Write-off of fuels and lubricants by receipts
Many organizations registered in various fields of activity use vehicles. The goals here can be very different: delivery of raw materials and consumables, delivery of finished goods to the consumer. Writing off fuel and lubricants from gas station receipts is a sore spot for every accountant. This must be done correctly in order to optimize and control costs in this area. Do you want to know how to write off fuel and lubricant expenses using checks? This article provides current standards and requirements and provides practical advice.
Main supporting document
Data from electronic control systems and waybills can be the main confirmation of target fuel consumption. They must contain information that can be used to determine the amount and purpose of fuel consumed.
But in order to include the costs of fuel and lubricants in the tax base, it is necessary to properly confirm the costs of their acquisition. When paying in cash, a gas station cash receipt can be used for this. In a situation where gasoline is purchased using coupons, their stubs perform this function.
A little theory
Fuels and lubricants include a fairly large list of substances: gasoline, gas, diesel fuel, oils, lubricants, brake and coolants. You can purchase them both in cash and by bank transfer. The main advantage is the possibility of reducing taxes. After all, gasoline costs can be taken into account in the cost of goods and services. The Tax Code has removed the restriction, and now this article can account for any percentage, although previously it should not have exceeded 50%. But it is important to arrange everything correctly.
The primary document for writing off expenses for fuel and lubricants is a waybill. It contains technical data of the vehicle, standard and actual fuel consumption, and records the route of movement. The waybill is the basis for writing off expenses for fuels and lubricants. The current legislation establishes mandatory details, as well as several samples for various types of transport (cars and trucks), depending on the range of movement. Each waybill is recorded in a journal. At the same time, regularity is not standardized in any way; PLs can be compiled once every few days or weeks.
You can get fuel at a gas station:
- for cash;
- according to the statement;
- by coupon;
- by payment card.
This can only be done by a responsible person authorized by the organization, usually the driver. In case of payment in cash, he is obliged to receive a cash receipt, which is subsequently attached to the reporting. Funds are issued to the driver in the accounting department in advance. Further, responsible persons are required to provide receipts for fuel and lubricants according to the advance report. They are the documentary evidence of the fact of purchase of fuel. After closing the advance payment report, the driver can receive the next amount in his hands. Each check must contain the following details:
- seller information;
- price;
- fuel volume;
- date of.
An urgent question is how to take into account VAT in receipts for fuel and lubricants. In accordance with current regulations, tax deduction is carried out on the basis of an invoice. If the seller does not issue it, then VAT cannot be taken into account in profit expenses. Thus, ordinary checks, in which the tax is highlighted as a separate line, are not accepted for reporting. Therefore, make sure that the seller at the gas station immediately issues an invoice.
Home Legal advice Where to write off fuel and lubricants without waybills
Rules applied when accounting for fuel and lubricants How is fuel consumption justified? The main document confirming the volume of write-off. Is it possible to write off fuel and lubricants without a waybill? Rules applied when accounting for fuels and lubricants For the purposes of all types of accounting (warehouse, accounting, tax, management), fuels and lubricants (fuels and lubricants) are ordinary inventory items that are subject to generally accepted rules. That is, when purchased, they must be capitalized, and when consumed, written off from accounting. But the volume of capitalization and write-off must be confirmed by documents, i.e., be justified. A peculiarity of the acquisition of fuels and lubricants is that in fact they rarely enter the territory of the person using them, since most often refueling of vehicles is carried out at specialized gas stations located outside this territory, and the fuel is immediately released for use.
Example No. 2: about the absence of a route to the submarine
A similar decision was made by the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region, when the tax authorities wanted to prove that if the PL did not contain information about the route, then the document did not confirm the costs of purchasing fuel and lubricants. The circumstances of the case were as follows.
When justifying expenses, the company provided initial documents confirming that fuel was received from suppliers and the volume of car refueling. In addition, payment orders were presented, as well as expense norms, which were approved by order of the authorities, PL, which contained all the necessary details (confirming mileage), information on fuel consumption, documents for the write-off of gasoline, properly executed.
