When is the commission agent's report prepared?
If a manufacturer, seller or distributor engages an intermediary to sell his own inventory, then he enters into a commission agreement with him and pays him a fixed remuneration (Article 990 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Another example of a commission is mediation in the provision of a service or the purchase of any goods, materials, or valuables. There are always two parties involved in a commission agreement:
- the principal is the owner of the goods and materials, that is, the one who owns the goods being sold;
- commission agent is an intermediary in the sale, that is, the one who actually concludes the transaction with the end buyer.
IMPORTANT!
If an intermediary conducts one or more transactions with a third-party client on its own behalf, then only the commission agent acquires the rights and obligations under the completed transaction, despite the ownership rights to the goods and materials and the financial participation of the principal. All transactions are carried out at the expense of the principal.
The Civil Code explains what a report to the principal is - the final document confirming the results of the transaction (Article 999 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The commission agent is obliged to report to the customer; this is established at the legislative level. The reporting period is a maximum of 30 days after the transaction is closed or another period specified in the commission agreement.
ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to reflect transactions under a commission agreement in the commission agent’s accounting. Use these instructions for free.
to read.
Accounting for transactions under a commission agreement with a commission agent
The commission agent carries out entrepreneurial activities that are aimed at generating profit from the provision of intermediary services for concluding transactions for the purchase and sale of property owned by the principal.
The remuneration due to the commission agent under the agreement is for him income from ordinary activities (clause 5 of the Accounting Regulations “Income of the Organization” PBU 9/99, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n):
Income from ordinary activities is revenue from the sale of products and goods, receipts associated with the performance of work, provision of services (hereinafter referred to as revenue).
Consequently, under a commission agreement, the commission agent who provides paid services to the principal always receives and reflects in the accounting accounts only the proceeds from the sale of intermediary services (commission).
When selling an intermediary service, the commission agent has a turnover for the sale of services (in the amount of the commission), which is reflected in the credit of account 90 “Sales” / subaccount 90-1 “Revenue”.
When reflecting the commission fee in the commission agent's accounting, the following entry is made: Debit 76/subaccount “Settlements with the principal” Credit 90 “Sales”/subaccount 90-1 “Revenue”.
When reflecting revenue from intermediary operations in the accounting accounts of the commission agent, it is necessary to remember that receipts from other legal entities and individuals under commission agreements in favor of the principal are not recognized as income of the organization (clause 3. Accounting Regulations “Income of the Organization” PBU 9/99, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n):
For the purposes of these Regulations, receipts from other legal entities and individuals are not recognized as income of the organization:
under commission agreements, agency and other similar agreements in favor of the principal, principal, etc.;
The following entries are made in accounting:
receiving funds from customers: Debit 51 Credit 76/subaccount “Settlements with customers”;
reflection of debt to the principal: Debit 76/subaccount “Settlements with customers” Credit 76/subaccount “Settlements with the principal”;
transfer of funds to the principal: Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements with the principal” Credit 51.
When executing a commission agreement, the commission agent bears the costs associated with the execution of the order, which are carried out at the expense of the commission fee and are included in the intermediary’s costs. Costs incurred by the commission agent in the process of carrying out intermediary activities (wages of workers, cost of utilities, rent, etc., in total representing the cost of the service provided by the commission agent) are taken into account in account 44 “Sales expenses”, intended for generalization of information on costs associated with the sale of goods, works, and services. Monthly turnover on the specified account is closed to the debit of account 90 “Sales” / subaccount 90-2 “Cost of sales”.
In accounting, such costs are reflected by the posting: Debit 90-2 Credit 44.
At the same time, the disposal of assets under commission agreements in favor of the principal is not recognized as expenses of the organization (clause 3 of the Accounting Regulations “Expenses of the Organization” PBU 10/99, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n):
For the purposes of these Regulations, the following assets are not recognized as expenses of the organization:
under commission agreements, agency and other similar agreements in favor of the principal, principal, etc.;
Consequently, if a commission agent sells a commission product (or purchases it for the principal), then expenses for the sale of goods (or for their acquisition) arise and are reflected in the principal’s accounts.
