What is this?
An invoice can be issued or presented by the seller (as well as entities such as the contractor) to the buyer after he has fully received the goods (services) that he ordered.
Such a document is used in Russia for the purpose of accounting for VAT taxes. The purpose of the invoice and its details are specified in the Code of the Tax System of the Russian Federation. Information about this document is indicated in article No. 169.
An invoice should be issued no later than 5 days after receipt of goods or final provision of services.
Creating a document
There are the following ways to create an Invoice received :
- based on another document;
- from the list of documents Invoices received ;
Method No. 1. Creation based on another document
Invoice document can be entered based on the following documents:
- Cash receipt;
- Advance report;
- Debiting from the current account;
- Receipt (act, invoice);
- Receipt of additional expenses;
- Return of goods from the buyer;
- Commissioner's sales report;
- Reflection of VAT for deduction;
- Debt adjustment;
- Receipt of intangible assets;
- Sales report to the consignor;
- Redemption of leased items.
It is this method of creating the Invoice document received that is the most rational, because when creating a document:
- the document transaction type will be automatically determined;
- Most document fields will be filled in automatically based on the base document.
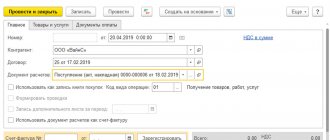
to create an Invoice received on the basis of another document:
- from the document form; You must enter the invoice number and date and click the Register .
- from the document form by clicking the Create based ;
- from the list of supporting documents; In the list of base documents, select the required document, click the Create based on button – Invoice received.
Method No. 2. Create from a list of documents
This method of creating an Invoice document received is acceptable, but not rational, because When creating this document “manually”, you have to independently select the type of operation and fill out the fields of the document. All this significantly increases the risk of error.
the received Invoice document to create Method No. 1 Creation based on another document.
Method No. 2 can be used if it is not possible to correctly register an incoming invoice based on another document.
The Invoice received document is created through the section Purchases – Purchases – Invoices received.
In the list of documents Invoices received, click the Create and select the desired type of transaction.
See also:
- Document Invoice received transaction type for receipt
- Document Invoice received type of transaction for advance payment
- Document Invoice received type of transaction for advance payment by the principal for purchase
- Document Invoice received transaction type Adjustment invoice
- Document Invoice received transaction type Correction of invoice
- Document Invoice received type of transaction Correction of own error
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Document Invoice, received transaction type Invoice for receipt Document Invoice, received transaction type for receipt allows you to register in…
- Document Invoice received for advance payment Document Invoice received for advance payment is intended for registration of invoices received…
- Adjustment Invoice vs Corrective Invoice...
- Document Invoice issued for sale...
Regular invoice or invoice – what to choose?
The question often arises whether an invoice issued for payment can replace the most ordinary invoice required to document existing expenses, and also what to ultimately choose - an invoice or an invoice.
It cannot be said that these two concepts are identical, or that they can be replaced by each other. To determine the choice, it is worth understanding the difference between an invoice and an invoice, and identifying specific situations for which one or another option is suitable.
An invoice is a document issued by the accounting department, which is drawn up on the basis of an agreement for the execution of services or purchase and sale. The invoice clearly states the amount that the client must send to the current account or pay through the cash register. An invoice is issued for goods, services, and after work has been completed. An invoice can be issued every month or once a year if regular payment for the same type of goods or services is expected.
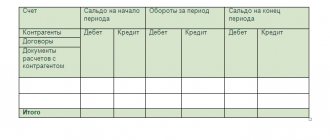
The account requires registration of the following positions:
- Name of product;
- unit of measurement;
- the established cost of the product (each item) or service;
- quantity;
- payment details.
The invoice is issued by the seller or contractor himself after the delivery of the goods has been completed and the completion of the work. This document is required only for those organizations that are subject to the general taxation system. An invoice is needed to pay taxes and reimbursement for added value. In other cases and on other taxation systems, an invoice is not needed, since its presence is not mandatory.
What you need to know about the invoice
1) serial number and date of the invoice;
2) name, address and identification numbers of the taxpayer (tax agent) and the buyer;
3) name and address of the shipper and consignee;
4) the number of the payment and settlement document in case of receiving advance or other payments for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services);
5) name of the goods supplied (shipped) (description of work performed, services provided) and unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it);
6) quantity (volume) of goods (work, services) supplied (shipped) according to the invoice, based on the units of measurement adopted for it (if it is possible to indicate them);
6.1) name of the currency;
6.2) identifier of the government contract, agreement (agreement) (if any);
7) price (tariff) per unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it) under the agreement (contract) excluding tax, and in the case of using state regulated prices (tariffs) that include tax, taking into account the amount of tax;
the cost of goods (work, services), property rights for the entire quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights without tax;
9) the amount of excise tax on excisable goods;
10) tax rate;
11) the amount of tax imposed on the buyer of goods (works, services), property rights, determined based on the applicable tax rates;
12) the cost of the total quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, taking into account the amount of tax;
13) country of origin of the goods;
14) number of the customs declaration;
15) code of the type of product in accordance with the unified Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity of the Eurasian Economic Union. The information provided for in this subparagraph is indicated in relation to goods exported outside the territory of the Russian Federation to the territory of a member state of the Eurasian Economic Union.
