Why are off-balance sheet accounts used in accounting?
Off-balance sheet accounts are auxiliary. Balances from these accounts are not included in the balance sheet and are reflected behind the balance sheet, hence their name. This takes into account property that the company uses but does not own. This property is temporarily in the circulation of the company and is provided on the basis of a specific agreement. This could be rented premises or equipment transferred for safekeeping of valuables or raw materials for processing.
The most important thing is that off-balance sheet accounts allow you to reliably and completely reflect information about the organization’s work and its property. Therefore, off-balance sheet accounting is also important for regulatory authorities: for example, if a company does not maintain it, the auditor is unlikely to give a positive conclusion after an audit, and sanctions can also be expected from the tax office.
Information about assets that are recorded in off-balance sheet accounts will be useful to the entrepreneur himself for management accounting and planning. They can also explain a lot to inspectors during an inspection: for example, if you rent fixed assets and reflect them on account 001, then you will have fewer questions about the costs of their maintenance.
Account 27 “Material assets issued for personal use to employees (employees)”
The procedure for applying account 27 has been adjusted. According to the new edition of clause 385 of Instruction 157n, account 27 is used when accounting for uniforms, special clothing, material assets related to fixed assets and other property issued by an institution for permanent personal use to employees for the performance of official duties. ) duties involving the use of received property, including outside the territory of the institution, outside the duration of the current working hours, in order to ensure control over its safety, intended use and movement.
Analytical accounting of the account is carried out in the context of employees (users of property), objects of property (names of uniforms), locations of objects (addresses) and KOSGU codes.
How is property taken into account off the balance sheet?
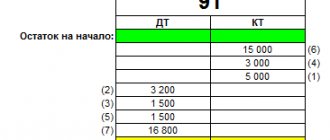
Accounting for off-balance sheet accounts is carried out according to a simplified scheme - without double entry. The accounts behind the balance sheet look like a table with two columns: one for reflecting debits, the other for credits; the same amount does not need to be entered in them.
- In the debit column, the receipt is recorded: receipt of objects, issuance or receipt of security.
- The loan column records the expense: disposal of the object or termination of collateral.
As with regular accounts, the company registers and writes off values on off-balance sheet accounts. It is also possible to sell off-balance sheet property: then it is registered in the credit of the corresponding off-balance sheet account, and the money received is reflected as income from sales and VAT is added. This income will be included in the income tax base. At the same time, the initial cost of the asset, which was taken into account during commissioning, is not reflected in accounting, so as not to distort the financial results.
Types of off-balance sheet accounts and their accounting
The required type of off-balance sheet account is determined depending on what kind of object is subject to accounting. There are the following types of ES:
- 001 “Fixed assets leased.” Their cost must be confirmed by an agreement concluded with the lessor.
- 002 “Valuables taken under safekeeping.” Typically, an agreement is concluded in relation to these objects, after the fulfillment of the terms of which the values become the property of the enterprise. Until this moment, the company's objects will not belong to the company. The condition is certain deductions. The postings must indicate their size.
- 003 “Raw materials taken for processing.” Materials for processing can be indicated on off-balance sheet accounts only if they were transferred by the customer and the manufacturer does not pay their cost.
- 004 “Materials for commission.” The products that were taken by the commission agent for sale are indicated.
- 005 “Equipment intended for the performance of installation services.” The equipment used to perform installation services is indicated.
Off-balance sheet accounts reflect assets owned by the enterprise that have been written off as expenses:
- 006 “Reporting forms”. May include various receipts and subscriptions.
- 007 “Bad debts written off at a loss.” Displayed on accounts for five years. It is assumed that during this time the financial position of the debtor may change.
Off-balance sheet accounts are relevant for collecting information necessary as additional information to the explanations of the statements:
- 008 “Collateral received.” Needed to store data on transferred guarantees to ensure compliance with conditions;
- 009 “Issued collateral.” Relevant for collecting information on issued guarantees to ensure payments.
- 011 “Funds received for rent.” This account is placed in the reporting of both the lessor and the tenant.
All account data is indicated in a special accounting plan. An enterprise can open other accounts that are not in the plan if this is required to support its activities.
An organization has the right to open a sub-account to an existing off-balance sheet account or introduce a new account if it is not provided for in the plan. The main thing is that this change is properly spelled out in the accounting policies.
IMPORTANT! Organizing off-balance sheet accounts is extremely important. If, as part of a tax audit, objects are discovered that do not appear in the reporting, they will be written off as non-operating income. That is, they will be subject to income tax.
Features of accounting on the AP
Off-balance sheet accounts are presented in the form of a table with two columns. One of them displays debit, the other – credit. Accounting for APs is carried out using a simplified system. No double entry required. That is, you don’t have to write the same amount in debit and credit. The following transactions must be indicated in the debit column:
- getting objects;
- acquisition or issuance of security.
The loan column displays:
- disposal of the object;
- termination of security.
The debit will show the income, and the credit will show the expense.
Off-balance sheet accounts for accounting for other people's property
If a company disposes of property that does not belong to it, it is reflected in the accounts of this group. For example, account 001 contains fixed assets leased. Account 002 contains valuables accepted for safekeeping. Account 004 contains products taken on commission.