The commission agent's profit from the sale of a service is defined as the difference between the proceeds from its sale (commission) excluding VAT and the sales costs included in the cost of the service. The resulting financial result is written off monthly to account: 99 “Profits and losses” in correspondence with account 90 “Sales”/subaccount 90-9 “Profit/loss from sales”.
In a commission agreement, the commission agent is not the owner when purchasing or selling goods, that is, he only exercises the rights belonging to the principal. Based on the principle of assuming property separation, property that is the property of an organization is accounted for in the accounting records of the intermediary separately from the property of other legal entities owned by the organization (clause 2 of Article 8 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting” :
Property owned by an organization is accounted for separately from the property of other legal entities owned by the organization.
Accordingly, the property received by the commission agent from the principal is not reflected by him on balance sheet accounts as part of his own property, but is recorded on off-balance sheet accounts:
- for commission agreements related to the sale of consignment goods - on account 004 “Goods accepted on commission”;
- for commission agreements related to the purchase of goods for the principal - on account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping.”
The reflection of transactions in the accounting accounts of the commission agent depends on the type of agreement concluded by the parties to the commission agreement - for the sale or purchase of goods, as well as on the terms of the concluded agreement, in particular, on whether or not the commission agent participates in settlements between the principal and the buyers.
The commission agent participates in settlements
When making a transaction with the participation of a commission agent in the calculations, the cash flow diagram is as follows:
– proceeds from the sale of goods are transferred from the buyer to the bank account or to the commission agent’s cash desk;
– the commission agent, as a rule, withholds his remuneration from the amount received;
– the remaining amount is transferred to the owner of the goods – the consignor.
Example 1.
CJSC "Committent" transferred goods to LLC "Commissioner" for sale. According to the agreement, the goods must be sold for 240,000 rubles (including VAT - 40,000 rubles). The cost is 120,000 rubles. The amount of commission is 24,000 rubles (including VAT - 4,000 rubles).
LLC "Commissioner" completely sold the goods received on commission. The costs associated with the sale of goods amounted to 6,000 rubles. According to the agreement, LLC “Commissioner” participates in the settlements and withholds its remuneration from the funds due to CJSC “Committent”.
LLC "Commissioner" will make the following entries in accounting:
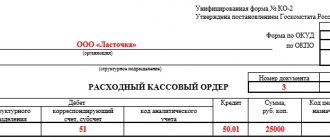
Debit 004 – 240,000 rubles – goods received under a commission agreement from CJSC Committent were capitalized;
Credit 004 – 240,000 rubles – goods were shipped to customers;
Debit 76/subaccount “Settlements with customers” Credit 76/subaccount “Settlements with the principal” - 240,000 rubles - reflects the debt of buyers to pay for goods and the debt to the principal;
Debit 44 Credit 02 (70, 69 ...) – 6000 rubles – costs associated with the provision of intermediary services are reflected;
Debit 51 Credit 76/subaccount “Settlements with customers” – 240,000 rubles – funds were received from customers to the settlement account of LLC “Commissioner”;
Debit 76/subaccount “Settlements with the principal” Credit 90-1 – 24,000 rubles – the amount of commission is reflected;
Debit 90-2 Credit 44 - 6,000 rubles - costs associated with the provision of intermediary services are written off;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68/subaccount “Calculations for VAT” - 4,000 rubles - VAT is charged on commission fees;
Debit 76/subaccount “Settlements with the principal” Credit 51 – 216,000 rubles (240,000 – 24,000) – funds were transferred to the principal minus remuneration;
Debit 90-9 Credit 99 – 14,000 rubles (24,000 – 4000 – 6000) – profit from the provision of commission services is reflected.
Settlements under the agreement without the participation of the commission agent in the calculations
If the intermediary is not involved in the settlements, then:
– proceeds from the sale of goods are transferred to the current account or cash register of their owner – the principal;
- after receiving the money, the principal transfers the remuneration to the commission agent due to him in accordance with the agreement.
