When insurance premiums are not required
The provisions of paragraphs.
5 p. 1 art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for a number of payments in favor of employees, for which contributions to compulsory social insurance do not need to be assessed. Among them: - payments (contributions) under voluntary personal insurance contracts for employees, providing for payment for medical services and concluded for a period of at least one year;
— payments (contributions) under contracts with medical organizations for the provision of medical services to employees, which are concluded for a period of at least one year. A prerequisite is that the medical institution has a license issued in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia, in its letter dated 05/07/2010 N 10-4/325233-19, also confirms that insurance premiums for payments under contracts concluded for a period of more than one year are not required.
Voluntary health insurance agreements may contain various conditions for compensation of expenses to an employee. Thus, an employee can be paid for treatment abroad or sanatorium-resort treatment. The employee may also be reimbursed for the amount of money spent on the purchase of medicines.
For example, LLC “Vesna” entered into an insurance agreement for its employees with the insurance organization “Health” for a period of 1 year. The agreement provides for the provision of medical assistance to Vesna employees on their trips abroad with the issuance of an international insurance policy. Accountant L. B. Osipova was on vacation in Morocco, where she suffered a broken arm. With her insurance policy, she went to the hospital, where she received the necessary medical care.
The cost of medical services provided to her is not subject to insurance premiums.
According to paragraph 5, paragraph 1 of Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it does not matter to whom the funds were paid under the VHI agreement: to the employee as compensation for expenses incurred by him or to the organization that provides medical services.
For example, S.N. Alekseev, an employee of Vesna LLC, contacted a dental clinic that had the appropriate license. After the treatment, S.N. Alekseev presented his insurance to the clinic, which Vesna LLC pays under a voluntary health insurance agreement concluded for a period of 1 year with the insurance company. Alekseev did not have to pay for dental treatment, since payment was made on the basis of insurance directly to the clinic’s bank account.
Insurance premiums under this VHI agreement paid by “Vesna” to “Health” should not be subject to contributions for compulsory social insurance.
How to justify expenses for voluntary health insurance
Expenses that can be taken into account as expenses that reduce taxable income must be incurred to carry out an activity aimed at generating income. They must also be documented and economically justified.
Justified expenses mean economically justified expenses, the assessment of which is expressed in monetary form.
Documented expenses mean expenses supported by documents drawn up in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. All this is stated in Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. How can these requirements be applied to the costs of voluntary health insurance for employees?
The main document confirming expenses is the voluntary health insurance agreement, which must be concluded in writing. Each insurer has its own standard contract form. But there are elements that must be there. The essential terms of the voluntary personal insurance contract are established by Article 942 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation:
- contract time;
- the moment the contract comes into effect - from the moment it is signed or from the moment the first insurance premium is paid;
- the period from which insured employees can receive medical care under the concluded contract (for example, after the contract comes into force);
- number and names of insured persons (the list is usually drawn up as an appendix to the contract);
- types of insured events and exceptions to them that are not covered by the contract;
- the amount, timing and procedure for making insurance contributions (for example, at a time or in installments);
- the amount of the insured amount (the value of the volume of medical care).
Current legislation does not directly limit the number of workers who can be insured, nor their composition, nor the terms of insurance.
But one should take into account the general requirements of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation that labor costs include expenses associated with the maintenance of these workers, provided for by the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation, labor agreements (contracts) and (or) collective agreements. Thus, according to Article 41 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the collective agreement may include the obligations of the employer, among which are the health improvement of employees and members of their families. Therefore, to confirm the validity of expenses, it is recommended to indicate the condition on voluntary health insurance for the company’s employees in employment and (or) collective agreements.
When are insurance premiums calculated?
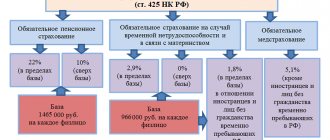
In cases where a VHI agreement is concluded for a period of less than one year, insurance premiums must be charged on all payments made under such an agreement. This means that to the income paid to the employee by the employer, it is necessary to add VHI payments attributable to this employee, and calculate insurance premiums from the received amount.
Mandatory insurance contributions are calculated monthly from taxable remuneration in favor of employees and are paid to the budgets of the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund no later than the 15th day of the month following the month in which they were accrued.
Read about the deadlines for paying insurance premiums here.
see also
- “Are insurance premiums charged for payments to donors?”;
- “On the calculation of insurance premiums from the cost of milk and compensation payments in exchange for milk.”
Labor costs
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows the costs of voluntary health insurance to be included in labor costs (Clause 16, Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But only if the following conditions are met.
