, as in the first method.
Next, you transfer the trade and material assets to the contractor and draw up the document “Transfer of raw materials for processing.”
As documentary evidence, you will be given a printed form of the M-15 document.
We advise you to print this form in three versions: one copy for your company, the second for the storekeeper, and the third you give to your counterparty.
As soon as your counterparty spends all the goods and materials and provides the accountant with the Act, the accountant writes off the materials to account 08. This is done in manual adjustment mode, since the standard document does not provide for the use of form 08.
The second method is convenient for those who value the printed form of the M-15 invoice. In this method, it is issued automatically, but there are also disadvantages, namely the adjustment of postings.
Taxation in construction
The basic principle that construction companies must adhere to when organizing their tax accounting is the economic justification of expenses and their documentary justification. This is the main relationship between accounting and tax accounting in construction in 2022.
Taxation and accounting in construction should be organized in such a way that the information forming the tax base for taxes makes it possible to understand:
- ways for a construction company to determine its income and expenses;
- algorithms for the formation of tax bases for all types of taxes and fees paid by a construction company;
- reserve formation schemes;
- mechanisms for temporary distribution of expenses and transfer of part of them to subsequent periods;
- other tax parameters (amount of tax liabilities as of the reporting date, etc.).
The nuances of tax accounting and filling out tax returns will help you understand the articles posted on our website:
- “What is the procedure for filling out an income tax return (example)?”;
- “How is separate accounting for VAT carried out (principles and methods)?”
Receipt of construction projects
No matter which method you choose, the following sequence will always be the same. All costs that you collected on account 08 are included in the cost of the constructed facility. After the work is completed, the contractor must provide you with a certificate of acceptance of the object and on the basis of this certificate you will have to generate a document called “Receipt of construction objects”.
The last stage is the acceptance of the object that was built for registration.
In this case, the amount for the object will consist of the cost of the work itself, as well as materials and customer-supplied materials.
Still have questions? Order a free consultation with our specialists!
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter
Initial cost
Fixed assets constructed by contract are accepted for accounting at their original cost (clause 7 of PBU 6/01). Include in the initial price:
- amounts paid to the contractor in accordance with the contract;
- amounts paid for information and consulting services related to the creation of fixed assets;
- the amount of VAT claimed (if the fixed asset will not be used in activities subject to this tax);
- other expenses directly related to the creation (for example, the cost of purchased materials; equipment intended for installation at the facility; costs of examining the safety of the facility, etc.).
This procedure is provided for in paragraph 8 of PBU 6/01, paragraph 5.1.1 of the Regulations approved by the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1993 No. 160, paragraphs 11–15 of PBU 2/2008.
A detailed list of expenses that form the initial cost of constructed (manufactured) fixed assets is given in the table.
During the operation of a fixed asset, its initial cost does not change. The exceptions are cases of completion (retrofitting), reconstruction, modernization, partial liquidation and revaluation of fixed assets. Therefore, if any costs associated with the construction (manufacturing) of an object (for example, interest on a loan) are incurred by the organization after its inclusion in fixed assets, do not change the original cost. And consider the costs as part of current expenses. This procedure follows from paragraph 14 of PBU 6/01.
simplified tax system
Organizations using the simplified system are required to keep accounting records, including fixed assets, in full (Part 1, Article 2 of Law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011). At the same time, in order not to lose the right to apply the simplification, the organization must control the residual value of fixed assets, which cannot exceed 100,000,000 rubles. (Subclause 16, Clause 3, Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For information on the features of accounting for fixed assets built (manufactured) using economic methods, when simplified, see How to take into account the receipt of fixed assets and intangible assets using the simplified tax system.
Situation: is it possible to take into account when calculating the single tax the costs of constructing a fixed asset built on an economic basis? The organization applies a simplification and pays a single tax on the difference between income and expenses.
Yes, you can.
The right to take into account the costs of constructing a fixed asset is in no way connected with the method of construction or manufacture of fixed assets (subclause 1, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, the organization has the right to take into account in expenses when calculating the single tax the costs of constructing a fixed asset using economic methods.
Accounting: creation by contractor
In the process of creating a fixed asset on an economic basis, an organization can attract contractors to perform individual works. Also take into account the cost of their services when forming the initial cost of the fixed asset being created (clause 8 of PBU 6/01). Make the following wiring:
Debit 08-3 Credit 60 (76) – reflects the cost of contract work for the construction of a fixed asset;
Debit 19 Credit 60 (76) – reflects VAT presented by the contractor.
For information on the specifics of accounting for fixed assets manufactured by contract, see How to reflect the construction of fixed assets by contract in accounting.