LLC "Commissioner" will make the following entries in accounting:
Debit 004 – 240,000 rubles – goods received under a commission agreement from CJSC Committent were capitalized;
Credit 004 – 240,000 rubles – goods were shipped to customers;
Debit 44 Credit 02 (70, 69 ...) – 6000 rubles – costs associated with the provision of intermediary services are reflected;
Debit 76/subaccount “Settlements with the principal” CREDIT 90-1 - 24,000 rubles - the amount of commission is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 /sub-account “Calculations for VAT” – 4000 rubles – VAT is charged on commission fees;
Debit 90-2 Credit 44 – 6,000 rubles – costs associated with the provision of intermediary services are written off;
Debit 51 Credit 76/subaccount “Settlements with the principal” -24,000 rubles – the amount of commission was received from the principal;
Debit 90-9 Credit 99 – 14,000 rubles (24,000 – 4000 – 6000) – profit from the provision of commission services is reflected.
When using the above accounting entry scheme, the following problem arises. Since the sales contract is concluded with the buyer by the commission agent, and the money is transferred to the principal’s account, the commission agent does not maintain any control over the receipt of payment for the shipped goods. At the same time, in the absence of payment for the shipped goods, the principal formally does not have the right to file claims against the buyer due to the absence of a direct sales agreement with him, since claims in this case against the buyer must be presented by the commission agent.
In order for the commission agent to be able to track payments by customers, the following can be provided in accounting:
Debit 62 Credit 76 - 240,000 rub. — the buyer’s debt to the principal is reflected;
Debit 76 Credit 62 - 240,000 rubles. – reflects the closure of debts in settlements between the buyer and the principal.
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Chief accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
How does a commission agent report?
There is no single reporting form established by law. Reporting is prepared in any form, which is secured in a separate appendix to the commission agreement. The register specifies all the requirements, conditions and results for a specific transaction and includes mandatory details for primary documents (Part 2 of Article 9 402-FZ of December 6, 2011).
General instructions on how to draw up a commission agent’s report:
- List the parties to the agreement.
- We indicate the number, date and place of reporting.
- We determine the period of work of the intermediary.
- We refer to the commission agreement.
- We describe the main terms of the transaction. As an option, we create a table. In it we indicate the volumes and cost of sales, the intermediary commission.
- Here are the results. It is necessary to indicate how much the commission agent sold/shipped inventory items and how much money he received. To confirm, you should list payment and settlement documents: invoices, delivery notes, acts.
- We sign the reporting register. Signatures are placed by official or trusted representatives of the parties.
According to the rules, the commission agent prepares a report to the consignor who signed, released and received the goods, that is, the final buyer has nothing to do with the preparation of commission reports. He purchases the products and transfers the money to the intermediary or directly to the principal, if such a condition is specified in the commission agreement. If the buyer settles with the intermediary, then along with the reporting the principal receives money (again, if this is specified in the contract) and all accompanying documents for the transaction. But the judicial authorities have a different position: if the parties did not agree on the transfer of money based on the results of the execution of the agreement, then the intermediary is obliged to transfer to the principal the funds from the sale of goods and materials as they are received (Information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 85 dated November 17, 2004).
The procedure for issuing “consolidated” invoices by the committent in “1C: Accounting 8”
We will consider the procedure for issuing “consolidated” invoices by the consignor when selling commission goods in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0, using the following example.
Example
The organization Trading House LLC (committent) entered into a commission agreement with Delta LLC (commission agent), under which the commission agent sells the principal's goods to customers for a fee. Under the terms of the agreement, the commission agent sells goods at prices not lower than the prices specified in the invoice for the transfer of goods and participates in settlements. The commission agent's remuneration is 10% of the proceeds for goods sold and is withheld from funds received from customers. The additional benefit belongs to the principal. Sequence of operations:
The sequence of operations is given in the table. |
Setting up the program
The organization Trading House LLC, which sells goods under commission agreements, needs to check the use of the functionality Sale of goods or services through commission agents (agents) in the Program Functionality directory (Section Main - subsection Settings - Functionality) on the Trade tab.
Transfer of goods to the commission agent
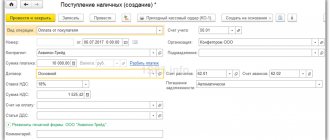
Registration of transaction 2.1 “Transfer of goods to a commission agent for sale” in the program is carried out using the document Sales (act, invoice) with the type of operation Goods, services, commission (section Sales - subsection Sales), Fig. 1.
