What applies to household equipment and accessories?
What may be included in the list of tools, household equipment and accessories (hereinafter referred to as material assets, MC) has not been determined by anyone. The organization regulates this itself. Typically it includes:
- office furniture and equipment;
- lighting;
- stationery;
- Appliances;
- means related to fire safety;
- hygiene products;
- cleaning equipment and materials;
- tools, etc.
It is possible to purchase such goods both by bank transfer and through accountable persons.
How to account for the purchase of materials through accountable persons, read in Art. “What kind of posting reflects the acquisition of material assets under the report.”
To organize accounting, it is necessary to correctly classify MC.
There are 2 options for inventory accounting:
- as part of fixed assets (fixed assets);
- as part of the MPZ.
In any option, objects are taken into account at their acquisition cost, which is the sum of all costs associated with the purchase. In general, VAT is not included in this amount. It is included in the price only if MCs are used for activities not subject to this tax (clause
2, 5, 6 PBU 5/01 “Accounting for inventories”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/09/2001 No. 44n, clause 8 PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 03/30/2001 No. 26n).
Inventory is classified as fixed assets if its useful life is more than 12 months and its cost is more than 40,000 rubles. (Clause 4 PBU 6/01). At a lower cost, it is allowed to take it into account as part of the inventory (clause 5 of PBU 6/01).
At the same time, the organization can set its own cost limit between fixed assets and inventories at the above limit. For example, how to take into account objects costing over 20,000 rubles as fixed assets, and cheaper ones as inventories. The cost threshold must be fixed in the accounting policy.
Let's consider a sample of accounting entries that are generated upon receipt, movement and disposal of fixed assets.
| Accounting entry | Action, document |
| Dt 08 Kt 60 (10, 71, 76) | The OS is purchased. Consignment note, form OS-1 |
| Dt 19 Kt 60 | VAT allocated. Invoice |
| Dt 01 Kt 08 | The cost of the OS has been determined. He is assigned an inventory number and an OS-6 inventory card is filled out. |
| Dt 20 (23, 25, 26...) Kt 02 | Depreciation has been calculated. There are 4 ways to calculate depreciation in accounting. The chosen method is recorded in the accounting policy |
| Dt 02 Kt 01 | Depreciation written off. This occurs at the time of disposal, sale, gratuitous transfer, shortage or damage to the OS |
| Dt 91.2 Kt 01 | The residual value has been written off. If the fixed assets are fully depreciated, the residual value is 0. Form OS-4 |
This is only a small part of the possible set of transactions for accounting for fixed assets in an organization.
Read more about asset accounting in Art. "Accounting for fixed assets - accounting entries."
As for documentation, in this case, for inventory, you need to use documents that are usual for registering OS or approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2003 No. 7. For example, such as:
- OS-1 - act of acceptance and transfer of an OS object;
- OS-2 - invoice for internal movement of fixed assets;
- OS-3 - act of acceptance and delivery of repaired, reconstructed, modernized OS facilities;
- OS-4 - act on write-off of an asset (except for vehicles), etc.
Or an organization can develop such documents independently. We remind you that they must contain the mandatory details specified in Art. 9 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ. Below we will present only unified forms.
What other documents may be required to register the OS movement, read here.
Inventory with a useful life of up to 12 months must be taken into account as part of the inventory. Moreover, regardless of its cost.
It is included in the organization’s warehouse based on the corresponding primary order:
- receipt in form M-4 (can be replaced with the corresponding stamp on the seller’s invoice).
After this, accounting cards are created for the registered objects, using, for example, form M-17.
What data is filled out in the M-17 form, read in Art. “Material warehouse card - form and sample.”
At this moment, an entry is made in the accounting records as the debit of account 10.9. The corresponding account depends on the method of receipt of inventories into the organization.
During the transfer of tools and accessories from the warehouse for the needs of the organization, a demand invoice is drawn up in form M-11. Also, forms M-8, M-15 (approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated October 30, 1997 No. 71a) are used as primary accounting documents.
To transfer special tools from the warehouse, it is necessary to first set limits, which are developed by the organization by decision of the manager.
Form M-8 is used both for issuing special tools and for monitoring compliance with the limit. It is written out in 2 or 3 copies.
