Issuance of reports from the cash register
The first possible way to issue money to a business traveler is to issue cash from the cash register.
Money is issued by drawing up an expenditure cash order based on an application from an employee approved by the manager, or an order from the director of the enterprise. How to properly process the issuance of money from the cash register, what requirements must be met, read the article “How to fill out a cash expense order (RKO)?”
The cash order will reflect the correspondence of the accounting accounts:
Dt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” (71-1, 71-2) Kt 50 “Cash” (50-1).
The use of subaccounts depends on the adopted working chart of accounts (clause 4 of PBU 1/2008).
To ensure consistency between the work of the accountant and the computer accounting programs used, it is advisable to approve the subaccounts recommended by the developers. For example, it is advisable to count. 71 use subaccounts:
- 71-1 - for payments in rubles;
- 71-2 - in currencies.
You can open sub-accounts for account 50:
- 50-1 “Organization cash desk”;
- 50-2 “Operating cash desk”;
- 50-3 “Money documents”.
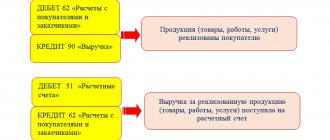
When issuing money from the cash register, the posting will look like this: Dt 71-1 Kt 50-1.
When traveling abroad, it is allowed to issue money in foreign currencies. Reflect the receipt of money to the cash desk from a foreign currency account by posting Dt 50 Kt 52.
In this case, it is advisable to create a separate sub-account for account 50 for each type of currency. Reflect the issue from the cash desk in foreign currency for a foreign business trip by posting Dt 71-2 Kt 50 (sub-account corresponding to the currency).
If funds for a business trip are issued in foreign currency, then exchange rate differences appear. Exchange rate differences will arise if the date of receipt of currency at the cash desk and the date of its issue do not coincide. It is necessary to determine the difference between the amounts recalculated at the official rate for each date - the date of receipt of money in the cash register and the date of its issue.
Reflect the positive exchange rate difference in accounting by assigning it to other income of the organization: Dt 50 (corresponding subaccount) Kt 91-1.
The negative difference goes to the organization's expenses: Dt 91-2 Kt 50 (corresponding subaccount).
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to take into account the costs of renting an apartment for employees on a business trip. Get free demo access to K+ and go to the Ready Solution to find out all the details of this procedure.
Travel expenses under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
When sending an employee on a business trip, the organization uses the simplified tax system to calculate travel expenses in the same way as under the OSNO. Having reimbursed the employee for all travel expenses stipulated by law, the enterprise has the right to reduce its income by them for tax purposes, subject to documentary confirmation and economic justification of the expenses incurred (subclause 13, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A distinctive feature is the date on which travel expenses are included in expenses. Since accounting for expenses on the simplified tax system is carried out on a cash basis, the date of recognition of expenses is considered to be the date of approval of the advance report. However, if the employee has spent his own funds and the company reimburses him for them, the reimbursed payments should be included in the book of income and expenses at the time of issuing money from the cash register (Clause 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
One more nuance. According to the Ministry of Finance, an individual entrepreneur without employees on a simplified basis cannot take into account the costs of his own trips. The department justifies this position as follows: a business trip is a trip by an employee at the direction of the employer. But an individual entrepreneur does not have an employer, just as he himself cannot be his own employee (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated February 26.
For more information about the recognition of expenses under the simplified tax system, read the material “List of expenses under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses””.
Travel allowances are transferred to a personal card
Currently, non-cash payments using bank cards are becoming widespread. Issuing travel allowances is no exception. It is also possible to transfer accountable amounts to an employee’s salary card (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, Treasury of the Russian Federation dated September 10, 2013 No. 02-03-10/37209, No. 42-7.4-05/5.2-554).
In accounting, the transfer of travel allowances should be reflected by posting Dt 71-1 Kt 51 - transfer of money for reporting.