Rice. 1. Transfer of goods to the commission agent for sale
The header of the document indicates:
Information about goods transferred for sale (name, quantity, price, VAT rate) and data for reflecting the operation in accounting are entered in the tabular section on the Goods tab.
Since an invoice is not drawn up when transferring goods from the principal to the commission agent, the information Not required is reflected in the Invoice line of the Sales document (act, invoice).
If necessary, by following the Signatures and (or) Delivery hyperlinks (Fig. 1), you can specify information about the transfer operation to issue an invoice (or UPD). After posting the document, the following entry is entered into the accounting register:
Debit 45.01 Credit 41.01 - for the cost of goods transferred for sale.
Registration of the commission agent's report for February
Registration of transactions 3.1 “Reflection of the sale of goods transferred to commission”; 3.2 “Calculation of VAT on sales transactions”; 3.3 “Write-off of cost of goods sold”; 3.4 “Reflection of commission agent’s deduction of commission”; 3.5 “Reflection of commissions in cost accounts”; 3.6 “Accounting for VAT on commission fees” in the program is carried out using the document Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales (section Sales - subsection Sales).
You can create a document Report of commission agent (agent) on sales based on the document Sales (act, invoice) by clicking the Create based button (Fig. 1).
On the Main tab in the document header the following is indicated:
Information for determining the amount of the commission agent's remuneration is filled in automatically with the data specified in the agreement from the directory Contracts of counterparties.
If the principal reissues a “consolidated” invoice to the commission agent on the basis of invoices drawn up by the commission agent for one date when selling goods to two or more customers, then in the document Sales report of the commission agent (agent) it is necessary to check the presence of the flag for the value Issue invoices consolidated (EDO is not supported), which is entered by default.
Actual buyers and the number of goods sold are entered manually on the Sales tab in accordance with the commission agent's report.
If a report is registered for the sale of goods, the transfer of which to the commission agent is reflected in the Sales document (act, invoice), then the document Sales report of the commission agent (agent) is recommended to be entered on the basis of the shipment document (Fig. 1) or using the Fill button. In this case, the header details and the tabular part on the Implementation tab will be filled with data from the base document.
As a result of automatic filling, in the upper part of the table, by default, the commission agent will be indicated as the buyer, and in the lower part - the nomenclature, price and quantity of goods that were transferred to the commission agent for sale.
To fill in information about real buyers and actual sales of goods based on the commission agent’s report, it is necessary to make changes to the upper and lower parts of the table.
The following information is indicated at the top of the table (Fig. 2):
Rice. 2. Sales agent report
For each line of the upper tabular part, information is indicated in the lower part (Fig. 2):
- about goods sold (name, quantity, price at which goods were sold, price of goods when transferred to the commission agent, tax rate);
- the amount of commission agent's remuneration and the amount of tax on remuneration;
- the account in which the transferred goods were recorded;
- accounts for recording income and expenses for the sale of goods;
- VAT account for the sales transaction.
Thus, each row in the top table corresponds to a separate bottom table. The transition between lower tables is carried out by moving through the rows of the upper table. For the example under consideration, three rows were created in the upper table, for each of which a separate lower table was filled in (Fig. 2).
After posting the document Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales, the following accounting entries will be entered into the accounting register:
Debit 90.02.1 Credit 45.01 - for the cost of goods sold, for each line of the lower tabular part;
Debit 60.01 Credit 76.09 - for the total amount of commission withheld;
Debit 76.09 Credit 90.01.1 - for the sale price of goods including VAT, for each line of the lower tabular part;
Debit 44.01 Credit 60.01 - for the cost of intermediary services excluding VAT;
Debit 90.03 Credit 68.02 - for the total amount of accrued VAT on the sales transaction;
Debit 19.04 Credit 60.01 - for the total amount of VAT presented by the intermediary for commission fees.
For tax accounting purposes for corporate income tax, the corresponding amounts are also recorded in the resources Amount Dt and Amount Kt for accounts with the NU attribute.