Inventory can be released from the warehouse to intermediate units without indicating the exact quantity of required inventory. As it is used, the unit draws up acts (reports) in any form, but with mandatory disclosure of such details as name, quantity, cost, confirmation of the feasibility of its use.
The method of writing off inventory for production must be fixed in the organization’s UP (clause 73 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n, clause 16 PBU 5/01):
- at the cost of each unit of inventory;
- FIFO;
- at average cost.
For a detailed description of each of the above methods, see here.
If the inventories are damaged or lost, a write-off report is drawn up indicating the reason for disposal, and the losses are written off.
Read more about write-offs in the article “The procedure for writing off materials in accounting (nuances).”
The write-off of inventory is reflected in the following accounting entries.
Let's look at inventory accounting as part of the inventory using an example.
Example
In February, LES LLC purchased computer chairs (5 pieces) for employees at a cost of 16,155 rubles, including VAT - 2,464.32 rubles.
The organization’s CP states that for accounting purposes, fixed assets costing less than 40,000 rubles. are written off as expenses when they are put into operation. At the same time, an entry is made on off-balance sheet account 012 “Materials transferred for operation.”
In October, the management of LES LLC decided to move to a new office, which already had all the necessary furniture. In this regard, it was decided to sell the chairs to one of the employees. The transaction amount was 11,150 rubles. (including VAT - RUB 1,700.85).
The following entries were made in accounting.
In February:
- Dt 10.9 Kt 60 — 13,690.68 rub. (come computer chairs);
- Dt 19 Kt 60 — 2,464.32 rub. (we charge VAT);
- Dt 68 Kt 19 — 2,464.32 rub. (we accept VAT for deduction);
- Dt 26 Kt 10.9 - 13,690.68 rub. (we take into account the cost of computer chairs in the costs);
- Dt 012 - RUB 13,690.68. (we take into account computer chairs put into operation).
In October:
- Dt 62 Kt 91.1 - 11,150 rub. (we reflect revenue from the sale of computer chairs);
- Dt 91.2 Kt 68 - 1,700.85 rub. (we charge VAT on revenue);
- Kt 012 - RUB 13,690.68. (we write off sold computer chairs).
When generating income tax calculations for 12 months of LES LLC:
- we include in expenses for February the cost of computer chairs included in expenses - 13,690.68 rubles;
- we include in income the proceeds from the sale of computer chairs - 8,474.58 rubles.
Furniture defects for write-off in accounting
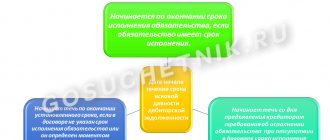
Furniture can be written off for two main reasons:
- its operation became impossible due to the appearance of defects;
- service life has expired.
The reasons for the occurrence of defects in furniture for write-off may be:
- mechanical in nature (breakage of the crosspiece of a chair, failure of the retractable mechanism of a cabinet shelf, cracks, chips, etc.);
- chemical-physical nature (damage to the surface as a result of exposure to high temperature or chemicals, fading from sunlight, etc.);
- other properties (upholstery wear, frame corrosion, etc.).
Other examples of reasons for furniture write-off: loss of shock-absorbing properties of upholstered furniture as a result of sagging central springs, thinning of the sofa upholstery, deformation of cabinet elements due to high room humidity, etc.
Rvost. ≥ Ref,
Rvost. — expenses for restoration (elimination of defects) of furniture;
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q4eFaky7rmE
Spr - the cost of purchasing a new similar piece of furniture.
If the condition is met, the repair is not economically feasible, and the furniture can be safely written off.
And one moment. If the furniture has no obvious defects, but does not meet modern design requirements and its appearance can scare away potential clients of the company or worsen its image, you should think about replacing it.
At the same time, you can sell furniture that is outdated by your standards (if its service life has not expired). If the service life of such furniture has expired, you have a justified reason for reflecting it in the write-off act (see below).
Find out how to return goods of inadequate quality here.
Furniture in a company can be used not only in office premises, but also in canteens, production workshops, warehouses and other departments of the company.
The resulting damage can be divided into defects in appearance and loss of mechanical properties and functions.
External damage includes the following:
- pollution that cannot be eliminated;
- damage to upholstery, paint and other top coverings;
- discoloration (fading, abrasions).
