How to draw up an act for writing off materials
In any production one cannot do without writing off material assets. The reasons may be different, but there must always be a documented basis for the process. How is an act drawn up when writing off materials? Production processes are invariably accompanied by user consumption of raw materials and material assets.
Consumed materials must be shown in accounting. That is, the expense must be documented to confirm the write-off. How to properly prepare an act when writing off materials?
It is not only raw materials used for production that are subject to write-off.
Any materials and valuables consumed by the business entity are written off.
In addition to the fact that confirmation of write-off is important for the reliability of accounting, documentation also plays a huge role for taxation.
When and what to write off and how to formalize it?
The standard process of writing off materials is carried out once a month. In this case, only those values that are officially accepted for accounting can be written off. The procedure is accompanied by the creation. The amount of materials consumed is determined taking into account the volume indicated in the receipt documentation as an initial indicator. Any consumption of material is confirmed by consumable documents. These data are indicated in the act with reference to supporting documents.
It is also important to take into account natural losses when writing off materials.
For example, individual materials may decrease in volume at or . If normal losses are ignored, over time they can accumulate and become significant, leading to shortages.
Reasons for writing off a galvanized bucket
Contents Utensils made of metal are mainly produced in two ways: the casting method and the plastic deformation method, this is determined by the type of metal or alloy used. Each method is characterized by certain defects, for this reason they are considered separately. Rodina, T.G. Commodity research of homogeneous groups of non-food products: Textbook for bachelors / L.G.
Eliseeva, T.G. Rodina, A.V. Ryzhakova; Ed. L.G. Eliseeva. - M.: Dashkov and K, 2013. - 930 p. Shells are open or closed cavities in the body of goods.
Cracks are through or non-through ruptures of metals that appear in a hot or cold state.
Warping is a distortion of the shape and size of goods under the influence of internal stresses (with uneven cooling). Underfilling is the result of incomplete filling of the mold with molten metal. A junction is a through or surface depression or gap with rounded edges. Appears during interruptions in pouring metals.
Chill (a defect in cast iron cookware) is the formation of free cementite in the surface layer in the form of a light crust.
Mechanical damage - dents, nicks, damage to the integrity of the casting (formed when the mold is knocked out). Defects of stamping are observed in all types of steel utensils, utensils made of copper alloys, and sheet aluminum: Fractures - rupture of metals during deformation. Nicks are the introduction into the surface of a product of pieces of metal that have fallen into the stamp.
Dents are local deformation of goods due to mechanical stress.
Corrugations are wavy folds on the surface of a product.
Defects in utensils made of metal
Utensils made of metal are mainly produced in two ways: the casting method and the plastic deformation method, this is determined by the type of metal or alloy used.
Each method is characterized by certain defects, for this reason they are considered separately. Rodina, T.G. Commodity research of homogeneous groups of non-food products: Textbook for bachelors / L.G. Eliseeva, T.G. Rodina, A.V. Ryzhakova; Ed. L.G. Eliseeva. - M.: Dashkov and K, 2013. - 930 p. Shells are open or closed cavities in the body of goods.
Cracks are through or non-through ruptures of metals that appear in a hot or cold state.
Warping is a distortion of the shape and size of goods under the influence of internal stresses (with uneven cooling).
Underfilling is the result of incomplete filling of the mold with molten metal.
A junction is a through or surface depression or gap with rounded edges. Appears during breaks in pouring metals.
Chill (a defect in cast iron cookware) is the formation of free cementite in the surface layer in the form of a light crust.
Mechanical damage - dents, nicks, damage to the integrity of the casting (formed when the mold is knocked out).
Stamping defects are observed in all types of steel utensils, utensils made of copper alloys, and sheet aluminum:
Fractures are the rupture of metals during deformation.
Nicks are the introduction into the surface of a product of pieces of metal that have fallen into the stamp.
Dents are local deformation of goods due to mechanical stress.
Corrugations are wavy folds on the surface of a product.
Burrs are sharp, uneven edges of products.
Drawing is the spiral-shaped and concentric marks of a press when processed on pressing machines.
Side waviness is the deviation of the edge of the pan from the specified shape.
Thickening or thinning is observed in individual parts of goods.
Defects of the protective and decorative coating include:
Enamel rebound is a local absence of enamel due to its detachment.
Scaly (“fish scales”) - chipping of enamel in the form of small scales on the convex surfaces of the body and bottom of goods.
Hairline cracks (cec) are a system of tiny cracks in places during welding of reinforcement due to uneven cooling or impacts.
Exposure of metals or ground enamel.
Bubbles, boils - local swelling of the enamel when, during firing, gaseous inclusions do not have time to release.
Craters are burst bubbles.
Enamel burnouts are exposure of soil or metals due to burnout of the enamel.
Matt spots are areas of zinc coating characterized by a lack of shine.
