Accounting for settlements with suppliers when purchasing OS
Postings reflecting the acquisition of a fixed asset allow, along with the reflection of debt to organizations, to ensure the correct formation of the initial cost of the fixed asset. For accounting purposes, all costs related to fixed assets are reflected by entries in the debit of account 08 in correspondence with the corresponding accounts. Particular attention should be paid to the procedure for reflecting VAT in accounting:
- if the fixed asset is planned to be used in activities, the results of which are subject to VAT, then it is subject to reimbursement from the budget;
- otherwise, the VAT amounts issued by the supplier should be included in the cost of the fixed asset.
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| Postings on receipt of fixed assets for production purposes involved in activities subject to VAT | ||||
| 08.4 | 60 | The cost of the OS object is taken into account. debt to the supplier is reflected | price without VAT | |
| 19.1 | 60 | VAT charged by the supplier is taken into account | VAT | |
| Postings for the receipt of a fixed asset that is NOT involved in activities subject to VAT | ||||
| 08.4 | 60 | The cost of the OS object is taken into account. debt to the supplier is reflected | Value with VAT | |
| Suppliers' invoices for received operating systems have been paid | ||||
| 60 | 50-1 | In cash from the company's cash desk | ||
| 60 | 51 | By cashless transfer from the company's account | ||
| 60 | 55 | By bank transfer from special accounts of the enterprise | ||
| 60 | 71 | Through an accountable person | ||
Acquisition of a non-current asset
Costs for the acquisition of equipment, which will subsequently be taken into account as a fixed asset, are accounted for in account 08.04 “Purchase of fixed assets” (1C chart of accounts).
In accounting, expenses associated with the delivery of fixed assets are taken into account in the initial cost of fixed assets (clause 8 of PBU 6/01, Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n).
In tax accounting, delivery costs are also taken into account in the initial cost of fixed assets (Clause 1, Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Fixed assets, the acquisition of which will incur additional costs taken into account in the initial cost, must be taken into account as a standard option, because the simplified version does not imply an additional increase in the cost of the OS.
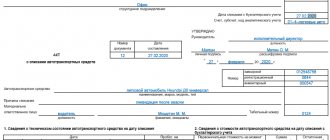
Let's create a document Receipt (act, invoice) type of operation Equipment in the section OS and intangible assets - Receipt of fixed assets - Receipt of equipment.
On the Equipment it is indicated:
- Nomenclature is an acquired non-current asset from the Nomenclature directory.
- The accounting account is filled in the document automatically depending on the settings in the Item Accounting , but it can be changed manually. In our example, for the Item Type Equipment (fixed asset objects), account 08.04.1 “Purchase of fixed asset components” is set. PDF
More details Setting up item accounting accounts
In the document Receipt (act, invoice) type of operation Equipment, you cannot indicate account 08.04.2 “Purchase of fixed assets”: it is intended for accepting fixed assets for accounting only in a simplified version.
Postings according to the document
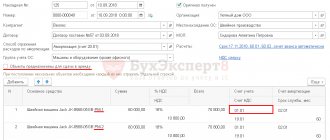
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 08.04.1 Kt 60.01 - acceptance of non-current assets for accounting;
- Dt 19.01 Kt 60.01 - acceptance of VAT for accounting.
Reflection of additional costs to bring the OS to a usable state
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| The cost of services for fixed assets involved in activities subject to VAT is reflected. | ||||
| 08.4 | 60 | The cost of services for the asset and the debt to the company that provided the services are taken into account | ||
| 19.1 | 60 | VAT charged by the supplier is taken into account | ||
| Cost of services for a fixed asset NOT involved in activities subject to VAT | ||||
| 08.4 | 60 | The cost of services for the asset and the debt to the company that provided the services are reflected | ||
| Invoices for services rendered have been paid | ||||
| 60 | 50-1 | In cash from the company's cash desk | ||
| 60 | 51 | By cashless transfer from the company's account | ||
| 60 | 55 | By bank transfer from special accounts of the enterprise | ||
| 60 | 71 | Through an accountable person | ||
Tax accounting of transport costs
In tax accounting, the algorithm for accounting for fixed assets is regulated by Chapter. 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, fixed assets include those that are owned by the copyright holder, with a useful life of more than 1 year and a value of over 100,000 rubles. In this case, the asset must be used as a means of labor for production, work or management purposes (clause 1 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An asset is accepted for tax accounting at its original cost, which is formed from the amounts of expenses:
- for its acquisition;
- construction;
- manufacturing;
- delivery;
- bringing to working condition, etc.