As for mechanical functions, this type of defect in some cases makes further operation of objects impossible. These include:
- breakdown of functioning mechanisms, such as adjustment of height, tilt, opening/closing;
- damage to legs, frames, walls, making objects unsuitable for use;
- deformation of surfaces, seats.
How can defects in upholstered furniture be identified for write-off? In order for the company to be able to legally write off, it will be necessary to conduct an inventory, during which it will be determined that the valuable properties of this property have been lost.
In the future, it will be necessary to determine whether it would be rational to transfer the furniture for repairs. To do this, it is necessary to compare the costs required to repair the damage and the purchase of new similar pieces of furniture.
Reasons for different types
The reasons for write-off largely depend on the type of furniture. Let's look at the most common of them.
Office chairs and armchairs
Among the reasons causing the need to write off office chairs and chairs, the following points can be highlighted:
- damage to the leg, back, armrest;
- seat deformation;
- faded upholstery;
- scratches and holes in the upholstery material;
- loss of aesthetic properties of wood.
Closet
- breakdown of fittings (mechanical parts);
- the formation of noticeable gaps due to weakening or unsticking of tenon elements;
- warping of doors, insert shelves;
- breakdown of fittings;
- darkening of varnish;
- darkening of wood;
- destruction of the structure of the material due to the appearance of stains (during exposure to chemicals), aging, fading;
- corrosion;
- damage to the facing material by mold
Carpet
Despite the fact that carpet is not technically furniture, it is subject to write-off according to the same principle as other structures discussed earlier. Reasons include discoloration, formation of bald spots, spots, and holes.
Curtains
More often than not, curtains are susceptible to fading due to exposure to sunlight. But other defects may also form, such as the appearance of spots and holes.
Cushioned furniture
In addition to standard furniture, upholstered furniture is also subject to write-off. Such procedures are carried out in hotels, sanatoriums, and boarding houses. Structures located in public areas quickly deteriorate due to active use and negligence of visitors and staff.
The reasons for write-off measures include wear of the upholstery, sagging springs, cracks and chips.
Of course, an unaesthetic interior can easily ruin the organization’s reputation and reduce the flow of clients. In this regard, write-offs must be carried out in a timely and competent manner.
Write-off of furniture in accounting
In the event that the damaged furniture cannot be restored, the inventory commission, based on the results of the measures taken, makes a decision to write off this object.
The furniture write-off act (reasons are determined by the company independently) is a universal document for documenting the loss of material objects. There is no special form among the unified accounting documents, which gives companies the opportunity to independently determine the format of this document and secure the sample in internal documentation.
In addition to the reason for writing off the furniture, it is advisable to indicate the following information in the write-off act:
- names of pieces of furniture indicating the quantity that, according to the results of the inventory, are subject to disposal;
- their numbers in accordance with the data of the compiled inventory list;
- damage identified during the inspection;
- a justified decision of the commission to write off these material objects in accounting;
- information about the composition of the commission: position held, full name and signature.
Often management expresses a desire to write off some furniture, despite the fact that its useful properties have not yet been lost, but its appearance does not correspond to the prestige of the company. For some organizations, appearance is a significant factor and allows them to attract more partners to cooperate.
What should you do in this case? When furniture that does not have defects is written off, the organization can be guided by the technical passport of the item. In most cases, this document specifies the service life specified by the manufacturer.
The method of disposal of furniture items is used by companies, regardless of the reasons for which these objects are written off in economic accounting.
Act of recycling furniture in a budget institution
Furniture in a budget institution that has lost its functionality must be written off and disposed of. To carry out the procedure, as a rule, a special commission is created. Based on the results, a furniture disposal report is drawn up. We will look at what information it should contain in the article.
During recycling, rejected products, materials, packaging, other solid waste, as well as liquid discharges, etc. are processed. or those whose service life has expired. Consequently, the concept of “recycling” means additional processing of production or consumption waste. Therefore, the specifics of concluding a contract will depend on the scope of operations carried out by the contractor.
Legal entities, as a result of their economic and (or) other activities, waste of hazard classes I and II are generated, handle this waste independently if they own or have on another legal basis facilities for the neutralization and (or) disposal of waste of hazard classes I and II. In other cases, they transfer this waste to the federal operator in accordance with contracts for the provision of services for the management of waste of hazard classes I and II.
