List of non-contributory travel expenses
Employers who regularly or occasionally send employees on business trips may have a question: are business trips subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions?
See details about personal income tax on travel expenses in 2020.
And within the framework of this material, we will consider the issues of taxation of travel expenses with insurance premiums.
The concept of “travel expenses” is general. It combines various types of expenses, each of which has its own characteristics of being included in the contribution base or excluded from it. Therefore, there is no clear answer to the question of whether travel expenses are subject to insurance premiums.
For all listed expenses, except for daily allowance, a single rule applies: they are not subject to contributions if they are actually incurred and documented.
Next, we will tell you under what conditions certain types of travel expenses are subject to insurance premiums.
Daily allowances above the norm in 6-NDFL: examples
Let's consider various situations of drawing up calculations with excess daily allowances.
- Is it possible to withhold personal income tax after the advance report is approved, but until the end of the month?
Example
The employee was on a business trip within the country for 5 days, from December 1 to December 5. On November 30, he received an advance payment for the trip, including a daily allowance of 1,300 rubles. per day, total 6,500 rubles. The amount of daily allowance above the norm was (1,300 – 700) × 5 = 3,000 rubles. On December 7, the employee submitted the advance report for approval. On December 20, the company paid an advance on wages, the final payment of wages was made on December 30.
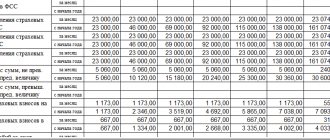
In the calculation for 2022, daily allowances are included in the following lines:
| Line number | Meaning |
| 110 | 3 000 |
| 140 | 390 |
| 160 | 390 |
| 021 | 10.01.2022* |
| 022 | 390 |
* The tax payment deadline is the business day following the date of payment of income, i.e. 01/31/2021. But since it is a holiday, the deadline is shifted to the next closest working date: 01/10/2022.
It is impossible to withhold tax on December 20, since this date precedes December 31, 2021.
- Is it possible to withhold personal income tax after the end of the month, but not when paying wages?
Example
The employee was on a business trip within the country for 5 days, from November 1 to November 5. On October 31, he received an advance payment for the trip, including a daily allowance of 1,300 rubles. per day, total 6,500 rubles. The amount of daily allowance above the norm was (1,300 – 700) × 5 = 3,000 rubles. On November 7, he submitted the advance report for approval. On November 20, the company paid an advance on wages, the final payment of wages was made on December 5. On December 1, this employee was paid vacation pay.
Daily allowances are included in the annual calculation as follows:
| Line number | Meaning |
| 110 | 3 000 |
| 140 | 390 |
| 160 | 390 |
| 021 | 02.12.2021 |
| 022 | 390 |
Personal income tax can be withheld for any payment following the last day of the month of approval of the advance report.
- What to do if the daily allowance was paid after a business trip?
Example
The employee went on a business trip to another country without having time to take an advance payment. I stayed there for 5 days, from November 1st to November 5th. On November 7, he submitted the advance report for approval. According to the report, in addition to compensation for other expenses, the employee is entitled to a daily allowance of 3,000 per day. The amount of daily allowance above the norm was (3,000 – 2,500) × 5 = 2,500 rubles. On November 11, the employee received full reimbursement for travel expenses. The final payment of wages was made on December 3.
Daily allowances are included in the annual calculation as follows:
| Line number | Meaning |
| 110 (previously 020) | 2 500 |
| 140 (formerly 040) | 325 |
| 160 (previously 070) | 325 |
| 021 (previously 120) | 06.12.2021 |
| 022 (previously 140) | 325 |
Despite the fact that the daily allowance was paid after the approval of the advance report, personal income tax cannot be withheld from this payment, since the income is considered received later - November 30, 2021.
Daily allowance
The legislation calls per diem expenses for employees sent on a business trip associated with living outside their place of permanent residence (Part 1 of Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The amount of daily allowance in commercial companies is fixed in internal local regulations. Insurance premiums are not subject to daily allowance in the amount of 700 rubles/day. for business trips in Russia and 2,500 rubles. /day when traveling abroad (clause 2 of article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Anything paid in excess of the specified limits is subject to insurance premiums. This rule does not affect only personal injury contributions. They are not subject to daily allowance in the amount prescribed by the employer in the local act.