Traces of oxides are oxides of zinc and aluminum embedded in the surface of the coating.
Zinc deposits are local thickenings and drips of the zinc coating.
Pockmarking is an uneven or insufficiently tinned surface.
Drip - strip thickenings, “drops” on tinned and zinc surfaces.
Dark spots (dots) - on galvanized steel utensils and utensils made of copper alloys.
Peeling of the coating layer.
Coating cracks.
Decoration defects are characterized by the following types:
Assembling the decal means breaking the design and tearing the paint.
Underburning of the paint - the paint does not melt completely, looks dull, matte, and does not adhere firmly.
Burnt paint - the paint is burnt out and abruptly changes its tone.
Burnout of the design - punctures and blisters on the surface of the paint.
Unclear outline of the drawing.
Erasure of the drawing.
Current standards do not provide for the division of utensils made of metal into grades; they can be standard in quality; non-standard, but suitable for implementation (meets safety requirements); marriage.
Galvanized bucket
No matter how modernized and modern your homestead may be, there are things that you cannot do without today, just like thirty or forty years ago. One of them is a galvanized bucket, traditionally used for various household needs. But, along with the undeniable advantages, the use of such buckets can cause some harm to health.
Today we will talk about the features of galvanized buckets and whether it is possible to heat water in them. The need to quickly heat a sufficiently large volume of water often arises in dacha conditions.
And many housewives have adapted to using galvanized buckets for these purposes.
But is it possible to do this and will the water heated in this way cause any harm? As you know, galvanized buckets are made of steel, then coated with a thin layer of zinc. When such a bucket is heated, zinc salts fall from its surface into the water, which in the future can lead to quite serious poisoning.
Therefore, such water should never be used for cooking or washing the body. But for household (washing, wet cleaning) and construction (preparation of various solutions) needs, water heated in a galvanized bucket is quite suitable. In addition, although a galvanized bucket can be used to transport water, it is still not worth storing water in it because of the danger of the same zinc salts getting into it.
Therefore, the water brought with the help of such a bucket must be poured as soon as possible into another container, for example, into an enamel or plastic bucket. On sale you can find galvanized buckets with a volume of 9 to 15 liters, both with and without a spout.
Blog
Plastic products: list the characteristics of the classification of plastic products, characterize the main methods of producing plastic products.
1. tableware and household goods: products for food products and products for non-food products;
– products for food products: for dry products (crusks, bread bins); for cold products (vases, jugs, jars); for hot foods (mugs, plates, spoons); other household products (trays for storing cutlery, trays).
– products for non-food products:
· for the bathroom and toilet: products for the installation of sanitary equipment (siphons, tubes, hoses), and accessories for bathrooms (laundry baskets, hangers, brushes, brushes, paper holders);
· for the garden and vegetable garden: for harvesting (berry pickers, fruit pickers), for watering the soil and spraying plants (hoses, watering cans, sprayers), for storage (boxes, barrels);
· furniture for the interior of residential premises (vases, flowerpots, cornices, furniture).
2. haberdashery goods: combs and combs; clothing accessories; decorations and decorative items; items for handicrafts.
3. cultural goods: stationery; photographic accessories; toys and games; art products; products for mass sports.
By type of plastic:
· plastics approved for contact with food;
· plastics for the manufacture of other goods.
By manufacturing method: injection molding (various shapes); extrusion method (rods, pipes, tapes, fibers, etc.); calendering (plates, sheets, films); stamping (soap dishes, cases, vases); hot pressing (large products).
By the nature of the finish: by color (black, white, colored and colorless); according to surface relief (smooth, embossed, granular, patterned);
According to the design of the product: according to the method of connecting nodes (solid and composite); according to the arrangement of units (on a leg, on a pallet, with and without handles, with and without a lid, with a spout, etc.)
Product shape: round, square, oval, conical, cylindrical; edge of the product: smooth or cut out; flat or hollow.
By size - in mm or cm.
By completeness: piece items, sets (for tourists and breakfasts), sets.
The main methods for producing plastic products:
injection molding - a thermoplastic material is loaded into a hopper, it heats up and acquires a viscous-flow state, then it is pushed under pressure into a cold mold, the plastic mass cools and hardens, acquiring its outline (there is a mark from the sprue on the products;
extrusion - solid polymer enters the extruder, is heated and extruded into profiles (of various shapes - sheets, pipes, films);
hot pressing - pressed polymer tablets are poured into a mold, they are heated and softened, then a matrix is lowered into the mass, molding occurs, the plastic hardens and is pushed out of the mold;
using sheets or film p/f by vacuum molding - a heated sheet of thermoplastic is heated to an elastic state, then installed in a mold and under the influence of atmospheric pressure the sheet is pressed against the walls of the mold, after molding the product is cooled and removed from the mold ( sinks, bathtubs, refrigerator containers),
hot stamping - a special workpiece is softened to an elastic state, then placed in stamps consisting of a punch and a matrix, and a product (open-shaped products) is formed using the punch.