The legal basis for the management of production and consumption waste in order to prevent the harmful effects of production and consumption waste on human health and the environment, as well as the involvement of such waste into economic circulation as additional sources of raw materials are contained in the Federal Law of June 24, 1998 No. 89-FZ “ On production and consumption waste" (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 89-FZ). This law establishes that production and consumption waste (hereinafter referred to as waste) are substances or objects that are generated in the process of production, performance of work, provision of services or in the process of consumption, which are disposed of, are intended for disposal or are subject to disposal in accordance with Federal Law No. 89-FZ.
You may be interested in:: Warehouse Rack Which Glass To Attribute 2022
If the furniture is damaged
Furniture purchased by an organization for use in public premises (offices, hotels, cafes, shops, doctors' offices, concert halls, etc.) falls into disrepair much more often than its domestic counterparts. As a result of intensive use, individual items may be broken, dirty, the upholstery may be torn, etc.
Information that the organization’s property has fallen into disrepair is recorded in the process of drawing up annual inventory documents or at the time such facts are discovered. The documents drawn up indicate the types of damage to furniture for further write-off, for example:
- damage to the furniture frame (legs, seats, backs of chairs and armchairs, walls, shelves and doors of cabinets and cabinets, legs and table tops, etc.);
- breakdown of mechanisms that ensure the operation of furniture (door hinges, drawer mechanisms, chair casters, etc.);
- deformation of individual parts of furniture due to wetness, excessive heat, etc.;
- wear and tear of the upholstery (fading, thinning, tearing, etc.);
- defects in furniture surface cladding (cuts, cracks, chips, etc.);
- irremovable stains on furniture surfaces, etc.
All of the listed damages can become a reason for writing off the furniture in the write-off act if an essential condition is met: the costs of eliminating these defects are equal to or exceed the cost of purchasing a similar new piece of furniture.
Information on the cost of repairs can be provided by organizations specializing in this type of service.
Furniture write-off act: sample
- Complete or partial physical wear and tear;
- Obsolescence;
- Deformation of the furniture frame;
- Breakdown of retractable opening mechanisms;
- Loss of appearance (damage or loss of cladding, cracks, etc.);
- Damage to furniture as a result of accidents, natural disasters, etc.
Upholstered furniture can be written off due to physical wear and tear and irreparable defects listed above. In addition, the reason for write-off may be the impossibility of further operation due to rubbing of the upholstery, sagging seats of chairs, sofas, broken springs and other damage, the cost of eliminating which will exceed the cost of new pieces of furniture.
Therefore, if the modernization of a fixed asset is unprofitable and implementation is difficult, management decides to liquidate it. In some cases, the need for write-off applies only to individual components of the object. In such cases, the cost allocation method allows for partial dismantling of the equipment.
- Administrative Code in Art. 8.2 prohibits throwing away equipment along with ordinary garbage, and the ban applies to both individuals and organizations.
- A separate ban on this action for legal entities is prescribed in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 340.
- Federal Law No. 89 prohibits enterprises from doing this on their own.
- Clause 2 art. 20 of Federal Law No. 41 of March 26, 1998 stipulates improper disposal of equipment as a violation of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation due to the content of valuable metals in it, which must be recycled and sent to the state fund.
- Specialized enterprises are allowed to dispose of equipment if they have the appropriate license, in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 524 of August 26, 2006.
29 Apr 2022 lawbellex 418
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Can a Guarantor's Car be Confiscated?
- Internet Extortion Article
- A bill on bringing to administrative responsibility for walking dogs
- How to Sign Up for a Travel Pass in State Services
Is it possible to write off boring but still usable furniture?
If the desire to purchase new furnishings for an organization is not due to the fact that the furniture has lost its performance qualities, but to another reason, for example, updating the overall design concept of a restaurant or the transition of a business to the “luxury” segment, which requires a more solid office environment, then there are no physical defects in the furniture for write-off .
In this case, you can be guided by the service life of the furniture established by the manufacturer in the technical data sheet.
Furniture manufacturers are required to set a service life for it in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 16, 1997 No. 720. After this period, furniture can become dangerous to people and the environment. Therefore you cannot use it.
If the service life of the furniture is established in the technical passport and by the time of write-off it has expired, then the reason for writing off the furniture in the write-off act can be formulated as follows:
“Write off office furniture in accordance with Appendix 1 to the act in connection with the expiration of the service life established by the manufacturer of the specified furniture LLC Furniture for Everyone in the technical passport (Appendix 2), as posing a potential danger to the health of employees, property of the organization and the environment in accordance with the standards of the Government Decree RF dated June 16, 1997 No. 720″.