You can learn about the important nuances of such an operation from the article “Transferring a sub-report to an employee’s card from a current account.”
Using a special card account
A posted employee can be issued a corporate bank card opened in his name - debit or credit.
Dt 55 “Special bank account” Kt 51 - transfer of funds from the current account to a special account.
If the card account is opened in foreign currency, then the transfer occurs from the foreign currency account: Dt 55 Kt 52.
How to reflect in the organization's accounting travel expenses associated with sending an employee on a business trip abroad if he independently purchased foreign currency to pay for travel expenses (hotel payment)? Read the answer to this question in ConsultantPlus by receiving trial demo access to the legal reference system. It's free.
It is recommended to open sub-accounts for account 55 to account for settlements in rubles and for accounting in foreign currency.
As funds are spent on the debit card, the movement of money should be reflected by posting Dt 71 Kt 55 - money was used (withdrawn) for travel expenses.
If you use a credit card opened on the basis of a bank loan agreement, then the crediting of money according to the credit line to the card account is reflected as follows: Dt 55 Kt 66 (67)
Also, as funds from the credit card are spent, we make an accounting entry Dt 71 Kt 55.
The interest accrued by the bank for the use of loan funds is reflected in the entry Dt 91-2 Kt 66 (67).
Salary during a business trip
The business trip period is paid not in the same way as regular work, but according to average earnings (Article 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Whatever the work schedule, average earnings are calculated based on the actual accrued wages and actual time worked for the 12 calendar months preceding the month when the business trip began.
Example
The employee was on a business trip from June 21 to June 25, 2022 (five working days).
All payments received by the employee for the period from June 2022 to May 2022 inclusive (12 months) are shown in table 1. Table 1
Payments to the employee for the period from June 2022 to May 2021
Month of billing period Type of payment Amount (rub.) June 2020 salary 30 000 July 2020 salary 30 000 August 2020 salary 30 000 September 2020 salary 30 000 October 2020 salary 30 000 November 2020 salary 30 000 December 2020 salary 5 714 sick leave 19 000 January 2021 salary 40 000 February 2021 salary 40 000 March 2021 salary 40 000 April 2021 salary 40 000 May 2021 salary 40 000 Total: 404 714 To calculate the average earnings, the accountant found out that out of the 12 months preceding the business trip, the employee worked only 11 fully, and from December 3 to December 25, 2022 (17 working days) was on sick leave. Sickness time must be excluded from the calculation period, and temporary disability benefits will not be included in the calculation. As a result, the average earnings were 385,714 rubles (404,714 - 19,000).
The accountant then calculated the number of working days in the billing period. It was 249 days. The number of working days taken into account when calculating average earnings is 232 (249 - 17). The average daily earnings is 1,662.56 rubles (385,714 rubles: 232 days). Salary during a business trip - 8,312.8 rubles. (RUB 1,662.56 x 5 days).
Note that some companies pay for business trips not according to average, but according to actual earnings. This option, although not entirely correct, is acceptable. The main thing is that the actual earnings during the business trip are not less than the average earnings, because otherwise the employee’s rights will be violated. To prevent this from happening, it is better to compare two salary values for each business trip: the first - based on average earnings, the second - based on actual earnings. And if the first value is not greater than the second, you can pay for the business trip based on the salary.
If a person worked on a business trip on his day off, and this is reflected in the timesheet, then such work must be paid double. There is an alternative option: at the employee’s request, provide payment in a single amount and give additional days off (Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Travel allowances issued in cash documents
Traveler's checks may be issued to posted employees. A traveler's check is an obligation of the issuer to pay the amount of the check to its owner. Accounting for traveler's checks is kept in account 50-3 “Cash documents”. The following entries must be made in accounting:
- Dt 50-3 Kt 60 (76) - purchase of traveler's checks;
- Dt 71 Kt 50-3 - traveler's checks issued.