Plastic products: list possible defects in plastic products, characterize the main components of the plastic composition.
All defects, depending on their origin, are divided into defects in composition, molding and finishing.
To composition defects
include foreign inclusions, reduced mechanical strength, increased water absorption, resulting from poor cleaning or contamination of raw materials, as well as from incorrectly selected fillers.
Forming defects
: warping (distortion of shape) of products made from thermoplastics should not exceed 1.0%, from thermosets - 0.5%, cracks, cavities, swelling (small or large bulges), chips (depressions due to mechanical damage), burrs (sharp protrusions along the edge or bottom), burrs (thickenings at the place where the mold is parted), protrusion of the sprue, marks, scratches, marks from ejectors (protrusions and depressions), technological joints (visible lines of connection between portions of the casting mass), marks from the part of the mold (thickened seam on the surface of the product). Defects such as protrusion of the sprue, marks from ejectors, are standardized by the ND depending on the type of plastic and the method of processing into the product. In finished products, defects that violate the integrity are not allowed - cracks, swelling, chips of certain sizes; shrinkage cavities more than 0.3 mm deep; scratches over 10 mm long over an area of 100 cm2 (more than two).
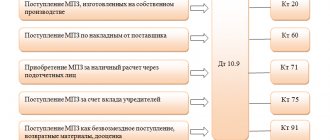
Reasons and grounds for writing off material assets
- /
- /
October 3, 2022 0 Rating Share We recommend a selection The reasons for writing off material assets can be varied: from identified defects to obsolescence.
Find out more in our material about the reasons and grounds for writing off valuables. Material assets are subject to write-off if they:
- Consumed during the normal production process in the manufacture of final products or semi-finished products.
- They have lost their original properties and cannot be used for their intended purpose.
In the first case, for the write-off of each batch of raw materials and materials, there is no need for a special written permission from management - the write-off is carried out according to established standards, which must be justified and approved by the head of the enterprise. The write-off process has its own characteristics, which will be discussed in one of the subsequent sections.
In the second case, writing off valuables requires an individual approach, and in each case, writing off is carried out on commission. Methods for writing off material assets should be reflected in the accounting policies of the enterprise. Detailed write-off processes (templates for documents for write-off, regulations for their execution and reflection on accounting accounts, other aspects) are prescribed in the internal regulations of the enterprise (Regulations on accounting and write-off of valuables, orders, instructions, instructions).
Sample act of writing off material assets
The defect will worsen during processing and cannot always be eliminated;
- the presence of stains from blood, paint, ink, mold, animal secretions, protein, oils, fats, fuels and lubricants, fuel oil, glue, medicines, perfumes, red wine, bleach, acids, alkalis that were on the product for a long time during operation, as well as the presence of stains resulting from independent attempts to remove them with chemicals, soap and water. These stains are generally difficult to remove and things with them are accepted without a guarantee of stain removal, and salt etchings are not removed;
- moth etchings, tears, cuts, holes, torn edges, loose hinges, abrasions. The defect cannot be repaired;
- loss or migration of color due to self-removal of stains. The defect cannot be repaired.
- Tears in the frame fabric of the carpet may occur. During operation over time, under the influence of moisture, mold, disinfectant pesticides, unskilled stain removal or washing, traces of cement, tar, glue, the backing frame fabric weakens, and during the cleaning process, tears may form on it;
- undergo shrinkage;
- cracks may form on the latex base of the rugs;
- Peeling of the secondary backing may occur in imported pile-tufted carpets, the reverse side of which, in order to increase strength, dimensional stability and imitate a woven structure, is duplicated with a secondary backing made of jute fabric or fabric containing polypropylene film thread in the warp and jute yarn in the weft. The secondary ground fabric has a loose structure like burlap and is loosely secured along the perimeter of the carpet in the overlock seams, which often leads to its detachment from the overlock seam during the use of the carpet;
- the rubber base of the carpet becomes brittle and begins to crumble;
- a tear in the foam base is formed;
- There may be tears and loss of pile in woolen looped carpets made in China;
- staining may appear on tapestries painted in red or blue tones;
- dye breakage and migration on silk carpets is possible.
c) hidden defects that may appear after dry cleaning:
All news
Write-off of business equipment
Contents Defects that arise during the molding of plastic products can have different origins.
We recommend reading: Notaries of bodies in Moscow
These may be defects associated with an unsuccessfully selected composition of the plastic (composition defects); defects caused by a violation of the molding technological regime and its incorrect selection (forming defects); as well as defects associated with insufficiently thorough mechanical processing or decoration of already molded products (finishing defects).