Typically, difficulties when working with such property are due to the fact that the accountant does not know the value of assets that the company does not own. This means it is unclear at what cost to take them into account. This problem can be solved in different ways:
- clarify the value of the asset from the owner - when renting or transferring for free use;
- use an independent assessment and obtain the appraiser’s assurance (although this method can be expensive) or find out the cost from a technical inventory bureau, if possible;
- reflect assets in a conditional or quantitative valuation - this is usually done when the value cannot be expressed in monetary terms, for example, in the case of strict reporting forms.
It is only important to reflect the chosen method in the company’s accounting policy.
Off-balance sheet accounting of own property
To record your own material assets, there are only two accounts on the balance sheet:
- account 006 “Strict reporting forms”;
- account 011 “Fixed assets leased out”.
These accounts will be useful for organizations with relevant specifics.
Thus, on account 006 you can take into account subscriptions, diplomas, shipping documents and other strict reporting forms. These documents reflect the balance sheet in the conditional valuation.
If a company rents out its property, off-balance sheet accounting may be necessary. It is necessary to reflect the leased fixed assets on account 011 if the agreement provides for accounting of the property on the balance sheet of the tenant (lessee). If there is no such condition, the lessor keeps records of fixed assets as usual - on balance sheet account 01. The lease is reflected in the debit of account 011. When the tenant returns the property, the lessor will write it off with an entry in the credit of account 011.
Off-balance sheet accounts for accounting for collateral
The second group of accounts is needed to account for collateral, deposits, sureties, bank guarantees, etc. Again the question arises, what value should be assigned to the collateral? For example, a company takes into account the collateral on its balance sheet, what value should be assigned to it - the value of the pledged asset or the amount of payment by the mortgagor? These amounts are not always equal, and more often the security is reflected at the value of the pledged asset. Then, if the pledgor fails to fulfill the obligation, the pledge holder will reimburse his loss from the value of the pledged property.
When receiving collateral, the accountant makes an accounting entry: Dt 008 (the value of the collateral received is reflected. When repaying the debt, the accountant makes an entry: Kt 008 (the value of the repaid collateral is written off in whole or in part).
Off-balance sheet accounts for other assets
The accounts of this group reflect the property that the company owns, but it is important to account for it separately. These can be idle, low-value or mothballed objects, special clothing, special equipment, customer-supplied materials.
Provided materials. If a company produces products from materials provided by the owner (vendor), then the materials themselves and the products made from them must be taken into account separately. To do this, use account 003 and evaluate the property according to the contract. The result of the work is transferred to the customer on its own or together with production waste.
Working clothes and special equipment. If special clothing and equipment are transferred to the company for disposal or use, they are accepted into the off-balance sheet account “Special equipment transferred for operation” (clause 23 of the Guidelines for the accounting of special tools, devices, equipment and clothing, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2002 No. 135n). Record the issuance and return of clothing or equipment in your personal personal protective equipment issuance card.
OS on off-balance sheet accounts
Fixed assets are assets that are not intended for sale, are capable of generating income and are used for more than 1 year for the production of products, provision of services, management purposes of the organization or provision for temporary use (clause 4 of PBU “Accounting for OS” 6/01, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n).
Fixed assets include buildings, equipment, machines, machines, etc. Accounting for business operations related to fixed assets is carried out using the following accounts in the Chart of Accounts (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n): 01, 02, 03, 07, 08.
You will find a list of key accounting entries for fixed assets accounting in the article “Accounting for fixed assets - accounting entries.”
However, in some cases, fixed assets may be reflected in off-balance sheet accounts:
- transfer or lease of fixed assets - accounts are intended for such operations. 011 and 001;
- equipment accepted for installation is recorded on the account. 005;
- depreciation of some types of OS is taken into account on the account. 010.
Let's take a closer look at each situation.
Inventory of off-balance sheet accounts
If a company conducts an inventory of property and liabilities - for example, when preparing annual accounting reports - it is also necessary to inventory off-balance sheet assets.
To do this, you will have to prepare separate statements for comparison (clause 4.1 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation on June 13, 1995 No. 49). Otherwise, the process is no different from regular inventory. Based on the results, all commission members and financially responsible persons sign inventory acts.
If a shortage of property accepted for commission or customer-supplied raw materials is detected, the company compensates the owner for the shortage, and the amount of losses is reflected among other expenses.
If surplus off-balance sheet property is discovered, it can be taken onto the balance sheet among other income. Or, for example, keep the excess goods accepted for commission in off-balance sheet account 002 “Inventory and materials accepted for safekeeping” until the committent makes a decision regarding the excess goods.
Data from off-balance sheet accounts in reporting
Off-balance sheet accounting information is included in the accounting records - in the explanations to the balance sheet and the financial results statement. The cost of leased fixed assets and the amount of security are indicated (Appendix No. 3 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation July 2, 2010 No. 66n). You can also include off-balance sheet property in the explanations in conditional and quantitative form.
Keep records in the Kontur.Accounting web service: simple accounting, the ability to add accounting accounts, ready-made accounting policies, salary block, reporting via the Internet. All newcomers receive a free trial period of two weeks.