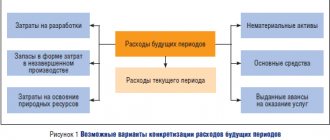
What costs can be attributed to future periods?
Based on the fact that in the Chart of Accounts and the instructions for its use, account 97 “Deferred Expenses” remains (and also in some PBUs this concept exists), it is possible to identify expenses that are written off to cost not immediately, but gradually. These are the costs:
- related to upcoming construction work (clause 16 of PBU 2/2008);
- made as a one-time payment for the right to use licensed software (clause 39 of PBU 14/2007).
In addition, the accountant himself may attribute some types of costs to the PBU if his specific case is not specified in any PBU.
To do this, it is necessary to comply with the conditions under which the costs incurred can be classified as expenses (clause 16 of PBU 10/99):
- the expense is made on the basis of a specific agreement in accordance with the requirements of the law and business customs;
- there is reason to believe that as a result of this operation the economic benefit of the organization will decrease;
- the amount of costs can be determined.
If at least one of the listed conditions is not met, then the expenses incurred cannot be considered expenses and must be reflected in accounting as accounts receivable.
How to determine the period and amount for writing off deferred expenses in accounting? The answer to this question was examined in detail by ConsultantPlus experts. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial demo access for free.
About the basic principles of grouping costs in accounting, read the article “List of the most frequently used cost items in accounting.”
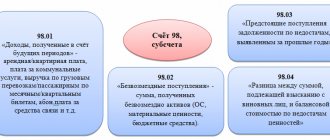
Accounting for expenses on account 97
Accounting for deferred expenses is carried out on active account 97. The debit of this account reflects expenses that were incurred in a given period, but related to future periods, and the credit reflects written-off expenses for the reporting period. The write-off of such expenses is reflected in the following entry: D97 K10,70,68,69.
Such expenses are written off gradually into the cost of production until the expiration date established by the institution (no more than 2 years); the write-off entry has the form D20, 23 K97.
Example:
For clarity, let’s look at an example of accounting for future expenses and the procedure for writing them off. The organization decided to insure its property for 6 months (from 01/01/2014 to 06/30/2014). The insurance company issued an invoice reflecting the amount insured. The organization pays this bill in full, but the organization can terminate the contract at any time and return the remaining funds. In this case, the insurance costs incurred cannot be written off immediately as expenses. Costs are distributed evenly over the entire insurance period, that is, the amount is divided into 6 months. Every month, 1/6 of the insurance amount is written off as the organization's expenses for the current month.
What entries need to be made in accounting in this example? How will account 97 be closed?
Postings for accounting for deferred expenses:
In this way, there will be a gradual write-off of future expenses; at the end of the insurance period, account 97 will be completely reset and closed.
What wiring needs to be done
When accounting for future expenses, the debit of account 97 records the amount of expenses incurred in correspondence with the funds accounts:
Dt 60 Kt 50, 51;
Dt 97 Kt 60.
The write-off of the share of produced production costs related to this period will be reflected in the credit of account 97 and the debit of the production cost accounts:
Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) Kt 97.
The procedure and timing for transferring incurred costs to the cost of production are calculated based on the type of costs. The main criterion for this is the contract, which must stipulate the duration of the service or material value. If this is not the case, then the accountant can independently choose the method for determining the period and reflect it in an internal document (order, regulation in accordance with clauses 4, 8 of PBU 1/2008).
Postings for writing off deferred expenses
After the procedure for classifying RBP, their value is reflected in accounting and is gradually written off using the following correspondence of accounts:
- Dt 97 Kt 60 (76) - costs are taken into account as part of the RBP;
- Dt 20 (25, 26, 44) Kt 97 - partial write-off of RBP.
An important nuance in this regard is the period for writing off the RBP. If it is not specified in the contract, it is determined independently, taking into account the method of writing off the RBP fixed by the accounting policy. This method can be used:
- algorithm for uniform write-off of RBP over the time established by order of the head of the company;
- the method of writing off RBP in proportion to sales income;
- other ways to write off RBP.
Mandatory inventory of BPO
When using account 97 to account for deferred expenses, an inventory must be carried out at the end of each year. The purpose of the inventory is to reconcile the turnover and balances of this account at the beginning and end of the reporting year. The inspection is carried out by the inventory commission on the basis of data from primary documents and accounting certificates on the write-off of RBP.
When conducting an inventory, it is also necessary to analyze the correctness of attributing costs incurred to the RBP (this is stated in paragraph 3.35 of Order No. 49 of the Ministry of Finance dated June 13, 1995). If something is purchased that can later be sold or exchanged, then this cannot be attributed to future expenses. Therefore, it is recommended to attribute these amounts to the corresponding assets - fixed assets, materials, advances issued - and reflect them on the appropriate accounts (01, 10, 60, 76).