Unfortunately, the use of traveler's checks is not common in the Russian Federation. They can only be exchanged for money, but even then not in all financial institutions. Therefore, this type of financial document is most convenient to use when traveling on business trips abroad. The use of traveler's checks as a means of payment has its advantages - both in the simplicity and safety of their use.
The organization can purchase and issue travel documents to the posted employee. The accounting of travel documents is carried out similarly to the accounting of cash checks in account 50-3.
What documents must be completed when sending an employee on a business trip?
In order to transfer daily allowance, the employee needs a reason, namely being sent on a business trip. Otherwise, such transfers of money from the employer will be recognized as income with subsequent calculation of personal income tax. Let's look at how to pay for time on business trips and what documents you need to prepare for this. Thus, when traveling around Russia, the document confirming the date of the business trip is usually a business trip order. In this case, the amount of daily payments must comply with the organization’s standards approved in the collective agreement or in the regulations on business trips. For foreign trips to the CIS countries and the Customs Union, as in Russia, a business trip order is issued. And when moving to other countries, a mark from the border guards in the passport and a corresponding order from the director of the enterprise are sufficient. As for the amount of payments, days of travel in Russia are paid according to domestic standards. Traveling on a business trip on the days of crossing the border - according to foreign ones. And, accordingly, the days of travel through a foreign country are according to foreign standards, and the dates of crossing the border on the way back are according to Russian standards.
How the writing off of travel expenses from accountable persons is taken into account in the accounts
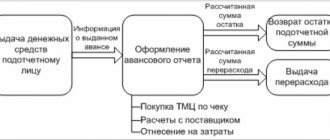
After the end of the business trip, the employee reports for the accountable amounts received. To do this, he draws up an advance report or another document, independently finalized and approved in the accounting policy.
From November 30, 2020, the organization can independently set the deadline for the accountable person to submit the advance report. The previous requirement that the JSC must be submitted no later than 3 working days after the expiration date for which the reports were issued, or from the date of return to work, has been cancelled.
Read everything about advance reports in the article “Features of advance reports in accounting.”
If there is an unused balance of travel allowances, the balance should be returned to the cash desk and reflected in the entry Dt 50 Kt 71.
The unspent balance can be transferred from the employee’s card to the organization’s current account: Dt 51 Kt 71.
The return of the balance to a special card account is reflected by posting Dt 55 Kt 71.
Travel expenses can be written off as follows:
- Dt 08 (10, 41...) Kt 71 - non-current assets, inventory and materials were purchased;
- Dt 19 Kt 71 - the amount of input VAT is reflected;
- Dt 20 (23, 26...) Kt 71 - expenses are charged to the cost of products (services, works);
- Dt 44 Kt 71 - expenses are recognized as commercial expenses or expenses for the main activities of a trading organization;
- Dt 91 Kt 71 - non-production expenses were approved and written off.
You can study this topic in more detail in the article “Accounting for settlements with accountable persons.”
Find out how to take into account travel expenses under the simplified tax system in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
Solving the problem of calculating travel expenses and mutual settlements with accountable persons
Many companies and individual entrepreneurs, in the course of their activities, are faced with the need to send employees on trips away from their place of permanent work in order to carry out certain assignments.
Such a trip is called a business trip (Article 161 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the employer is obliged to preserve for the posted worker his workplace, average earnings, and also reimburse the costs incurred by him, the list of which is established by law. In order to correctly and reasonably account for travel expenses, the accountant must have properly executed documents confirming the fact of the business transaction.
Accounting for travel expenses can be divided into 2 main stages:
- preliminary calculation and issuance of money on account to the business traveler;
- approval of the employee’s advance report on the amounts spent.
In order to pay an advance to an employee for business trip expenses, the accountant needs to calculate it based on internal documents:
- an order or instruction from the manager to send a company employee on a business trip, which indicates the employee’s full name, duration and purpose of the trip (to perform a work assignment);
- a written decision of the manager on an employee’s trip on a business trip using official or personal transport (if accepted).