Composition defects arise when the recipes are incorrectly selected or low-quality components of composite plastics are used, when their optimal ratio is violated. Composition defects include: foreign inclusions - visible foreign inclusions resulting from contamination of the plastic composition or equipment; reduced mechanical strength that occurs with low or excessive filler content. If the content is low, the filler does not have the proper reinforcing effect; if it is in excess, it is not completely wetted by the polymer; increased water absorption is the result of an excess amount of hygroscopic fillers.
Molding defects arise due to deficiencies in the design of the mold and molding machines, incorrect selection or violation of the plastic processing regime. Particularly important is compliance with the temperature regime and duration of the molding operation.
In case of deviations from the optimal molding temperature, uneven heating of the molds, rapid or
Describe the defects of plastic products
If the content is low, the filler does not have the proper reinforcing effect; if it is in excess, it is not completely wetted by the polymer; increased water absorption is the result of an excess amount of hygroscopic fillers.
Molding defects arise due to deficiencies in the design of the mold and molding machines, incorrect selection or violation of the plastic processing regime. Particularly important is compliance with the temperature regime and duration of the molding operation. With deviations from the optimal molding temperature, uneven heating of molds, rapid or slow cooling, destructive processes can occur, significant internal stresses may arise, causing deformation of products, appearance of defects in appearance, and also reducing mechanical strength.
The most common molding defects include the following: warping - distortion of the shape of products,
Causes of early wear of zinc coatings
› Home » Literature » Articles » Author: Corrosion management Most functional coatings are developed to protect the surface of steel under specific operating conditions.
It is on this basis that they are selected by specifiers and end users. To decide on a protective coating, the designer must either trust the supplier to recommend a suitable solution, rely on his own experience with the coating, or have knowledge of the quality of the coating and the environment in which the coating will be placed. The quality of coatings and compliance with standards play an important role in defense projects such as this vessel at Forgac's Dockyard in Newcastle, USA.
All coatings must be updated sooner or later. They are created in order to wear out and protect what is underneath them. If coatings wear out prematurely, the cost of restoration is not commensurate with the cost of initial treatment.
There are many reasons for coating defects.
Some of them are predictable, others are very difficult to determine.
Be that as it may, in most cases the causes of early wear are more likely to be related to human factors than to technology. GALVANIZED COATINGS All galvanized coatings are obtained in
Material write-off act
35983 Drawing up an act for writing off materials is required in cases where the material assets and inventories on the organization’s balance sheet have become unusable for some reason.
Write-offs occur in a strictly established manner and are recorded in the appropriate act.
FILES To write off material assets, the creation of a special commission is required.
It consists of financially responsible persons, as a rule, from different structural divisions of the enterprise.
It is their responsibility to identify and examine damage, defects or malfunctions of equipment, machinery, furniture, household equipment, tools and other valuables contained on the organization’s balance sheet. After recording such facts, they are authorized to draw up an act of write-off of materials.
As a rule, in large organizations there are specially developed clear instructions for such actions. To write off materials, there must be compelling reasons with documentary evidence. Write-off of materials cannot occur without compelling reasons, confirmed by a certain evidence base.
In particular, during the procedure for writing off materials, supporting documents can be used. So, these are: reports on products produced over a certain period (its volume, names, etc.); reports from financially responsible persons on the material assets used; written documents on the consumption of materials in excess of established standards (with justification for these facts);
Write-off of fixed assets in 2022: reasons, documentation, order
Any equipment has its own service life, after which it must be written off.
To do this correctly, you need to act in a certain order, regulated by law. We will look at how to write off fixed assets in 2022 in the article.
Any accountant directly involved in the acceptance, depreciation and write-off of fixed assets must clearly know the procedure and the required list of documents. Otherwise, the tax service may have questions regarding the legality of the write-off and the lack of required documents. Before writing off fixed assets at an enterprise, it is necessary to study the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 33n dated July 20, 1998.
It contains information about mandatory activities and documents and regulates the procedure for accounting for fixed assets. Contents Writing off fixed assets seems common and simple, but in reality the company needs to draw up a number of papers that would confirm the legality of disposal of fixed assets.
The disposal is preceded by the execution of an order to create a special commission, which is tasked with writing off fixed assets (documentary registration of the formation of such a commission is strictly necessary). It includes the following persons:
- chief accountant of the company;
- technical specialists;
- MOLs to which fixed assets subject to disposal are assigned.
During the creation of the commission, their powers are determined.
We recommend reading: Overhead costs for the apartment department
The guidelines provide for the inclusion of the following functionality in this list:
- The commission is inspecting the decommissioned facility.
