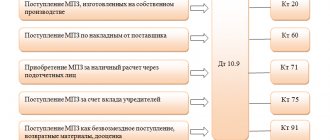
Compiling a document
There is no unified form for such an act. A company can develop its own form and secure it with a special order in its accounting policies. You can fill out the form by hand or on a computer. A prerequisite is that the signatures on the act be “live”, that is, the document typed on a computer must be printed and signed.
In order for a food disposal act to have legal significance, it must contain the standard details and information for such a document:
- Name of company.
- The name of the document and its number.
- Date and place of drawing up the act.
- Information about the composition of the commission. List the positions and names of the commission members.
- Information about the disposal procedure carried out. Here indicate the date of its holding and place, if desired.
- Information about food products: name, reason for disposal, quantity or weight of the product, price, total cost for each item and for all together. This item is usually presented in the form of a table.
- An indication that the product has been spoiled or has expired, etc. The commission confirms this fact, as well as the fact that the product was disposed of properly. In addition, you can indicate the method in which the goods were destroyed.
- Signatures of commission members with transcripts.
Attention!
Some categories of products after the expiration date may pose a threat to human health and life. In this case, it is necessary that the disposal procedure be agreed upon with Rospotrebnadzor. In addition, one copy of the act or a copy of it certified in accordance with all the rules of law will need to be sent to the department. This is necessary to confirm that potentially dangerous products have been destroyed.
Signing, approval and further application
The final form TORG-16 is signed by:
- chairman of the inventory commission;
- members of the inventory commission;
- person materially responsible for commodity values.
The head of the organization, after familiarizing himself with the circumstances of the act, makes a decision on the account of which resources to write off inventory items that are no longer subject to sale; information about this decision is also entered into the act.
After which the document is officially approved by the manager, indicating the full name, signature and date, which is the basis for the physical withdrawal of substandard goods from consumer circulation.
Form TORG-16 is reproduced in at least three copies, addressed to:
- financial services (accounting) to write off inventory items from the financially responsible person;
- the service on whose balance sheet the goods and materials were located;
- materially responsible person (for example, a warehouse worker).
After approval of the TORG-16 form, written-off inventory items are no longer subject to sale.
The act in form TORG-16 is the basis for:
- deductions from the salaries of those responsible (if there is evidence) of the cost of substandard goods;
- writing off losses in accounting and tax accounting as expenses.
The form of the unified form TORG-16 in Word format can be downloaded for free at the bottom of the article.
the second side of the form for the write-off of goods
Post Views: 4,357
Where is it used?
As a rule, this act is used in enterprises that are engaged in the production and transportation of products, their sale and storage. Accordingly, this category includes various stores, warehouses, shopping centers, and food processing enterprises.
If products are not sold within the expiration date, they are subject to write-off. This procedure is accompanied by the execution of a special act.
As you might guess, the sale of such a product will cause serious problems with the law. The smallest punishment that an organization faces involves a fairly large fine. This is why unconsumable products are written off. In essence, they are returned to managers and other representatives of suppliers and manufacturers. They are the ones who determine the future fate of the products.
Such actions have many advantages:
- positive impact on the environment;
- the ability to send illiquid assets for processing;
- reduction of waste in landfills, since discarded goods are not thrown into trash bins;
- reducing the risk of spreading dangerous infections.
Under what circumstances should a company generate a write-off report for food products?
Any organization engaged in activities related to the sale and processing of food products sometimes has to face a situation where:
- she does not have time to sell some of the purchased goods before the expiration date;
- food can spoil due to someone else's fault or due to external factors.
In any case, if a food product is not suitable for subsequent consumption, the company has a need to write it off.
The company should remember that when writing off products, it is imperative to find out why the damage occurred. After all, the procedure for accounting for the cost of write-off goods in tax expenses, as well as the accounting procedure, depends on this.
So, if the shelf life of a product has come to an end or if the product has deteriorated as a result of an emergency, then its cost when written off can be entirely attributed to expenses: like other expenses, expired goods are written off (subclause 49, paragraph 1, article 264), and damaged ones in as a result of an emergency - as non-operating expenses (subclause 6, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code).
If the product is no longer suitable for natural reasons (shrunken, melted, crumbled, weathered, etc.), then the cost of such products can also be included as expenses, but within the limits of natural loss (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 23, 2014 No. 03 -03-РЗ/24762).
Shortages of goods and their damage within the limits of natural loss norms are attributed to distribution costs, in excess of norms - to the account of the guilty persons. If the perpetrators are not identified or the court refuses to recover damages from them, then losses from shortages and damage to goods, by decision of the head of the company, are written off to the financial results of the trading company.
Strategy and tactics to combat write-offs
To reduce the amount of write-off to a reasonable rate, it seems advisable to use the following strategies and tactics.
The strategy is a continuous movement towards achieving an acceptable value of write-off of perishable goods at each stage of the company’s growth and comfortable balancing within the real boundaries of the achieved values of write-off of perishable goods in seasonality cycles, systematically narrowing and shifting the boundaries of the corridor to smaller values.
In Fig. 5 visualizes the proposed strategy.
The “Ladder” tactic is a constant movement towards the set strategic goal, solving problems step by step, taking them under dynamic control (reducing the influence of the reasons on the amount of write-off).
Let us illustrate the sounded tactics in Fig. 6. Each company sets the order of stages (steps of the ladder) itself, depending on the priority of the problems being solved.
For example:
Stage 1 - collection, accounting, storage, analytics of variables from the above formulas for calculating the write-off ratio;
Stage 2 - use of equipment and implementation of technology for packaging perishable food in a container for sealing with a gaseous environment (increasing shelf life);
Stage 3 - development of a product line using shock freezing.
Food disposal methods
Foods that are considered unfit for consumption should not simply be thrown into the trash. Such goods must be disposed of according to all rules. Food products that are approaching their expiration date may be sold with a corresponding label. Usually such goods are sold at a discount. If the product is spoiled, it must be disposed of. This is usually done by suppliers and manufacturers.
There are several main ways to dispose of food:
- Burial . Damaged goods are transported to special landfills or landfills. But you need to understand that not every product is subject to such disposal. When certain products rot, harmful microorganisms enter the soil. Attention is also paid to packaging, the decomposition of which has a negative impact on the environment. This method is most often used when disposing of vegetables, fruits and other organic goods.
- Burning . Everything is clear here; illiquid products are placed in fireproof tanks, where combustion occurs. Often, the ash obtained in this way is used to make fertilizers.
- Biorefinery . Used primarily to destroy organic products. A special compost pit is used here. It creates special conditions that accelerate the decomposition process. The resulting humus is then used to fertilize the soil.
- Grinding . There are factories that use special equipment. It is capable of shredding not only goods, but also any packaging. The result is a kind of shaving. After adding binders, this mass is used for the production of building materials.
- Feed production. Not all waste can be fed to animals. The list of such products is strictly regulated.
Tax accounting
The sale of goods is aimed at generating profit, which is subject to tax. Such payments can be reduced, among other things, due to expired goods. The organization, in addition to the internal audit, needs to conduct an examination.
In this case, it will be possible to reduce income tax. This rule also applies to VAT. If the company documents the validity of the destruction of expired products, then it can count on a deduction.
From other publications by our experts, you will learn about how stores use expired products and whether they can be eaten, what liability sellers face for selling unusable products, and what to do if you find or buy an expired product.
Writing off expired products allows you to reduce your organization's tax costs. But this will only be possible if the procedure is completed properly. The organization must be guided not only by local regulations, but also by current legislation.