Having examined the case materials, the court came to the conclusion that the tax authorities did not prove the unreasonableness of the expenses. Lack of information about the route does not serve as a basis for refusal to confirm expenses.
Thus, companies may well include gasoline costs as part of tax expenses based on papers that confirm the purchase of gasoline, as well as a self-developed PL form, even if it does not contain the route. In addition, the PL can be issued for any period – from 1 day to 1 month.
If it does not follow from other documents that the trip was of a non-production nature (for example, based on the director’s instructions made in writing), then the company can take these expenses into account when calculating income tax, even if the trips were made for personal purposes.
Is it possible to write off gasoline without a waybill?
If disagreements with controllers regarding the use of your own standards still arise, then you should go to court. As practice shows, arbitrators take the side of enterprises.
Examples include the decisions of the Federal Arbitration Courts of the Ural (dated June 10, 2002 in case No. F09-1180/02-AK) and Northwestern (dated March 5, 2002 in case No. A56-23095/01) districts. VAT deduction Another problematic issue is the VAT refund when purchasing fuels and lubricants in cash at a gas station.
Attention According to paragraph 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code, an invoice is required to offset the tax. Usually the driver only receives a receipt. Therefore, VAT cannot be refunded, even though the tax amount may be shown as a separate line on the receipt. This opinion was expressed, in particular, by the capital’s tax inspectors (letter from the Department of Taxation in Moscow dated October 16, 2001.
It’s impossible to write off fuel without a waybill
Write-offs of lubricant, brake fluid, and antifreeze are calculated in accordance with approved consumption standards. Fuel consumption rate can be increased by 20%:
- during major repairs;
- when used for five years.
In this case, the consumption of lubricant during major repairs of units equipped on a vehicle is established from one filling tank of the lubrication system.
At the same time, the consumption of brake, cooling, and other types of working fluids depends on the volume of fuel filled and refueling in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
The procedure for accounting and writing off fuel and lubricants according to waybills in 2017-2018
Important For example, this may be applicable to estimating the fuel consumption of a business delivery service that transports workers to and from work on the same route day after day. The number of such trips is always under control. Accordingly, taking into account their unambiguous length and the link to each of them with a volume of fuel in a fixed amount, calculated according to the standards, the total volume of write-off will also be justified.
Thus, there are still certain options that allow you not to use a waybill to justify the amount of fuel to be written off, but there are not many of them. And you will definitely have to explain them to the inspectors.
But in a situation where a waybill has been issued, unnecessary questions during checks can be avoided. Read about whether the volume of consumed fuel and lubricants affects the amount of compensation for the use of personal vehicles by an employee.
Write-off of fuels and lubricants according to waybills
In the second, an agreement is concluded between the enterprise and the employee for the use of personal transport. The transaction is based on the instructions of Article 188 of the Labor Code, which sets out the conditions and procedure for paying compensation and compensation to the employee.
Info The contract is concluded with the mutual consent of the interested parties, but restrictions are introduced on the amount of compensation for transport depending on its make, model and modification. Fuel and lubricants are written off in accordance with the standards established by the enterprise.
And in conclusion, it should be noted that in tax accounting fuels and lubricants are allowed to be written off in the amount of funds actually spent. But they are considered justified if the costs do not exceed standard values.
An enterprise has the right to use the standards of the Ministry of Transport, but at the same time it can develop its own fuel consumption standards for each type of transport it has.
Writing off gasoline for business trips
In accordance with Art. 166 of the Labor Code, a business trip is understood as a trip by an employee by order of management for the required period for the purpose of fulfilling an official assignment outside of regular work. Traveling work is not considered business trips. Thus, business trips do not include trips by drivers who carry out freight transportation.
When traveling on a business trip, including when the director uses a personal car for business purposes, he is compensated for travel expenses, rental housing and additional expenses (per diems and other expenses that are carried out with the permission of the employer). This is stated in Art. 168 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Reimbursement is made on the basis of the Instruction of the USSR, the State Committee for Labor and the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions No. 62 “On official business trips within the USSR.” However, this document does not provide for payment for fuel. But its cost can be included in travel expenses for travel.