The information provided for in subparagraphs 13 and 14 of this paragraph is indicated in relation to goods whose country of origin is not the Russian Federation. The taxpayer selling the specified goods is responsible only for the compliance of the specified information in the invoices presented to him with the information contained in the invoices and shipping documents received by him.
Mandatory invoice details
Is this procedure legal?
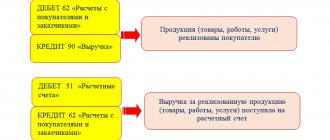
Since an invoice is necessary for the direct payment, an invoice reflects the goods transferred between the seller and the buyer, or indicates the actions performed.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code, an invoice is a document that serves as the basis for the acceptance of goods or work performed presented by the seller.
The supplier's products received must be accompanied by an invoice called “TORG-12” and, accordingly, an invoice. As for the representative, it is not accepted. Payment is legally implemented on the basis of an invoice.
The invoice is in euros, but the payment is in rubles: how to issue an invoice?
Question from Clerk.Ru reader Tatyana (Moscow)
Account in EURO. Payment in rubles. Should the invoice be issued in rubles?
In accordance with paragraph 7 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if under the terms of the transaction the obligation is expressed in foreign currency, then the amounts indicated in the invoice can be expressed in foreign currency. Thus, tax legislation provides for the possibility of indicating amounts in foreign currency on the invoice.
Please note that in paragraph 7 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation refers to the currency of the obligation, and not to the currency of payment. According to the Information Letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated November 4, 2002 No. 70, the concepts of currencies are separated: in which a monetary obligation is expressed (debt currency) and in which it must be paid (payment currency) (clause 1 of the Information Letter).
A monetary obligation may stipulate that it is payable in rubles in an amount equivalent to a certain amount in foreign currency or in conventional monetary units (clause 2 of Article 317 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). According to the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation, expressed in Letter No. 3-1-07/674 dated August 24, 2009, it is impossible to issue an invoice in foreign currency or in conventional monetary units (under an agreement for which the obligation to pay is provided in rubles in the amount , equivalent to a certain amount in foreign currency (conventional monetary unit)). Invoices can be issued in foreign currency only if, under the terms of the transaction, the obligation is payable in foreign currency.
Previously, the tax authorities took a different position. For example, in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated April 12, 2007 No. 19-11/33695 it is explained that in paragraph 7 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, we are not talking about payment in foreign currency, but about assessing the obligations of the parties. That is, the named norm of the Code applies not only to contracts with foreign partners, but also to contracts between Russian organizations, under which the cost of goods sold (work, services), transferred property rights is expressed in foreign currency (or in conventional units equivalent to foreign currency ), and payments are made in rubles, so the seller has the right to issue invoices in foreign currency.
A similar opinion is expressed in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated December 6, 2007 No. 19-11/116396.
The courts, referring to paragraph 7 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, adhere to the point of view that if, under the terms of the transaction, the obligation is expressed in foreign currency or conventional monetary units (and is payable in rubles), then the invoice can be issued in foreign currency or in conventional monetary units. For example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated March 17, 2008 No. F09-1590/08-C2 in case No. A47-3561/07, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Northwestern District dated January 11, 2008 in case No. A56-5204/2007. Thus, the issue is currently controversial.
If the buyer receives an invoice in foreign currency or in conventional monetary units (if the monetary obligation stipulates that it is payable in rubles in an amount equivalent to a certain amount in foreign currency or in conventional monetary units), there is a risk that the tax authorities will not accept VAT for deduction.
In this case, the issue of the buyer’s acceptance of VAT for deduction will have to be defended in court, or the seller (in accordance with the recommendations given in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 24, 2009 No. 3-1-07/674) should make corrections to the invoice data : from columns 4, 5, 8 and 9 of the invoice, exclude indicators in foreign currency (conventional monetary units) and replace them with rubles.
These corrections are made in accordance with the procedure set out in clause 29 of the Rules for maintaining logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books for value added tax calculations, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 N 914.
It’s very easy to get personal advice on any tax online - you just need to fill out a special form . Every day two or three of the most interesting questions will be selected, the answers to which you can read in Natalia Lobanova’s consultations.
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 15.
Sign up