Firstly, as you remember, the employer’s obligation to provide voluntary health insurance to employees must be stated in an employment or collective agreement.
Secondly, the VHI agreement was concluded in relation to employees (that is, VHI expenses in relation to relatives of employees are not taken into account for profit tax purposes, although they can be insured).
Example 1. VHI expenses for relatives of employees.
The VHI agreement was concluded for a period of one year. The number of insured persons is 152, of which 118 are employees of the company, 34 are their relatives who are not employees of the company. The company paid an insurance premium of 20,000 rubles. for one insured person in the total amount of RUB 3,040,000. (RUB 20,000 × 152 people). For profit tax purposes, it is possible to recognize the costs of paying insurance premiums under a VHI agreement only in relation to the company’s employees, that is, in the amount of RUB 2,360,000. (RUB 20,000 × 118 people). The remaining part of the insurance premiums paid for relatives of employees is in the amount of 680,000 rubles. (3,040,000 – 2,360,000) cannot be recognized for profit tax purposes.
Thirdly, the VHI agreement must be concluded for a period of at least one year. Concluding an agreement for a shorter period deprives the employer of the right to recognize expenses for tax purposes.
Fourthly, the cost of paying insurance premiums under a VHI agreement should not exceed 6% of the amount of labor costs. The total amount of labor costs is taken into account.
To determine the maximum amount of expenses, the duration of the agreement in the tax period is taken into account, starting from the date of its entry into force. For the convenience of accounting for the voluntary health insurance agreement, it is preferable to indicate that it comes into force on the 1st day of the month following the month of payment of the insurance premium, so as not to calculate the company’s salary for an incomplete month.
If an agreement is concluded in one calendar year and ends in another, the amount of labor costs to determine the limit of expenses accepted for tax purposes is calculated on an accrual basis starting from the date the agreement enters into force within the given tax period. And the calculation of the limit in the last tax period is carried out before the expiration date of the insurance contract (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 16, 2016 No. 03-03-06:1:54205).
The principle of calculating contributions for voluntary health insurance
In general, the formula by which insurance premiums are calculated is as follows:
B = C / KD * DP, where
B – the amount of contributions for a certain tax period;
KD – number of days of validity of the insurance contract;
DP – number of days in the reporting period.
Calendar days are used in the calculation formula. Accordingly, CD = 366 for a leap year and 365 for a regular year. The DP parameter is taken equal to:
- 28 – in February of a non-leap year;
- 29 – in leap year February;
- 30 – in April, June, September, November;
- 31 – in January, March, May, July, August, October, December.
The amount obtained as a result of the calculation must be checked for compliance with the limit (6% of labor costs). Expenses to reduce the tax base for income tax can only be accepted in this amount.
Expenses for employee health insurance in accounting
In accounting, this expense item will be included in expenses for the entire payment period. Insurance expenses are included in the debit of the expense account.
If an organization has entered into an agreement for an employee who is not officially employed, then this amount is recorded in “Other expenses.”
Thus, in tax accounting, the costs of the policy must coincide with the standards, and in accounting, the costs are taken into account without additional prohibitions. If there is a difference between the first and second, this amount is reflected in the company’s accounting.
Expenses for voluntary health insurance: income tax
When calculating income tax, expenses for voluntary health insurance reduce the tax base.
The conditions for accepting expenses to determine the tax base are similar to those applied under the simplified tax system.
VHI contributions will be taken into account when calculating income tax even if the list of insured persons has changed during the term of the contract (Article 450 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
For employees, it does not matter how long they have worked in the organization.
Even if this period is less than a year, a voluntary health insurance agreement is concluded in relation to this employee and the expenses incurred under it are accepted for tax accounting purposes.
Please note that in addition to the standard insurance program, companies also offer a deposit insurance program for VHI.
Determining the balance of the insurance premium
Check the unwritten off balance of the insurance premium at the end of the month preceding the dismissal of the employee using the report Calculation reference for writing off deferred expenses using the Calculation references in the Month Closing . PDF
Calculate the amount of the insurance premium attributable to the employee’s hours worked in the month of dismissal (separately in accounting and accounting records, if they do not coincide):
- 30,000 (amount of insurance premium under the contract) / 366 (number of days under the contract) * 20 (number of calendar days in the month until the date of dismissal) = 1,639.34 rubles.
The amount received will be recognized as an expense in the employee's last month of employment.
Calculate the amount that cannot be recognized as an expense:
- 25,000 (the balance of the unwritten off insurance premium at the beginning of the month according to the calculation certificate) – 1639.34 = 23,360.66 rubles.