Confirmation of the purchase of gasoline during the director’s business trip in a personal car is the PL. Based on its data, the cost and amount of gasoline that was consumed during the business trip is determined. Upon his return, the employee must submit documents on the purchase of fuel along with an advance report. These are cash receipts and gas station reports on gasoline filled. According to paragraphs. 5 paragraph 7 art. 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in tax accounting fuel costs are recognized on the day when the report is approved.
Is it possible to write off fuel and lubricants without issuing waybills, organization on the simplified tax system - 15%.
Primary documents are substantiated by the demand invoice, gas cards, gas station receipts for the actual volume of fuel used. An example of writing off fuel and lubricants using waybills. To complete the write-off, you should create a document “movement of materials”, drawn up using invoices.
The waybill must be filled out in accordance with the accepted fuel consumption standards that were consumed by an individual vehicle. To complete the write-off procedure, fill out:
- debit of account 1 401 01 272 “Consumption of inventories”;
- account credit 1 105 03 440 “Reduction in the cost of fuels and lubricants.”
Each enterprise has its own distinctive features, determined by the branch of production, which belongs to a separate sector of the economy.
Its activities must be fully accounted for in accounting.
How to write off fuel and lubricants if the organization does not keep waybills
It is among the primary documents. It indicates the route, its total mileage, the amount of fuel at the beginning of the working day and at the end of it. As a rule, the difference in fuel volumes is written off at its actual cost. Costs must be justified and not exceed established fuel consumption standards. As for income tax accounting, the cost of fuel and lubricants in accordance with Article 254 of the Tax Code can be included in material costs.
But they can be classified as other expenses in accordance with the requirements of Article 264 of the Tax Code. To avoid questions regarding the amount of fuel consumed, certain types of standards must be applied.
The waybill must be issued on a form with standard form No. 3, which was approved by a resolution of the State Statistics Committee. Its publication was made on November 28, 1997 under number 78. Although an enterprise can develop its own form, which is also not prohibited.
Legal norms
If difficulties arise when writing off fuel, you can refer to the following legislation:
- Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated June 14, 2008 No. AM-23-r introduced recommendations for rationing the consumption of fuels and lubricants.
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 6, 2010 No. 162n approves the chart of accounts for budget accounting and contains explanations for its application.
- Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicates that expenses can be taken into account for taxation if they are confirmed and due to production needs.
- Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation confirms that expenses for all types of fuel and lubricants can be taken into account when calculating income tax.
- Part 4 art. 9 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” determines the list of necessary documents for writing off fuel and lubricants.
- The requirements for issuing a waybill are specified in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 6, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/6700.
- To clarify the list of mandatory details of primary documents, you can refer to Order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia No. 152.
- The Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 16, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/354 states that printouts of data from electronic control systems can be used to justify the costs of fuels and lubricants.
- Explanations of the frequency with which documents must be drawn up so that they can be used as supporting evidence are contained in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 16, 2006 No. 03-03-04/2/77.
- You can refer to the Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 08/03/2010 No. 03-07-11/335 if you have problems with VAT deduction.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 745 and Letter of the Federal Tax Service No. 20-12/29007 can be useful when asking questions about justifying fuel costs.
It is worth clarifying that the rules related to the write-off of inventories are very numerous. The above list is not exhaustive.
How to write off gasoline expenses
The option of concluding an agreement with a vehicle refueling company to pay for fuel and lubricants non-cash using special cards cannot be ruled out. At the end of the past month, the gas station provides complete information about the volume of fuel, its cost, which was supplied by it using the fuel card. Capitalization is carried out to account 10 by a material accountant or an individual account of the second order is opened. The consumed amount of fuel and lubricants is written off on the following accounts:
- 20 “Main production”;
- 26 “General business expenses”;
- 44 “Sales expenses”.
The choice of account remains with the enterprise, which must take into account the specifics of production activities, technical characteristics, make and model of individual vehicles. In such a situation, fuel is written off based on the waybill filled out by the driver. A. Petukhov, auditor Vehicles, as you know, require constant “gasoline investments”. To justify such expenses, you need to properly prepare the documents.
One of them is a waybill. Daily rigmarole? The form of the waybill is given in the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated November 28, 1997 No. 78. It also talks about responsibility for the correct execution of the document.