The reasons for writing off upholstered furniture are determined similarly. If the furniture has lost its performance qualities - the upholstery is torn, worn out or dirty, the frame is broken or deformed, etc., then it can be written off if the cost of repair costs is comparable to the cost of a new similar item.
If upholstered furniture has no physical damage, then the basis for write-off may be the expired service life established for it.
Act on writing off furniture that has fallen into disrepair, sample - how to write off furniture in an organization
- the name of the furniture structures that are being written off;
- total quantity (in units);
- identification codes and signs;
- the results of the inspection by a commission including senior employees of the organization;
- causative factors (breakage, deformation, defects);
- general conclusion;
- signatures belonging to responsible parties.
- Write-off due to breakdown or wear and tear. At the same time, financial and labor costs for repairs, elimination of breakdowns, and replacement of spare parts are close to the cost of a similar product on the market or even exceed it. It is clear that in such conditions it is more profitable to write off a piece of furniture and, possibly, dispose of the usable spare parts remaining after liquidation (for example, from an office chair).
- Write-off due to “obsolescence”, when property becomes obsolete when more modern models of similar property appear on the market, with more efficient performance characteristics. In relation to furniture, we can talk about the desire of management to find a new design solution for an office or workspace and complement the new design with appropriate furniture.
The most common breakdowns
Before we begin to analyze specific methods for repairing a computer chair, let's look at what breakdowns occur most often.
Modern manufacturers produce a wide variety of computer chairs. They may differ in their design and upholstery materials, but the basic design elements in most cases remain unchanged.
The basis of any computer chair is a gas lift system. With this system we can comfortably raise the seat height and also simply lower it at any time with just one movement of the lever. This system is installed on legs equipped with wheels. With the help of such wheels you can not only have fun rolling on parquet or laminate flooring, which by the way can cause damage, but also conveniently move along the workplace. Next comes the seat, which is connected to the backrest by means of a special fixed spring. Some chair models may have additional armrests.
What can break first?
First of all, the moving parts that take on the maximum load fail. The gas lift often breaks down. At some point it may lose its tightness. This can be seen by the fact that the chair cannot maintain its height and always sinks to the very bottom under your weight.
In addition, wheels can often break. We may accidentally run into something, the wheel may turn up unsuccessfully, and so on. In this case, the chair will lose stability, which we will feel immediately.
Among the moving parts that often become loose and even break is the backrest fastening. Here, the spring and retainer are primarily susceptible to breakage.
Let's look at each of these breakdowns and turn to the recommendations of professionals for eliminating them.
Learning how to repair an office chair gas lift
The gas lift device is simple and at the same time quite effective. The principle of its operation is the flow of specially pumped gas into the cylinder of the device. Its chamber is divided into two parts by a valve. The lever opens this valve, and we can either lower the valve down under our own weight, or release the seat, and it will begin to rise up under the influence of the same gas.
The main cause of failure is depressurization of the device, due to which the valve moves freely in the cylinder and cannot maintain the desired level. It is almost impossible to fix this problem at home, and in most cases you just have to replace the gas lift with a new one. And such a replacement, with simple tools, can be made even by a non-professional.
For this we need:
- curly screwdriver;
- hammer;
- punch.
First of all, remove the seat and backrest. A screwdriver will help us with this. After this, we separate the seat from the swing mechanism. We remove the protective casing and separate the gas cartridge from the swing mechanism. After this, we knock the cartridge out of the cross. Now you can start assembling the chair with a new gas lift.
How to fix the back
Various breakdowns can occur with the backrest. For example, at some point we may lean back too much and the spring may not hold up. Also, with our careless attitude, we can ruin the upholstery, which will only have to be changed. Let's look at each of these two cases.
The mechanism connecting the seat and backrest is called permanent contact. Using this mechanism, we can fix the position of the backrest at a variety of angles. Often this mechanism breaks down when we are a little overzealous with the clamping screw. By squeezing such a screw, we can break the thread and then only replacing it will help us out. Before you start repairing, buy a new screw. As a rule, the permanent contact is covered with a plastic casing, which can simply be removed by snapping it. If you can’t turn the nut, then use a grinder to dismantle it. After you get rid of the old bolt, you can reassemble the mechanism with the new bolt.