The results of the inspection are recorded in a report in form No. INV-11 or on a self-developed form in 2 copies. One copy remains with the commission, the second is transferred to the accounting department.
Form No. INV-11 and you can see a sample of how to fill it out for free by clicking on the picture below:
How to reflect BPR in accounting?
Accountants keep records of such expenses on account 97 “Deferred expenses”. In debit you reflect the costs that you incurred, and in credit you reflect their gradual write-off as expenses.
Postings: Dt 97 - Kt 51(60) - we took into account the costs as RBP. Dt 20 (26, 44, 91) - Kt 97 - we included in deferred expenses the share that relates to the current period.
How to take into account RBP when paying taxes?
According to the law, expenses must correspond to the terms of transactions and the periods when these transactions were made. In general, you need to look at the transaction documents.
If, according to the agreement, the transaction is extended over three periods, then the expenses must be taken into account when taxing in each period. For example, you buy a license and it is valid for three years. Over the course of three years, you can gradually write off expenses, and these payments are reflected in your tax return each time. If it is not possible to determine from the transaction documents the period to which the expenses are tied, then the organization independently determines this period.
How to reflect deferred expenses on the balance sheet
You again have two options:
- reflect expenses as a highlighted item in the “Inventories” group;
- reflect expenses as a separate group in the “Current assets” section.
Next, when filling out the balance in debit, we indicate the balance of this account and enter there the remaining expenses that have not yet been written off by the end of the reporting period.
How to conduct an inventory of BPO
In order to carry out the inventory correctly, you need to check the turnover and balances of the 97th account with the primary account, that is, with the accounting certificates for the write-off of the RBP. The result must be formalized in a special act in form No. INV-11. The inventory of BPO is carried out as part of the annual inventory.
The accounting web service Kontur.Accounting allows you to reflect future expenses in tax and accounting.
Get acquainted with the capabilities of the service for free for 14 days, keep records, calculate salaries, report online and work in the service together with colleagues. Try for free
Deferred expenses in tax accounting 2021
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not define the concept of “future expenses”. But there are expense clauses that reduce the taxable base gradually over a period. These, in particular, include (Article 262, Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) costs:
- for insurance - voluntary medical, CASCO, OSAGO;
- for the acquisition of land;
- for research and development;
- to study natural deposits;
- for product certification.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses in 2022 when calculating income tax are taken in the time period to which they are relevant for taxpayers who determine expenses and income on the accrual basis. The amount of expenditure is established taking into account the provisions of Art. 318-320 of the tax code.
The period to which the expenses incurred must be attributed is determined from the terms of the transaction. If there is no document by which it is possible to determine the distribution of expenses between income, then taxpayers establish a write-off method (uniformly, in proportion to the volume of production or income, etc.) independently and fix it in the accounting policy of the organization.
How to correctly reflect the peculiarities of accounting in the accounting policy, read the article “PBU 1/2008 “Accounting Policy of the Organization” (nuances)”.
The legislative framework
The very concept of deferred expenses (hereinafter referred to as FPR) logically follows from the assumption of temporary certainty of economic activity or the accrual principle enshrined in PBU 1/2008.
Law No. 402-FZ does not contain a breakdown of these expenses. Turning to PBU 10/99, we see that “expenses are recognized in the income statement ... through their reasonable distribution between reporting periods, when expenses determine the receipt of income over several reporting periods and when the relationship between income and expenses cannot be clearly defined or determined indirectly." Thus, the introduction of a mechanism for distributing expenses between reporting periods required the emergence of the concept of BPR.
We find a mention of this type of expense in PBU 2/2008: “... expenses incurred in connection with upcoming work are taken into account as deferred expenses. As contract revenue is recognized, contract expenses are written off to determine the financial result of the reporting period.”
And also in PBU 14/2007: “Payments for the granted right to use the results of intellectual activity or means of individualization, made in the form of a fixed one-time payment, are reflected in the accounting records of the user (licensee) as deferred expenses and are subject to write-off during the term of the agreement.”
Thus, RBP are expenses that actually occur in one period, but in their meaning and purpose should be attributed to subsequent reporting periods or periods.
The most common examples of BPR are: insurance costs, license fees, costs in connection with future construction work, software, costs for repairs of fixed assets, etc.
Reflection of BPM in the balance sheet
In accordance with clause 65 of Regulation No. 34n, expenses made in one reporting period, but related to the next, must be reflected on the balance sheet lines in accordance with the conditions for recognizing assets in groups of items (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 6, 2013 No. 07-01-06 /21876). As a rule, balance lines are used for this: 1110, 1150, 1210, 1260.
Find out which balance line to choose to display future period expenses in ConsultantPlus. Get trial demo access to the K+ system and find out the answer to this question for free.