It is borne by the director of the company, as well as employees who are responsible for the operation of vehicles and participate in the preparation of the waybill. For entrepreneurs, the form of waybill was approved by order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated June 30, 2000.
№ 68.
When preparing a document, you need to fill out all the details, indicate the serial number, date of issue, and affix the organization’s seal. In addition, it is necessary to record each point the vehicle travels (letter from Rosstat dated February 3, 2005.
No. ИУ-09-22/257).
Where to write off fuel and lubricants without waybills
Fuel and lubricants are a type of inventory to which the usual rules for accounting for inventory and materials apply: they must first be capitalized and then written off, justifying the amount of write-off. What complicates fuel accounting is that, as a rule, it is purchased outside the location of the vehicle owner (legal entity or individual entrepreneur), immediately entering the tank of a working car, and must be taken into account in relation to each unit of the car.
The amount of write-off is justified when the amount of fuel consumed is determined in relation to the nature of the auto work performed according to the fuel consumption standards corresponding to this work. Consumption rates are developed by the owner independently or taken from those recommended by the Ministry of Transport. And the Russian Ministry of Finance considers the waybill to be the only document capable of confirming the amount of work done on the car. Therefore, the financial department considers this document the most suitable for justifying the volume of fuel and lubricants being removed from the register and indicates that its absence leads to the emergence of income subject to personal income tax for an individual using official transport without a waybill (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 11, 2014 No. 03-04 -05/28243). Is it possible to write off fuel and lubricants without a waybill? Is it possible to write off fuel and lubricants without waybills? The Ministry of Finance admits (letter dated June 16, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/354) that the amount of work performed can be confirmed in another way. For example, data from the GLONASS system or other similar systems that allow you to reliably determine the path taken by the car. In addition, it will not be necessary to have a waybill if the route is strictly defined and does not allow deviations.
Updated fuel consumption standards.
All types of fuel are written off based on their actual consumption, but not higher than the approved fuel consumption standards.
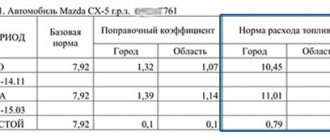
The consumption standards for fuel and lubricants in road transport are established by Methodological Recommendations put into effect by Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated March 14, 2008 No. AM-23-r (hereinafter referred to as Order No. AM-23-r, Methodological Recommendations). According to these recommendations, the fuel consumption rate in relation to road transport implies the established value of the fuel consumption rate when operating a vehicle of a specific model, brand or modification. The standards are intended for calculating the standard value of fuel consumption at the place of consumption, for maintaining statistical and operational reporting, determining the cost of transportation and other types of transport work, planning the needs of organizations to provide petroleum products, for calculating the taxation of enterprises, implementing a regime of economy and energy saving of consumed petroleum products, conducting settlements with vehicle users, drivers, etc.
It is worth noting that from April 6, 2022, these standards have been updated for some cars and trucks (buses, vans) of domestic production and the CIS countries, which have been produced since 2008. Also, from this date, the new edition contains the maximum values of winter surcharges to fuel consumption standards for the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and their parts. The changes were made by Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated 04/06/2018 No. NA-51-r.
Are autonomous institutions obligated to apply the fuel and lubricants standards established by Order No. AM-23-r? To be guided by Order No. AM-23-r, the following is prescribed:
Ministry of Justice - for the purpose of organizing the operation of vehicles (Letter dated September 21, 2009 No. 03-2609);
Ministry of Finance - when determining the validity of expenses incurred for the purchase of fuel (letters dated January 27, 2014 No. 03-03-06/1/2875, dated January 30, 2013 No. 03-03-06/2/12, dated June 3, 2013 No. 03-03 -06/1/20097, dated 09/03/2010 No. 03-03-06/2/57, dated 01/14/2009 No. 03-03-06/1/6).
At the same time, it should be taken into account that the norms established by Order No. AM-23-r are advisory in nature, and failure to comply with the procedure provided for therein does not entail the application of administrative liability measures and budget coercive measures, orders to eliminate violations of budget legislation (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 13.12 .2013 No. 02-10-010/55111).
