What it is
The main activity of the company brings it not only income, but also requires expenses for maintenance and development. An increase in economic benefits is considered income, and the occurrence of additional obligations is considered an expense. In accounting, all these transactions are reflected in account 90 “Sales”. But there are also revenues and expenses not related to the main activity that also need to be taken into account. For these purposes, according to Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94N, 91 accounting accounts “Other income and expenses” were opened. It relates to financial performance and is intended to reflect the positive and negative results of other activities of the enterprise. After the latest revision of the Chart of Accounts, it performs two roles:
Profit and loss
- Serves to reflect the result of non-core economic activities.
- It is collective and serves to collect and store information on transactions not related to the main type of activity.
Role in accounting
Application of Dt 91 and Kt 01 when selling assets
When selling an OS, the seller creates accounts:
- Dt 62 Kt 91/1 - we record income from the sale of fixed assets;
- Dt 91 Kt 68 - reflect VAT;
- Dt 02 Kt 01 - write off accumulated depreciation charges;
- Dt 91/1 Kt 01/disposal - write off the residual value of fixed assets.
When closing the month, the financial result of the operation is revealed. Balances on subaccounts 91/1 and 91/2 are written off to subaccount 91/9. If the balance is debit, then a loss is recognized for the transaction; if it is a credit, a profit is recognized.
ATTENTION! From 2022, new FSB 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” and 26/2020 “Capital Investments” are mandatory. You can start applying these standards earlier. To switch to the application of new standards, it is necessary to make changes or additions to the accounting policies.
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail what will change in accounting for fixed assets and capital investments when applying FAS 6/2020 and FAS 26/2020. Get trial demo access to the K+ system and switch to the Ready Solution for free to learn all the nuances of the innovations.
During liquidation, on the day of signing the act of writing off fixed assets, the following entries are made: Application of entries during liquidation of OSDt 02 and Kt 01/disposal - write off accumulated depreciation;
- Dt 91 and Kt 01 (Dt 91/1 and Kt 01/disposal) - write off the residual value of fixed assets.
Read more about the write-off of fixed assets in the article “Unified Form No. OS-4 - Act on the write-off of an fixed asset.”
If the OS is liquidated before the expiration date, then it does not have time to fully depreciate. Thus, at the end of the month a debit balance is formed for this business operation, the amount of which is subsequently applied to reduce the financial result.
What is it used for?
All transactions that generate income or expenses that are not related to the main activity of the company are reflected in the accounting department in subaccounts 91. The Accounting Regulations (PBU) 9/99 oblige two types of income and expenses to be attributed to them:
- operational, are directly related to the economic activities of the enterprise, but are not the goal;
- non-operating, formed due to the consequences of the economic activities of the organization.
Additional Information! They are shown separately in the financial statements.
Expenses
Account characteristics
During the reporting period, account 91 and its subaccounts collect data on transactions related to other types of activities that form its characteristics.
Active or passive
You can easily answer question 91 whether an account is active or passive; just look at how accounting transactions are reflected on it. Receipts are posted as a credit and expenses as a debit. Thus, it is active-passive in accounting. At the end of the reporting month, it must be closed; to do this, all balances must be transferred. At the beginning of a new period, the balance should be zero.
What does debit and credit show?
The following transactions will be taken into account on the debit of account 91:
- Expenses associated with the provision of temporary use of company assets, securities, provision of patents and rights to inventions, as well as participation in the authorized capital of third-party enterprises.
- The identified residual value of assets, as well as the actual cost subject to write-off.
- Costs incurred in a foreign currency other than the Russian ruble upon the sale, write-off or disposal of the company's assets.
- Costs associated with the manipulation of the old one.
- Interest paid to lenders for borrowing money.
- Expenses for services provided by credit companies.
- Payment of penalties, penalties, and fines to suppliers for violation of contract terms by the company.
- Costs associated with mothballed production facilities.
- Compensation to the injured party for losses caused by the company.
- Losses incurred from previous years that are recognized in the current reporting period.
- Transfer of funds to reserves due to a decrease in the value of securities, material assets, and doubtful debts.
- Write-off of irrecoverable receivables upon expiration of the statute of limitations.
- Exchange differences resulting from currency exchange.
- Legal costs.
Securities
Credit account 91 will show the following transactions:
- Income from the temporary use of enterprise assets.
- Profit received from intellectual property: patents for inventions, industrial designs.
- Receipts from securities and participation in the authorized capitals of third-party companies.
- Income from simple partnership agreements.
- Profit from the sale or write-off of fixed assets and other assets of the enterprise, received not in Russian currency.
- Income from old transactions.
- Interest on cash loans issued to third parties.
- Receipts from suppliers of penalties, fines, penalties for improper compliance with the terms of contracts.
- Receiving assets for free use.
- Receipts for compensation of losses from third parties.
- Income from profits of previous years received in the current reporting period.
- Accounts payable that are not subject to payment after the expiration of the statute of limitations.
- Exchange differences resulting from currency exchange.
Note! All transactions relating to other expenses and income are contained in Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 115N dated September 18, 2006.
What are other expenses?