Replacing the upholstery is a very simple matter. Let's look at the whole process step by step:
- Unscrew the adjusting screw from below and remove the backrest.
- Unclip the rear decorative trim.
- We tear off the old upholstery from the paper clips.
- At this moment, you can wash the foam rubber, taking advantage of the moment.
- Now you can take new upholstery and repeat the whole process in reverse order.
Repairing chair wheels
The wheels of an office chair are part of the base of the chair - the crosspiece. It happens that a broken wheel in the process also breaks one of the spokes on which it was attached. In this case, we recommend that you completely replace the entire crosspiece, since the plastic gluing may not be as reliable for this structural element. It is also worth doing in the case when an entire spoke of the cross breaks off.
To replace a whole crosspiece, you must first get a new one. We recommend ordering a more powerful crosspiece model, since most models are completely unified. The tools you will need are a hammer and pliers.
First of all, make sure that the new cross has its own wheels. Otherwise, you need to turn the chair over with the seat down and first remove the wheels from the broken crosspiece. Next, we take a hammer in our hands and, using a drift, carefully knock out the gas lift from the cross. After we got rid of the old cross, we can start assembling. The order is reversed - place the gas lift on the new crosspiece and, if necessary, secure the wheels.
Replacing wheels will not require much effort from you at all. Specialists have special grips for this, but everything can be done without them. We turn the chair over, confidently take the wheel and forcefully pull it out of the socket. If necessary, you can help yourself a little with a straight screwdriver.
Repairing office chair armrests
Of all the possible types of repair, the simplest, perhaps, is the repair or replacement of armrests. In some models of chairs, the armrests may not be very comfortable, and they can also break in the same way as, say, a crosspiece. We can break the armrest by leaning on it poorly, or simply by touching it.
As a rule, armrests are attached with several screws. Using a screwdriver, you can unscrew the armrest fastenings in a minute and just as quickly screw on new ones.
As a rule, armrest mounts are designed for several types of armrests. You can take advantage of this moment and order armrests that will be more comfortable for you.
Repair yourself and save money
As we have seen, repairs are not such a difficult matter. We can spend about half an hour on everything, and we won’t have to buy new furniture. Moreover, to carry out simple repairs you do not need to have special equipment - the simplest tools that can be found in every home will do.
Causes and types of breakdowns of office chairs
Chairs in offices fail for various reasons. To restore such furniture requires diagnostics and identification of the exact type of damage.
Office chairs can fail as a result of: • improper use; • long service life; • large loads on the structure; • wear of components and mechanisms. In some cases, for example, when the armrest has become loose, it is possible to correct the situation yourself. However, in more complex situations, by the way, the breakdown of a metal cross, which requires the use of welding and special tools, it is necessary to call a specialist. In most cases, the most movable elements of furniture break - casters, gas lift, crosspiece, armrests. 1. Wheels falling out of the crosspiece. First, determine the type of cross. It is made of plastic or metal. The rollers may fall out as a result of a violation of the integrity of the hole in the cross where they are inserted or due to a breakdown of the wheel itself. 2. Gas elevator malfunction. If the chair does not rise when you press the lever, then the gas lift valve may be damaged. The operation of the metal gas elevator control knob may be impaired, or the piastra, the swing mechanism, was initially secured incorrectly. If you sit in a chair and it starts to fall, and after getting up from it it starts to rise, then the gas lift is definitely broken. 3. Impossibility of installing the backrest. If it is not located exactly in relation to the seat, then the fastening at its base has been damaged, that is, there is no thread in the nut or the body of the permanent contact screw into which the nut is inserted has burst. It happens that the backrest does not fasten in the specified position at the bottom when twisting the permanent contact handle. Here the permanent contact itself is broken. 4. Failure of the crosspiece. Most often the plastic model gets damaged. In this case, the steel ring in the crosspiece seat may crack or separate and may not hold the gas lift. 5. Unreliable armrests. They can become loose, fall out or break easily (if plastic products) due to careless use. When replacing, you should give preference to metal analogues with plastic linings.
Accurate diagnosis of the cause of an office chair breakdown will allow you to quickly repair it and save on a new purchase.