Sample act on write-off of soft and household equipment
Approved by Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of Russia dated May 16, 2003 N 750
Agreed by letter of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated April 10, 2003 N KL-01-21/1381
Form N 421-APK
ACT N _____ FOR WRITTEN OFF INVENTORY AND HOUSEHOLD SUPPLIES ————— ¦ Codes ¦ +————-+ OKUD form ¦ ¦ I approve +————-+ Date (day, month, year) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ Manager +—+—-+—-+ ________________ ______________ Organization __________ according to OKPO ¦ ¦ personal signature transcript +————-+ signatures Department (site) ¦ ¦ “__” __________ 200_ +————-+ Farm ¦ ¦ +————-+ Brigade ¦ ¦ ————— —————————————————————— ¦ N ¦Name¦Inven-¦Koli-¦Price ¦Amount, ¦Correspondent- ¦Reason ¦ ¦p/p¦ object ¦tararary¦honest-¦ ¦ rub. ¦account- ¦write-off¦ ¦ ¦ ¦number ¦in ¦ ¦ ¦tov ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦debit¦credit¦ ¦ +—+——— —+——+——+——+——+——+——+———+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +—+————+——+——+—— +——+——+——+———+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +—+————+——+——+——+——+——+——+ ———+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +—+————+——+——+——+——+——+——+———+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +—+————+——+——+——+——+——+——+———+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ —-+——— —+——+——+——+——+——+——+——— The commission found that the above items had become unsuitable for further use and were subject to write-off. All waste unsuitable for use in production was destroyed in the presence of the commission by __________________ __________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Chairman of the commission ___________ ______________ _________________ position personal signature signature transcript Members of the commission: ___________ ______________ _________________ position personal signature signature transcript ___________ ______________ _________________ position personal signature signature transcript ___________ ______________ _________________ position personal signature decoding of signature Materially responsible person ___________ ______________ _________________ position personal signature decoding of signature Reverse side of form N 421-APK Calculation of results from the liquidation of objects —————————————————————— ¦ Costs of liquidation ¦ Received from liquidation ¦ +————————————+—————————+ ¦ title of documents ¦ articles ¦ amount ¦ title ¦ articles ¦ amount ¦ ¦ ¦ costs ¦ ¦ documents ¦costs ¦ ¦ +———————+——-+——+————+——-+——+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———————+—— -+——+————+——-+——+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———————+——-+——+————+——-+— —+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———————+——-+——+————+——-+——+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————— ——+——-+——+————+——-+——+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ———————-+——-+——+————+ ——-+——- Amount of depreciation ___________________ rub. Results from liquidation __________________________________________ In the card (book) the write-off of property about ___________ Chief Accountant ___________________ ____________________________ personal signature signature transcript
Despite the fairly simple design, during operation of the bayonet shovel it can fail. This may occur due to non-compliance with the requirements for the load on the tool, for example, when developing excessively hard soils, or performing work unusual for a shovel. We list the main damage to a bayonet shovel that can be repaired with your own hands, the causes of these damages, as well as the technology for repairing this tool.
Damage to the wooden part (handle) of the shovel.
This type of damage can occur when digging through very hard soil, such as dried clay.
If you stick a shovel into the ground and try to lift it with the soil, the handle may not hold up and crack or even break.
In this case, you will most likely have to replace the cutting. Using pliers, a screwdriver or wire cutters, we pull out the handle fasteners (the type of tool used depends on how the metal part is secured - a nail or a self-tapping screw). Next, remove the broken part of the handle. If a part remains in the shovel, it can be knocked out with a hammer and a metal pin. As a pin, you can use a piece of reinforcement, a thick screwdriver, or even a piece of a stick or strip a little thinner than the handle of a shovel.
Using a knife or plane, we sharpen a new handle and hammer it into the metal part. At the same time, he must fit tightly into it. It may be necessary to trim the sharpened part a little at an acute angle so that the protruding part of the handle does not rest during work. After this, we fix the metal part to the handle.
This can be done with nails or screws. In the first case, you need to take a thick nail with a cross-section slightly smaller than the diameter of the mounting hole. After this, we cut it off using a grinder, a file or a hacksaw so that the nail with the head becomes 1 - 1.5 cm shorter than the diameter of the handle. Next we hammer it into the hole. If you decide to go with a self-tapping screw, we note that it holds dynamic loads much better.
As a self-tapping screw, it is necessary to select a thick version that is suitable for the diameter of the hole for fastening, and also 1 - 1.5 cm shorter than the diameter of the handle. A roofing screw with a hex key head is perfect for these purposes.
Crack in the metal part.
Due to heavy loads, a crack may occur in the metal part at the junction of the flat part and the fastening part. Such a defect can be partially eliminated using conventional electric welding.
We remove the metal part from the handle and clean the gap or crack from rust. Next, we weld the crack along its entire length, if necessary, aligning the torn parts as closely as possible. The metal on the shovel is quite thick, so a 3 mm thick electrode will be just right. After that, use a grinder to clean the seam. All that remains is to re-attach the shovel to the handle and you can use it. Of course, the shovel will not have the initial strength, but it is easily suitable for loose and loose soils. The only requirement for such a repair is that the metal part must be made of steel.