Based on what is written in these two local documents, as well as the business travel regulations developed and adopted by the company, the accountant calculates a cash advance, which includes:
- the cost of tickets for travel to and from the business trip;
- payment for hotel accommodation;
- daily allowance for each day you are on a business trip;
To learn whether to pay an employee a daily allowance for days on the road if the ticket includes meals, read the material “A business trip ticket includes meals - should an employee be paid a daily allowance for days on the road{q}.”
- other expenses permitted by management.
Is it possible to take into account taxi expenses of a business traveler when taxing, read the article “Reflecting taxi expenses in tax accounting (nuances).”
The Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation considers it possible to take into account in tax expenses the special clothing issued to employees sent to the Far North. Read more in the publication “Warm clothes for a northern business trip can be written off as expenses.”
The daily allowance does not depend on travel and housing costs. This separate expense item is defined as the funds needed to perform work and stay during a business trip (for food).
Daily allowances are not limited by law, and every commercial organization has the right to establish their amount by internal act. At the same time, you need to remember that there is a limit above which personal income tax must be calculated and withheld from the employee, as well as insurance premiums must be calculated. In 2019-2020, this limit is 700 rubles. per day for business trips in Russia and 2,500 rubles. - for business trips abroad.
Daily allowances are paid for all days on a business trip, including weekends and non-working holidays, as well as travel days and forced stops (clause 11 of the regulation on the specifics of sending employees on business trips, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749). The employee does not need to report for the use of daily allowances.
Other expenses may include expenses for mobile communications, the Internet, and payment for goods and services necessary for work.
The employee receives an advance at the organization's cash desk or by non-cash transfer to a card and, before the end of 3 days after returning to his permanent place of work, reports to the accounting department for the money received.
See also: “We arrange and pay for business trips.”
A business trip abroad is processed in the same way as in Russia, only it has some features:
- Additional expenses are added for obtaining a visa, a foreign passport, consular and other fees necessary for traveling abroad (subclause 12 of Article 264 of the Tax Code).
- The daily allowance limit, exempt from personal income tax and contributions when traveling to another country, is 2,500 rubles.
- When traveling abroad, the time for calculating daily allowances is determined by travel documents, and in case of their absence, by travel documents or by supporting documents of the receiving party (clause 7 of the regulations on business trips No. 749).
- Primary documents drawn up in a foreign language must be translated into Russian (clause 9 of the Accounting Regulations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n).
If an employee purchased currency on his own, then when drawing up a report he must attach certificates of purchase. If such a certificate is not available, then the expenses will be recalculated at the rate of the Central Bank at the time of receipt of accountable money (clauses 5, 6, 7 of PBU 3/2006).
After the report is approved:
- the balance of the advance, returned in foreign currency, is credited to the cash desk with conversion into rubles at the official exchange rate on the date of receipt of money;
- overexpenditure made in foreign currency is issued to the employee in rubles, recalculated at the exchange rate on the day the advance report is approved.
For daily allowances in foreign currency, that part of them that is subject to personal income tax must be recalculated into rubles at the rate on the last day of the month in which the advance report was approved (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 1, 2016 No. 03-04-06/64006).
IMPORTANT! If the company’s local regulatory act specifies the amount of daily allowance in foreign currency and pays the employee in rubles, then there is no need to recalculate (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 22, 2016 No. 03-04-06/23252).
An approved advance report - in Form AO-1 or an independently developed form - with documents attached to it confirming expenses incurred in the interests of the company will serve as the basis for reflecting these expenses in accounting.
We suggest you read: How to return incorrectly credited amounts to a client’s account
What should an accountant recalculate and check?{q}
The accountant, when checking the advance report, makes an adjustment calculation of daily allowance (if the business trip was shorter or longer than planned) on the basis of travel tickets, from which he takes the departure date and return date. The departure day is considered to be the current day if the departure time on the tickets is before 24:00 inclusive, and the next day is from 00:00.