Let us show with an example how to calculate insurance premiums for travel expenses in excess of the norm in 2022:
Employees of Transport Logistics LLC are paid a daily allowance for domestic business trips in the amount of 1,350 rubles per day. This amount is fixed in the collective agreement.
In March 2022, manager Ilyin A.A. was on a business trip in Kaluga for 5 days. He was paid a daily allowance of 6,750 rubles. (5 days × 1,350 rub./day).
At the same time, for the purpose of calculating contributions to compulsory pension, social and health insurance, the accountant divided the daily allowance into two parts:
- non-taxable contributions in the amount of 3,500 rubles. (5 days × 700 rub./day);
- taxable contributions 3,250 rub. (6,750 rubles ─ 3,500 rubles) or (5 days × (1,350 rubles/day ─ 700 rubles/day)).
Thus, daily allowances as one of the types of travel expenses in excess of the norm are subject to insurance contributions.
Daily allowances for employees working under civil contracts
If an employee sent on a business trip works under a civil contract, it is impossible to rely on the norms of legislation in force in the case of an employment relationship between the employee and the company.
Since the norms of labor legislation and other acts containing norms of labor law do not apply to employees working under a GPC agreement in accordance with the provisions of Article 11 of the Labor Code.
Accordingly, the guarantees and compensations provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, including those related to business trips, apply only to employees who have entered into an employment contract with the organization and are not applicable in the case of a GPC agreement.
A similar rule is contained in paragraph 2 of Resolution No. 749:
- Employees who have an employment relationship with the employer are sent on business trips.
Thus, if an employee works for a company under a GPC agreement, then sending him on a trip for official purposes is not a business trip .
This means that the organization has no obligation to compensate such an employee for travel expenses. Therefore, in order not to increase the price of the GPC agreement (remuneration amount) by the amount of expenses associated with the business trip, as well as not to pay “extra” taxes, the possibility of paying compensation amounts to the executor of the assignment must be provided for in the GPC agreement.
Travel expenses from the place of business trip
According to the general rules, compensation for the cost of travel to the place of business trip and back is considered travel expenses and is not subject to insurance premiums (clause 2 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This rule ceases to apply if the employee decides to stay at the location for the duration of the vacation after the end of the business trip. In this case, compensation for travel expenses from the place of business trip to the place of work loses the status of travel expenses and turns into the employee’s taxable income (clause 1 of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In such a situation, tax inspectors consider the end of the business trip to be the last day before the vacation (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated December 6, 2019 No. 03-04-06/94974, Federal Tax Service dated May 11, 2018 No. BS-4-11/8968).
We reflect daily allowances in 6-NDFL
Clause 3 art.
217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that there is a limit for daily allowances, from which personal income tax is not paid. This is 700 rubles. per day for business trips around the country and 2,500 rubles. per day for foreign business trips. If, according to internal regulations, the employer issues large amounts of daily allowance, then everything issued in excess of the limit is subject to personal income tax. Accordingly, taxable income must be reflected in 6-NDFL. Read more about the rules for paying daily allowance here .
For 2022, the calculation of 6-NDFL is presented in a new form. A sample of how to fill it out can be viewed in ConsultantPlus, free of charge, by signing up for trial access.
When filling out this form regarding the daily allowance, you need to proceed as follows. Show the amount of income on page 110 only to the extent of the excess. The option in which the full amount of income is shown on page 110 and a deduction for the amount of the limit on page 130 is not suitable. As explained in the Federal Tax Service letter No. BS-4-11/13984 dated 08/01/2016 (question 3), page 130 includes amounts in accordance with the codes of the types of deductions listed in the Federal Tax Service order No. ММВ-7-11/ dated 09/10/2015 [email protected] , but there is no daily allowance limit.