Deterioration of the cutting properties of the shovel.
Over time, the shovel begins to become dull - this means the cutting edge. As a result, more and more effort is required to drive a shovel into the ground. This can be easily removed with a sharpening machine.
We sharpen the blade like a regular table knife on both sides and the shovel again begins to cut the soil like butter.
If you don't have an electric sharpener, you can do this with a hand-held sharpening stone or file, although in this case it will take a lot more time and effort. The edge must be sharpened to rounding (the vertical edges of the metal part.
The procedure for writing off plastic containers
Industrial equipment is technical items that are involved in the production process, but cannot be classified as equipment or structures.
Household equipment is office and household items that are not directly used in the production process. The list of property that relates to inventory and household supplies is not established by law. When writing off inventory and utensils, an act must be used (f.
0504143). Regardless of which group of non-financial assets (OS or MH) plastic containers and a culinary hammer are taken into account, the act of write-off of soft and household equipment is used for write-off (f.
0504143). Rationale How to register and reflect household supplies in accounting and taxation The list of property that relates to inventory and household supplies is not established by law. In practice, inventory and household supplies mean: furniture and interior items (tables, chairs, racks, shelves, mirrors, etc.)
P.); equipment for cleaning territories, premises and workplaces (containers, wheelbarrows, buckets, shovels, rakes, mops, brooms, brooms, etc.); lighting, household and other appliances (lamps, scales, clocks, etc.)
P.); fire extinguishing means (hook, bayonet shovel, conical bucket, fire crowbar, felt felt, axe, fire extinguisher, fire cabinet, etc. (except for pumps and mechanical fire escapes)); tools (fitting tools,
Write-off of business equipment
Contents Manufacturing, purpose and scope of application of galvanized buckets As you know, a galvanized bucket is a container used for storing and transporting liquid and bulk materials and substances over short distances.
In addition, galvanized buckets can be used for storing various small parts, when loading garbage and during cleaning. The range of use of all buckets, including galvanized ones, is very wide. Galvanized buckets will serve well when loading solutions, wood and metal shavings and sawdust, gravel, sand: their high strength makes it possible to quickly scoop up materials without using shovels, directly, without scattering them, which is not always possible to do using fragile plastic buckets.
They are often used to extinguish fires or as a container for garbage. In Ukraine, the most popular are galvanized buckets of 10 liters, although there are similar buckets of 7 liters, 12 liters, and also galvanized buckets of 15 liters.
In the construction field of human activity, a galvanized bucket is simply necessary. Here it is used for transferring and preparing enamels, varnishes, adhesives, finishing solutions and for delivering water. For ease of transportation, it is equipped with a metal shackle that can withstand weight up to 15 kg, and has a durable body that does not change shape.
The increased strength and long service life of this cookware is achieved due to the fact that thin material is used for its manufacture.
Galvanized buckets - purpose, application, price
Production, purpose and scope of galvanized buckets
As you know, a galvanized bucket is a container used for storing and transporting liquid and bulk materials and substances over short distances. In addition, galvanized buckets can be used for storing various small parts, when loading garbage and during cleaning. The range of use of all buckets, including galvanized ones, is very wide. Galvanized buckets will serve well when loading solutions, wood and metal shavings and sawdust, gravel, sand: their high strength makes it possible to quickly scoop up materials without using shovels, directly, without scattering them, which is not always possible to do using fragile plastic buckets. They are often used to extinguish fires or as a container for garbage. In Ukraine, the most popular are galvanized buckets of 10 liters, although there are similar buckets of 7 liters, 12 liters, and also galvanized buckets of 15 liters.
In the construction field of human activity, a galvanized bucket is simply necessary. Here it is used for transferring and preparing enamels, varnishes, adhesives, finishing solutions and for delivering water. For ease of transportation, it is equipped with a metal shackle that can withstand weight up to 15 kg, and has a durable body that does not change shape. The increased strength and long service life of this utensil is achieved due to the fact that thin sheet metal is used for its manufacture, protected from rust and from the effects of various chemical compounds by a special coating, which distinguishes a galvanized bucket from its functional analogues produced by industry. If we compare them with plastic buckets, the disadvantage of greater weight is more than offset by the fact that they can store a wide range of chemically active substances (solvents, etc.) that do not come into contact with the protected metal, but can change not only the properties , but also the structure of polymers. All of the above is the reason that our contemporaries, who have decided to make repairs in their apartment/house, tend to buy galvanized buckets, giving them preference over all other utensils with similar functional purposes.
But remember that since boiling water causes the formation of zinc salts that are harmful to human health, you cannot cook food in this container. It is prohibited to preserve, in other words soak, pickle or pickle cucumbers, cabbage, mushrooms and other similar vegetable preparations in galvanized buckets.