After commissioning, the initial cost of the object is written off as expenses through the depreciation mechanism. Thus, tax accounting of fixed assets is similar to accounting (with the exception of the limiting size of their valuation), and transport costs are included in the initial cost of the fixed assets object.
Example (continued)
Since the initial cost of our fixed asset is less than 100,000 rubles, then in tax accounting the entire amount of costs for the purchase and delivery of the machine will be included in the costs at a time. At the same time, taxable temporary differences arise between accounting and tax accounting, since in accounting the initial cost of fixed assets will be written off in equal shares over 5 years. Such differences are regulated by the norms of PBU 18/02 “Accounting for income tax calculations” and form a deferred tax liability (DTL). To reflect it in accounting, entries Dt 68 Kt 77 are used:
| Dt | CT | Sum | Calculation | Operation |
| 01 | 08 | 47 015,00 | The machine is put into operation | |
| 68/NP | 77 | 9403,00 | 47 015,00 × 20 % | IT was formed |
Further, at the end of each month, the accountant of LLC “Style”, along with the calculation of depreciation, will also pay off the tax liability. These transactions will be reflected in the accounting records as follows:
| Dt | CT | Sum | Calculation | Operation |
| 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) | 02 | 783,58 | Depreciation accrued | |
| 77 | 68/NP | 156,72 | 783,58 × 20% | Monthly repayment of IT |
Reflection of interest on credits (loans) used for the purchase of fixed assets
When creating entries to reflect interest accrued on loans and credits used to purchase fixed assets, special attention should be paid to the difference in requirements for accounting for these transactions in accounting and tax accounting: Accounting
— the amounts of interest accrued before the facility was put into operation increase the cost of the non-current asset (entry Dt 08 - Kt66, 67).
Interest accrued after commissioning is included in other expenses of the organization (entry Dt 91 - Kt 66.67). Tax accounting
- for tax accounting purposes, the amount of accrued interest is included in the expenses of the reporting period, within the limits established by Article 269 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| Postings reflecting the accrual of interest on loans and borrowings before the facility is put into operation | ||||
| 08.4 | 66 | The cost of interest on short-term loans is taken into account | ||
| 08.4 | 67 | The cost of interest on long-term loans is taken into account | ||
| Interest on loans and borrowings (used for the purchase of fixed assets) accrued after the object is put into operation | ||||
| 91.2 | 66 | The cost of interest on short-term loans is taken into account | ||
| 91.2 | 67 | The cost of interest on long-term loans is taken into account | ||
Accounting for non-depreciable fixed assets with non-zero tax value
Let's assume that the organization does not exclude the possibility of selling non-depreciable assets in the future. In this case, the tax value of the object should not be written off, otherwise it cannot be taken into account as expenses upon sale or other disposal.
Example 2
The organization KRUG LLC applies OSNO, PBU 18/02 using the balance sheet method and pays VAT. The income tax rate is 20%.
In January 2022, the organization takes into account residential premises, which are used as a service apartment for the temporary accommodation of arriving specialists. The initial cost of the apartment in accounting and tax accounting is the same and amounts to 8,000,000 rubles.
The organization has established a useful life of 400 months for the apartment. The linear method of calculating depreciation in accounting and tax accounting is used. In accounting, depreciation expenses for the apartment are taken into account on account 26.
Despite the fact that a service apartment under the conditions of Example 2 is used for production purposes, in the opinion of the Russian Ministry of Finance, such an object does not meet the criteria for depreciable property, therefore, for profit tax purposes, it does not belong to fixed assets subject to depreciation (letters dated January 24, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/3843, dated November 24, 2014 No. 03-03-06/2/59534). At the same time, there is a court decision according to which the calculation of depreciation on housing assets is legal (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated July 16, 2009 in case No. A33-14312/2006).
Regulatory authorities allow depreciation to be charged on residential premises if they clearly generate income, for example, in the form of rent. Expenses in the form of depreciation of a service apartment must be confirmed by a lease agreement drawn up in accordance with the law (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 7, 2009 No. 03-03-06/2/231, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 12, 2012 No. 16- 15/ [email protected] ).
Let's assume that the organization does not want disputes with the tax authorities and does not include a service apartment as part of the depreciable property. However, the tax value of the property is not written off, since the apartment can be rented out or sold in the future.
In this case, when preparing the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets
on the
Tax Accounting
Accrue depreciation
checkbox should be cleared (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Acceptance of non-depreciable fixed assets with non-zero cost for accounting
When posting a document, an accounting register entry is entered:
Debit 01.01 Credit 08.04.1
- for the initial cost of the fixed asset (RUB 8,000,000).