Entries are entered into the Sales VAT register for the sales book for each customer, reflecting the accrual of VAT payable to the budget.
An entry with the type of movement Receipt and with the event Submitted VAT by the Supplier is entered into the VAT presented register for the amount of VAT presented by the commission agent for the commission.
Also, when posting the document Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales, as mentioned above, the document Invoice issued is automatically generated (operation 3.7 “Reissuing a consolidated invoice for goods sold”). Since a “consolidated” invoice is being generated, a link to the same invoice appears in each line of the upper part of the table in the Issued to commission agent column (Fig. 3). The created posted document Invoice issued is a “consolidated” invoice re-issued by the commission agent to the commission agent with indicators similar to those of the invoices issued by the commission agent to the buyer when shipping goods on this date (clause 1 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved. Resolution No. 1137).
Rice. 3. Formation of a consolidated invoice
From any row at the top of the table in the Agent's Sales Report document, you can go to this reissued “consolidated” invoice.
In the new posted document Invoice issued, all fields will be filled in automatically based on the data in the document Sales report of the commission agent (agent). In this case, in the field Operation type code the value 27 will be indicated, which corresponds to the preparation of an invoice based on two or more invoices for the sale of goods (work, services), property rights in the case provided for in paragraph 3.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Appendix to Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] ).
By clicking the Print button in the document Invoice issued (Fig. 3), you can view the form of the invoice and print it in two copies (clause 6 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Resolution No. 1137).
In the “consolidated” invoice reissued to the commission agent in accordance with the Rules for filling out the invoice, approved. Resolution No. 1137 will indicate:
- in line 1 - the date of issue of the “consolidated” invoice by the principal, which coincides with the date of the invoices issued by the commission agent (agent) to the buyer. The serial number of the invoice is indicated by the committent in accordance with its chronology (clause “a”, clause 1 of the Rules);
- in lines 2, 2a and 2b - the name and location of the principal (principal) in accordance with the constituent documents, identification number and code of the reason for registration of the principal (principal) (clauses “c”, “d”, “e” clause 1 of the Rules);
- in line 4 - the names of all consignees and their postal addresses from the invoices issued by the commission agent (through the sign “;” (semicolon) (clause “g” of clause 1 of the Rules);
- line 5 is filled in in case of receipt of payment, partial payment for the upcoming delivery of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights. In this case, line 5 indicates the details (number and date of preparation) of payment and settlement documents on the transfer of funds by buyers to the commission agent (agent) and by the commission agent (agent) to the committent (principal) (through the sign “;” (semicolon) (paragraph “ 3" clause 1 of the Rules);
- in lines 6, 6a and 6b - names, locations, INN/KPP of buyers in accordance with the constituent documents from invoices issued by the commission agent (through the sign “;” (semicolon) (paragraphs “and”, “ j", "l" clause 1 of the Rules);
- in columns 1-11 the data corresponding to the data from the invoices issued by the commission agent is indicated (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 02/04/2010 No. ШС-22-3 / [email protected] ). In this case, the names of the shipped goods are indicated in separate positions for each buyer (clause “a”, clause 2 of the Rules).
After the Invoice document has been issued, entries are made in the Invoice Journal register for each buyer of goods.
Despite the fact that since 01/01/2015 the principals (principals) do not keep a log of received and issued invoices, register entries in the Invoice Log are used to store the necessary information about the issued invoice.
To register an invoice for remuneration received from a commission agent (operation 3.8 “Registration of an invoice for commission”), you must enter the number and date in the Invoice for remuneration number and from fields on the Main tab of the document Sales report of the commission agent (agent) respectively. incoming invoice and click the Register button. In this case, the document Invoice received will be automatically created, and a hyperlink to the invoice will appear in the form of the basis document.
The fields of the Invoice document received will be filled in automatically based on information from the document Sales report of the commission agent (agent).
In addition, in the Invoice document received:
- in the Ground Documents field there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding report of the commission agent;
- in the Transaction Type Code field the value 01 will be reflected, which corresponds to the acquisition of goods (work, services), property rights (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ).