Compliance with a number of necessary conditions will help extend the service life of basins and buckets in everyday life. Thus, table salt, washing powders, alkalis, acids and their solutions are dangerous for galvanized coating: by entering into a chemical reaction with zinc, all these substances destroy, thereby destroying the coating made from it. To clean galvanized cookware, it is recommended to use special products, the simplest of which is crushed chalk.
The starting material from which these containers are made are sheets of various steel, including black, onto which molten zinc is applied. Galvanized buckets - single-seam. The joints between the bottom and the side surface are treated with sealant, which eliminates even the slightest leakage, and the presence of stiffening ribs increases their strength. With all the many areas of application of galvanized buckets, we should not forget that salt, washing powders, alkalis and acids are dangerous for zinc: when this metal enters into a chemical reaction with the above substances, the zinc coating is destroyed. This leads to corrosion of the metal and the appearance of rust, which eats the metal, causing holes to appear in the buckets quite quickly.
Manufacturer of galvanized buckets - Ukraine, available in capacities of 7, 10, 12, 15 liters.
The procedure for writing off material assets
We report the following: As a general rule, headphones, racks, and magnetic boards are included in fixed assets, since their useful life is more than 12 months. Headphones are classified as machines and equipment, racks and magnetic boards are classified as industrial and household equipment. Since the cost of these fixed assets is more than 3,000 rubles, they do not need to be written off from the balance sheet and reflected in an off-balance sheet account 21
“Fixed assets worth up to 3,000 rubles inclusive in operation”
Over time, fixed assets physically wear out and become obsolete.
If the object is impossible or its further use is not economically feasible, then it is written off from the register. Typically, fixed assets are liquidated and written off from the register under the following circumstances: the object is under reconstruction, when part of the object is being liquidated. Before liquidating property that is impossible or unprofitable to use, it is necessary follow a number of procedures and fill out the necessary documents. Typically, the write-off of a fixed asset is formalized in the following sequence: 1. the financially responsible person brings to the attention of management information about the need to write off a fixed asset (for example, by means of a memo); 2.
; 3. ; 4. (or gives a conclusion about the inappropriateness of writing off the object); 5. ; 6. . How to document it and reflect it in accounting is given below in the materials of the Glavbukh System. The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the Glavbukh 1 System.
Recommendation:
Reason for discarding the mop
Typically, the write-off of a fixed asset is completed in the following sequence: 1.
the financially responsible person brings to the attention of management information about the need to write off a fixed asset (for example, by means of a memo); 2.
; 3. ; 4. (or gives a conclusion about the inexpediency of writing off the object); 5.
; 6. . How to document it and reflect it in accounting is given below in the materials of the Glavbukh System. The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the Glavbukh 1 System.
Recommendation: How to register and reflect household supplies in accounting and taxation. The list of property that relates to inventory and household supplies is not established by law.
In practice, inventory and household supplies are understood as: Criteria for belonging to OS or MH Inventory and household supplies can be taken into account in accounting as part of fixed assets or as part of inventories.
Enter the site
How would everything be interchangeable and in case of breakdown/wear you can buy a separate part to replace it - when replacing it in the future, then we immediately write it off as a cost?
— Do I need to do a completion certificate? I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:
A notification is being sent.
[e-mail hidden] Minsk Posted by 262 Reputation: December 4, 2013, 5:01 pm Finski, the cost of transferring inventory into operation is debited from account 10.9.
Is the quantity written off at the time of knockout due to a breakdown, for example? no further suitability. I would not complete the mop, but would write everything off separately, because... If, for example, a pen or holder breaks, you simply write it off and buy new ones.
And so, complete the mop (a complete set certificate is needed), and then when
Mop life
"" is the period of time during which the manufacturer undertakes to provide the consumer with the opportunity to use the mop for its intended purpose and is responsible for significant deficiencies that may arise in the mop.
New: express test - whether the product can be returned to the seller is available at Article table of contents During the service life of the mop, the consumer has every right to:
- possibility of using a mop;
- repair and proper maintenance of the mop;
- presenting demands for the free elimination of significant defects of the mop, even if the warranty period has expired;
- compensation for damage caused by the mop.
If the service life of the mop is not established, then the manufacturer is obliged to ensure the above consumer rights for 10 years.
Thus, as a rule, it is much more profitable for the manufacturer to set a service life than not to set it.
is established by the manufacturer, while the manufacturer (performer, seller) is obliged to promptly provide the consumer with the necessary and reliable information, which must necessarily contain information about the service life of the mop.
in accordance with , the manufacturer is obliged to establish the service life of durable goods, including components (parts, assemblies, assemblies), which after a certain period can:
- pose a danger to the life and health of the consumer,
- cause damage to his property or the environment.