REMINDER! If the trip was made by personal transport, then the daily allowance is calculated according to the waybill and accommodation invoices, according to which the accountant can track the date of arrival and departure to calculate the day on a business trip.
If there are no travel documents, as well as papers confirming the fact of residence at the place of business trip, the employee provides an official note about the actual length of stay on the business trip, confirmed by the record of the receiving party. The responsible person of the organization to which the employee was sent must put a mark on the date of arrival and departure (clause 7 of the Regulations on business trips dated October 13, 2008 No. 749).
If an employee has used official or personal transport and needs compensation for its use and gasoline, then he must submit a memo, a waybill that calculates the mileage traveled, and attach invoices and receipts for the purchase of fuel. The possibility of reimbursement of such expenses should be provided for in the accounting policy.
Housing rental documents confirming payment must also be checked: checks, receipts, rental agreement, receipt from the owner of the house or apartment. During the verification, the amount actually paid and confirmed is taken into account and approved.
For information about the specifics of taxation in settlements with accountable persons, including when sending employees on a business trip, read the article “Procedure for taxation of settlements with accountable persons”.
Let's consider what entries in 2019-2020 for accounting for travel expenses are provided for by the Chart of Accounts.
Dt 71 Kt 50, 51 - money was paid for travel expenses.
Dt 20, 23...44 Kt 71 - daily allowance, travel tickets (without VAT), hotel bill (without VAT);
Dt 19 Kt 71 - VAT for travel and housing is reflected;
Dt 68 Kt 19 - accepted for deduction of VAT for transport and accommodation;
Dt 20, 44, 91-2, 08, 10... Kt 71 - other expenses are taken into account;
Dt 50 Kt 71 - return to the organization’s cash desk the balance of the advance;
Dt 71 Kt 50 - compensation for overruns.
Dt 70 Kt 68 - personal income tax is withheld from daily allowances exceeding the limit.
An advance for a business trip abroad can be issued in rubles or foreign currency. In order to receive cash currency, an organization can:
- withdraw money from your foreign currency account;
- buy currency from a servicing bank;
- give the employee money to buy currency at the bank.
An advance can also be issued non-cash by issuing a plastic bank card to the employee.
Situation: is it possible to issue an advance from the cash desk for a foreign business trip in foreign currency{q}
There is no clear answer to this question in the legislation.
Currency legislation allows payments in foreign currency related to business trips abroad (Clause 9, Part 1, Article 9 of Law No. 173-FZ of December 10, 2003). However, nowhere does it say that payments in foreign currency can be made through the cash register. Moreover, Part 2 of Article 14 of the Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ states that resident organizations can make payments in foreign currency only through bank accounts.
The Bank of Russia, in letter dated July 30, 2007 No. 36-3/1381, expressed the opinion that issuing a foreign currency advance for foreign business trips from the cash desk does not contradict currency legislation (clause 9, part 1, article 9 of the Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ). However, in letter dated August 31, 2007 No. 12-1-5/1970, the Bank of Russia expressed the opposite point of view.
Since transactions with currency must be carried out through bank accounts, issuing cash currency as an advance for a business trip abroad does not comply with the law (Part 3 of Article 14 of the Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ). This conclusion was made in relation to a foreign representative office, but it can also be extended to Russian organizations.
Payment of daily allowances
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description |
| 71 | 50 (51) | Issuance of funds from the cash register (transfer to a bank card) for travel expenses |
| 20 (26, 44, etc.) | 71 | Reflection of travel expenses in production or sales expenses |
| 71 | 50 (51) | Reimbursement to an employee for overexpenditure on travel expenses from the cash register (account) |
| 50 | 71 | Refund of unspent funds paid for travel expenses |
Example
Results
The posting when issuing money to the travel expenses account will depend on the source of the issue - be it cash, non-cash money, cards or monetary documents.
Examples of transactions for settlements with accountable persons are given in the article “Procedure for settlements with accountable persons - transactions”.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.