Registration in the purchase book of an invoice for commission services received from a commission agent (operation 3.9 “Application for deduction of input VAT on commission fees”) can be done by checking the box in the line Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by the date of receipt of the document Invoice received, if committent:
- does not maintain separate accounting (in the accounting policy settings (section Main - subsection Settings - Taxes and reports) on the VAT tab, the flag for the value Maintains separate accounting of incoming VAT by accounting methods is not set);
- does not transfer the tax deduction for the purchased commission agent service to the following tax periods in accordance with paragraph 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
After posting the document, an accounting entry is generated:
Debit 68.02 Credit 19.04 - for the amount of VAT claimed for tax deduction on commission fees for February 2022.
An entry is made in the information register of the Invoice Journal to store the necessary information about the received invoice. An entry is made in the Purchase VAT accumulation register about the amount of tax presented by the commission agent for the intermediary service to create a purchase ledger entry for the first quarter of 2022.
An entry with the type of movement Expense is entered into the VAT register for the amount of VAT accepted for deduction.
How to take into account a report in 1C
Commission reporting must be reflected in the accounting department - postings are generated in the working accounting program. The procedure for reflecting the commission agent’s report in 1C depends on the operation - purchase or sale. For each transaction, it is mandatory to create a counterparty, fix the commission agreement and the amount of remuneration to the intermediary, enter the number, reporting date and currency of the transaction.
Purchase
Reflect the purchase for the consignor in this way:
- Generate goods receipt. The receipt of inventory items is reflected on the off-balance sheet in the debit of account 002 (entry - DT 002).
- Create a purchase report. Some data will be pulled up automatically, some information will have to be entered manually. The owner's debt to the supplier is formed on the account. 76.09. As soon as the accountant carries out the reporting operation, the principal's debt will appear in the turnover.
Sale
We generate a commission agent’s report based on the invoice: in the accounting we reflect the receipt and sale of goods, settlements with the buyer and customer, remuneration from the principal. The invoice must reflect the full cost of the goods and the amount of commission.
We reflect the sale according to the instructions:
- In “Purchases” we register the receipt of inventory items.
- In “Sales” we reflect the implementation of inventory items. We reflect it by posting through the off-balance sheet KT 004.01.
- In “Purchases” we create a sales report.
- We record payment from the buyer. In the “Bank and cash desk” section we reflect the transfer of funds transferred by the buyer to the principal’s bank account.
- We look at the correctness of the transactions performed through the balance sheet. With correct calculations, the intermediary always has a zero final balance.
How to reflect in accounting
If you are generating a commission agent’s report for the principal, make entries for the commission agent in the accounting as follows:
| Debit | Credit | Accounting transaction |
| 90.02 | 45.02 | Write-off of cost of goods sold |
| 76 | 62.01 | Withholding of the intermediary commission from the proceeds received |
| 62.01 | 90.01 | Posting revenue from the sale of inventory items |
| 44.01 | 76 | Reflection of commission costs |
| 90.03 | 68.02 | VAT calculation on goods |
| 19.04 | 76 | VAT accrual on commission fees |
Shopping
It happens that a company, when purchasing necessary goods, also resorts to the help of intermediaries. To do this, they conclude, for example, an agency or commission agreement with an intermediary. Under a commission agreement, an intermediary may be instructed to buy goods on his own behalf for the principal.
The procedure for filling out and registering invoices in this situation can be found in Berator
The commission agent (agent) must receive an invoice from the seller of goods and register it in part 2 of the register of received and issued invoices. There is no need to record this invoice in the purchase ledger.
Based on the information specified in the seller's invoice, the commission agent (agent) issues two copies of the invoice. In this document, the intermediary indicates the date of the invoice issued to the commission agent (agent) by the seller, but the commission agent (agent) assigns the number to the invoice independently. In addition, the name, address, tax identification number and checkpoint of the seller are indicated. When filling out the line dedicated to payment and settlement documents, you need to indicate the details of the documents on the transfer of funds in advance by the commission agent (agent) to the seller and by the committent (principal) to the commission agent (agent).