, including components (parts, assemblies, assemblies), which after a certain period may pose a danger to the life, health of the consumer, cause harm to his property or the environment, are contained in a special list approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
In all other cases, establishing the service life is the right of the manufacturer, i.e.
it may not set a service life.
Ask! Moscow and Moscow region St. Petersburg and region All regions of Russia Our lawyers!
Call! Or write to CHAT at the bottom of the page.
Reasons for writing off furniture. Types of furniture damage
→ → Update: June 26, 2022
The interior design of work premises can be updated for various reasons.
This may be the need to replace pieces of furniture that have fallen into disrepair, but there may also be a desire of management to change the design of the offices, decorating them in a single corporate manner.
How to correctly formulate in this case the reasons for writing off the furniture and what types of damage to the furniture will be the reason for drawing up a document on its write-off, we will consider further.
Furniture purchased by an organization for use in public premises (offices, hotels, cafes, shops, doctors' offices, concert halls, etc.) falls into disrepair much more often than its domestic counterparts.
As a result of intensive use, individual items may be broken, dirty, the upholstery may be torn, etc.
Information that the organization’s property has fallen into disrepair is recorded in the process of drawing up annual inventory documents or at the time such facts are discovered.
The documents drawn up indicate the types of damage to furniture for further write-off, for example:
- damage to the furniture frame (legs, seats, backs of chairs and armchairs, walls, shelves and doors of cabinets and cabinets, legs and table tops, etc.);
- breakdown of mechanisms that ensure the operation of furniture (door hinges, drawer mechanisms, chair casters, etc.);
- deformation of individual parts of furniture due to wetness, excessive heat, etc.;
- wear and tear of the upholstery (fading, thinning, tearing, etc.);
- defects in furniture surface cladding (cuts, cracks, chips, etc.);
- irremovable stains on furniture surfaces, etc.
All of the listed damages can become a reason for writing off the furniture in the write-off act if an essential condition is met: the costs of eliminating these defects are equal to or exceed the cost of purchasing a similar new piece of furniture.
Information on the cost of repairs can be provided by organizations specializing in this type of service. In this case, you can be guided by the service life of the furniture established by the manufacturer in the technical data sheet.
Furniture manufacturers are required to set a service life for it in accordance with. After this period, the furniture may become dangerous to people and the environment.
Therefore you cannot use it. If the service life of the furniture is established in the technical passport and by the time of write-off it has expired, then the reason for writing off the furniture in the write-off act can be formulated as follows:
“Write off office furniture in accordance with Appendix 1 to the act due to the expiration of the service life established by the manufacturer of the specified furniture LLC Furniture for All”
in the technical passport (Appendix 2), as posing a potential danger to the health of employees, the organization’s property and the environment in accordance with the standards of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 16, 1997 No. 720.”
If upholstered furniture has no physical damage, then the basis for write-off may be the expired service life established for it.
Also read:
Accountant forum:
Subscribe to our channel at
The main reasons for writing off furniture (tables, chairs, etc.)
Inventory accounting Expand the list of categories Subscribe to a special free weekly newsletter to keep abreast of all changes in accounting: Join us on social media.
networks: VAT, insurance premiums, simplified tax system 6%, simplified tax system 15%, UTII, personal income tax, penalties We send letters with the main discussions of the week >> Tax-tax January 07, 2022 The reason for writing off a chair, table, cabinet or office chair is the loss of most of the operational characteristics and criteria allowing the further use of the written-off item.
Let's consider the question in more detail. When we talk about furniture, we mostly think about office furniture.
Although this could also be the setting of retail or industrial premises, as well as catering premises.
General points for which furniture may be considered unsuitable for further use are:
- Partial or complete loss of basic mechanical functions:
- damage to legs, back, armrests, walls;
- deformation of the chair seat or work surface of the table;
- breakdown of mechanisms (for example, adjusting the height or tilt of the back of an office chair).
- Fatal appearance defects:
- indelible stains;
- noticeable defects in upholstery or painting (varnishing);
- Changes in color or durability of the upholstery (for example, as a result of exposure to sunlight).
NOTE! The decor of an office or restaurant hall is often the “face” of the owner company, so the role of appearance defects in determining the reasons for the write-off of a table or chair can be no less important than the loss of operational characteristics. The decision to write off furniture with defects is usually made if the estimated cost of repair (restoration) is commensurate with or higher than the cost of purchasing new items with similar characteristics.
The completed act should reflect:
- name and quantity of furniture being written off;
- identifiers (for example, accession numbers);
- results of inspection of furniture by a commission consisting of responsible employees of the enterprise;
- reasons for writing off furniture, according to inspection by the commission;
- the final conclusion of the commission on write-off;
- signatures of responsible persons - members of the commission, financially responsible person and manager.
Example APPROVED General Director Andriyanov M.