The date of receipt of income in the form of daily allowance is recognized as the last day of the month when the manager approves the advance report (subclause 6, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This date cannot be the day the money is issued, since at that moment there is still no supporting document, the accomplished fact of the business trip, and the employee receives an advance, which can be returned in case of early arrival back or cancellation of the trip.
The employer must withhold tax when the next payment of funds to the employee occurs after the date of receipt of income (clause 4 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The Federal Tax Service does not allow tax to be withheld before this date (letter from the Federal Tax Service dated July 25, 2014 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] ).
As a rule, personal income tax on excess daily allowances is withheld on the day the salary is issued for the month in which the advance report is approved. The tax transfer (pages 021-022) is made the next day after the withholding (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
See also “How is a one-day business trip paid?”
Check whether you correctly reflect various payments to employees in 6-NDFL using the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Additional services on the train
The cost of travel to and from the business trip may include the cost of service. For example, when purchasing a ticket for a luxury carriage on long-distance trains (clause 33 of the Rules for the provision of services, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 2, 2005 No. 111).
The composition of the range of services is determined by the carrier. In each train, taking into account the schedule and the duration of the passengers' stay on the route, it may vary. Paid services include: provision of guaranteed food, printed materials, sets of sanitary and hygienic items (Order of the Ministry of Transport dated July 9, 2007 No. 89).
Compensation for the cost of paid services included in the ticket price is not included in the contribution base, since the cost of such services forms the single cost of travel on the train (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 08/07/2017 No. 03-04-06/50386).
Use of personal transport by a business traveler
An employee can also go on a business trip in his own car. In order not to impose contributions on compensation related to the exploitation of an employee’s property, several conditions must be met (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 28, 2019 No. 03-15-06/21254):
- The types of expenses subject to compensation are prescribed in the collective agreement, for example: for the purchase of fuels and lubricants, repair of a vehicle during a business trip.
- The employee agrees with the employer on the fact of going on a business trip in a personal car.
- Expenses are supported by documents.
Useful information about compensation:
- for unused vacation without dismissal;
- personal car without personal income tax and contributions;
- rental housing for an employee;
- delay of wages.
Contributions with inadequate documentary evidence of expenses
Not only the absence of an advance report can serve as a basis for charging contributions for the amount of travel expenses, but also incorrectly executed or missing supporting documents.
A direct indication of the need for documentary evidence of travel expenses is contained in paragraph 2 of Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which contains a list of amounts not subject to contributions.
Tax legislation does not have a specific list of supporting documents that can be used to confirm travel expenses. At the same time, the Ministry of Finance has repeatedly reminded that supporting documents are drawn up in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation when traveling around our country or are drawn up according to business customs when traveling abroad.
You can also justify travel expenses with documents that indirectly confirm the expense, including a business trip order, travel documents, and a report on the work performed.
It should be clear from the supporting documents what expenses were incurred (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated September 23, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/72905, dated August 20, 2019 No. 03-01-15/63722).
When an employee attaches cash receipts and financial statements to an advance report for a business trip, they will not confirm expenses if they do not contain the details specified in clause 1 and clause 6.1 of Art. 4.7 of the Law “On the Application of CCP” dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ. If there is no QR code in the receipt, expenses are not recognized as properly documented (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 14, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/78500).
Daily allowance for business trips abroad
When sending employees on a business trip abroad, a special procedure for paying daily allowances applies.
According to paragraph 16 of Resolution No. 749, payment of daily allowances due to an employee in connection with a foreign business trip is carried out in accordance with the Federal Law of December 10, 2003. No. 173-FZ “On currency regulation and currency control.”
According to paragraph 9 of paragraph 1 of Article 9 of Law No. 173-FZ, foreign exchange transactions are allowed between residents when paying waste to individuals related to a business trip outside the territory of the Russian Federation.
That is, a Russian organization can issue daily allowance to an employee going on a business trip abroad in the currency of the country where he is going and this will not contradict the provisions of the current legislation.