The commission agent (agent) transfers the first copy of the invoice to the principal (principal) along with the goods purchased for him and a certified copy of the seller’s invoice. The principal (principal) registers this invoice in part 2 of the journal of received and issued invoices and, having accepted the values for accounting, in the purchase book. The second copy of the invoice remains with the commission agent (agent). He records it in Part 1 of the log of invoices received and issued. This invoice is not recorded in the sales ledger.
note
if the commission agent applies the simplified tax system and at the same time draws up invoices for the principal for goods purchased for him based on the invoices of sellers, then the principal also has the right to deduct VAT presented by the “simplified” commission agent (letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 30, 2014 No. 03-07-14/48815).
From January 1, 2015, commission agents (VAT payers and non-payers) are obliged to:
- submit to the inspection a VAT return in electronic form, as well as a log of received and issued invoices;
- reflect in the declaration the information specified in the journal of received and issued invoices.
A situation may arise when an agent purchases goods (work, services) for several principals from one seller. In this case, each of the principals will receive a certified copy of the seller's invoice from the agent. And in the invoice issued by the agent to a specific principal, in the column “Quantity (volume)” a smaller quantity of goods is indicated than in the transmitted copy of the seller’s invoice. However, such a discrepancy is not a basis for refusing to accept for deduction by the principal the amount of VAT indicated in the invoice issued to him by the agent (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 14, 2014 No. 03-07-15/11221).
After the acceptance certificate for the intermediary services provided is drawn up and signed by the parties, the commission agent issues two copies of an invoice for the amount of his remuneration. The first copy is transferred to the committent (principal). He records it in part 2 of the journal of invoices received and issued and in the purchases ledger.
The second copy of the commission invoice remains with the commission agent (agent), who registers it in part 1 of the journal of received and issued invoices and the sales book.
When transferring remuneration to a commission agent in the form of an advance payment, the principal must register an invoice from the commission agent in the purchase book.
EXAMPLE 2 LLC "Aktiv" (committent) entered into a commission agreement with LLC "Passive" (commission agent) for the purchase of woodworking machines.
According to the agreement, “Passive” must, on its own behalf, buy four machines for “Active” for a total amount of 118,000 rubles. (including VAT). The amount of commission established by the contract is 5900 rubles. Invoices should be written like this. 1.
“Passive” receives an invoice from the supplier and registers it in part 2 of the log of received and issued invoices.
2.
“Liability” based on the supplier’s invoice is two copies of the invoice in the amount of 118,000 rubles.
He transfers one copy to “Aktiva” along with the machines, the second one is registered in part 1 of the log of received and issued invoices. 3.
“Passive” issues two copies of an invoice for the amount of its remuneration – 5900 rubles.
(including VAT). He transfers one copy to “Aktiva”, the second one is registered in part 1 of the log of received and issued invoices. After signing the acceptance certificate for services under the commission agreement, “Passive” registers this invoice in the sales book. 4.
“Asset” registers both invoices of “Liability” in part 2 of the log of received and issued invoices. In the purchase book, these invoices are registered as follows: · an invoice for the amount of 118,000 rubles. – after the goods are received; · an invoice for the amount of 5900 rubles. – on the day of signing the acceptance certificate. For samples of invoices, as well as entries in the “Asset” and “Liability” purchase and sales books, see Berator
note
From January 1, 2015, the number of invoices drawn up when carrying out transactions under commission agreements and agency agreements is being reduced. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 29, 2014 No. 1279 introduced important changes to the current rules for drawing up invoices, which were approved by Decree No. 1137.
From this date, commission agents (agents) can combine information about all sellers when issuing an invoice to the principal (agent), and principals - about all buyers when issuing an invoice to the commission agent (agent) in one consolidated invoice. This information - the names of counterparties, their tax identification number and checkpoint, location, names of shippers and consignees, details of payment and settlement documents - will need to be entered into the appropriate lines of the invoice, separated by the sign “;” (semicolon).
The best solution for an accountant
Berator is an electronic publication that will find the best solution for any accounting problem. For each specific topic there is everything you need: a detailed algorithm of actions and postings, examples from the practice of real companies and samples of filling out documents. Go to Berator Online – e.berator.ru