If Order No. AM-23-r does not establish fuel and lubricant standards for a vehicle used in an institution, how can fuel consumption be justified? In accordance with paragraph 6 of the Methodological Recommendations for models, brands and modifications of automobile equipment for which the Ministry of Transport has not approved fuel consumption standards, heads of local administrations of regions and organizations can put into effect by their order standards developed on individual applications in the prescribed manner by scientific organizations, carrying out the development of such standards using a special program-method. Before the adoption of a local act approving the standards, the institution can be guided by the relevant technical documentation and (or) information provided by the car manufacturer (letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 11, 2012 No. 03-03-06/4/71, dated June 10, 2011 No. 03-03 -06/4/67).
How to write off fuel and lubricants without waybills sample
If the enterprise is not a motor transport enterprise, then it is not required to draw up a daily waybill. Each enterprise has the right to set the frequency of filling it out, based on its production activities - daily, every ten days or monthly.
The only condition is the correct justification for the consumption of fuel and lubricants, the possibility of determining it in order to write it off on the basis of the waybill. Rules The enterprise should decide on the accounting method in order to be able to write off consumed fuel.
As a rule, the driver refuels the vehicle himself using the funds allocated for these purposes, after which he submits an advance report to the accounting department of the enterprise. He encloses a gas station receipt for the purchase of fuel from him.
The material accountant credits fuel to account 10 “Materials”.
The concept of fuels and lubricants
Let's start by looking at the very concept of “fuel and lubricants”, what it includes.
Explanation of fuels and lubricants - “fuels and lubricants”. From the name it is clear that this includes not only fuel, but also related materials necessary for the normal functioning of the vehicle.
Fuel and lubricants include:
- All types of fuel (gas, diesel, gasoline);
- Lubricants (oils, lubricants used in the process of repair, maintenance and operation of vehicles);
- Brake and coolant fluids.
The procedure for writing off fuels and lubricants
Fuels and lubricants are written off as expenses based on so-called standards. What are these standards and where do you get them?
First of all, it should be noted that there are standards for the write-off of fuel and lubricants established by the Russian Ministry of Transport. But the use of these standards is not necessary; the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows you to develop your own standards for the consumption of fuel and lubricants and use them for write-off.
Everything is clear with the standards approved by the Ministry of Transport; take the established standard for writing off fuel and other related materials for your type of transport and write it off.
If you want to develop your own standards, then read below.
★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased
If you have not found the answer to your question, then you can get an answer to your question by calling the numbers ⇓ Free legal advice Moscow, Moscow region call
One-click call
St. Petersburg, Leningrad region call: +7 (812) 317-60-16
One-click call
From other regions of the Russian Federation call
One-click call
Calculation of fuel consumption rates
Calculation of the write-off rate for fuel and lubricants can be done in two ways:
- Use the technical documentation available for the vehicle, on the basis of which to develop standards for the use of fuel and lubricants depending on seasonality, time of year (winter fuel consumption is significantly higher than summer), it is also important to take into account road congestion.
- Establish standards based on an analysis of the actual use of transport and measurements. This method is used much more often than the first, so we will analyze it in more detail.
How to correctly measure fuel consumption?
The first step will be to create a commission to monitor correct measurements.
Measurements of fuel use are carried out as follows: the empty tank of the vehicle is filled to the maximum with fuel, the amount of fuel filled is noted, and the speedometer data is recorded. After this, the vehicle is used in normal mode until the fuel tank is empty, after which the speedometer data is again recorded. By subtracting the initial speedometer reading from the last one, the car's mileage is obtained - the number of kilometers that the vehicle managed to travel on a full tank of fuel. Now the fuel consumption per 1 km is calculated, for which the volume of fuel poured is divided by the distance traveled by the car using this fuel. This will be the norm for fuel consumption.
Since the conditions under which a vehicle is used can vary significantly, it is necessary to take measurements in different conditions. When measuring fuel consumption, you need to take into account:
- time of year (take measurements in the cold and warm seasons);
- traffic congestion;
- How difficult is the traffic on the roads (presence of traffic jams);
- idle vehicle with the engine running.