Can an employer save on taxes through voluntary health insurance? Lawyer explains
Voluntary health insurance (VHI) for employees is an additional expense for the employer, and not a benefit from tax savings. It is a mistake to believe that the employer chooses where to pay - to the budget or to pay for insurance. He will pay less to the budget. Voluntary health insurance is a social burden for organizations that does not entail quick benefits in terms of money, but long-term benefits in terms of personnel.
Medical insurance is one of the main components of the social package offered by some employers to their employees. Even small companies try to provide employees with a minimum social package. Why does an employer need this? First of all, such incentives can attract and retain valuable personnel. Taking care of employees is an additional plus to the employer's assessment. In addition, if a person can receive a sufficiently large range of medical services under VHI in a place convenient for him at a time convenient for him, the employer has a chance “not to lose an employee” during medical examinations: private clinics have a fairly flexible work schedule, including and on weekends. And timely examinations and treatment ensure the efficiency of staff.
As for the conditions of VHI themselves, different insurance companies, in the fight for the client, try to offer the widest possible choice of insurance options. And, accordingly, offer the employer a choice of services from various clinics.
VHI may include services such as:
- outpatient services;
- calling a doctor at home;
- ambulance;
- dentistry;
- emergency hospitalization;
- planned hospitalization;
- telemedicine.
The longer the list of services, the more expensive the insurance.
Currently, most insurance organizations allow employers to choose different content of services for employees. For example, for top management, VHI insurance may provide for planned hospitalization, but for employees who have been working in the company for less than two years, only outpatient care and emergency care.
Since social security for workers is important for maintaining stability in society, the legislator included the costs of voluntary health insurance in labor costs, that is, costs that reduce the tax base for corporate income tax. Fair decision. It would be strange to pay taxes on money spent on employee insurance.
But here you should keep in mind the legal restrictions:
- the employer’s obligation to issue voluntary health insurance for employees must be specified in the collective or employment agreement;
- the insurance company must have an appropriate license;
- the voluntary health insurance agreement must be concluded only in relation to employees (expenses for relatives of employees, for retired employees and for “non-working people” working under the civil process of employment are not grounds for reducing the tax base);
- the VHI agreement must be concluded for a period of at least one year;
- expenses under a voluntary health insurance agreement do not exceed 6% of the amount of labor costs. By the way, if the employer pays employees for vouchers (both tourist and sanatorium-resort treatment), the total expense for VHI and vouchers should be no more than 6%).
For example, an organization employs 50 people, and annual labor costs amount to 30 million rubles. Thus, the company can spend no more than 6% of this amount per year, that is, no more than 1.8 million rubles, on voluntary health insurance for employees, payment for tourist packages and expenses for sanatorium and resort treatment.
If any of the specified conditions are not met, the tax authority will not accept such insurance payment as expenses (or will accept it in a limited amount). For this purpose, VHI almost always provides for the replacement of insured persons at the request of the employer. In this regard, an urgent problem for an accountant who monitors accounting under a VHI agreement is timely notification of the insurance organization about the removal of a dismissed employee from service under a VHI agreement and the connection of a newly hired employee. Otherwise, the costs of paying for the employee’s voluntary health insurance may not be taken into account by the tax authority.
It is a mistake to think that employee health insurance gives the employer the opportunity to save on taxes. As mentioned above, indeed, the tax base for income tax will be reduced, but only by the amount of the contract with the insurance organization.
| Insurance Company | The number of employees | What is included | Cost of annual insurance |
| "Reso guarantee" | 2–9 | Attaching to the network of clinics “Policlinika.ru”, dentistry. | 22.5 thousand rubles. |
| "Russian Standard Insurance" | 10–30 | Attaching to the network of clinics “Policlinika.ru”, dentistry. | 16.2 thousand rubles. |
| "VSK insurance house" | 6–10 | Expanded program, connection to a network of clinics, home care. | 70 thousand rubles. |
| "Absolute insurance" | 10–25 | Service in standard-class clinics, dentistry | 25 thousand rubles. |
*Source: medoins.ru
In an economically unstable period, saving on voluntary health insurance can take different forms. From completely abandoning it to looking for options to reduce the cost of the contract. Insurance companies are increasingly offering VHI options with a deductible (when the employee pays a certain percentage of the cost of medical services); in some organizations, employees are offered to reimburse the employer’s expenses for VHI. For example, under the terms of such insurance, the client pays 15% of the cost of services of a medical institution, the remaining amount is paid by the insurance company.
In general, when concluding a contract of voluntary medical insurance for employees, the employer must carry out painstaking work to compare insurance conditions in various insurance companies. Not a formal approach, but the employer’s interest in real convenience for employees will achieve the desired goal - the obvious value of VHI in the eyes of employees.