The concept of “other expenses” is spelled out in the same chapter of the PBU, but in section 10/99. Here is an open list of expenses - this means that the accountant can classify as other expenses whatever he deems necessary. However, this can be done if there are no contradictions with current legislation and the accounting policies of the enterprise.
Most often, this type of expense includes:
- losses from the sale of own funds;
- expenses related to the company’s bank account;
- a fund for doubtful debts, the formation of which is the responsibility of each organization, regardless of size;
- various fines imposed on the company.
How to close an account
The law obliges organizations to close monthly accounts that collect information about income and expenses from the company’s main and secondary activities. Accounting account 91 allows you to do this in several stages:
- The difference between debit and credit is transferred monthly to subaccount 91.09, and the indicators are also transferred to account 99 “Profits and losses” at a synthetic level.
- At the end of the annual reporting period, analytical levels should be closed and the balance sheet reformed.
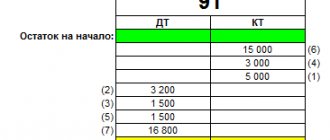
In order to correctly close account 91 at the end of the month, you first need to calculate the balance amount for all subaccounts in order to have a complete picture of what will be included in the next reporting period. To identify the interim financial result, you need to compare the results for the debit of subaccount 91.2 and the credit of subaccount 91.1. The resulting debit balance indicates losses, while the credit balance indicates the company’s profit in the reporting period.
What entries will the accountant make to close account 91:
- Dt91.1 - Kt91.9 - the income part is closed.
- Dt91.9 - Kt91.2 - the consumable part is closed.
- Dt91.09 - Kt99 - profit taken into account.
- Dt99 - Kt91.09 - loss taken into account.
After the monthly closure of the synthetic account level 91, analytical information continues to be collected on it throughout the year, reflecting:
- Types of income and expenses.
- Expenditures.
- Divisions.
In order to reset all analytical balances on account 91, at the end of the year the enterprise must undergo a balance sheet reformation. What entries will the accountant make to close 91 accounts at the end of the year:
- write-off of the balance of other expenses is expressed by the following accounting entries Dt91.01 - Kt91.09;
- expenses Dt91.09 - Kt91.2 are closed.
After this, all that remains is to close the resulting total to account 99 “Profits and losses”. Depending on the financial result, one of two postings will be made:
- Dt91.9 - Kt99 - reflects the profit generated at the end of the reporting year.
- Dt99 - K91.9 - a loss was recorded that was not received from the main activity.
All transactions on account 91 must be documented. What documents may regulatory authorities request:
- Invoices.
- Accounting certificates.
- Acceptance and transfer acts.
- Inventory records.
- Depreciation statements.
Important! If you do not close account 91 and transfer analytical and synthetic accounting data from it to account 99, then its balance at the end of the year will be reflected in the balance sheet. As a result, the accountant will not be able to formulate the correct result of the company’s financial activities.
Accountant closes the month
What can be classified as other income and expenses?
Account 91 is closed based on the results of the reporting period, taking into account the amounts of income in the form of:
- proceeds from operations related to the rental of property (intangible and fixed assets);
- dividends when participating in the capital of other companies and interest on purchased securities;
- one-time receipts of funds from the sale of materials and objects from fixed assets;
- amounts of fines and penalties paid by counterparties under supply and service contracts;
- positive results of asset revaluation;
- exchange rate differences when conducting currency transactions.
Closing 91 accounts involves writing off both the income and expenses of the enterprise, including:
- costs of renting property;
- interest accrued on loans;
- commission fees to banks;
- monthly contributions to reserves;
- compensation for losses, payment of fines;
- depreciation of assets;
- charitable payments.
Existing subaccounts
Account 91 has several mandatory subaccounts in the following groups of income and expenses:
- 91.1 “Other income” - it records assets that are not the result of the main activity.
- 91.2 “Other expenses account” - expenses spent on operations not related to the main activity are reflected here.
- 91.3 “VAT” - serves to reflect value added tax.
- 91.9 “Balance of other income and expenses” - serves to reflect the balance of other income and expenses received in the reporting month.
Information reflected on account 91 1 and account 91 2 is accumulated over an annual period. Each month, a balance is determined from them, which is written off from subaccount 91.9 to account 99 “Profits and losses”. Therefore, account 91 always has a zero balance at the reporting date. At the end of the year, all subaccounts are closed to subaccount 91.9.
Analytical accounting should be kept separately for each type of income and expense. This should ensure the ability to identify the financial result of the company’s business activities separately for each operation.
Subaccounts
Typical transactions for account 91
Debit account turnover is formed by the company's expenses, credit turnover is created due to income. For 91 accounts, organizations open 3 sub-accounts:
- 91.1 for the income part (loan entries).
- 91.2 for the expense base (debit entries).
- 91.9 to form the overall balance for income and expense transactions.
Income can be recorded by debit 91.1 in correspondence with the accounts:
- 10 in case of receipt of returnable materials;
- 08 when reflecting the fact of receipt of assets in accordance with the exchange agreement;
- 14 if the reserve amount is restored.
Until the moment when account 91 is closed, it is necessary to reflect the expense portion of loan 91.2 in correspondence, for example, with the accounts:
- 52 in cases of writing off negative exchange rate differences;
- 60 for additional costs incurred to obtain a loan.