Having carried out measurements under various conditions, several standards are obtained that should be followed in the process of writing off fuel as expenses.
In addition, the enterprise can take a slightly different route: take measurements for a standard situation, and develop correction factors for various deviations of operating conditions from the norm.
The results obtained must be approved by an act signed by the members of the previously created commission.
When determining and setting for yourself standards and limits for the use of fuel and lubricants, you need to remember that the obtained values must be economically justified and not overestimated. You should not artificially increase consumption standards, because the Tax Inspectorate may have questions that are not very pleasant for you.
We have sorted out the calculation of fuel consumption rates, now let’s look at how accounting for fuels and lubricants occurs at an enterprise, what transactions need to be made during operation.
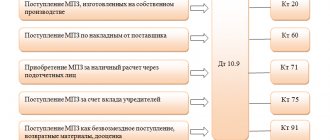
Accounting for fuel and lubricants and wiring
In accounting, fuels and lubricants are written off either as sales expenses (for trade organizations) or as production costs (for manufacturing organizations).
Thus, the accounting account to which the costs of fuel and lubricants should be attributed is 44 or 20 (23, 26). The debit of these accounts corresponds with the credit of the materials accounting account (account 10), on which a separate sub-account is opened for accounting for fuel and lubricants.
Posting for write-off of fuels and lubricants:
D20, 23, 26 (44) K10.3 – the cost of used fuels and lubricants is written off as enterprise expenses.
The 20th account is used if the transport is used for work needs, for example, delivering goods to customers.
The 23rd account is usually used by large enterprises with a larger number of vehicles.
Fuel and lubricants for vehicles used for business purposes are written off to the 26th account.
It would be logical to make an entry for writing off fuel and lubricants for the amount of fuel actually consumed, but, as a rule, it is very difficult to determine the exact amount of fuel used, which is why fuels and lubricants are written off according to established standards.
Fuel and lubricants are accepted for accounting in accounting on the 10th account.
Materials are purchased, as a rule, in cash or by bank transfer. In the first case, cash is given to the driver for reporting; after purchasing the necessary fuel and lubricants, the driver reports on the amount spent using an advance report. The driver's remaining money is handed over to the company's cash desk. When purchasing materials by bank transfer, non-cash funds are debited from the company's current account.
The wiring looks like this:
- D71 K50 – cash issued on account.
- D10.3 K71 - materials purchased for cash are accepted for accounting.
- D60 K51 – payment is transferred to the supplier.
- D10.3 K60 – materials purchased by bank transfer are accepted for accounting.
- D19 K60 – VAT on purchased materials is allocated (if allocated).
Any posting is carried out only on the basis of a supporting document.
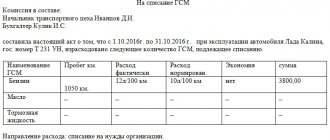
Posting for the write-off of fuel and lubricants is carried out on the basis of a waybill and a certificate for the write-off of fuel and lubricants. The waybill can be used to write off fuel as an expense, and the act can be used to write off other lubricants.
Waybill samples:
- passenger car;
- truck.
The posting of acceptance of fuel and lubricants for accounting is carried out on the basis of an advance report and a document confirming the fact of payment, for example, a check (for cash payments) or a delivery note, an invoice and documents confirming payment (for non-cash payments).
In addition to the above, accounting for fuels and lubricants at an enterprise also includes conducting periodic inventories (daily, weekly, monthly - at the discretion of the organization itself).
In order to check the remaining fuel with the accounting data, you can go in two ways.
Add gasoline or other used fuel into the car tank until the tank is full, then subtract the added volume from the volume of the full tank, then check the resulting value with the data in account 10.3.
Drain the remaining fuel from the tank, measure its quantity and compare it with the accounting data on the 10th account.
Rate the quality of the article. We want to be better for you:
If the enterprise is not a motor transport enterprise, then it is not required to draw up a daily waybill. Each enterprise has the right to set the frequency of filling it out, based on its production activities - daily, every ten days or monthly.
The only condition is the correct justification for the consumption of fuel and lubricants, the possibility of determining it in order to write it off on the basis of the waybill.