At the same time, special fields of the accounting register are filled in:
Amount Dt NU: 01.01
and
Amount Kt NU: 08.04.1
- for the tax value of the apartment (RUB 8,000,000).
Thus, at the end of January there is no difference between the book value and tax value of the fixed asset.
When performing a regulatory operation Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU 18
for January, deferred tax for the type of asset
Fixed assets
is not recognized.
Starting from February 2022, the service apartment begins to be depreciated only in accounting. When performing a routine operation Depreciation and depreciation of fixed assets
An accounting entry is generated:
Debit 26 Credit 02.01
- for the amount of depreciation of the apartment (8,000,000 rubles / 400 months = 20,000 rubles).
In tax accounting, depreciation is not calculated in accordance with the established settings. At the end of February, the book value of the apartment decreases and amounts to RUB 7,980,000. (RUB 8,000,000 – RUB 20,000). The tax value of the property does not change and remains RUB 8,000,000. The resulting difference is a deductible temporary difference, since it will lead to the formation of deferred income tax, which, with a certain degree of probability, can reduce the amount of income tax payable to the budget in subsequent reporting periods (clause 11 of PBU 18).
When performing a regulatory operation Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU 18
, a deferred tax asset is recognized by type of asset
Fixed assets
Debit 09 Credit 99.02.О
- for the amount of ONA recognition (20,000 x 20% = 4,000 rubles).
A detailed calculation of IT is presented in the Help-calculation of deferred tax
for January 2022 (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Help-calculation ONA
As the apartment is depreciated in accounting, a temporary difference by type of asset Fixed assets
will increase monthly by 20,000 rubles.
Accordingly, the amount of recognition of ONA will increase. By the end of 2022, BP by type Fixed assets
is 220,000 rubles, and IT is recognized in the amount of 44,000 rubles. (RUB 220,000 x 20%).
If the apartment is not sold during its useful life, then after 400 months the object will be fully depreciated and the book value will become zero. The tax value will not change and will be 8,000,000 rubles, therefore, IT will be recognized in the amount of 1,600,000 rubles.
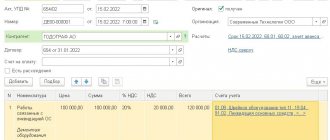
Now let’s assume that from October 2022, the service apartment begins to generate income in the form of rental payments. From this moment on, the fixed asset can be depreciated in tax accounting. Then in September 2022 you will need to create a special document Changing the state of the OS
(section
OS and intangible assets
-
OS depreciation parameters
), which is intended to suspend or resume the calculation of depreciation on fixed assets.
Document header Changing the OS state
should be filled in as follows (Fig. 7):
- in field Event
– indicate the name of the event in the life of the fixed asset, which is reflected in the document.
Events that happen to fixed assets are stored in the OS Events
, which is filled in independently by the user; - don't set flag Reflect in accounting
, since nothing changes in accounting;
- set flag Reflect in tax accounting
, since a change in state affects tax accounting;
- set flag Affects the calculation of depreciation (wear and tear)
, since the document will affect the calculation of depreciation;
- set flag Calculate depreciation (wear and tear)
to resume accrual of fixed assets depreciation. This change will apply starting next month.
In the Fixed Assets
indicate the name of the service apartment for which depreciation is included in tax accounting.
Rice. 7. Changing the OS state
When posting a document Change of OS state
accounting entries are not generated, but entries are entered into the registers of the OS accounting subsystem:
- Calculation of depreciation of fixed assets (tax accounting)
;
- OS Events
.
By the end of September 2022, the taxable difference by type of fixed assets
is 160,000 rubles, and IT is recognized in the amount of 32,000 rubles. (RUB 160,000 x 20%).
From October 2022, the apartment begins to be depreciated also in tax accounting, therefore the resulting amounts of VR and ONA by type of assets and liabilities Fixed assets
don't change.
The further “fate” of BP and ONA will depend on many factors. For example, on whether the accrual of depreciation in accounting and (or) tax accounting will be continued or suspended.
Postings reflecting exchange rate and amount differences for fixed assets
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| Postings reflecting exchange rate differences for fixed assets | ||||
| 91.2 | 60 | Negative exchange rate differences reflected | ||
| 60 | 91.1 | Positive exchange rate differences reflected | ||
| Postings reflecting the amount differences for fixed assets | ||||
| 91.2 | 60 | Negative amount differences for fixed assets are reflected after the object was accepted for accounting | ||
| 60 | 91.2 | Positive amount differences for fixed assets are reflected after the object was accepted for accounting | ||
Real estate accounting
Real estate accounting is carried out in accordance with these acts:
- Accounting regulations established by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 26 n dated March 30, 2001.