Payment of daily allowance to an employee in foreign currency when the employee is sent on a business trip outside the territory of the Russian Federation is carried out in amounts determined by:
- collective agreement,
- local regulatory act (order, regulations on business trips, etc.).
During the travel time of an employee sent on a business trip outside the territory of the Russian Federation, daily allowances are paid:
- When traveling through the territory of the Russian Federation - in the manner and amount determined by the collective agreement or local regulations for business trips within the territory of the Russian Federation
- When traveling through the territory of a foreign state - in the manner and amount determined by a collective agreement or local regulations for business trips on the territory of foreign states.
When an employee travels from the territory of the Russian Federation, the date of crossing the state border of the Russian Federation:
- included in days for which daily allowances are paid in foreign currency.
When traveling to the territory of the Russian Federation, the date of crossing the state border of the Russian Federation:
- included in days for which daily allowances are paid in rubles.
The dates of crossing the state border of the Russian Federation when traveling from the territory of the Russian Federation and to the territory of the Russian Federation are determined by the marks of the border authorities in the passport.
When an employee is sent on a business trip to the territory of 2 or more foreign states, daily allowances for the day of crossing the border between states are paid in foreign currency according to the standards established for the state to which the employee is sent.
In accordance with paragraph 19 of Resolution No. 749, when sending an employee on a business trip to the territory of the CIS member states with which intergovernmental agreements have been concluded, on the basis of which border authorities do not make notes on crossing the state border in documents for entry and exit, the date of crossing the state border The borders of the Russian Federation when traveling from the territory of the Russian Federation and to the territory of the Russian Federation are determined by:
- according to the marks in the travel certificate, issued as for a business trip within the territory of the Russian Federation.
In case of a forced delay in transit, daily allowances for the delay are paid according to the decision of the head of the organization upon presentation of documents confirming the fact of the forced delay.
An employee who went on a business trip to the territory of a foreign state and returned to the territory of the Russian Federation on the same day is paid daily allowances in foreign currency in the amount of 50% of the rate of expenses for the payment of daily allowances established by the organization for business trips to the territory of foreign states.
When an employee is sent on a business trip to the territory of a foreign state, he is additionally reimbursed for:
- expenses for obtaining a foreign passport, visa and other travel documents;
- mandatory consular and airport fees;
- fees for the right of entry or transit of motor vehicles;
- expenses for obtaining compulsory health insurance;
- other mandatory payments and fees.
Reimbursable expenses include, inter alia, employee expenses associated with the exchange of Russian rubles for foreign currency.
Results
Insurance premiums for travel expenses in 2022 are not charged if they are actually made and documented. But this rule does not apply in all cases. You will have to charge contributions for daily allowances paid in excess of the established norms, except for contributions for injuries, as well as for amounts of expenses that are not documented.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2008 No. 749
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What expenses are reimbursed to a posted worker?
There are often cases when employers are forced to send their employees outside the location of the organization to resolve official issues.
Trips for a certain period of time, on a specific official assignment from a manager, to another locality or abroad are called business trips. While an employee is on a business trip, he is paid the average salary (Article 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The calculation of average earnings is regulated by the regulation “On the specifics of the procedure for calculating the average salary”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2007 No. 922 (Part 7 of Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and Art. 139 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Before the start of a business trip, the employer must:
- establish the amount and procedure for paying travel expenses to an employee;
- prepare the documents necessary to send an employee on a business trip.
These aspects are regulated by the regulation “On the specifics of sending employees on business trips”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2008 No. 749.
In accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee is reimbursed for the following business trip expenses:
- for travel;
- rental of residential premises;
- additional living expenses (per diem);
- other expenses for the performance of official tasks (with the permission of the manager).
As a rule, an organization develops internal documents or a collective agreement that defines the procedure and amount of reimbursement for these expenses.
You can find an example of such an internal document in the article “Regulations on official business trips - sample”.
The procedure for reimbursement of business trip expenses to employees of various federal government bodies, institutions and funds, as well as municipal institutions is determined by regulatory legal acts of the government of the Russian Federation, local governments, and state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (Part 2 of Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).