- Guidelines for accounting for OS No. 91.
the write-off of buildings and other real estate in accounting ?
Accounting should not contradict general rules. There are conditions for real estate to be included in the list of fixed assets (hereinafter referred to as fixed assets):
- Real estate is necessary for conducting the main activities of the company (sale of products, provision of services).
- The facility will be in operation for longer than a year.
- The company does not plan to resell.
- The facility is expected to provide financial benefits. In this case, its acquisition will be considered justified.
The list of these conditions is given in paragraph 4 of PBU 6/01. These rules apply to all fixed assets to which real estate belongs. Accounting is carried out based on the cost of the object. This cost is formed based on the company’s actual expenses for purchase, assembly, and production. All taxes and government fees are deducted from this amount. However, registration fees may be included as expenses because they are associated with the purchase. That is, expenses for state registration of real estate will be written off as current expenses. Write-offs are carried out in accordance with general accounting rules.
Question: In 2022, an organization acquired and registered a property that is used in transactions subject to and exempt from VAT. VAT was accepted for deduction in 2022. In what order should VAT be restored for periods of use of the property in VAT-free transactions in 2019? View answer
Purchasing objects taking into account the new rules is not considered a capital investment.
They are recognized as OS objects on the date of appearance of documents confirming their readiness for operation.
These may be documents such as a transfer and acceptance certificate, permission to put the facility into operation. Depreciation will be calculated on a general basis from the first day of the month following the month in which the property was accepted for accounting. In 2011, the procedure for accounting for objects was changed. In particular, new regulations abolished these conditions:
- Documents on registration of the object are optional.
- Actual operation is not necessary.
- Depreciation is not charged if the property remains on account 08.
How to reflect in accounting transactions for the acquisition of real estate (industrial building) ?
Since 2011, property has been accepted for accounting as fixed assets if it meets these requirements:
- Compliance with the provisions of paragraph 4.5 of PBU 6/01.
- Capital investments are completed.
- There are documents confirming readiness for use.
Registration for inclusion of property in the OS is optional. Depreciation of property will depend on when it is recorded. The month of acceptance for accounting is the month in which investments were completed and the object began to meet the characteristics specified in paragraph 4 of PBU 6/01. For depreciation, it is not necessary to transfer papers for registration. The object can be accepted into the OS on the date of signing the transfer and acceptance certificate.
Features of accounting for objects from the seller
If the property has been sold, its value is written off. Sales revenue is recognized in these cases:
- The company has ownership of the object, confirmed by documents.
- The amount of proceeds from the sale is known.
- There are indications that the firm will benefit economically from the sale.
- The buyer received ownership of the object.
- The costs of the operation can be clearly established.
Income and expenses from write-offs will be credited to profit and loss.
Accounting entries
The selling company makes the following transactions:
- DT02 KT01. Write-off of depreciation accrued on an object.
- DT45 KT01. Write-off of residual value.
- DT62 KT91.1. Proceeds from sale.
- DT91.2 KT68. VAT accrual.
- DT91.2 KT45. Write-off of residual value.
- DT91.9. KT99. Fixation of profit.
Tax documentation must reflect sales income, expenses, and profit from the sale.
Accounting for the purchase of objects
The company that purchased the property takes it into account regardless of whether the property is registered. Real estate is included in fixed assets, and therefore is included in a special depreciation group. From the first day of the month following the month of acquisition, depreciation begins to accrue. For tax accounting of objects, these conditions must be met:
- Papers have been sent for registration.
- The property has been put into operation.
As a rule, enterprises use the straight-line method of calculating depreciation. The rate is based on the useful life period. The time during which the property was used by the previous owner is deducted from this period. The useful life period can be determined by these methods:
- Based on total useful life.
- Remaining term.
If the second method is used, the company must have a document confirming the period of operation of the object by the previous owner. In the first option, the company sets the deadline independently. When purchasing real estate, the buyer must make these entries:
- DT08 KT60. Receipt of object.
- DT01 KT08. Acceptance of real estate for accounting as fixed assets.
- DT19 KT60. Allocation of VAT amount.
- DT68 KT19. Acceptance of VAT deduction.
Opposite each posting should be the date on which the accounting was completed.