Exporting goods and own products outside of Russia is a financially profitable operation for taxpayers. The legislation provides for a special procedure for calculating and refunding value added tax (VAT) for enterprises involved in export activities:
- the VAT rate on goods/services shipped for export is set at 0%;
- tax paid on the purchase of products intended for export abroad is subject to reimbursement from the state budget.
Due to the need to return from the budget VAT paid on Russian territory, fiscal authorities pay special attention to enterprises that use export operations. An unreasonably claimed VAT refund or failure to comply with the regulations for confirming the right to apply a preferential tax rate is fraught with substantial additional payments to the budget and penalties.
Specifics of export VAT
When purchasing goods or producing your own products/work, the cost of a unit of goods initially includes VAT paid to the supplier. When reselling such a product on Russian territory, the company will be forced to pay 10% or 18% of the sales amount to the budget.
If this product is sold to a foreign enterprise, then the exporter’s obligation to pay VAT disappears, since for such transactions a VAT rate of 0% is provided.
Example
Company A. purchased goods for sale in the amount of 118,000 rubles, paying the supplier VAT in the amount of 18,000 rubles. For sales, the company has two options - sell the goods to a Russian company, or transport them to a counterparty in Belarus. The profitability of both transactions should be determined. When selling in Russia:
The sales amount will be 150,000 rubles, of which VAT is 22,881 rubles.
Taking into account the “input” tax, company A. is obliged to pay VAT to the state in the amount of (22881 – 18000) = 4881 rubles. The profit from the operation will be 32,000 rubles, including VAT payable of 4,881 rubles. Net profit – 27119 rubles. When exporting to Belarus:
Sales will be the same 150,000 rubles, however, applying a 0% rate, the company does not charge VAT for payment. In addition, A. has the right to return from the budget the amount previously paid to the supplier in the amount of 18,000 rubles. The profit will be 32,000 rubles, plus the refunded VAT, for a total net profit of 50,000 rubles.
As can be seen from the example, export operations can almost double profits, which is undoubtedly beneficial for a Russian company. However, obtaining increased income is associated with the need to confirm to tax authorities the application of a zero VAT rate.
Formation and transmission of universal transfer documents
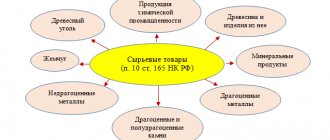
Since simplified companies and individual entrepreneurs are not VAT taxpayers, when performing transactions with traceable products they must issue not invoices, but universal transfer documents (UTD).
UPD is a document that combines elements of both an invoice and a primary transfer document. In addition, it indicates the traceability details of goods. When selling products that are subject to traceability, the UPD must be signed with an enhanced qualified digital signature and transferred to the buyer in electronic format through an EDI operator.
But in some cases, the UPD can be transferred to the buyer on paper. For example, if traceable goods are sold to individuals for purposes that are not related to entrepreneurship, or to self-employed persons who are payers of NAP.
Currently, there is no approved UPD form, but taxpayers using the simplified tax system can use document forms that they have developed independently. Or you can use the UPD form, which the Federal Tax Service recommended for use in Letter dated October 21, 2013 No. ММВ-20-3/ [email protected]
If a company independently develops an UPD form, then it should contain:
- registration number of the batch of traceable products;
- unit of measurement of traceable products;
- quantity of traceable products in the traceability quantity unit.
If the traceable goods do not originate from a member country of the EAEU, then the UTD must also indicate the country of origin of the product and the registration number of the declaration for it (clause 5.2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
After July 1, 2022, in the UPD it is necessary to fill out line “5a” - “Shipment document No.” (Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated June 17, 2021 No. 3G-3-3 / [email protected] ).
The current forms of the main and corrective UPD are presented in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated May 28, 2021 No. EA-4-15/7407.
How to confirm the zero rate for an export transaction
The list of customs documentation attached to the VAT return and justifying the lawful application of the zero tax rate depends on the direction of export operations:
- export of goods to the countries of the Eurasian Economic Union (former republics of the USSR);
- shipment to other countries outside the EAEU.
Export to EAEU countries
When moving goods to the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) - Belarus, Armenia, Kazakhstan or Kyrgyzstan - simplified customs regulations are applied, so the list of documents required to justify the application of a 0% rate is quite limited. The seller must present the following documents to the tax service:
- transport and shipping documents for export cargo;
- application documents for the import of goods and confirmation of payment of indirect tax payments by the buyer;
- a contract between a Russian seller and a buyer from the EAEU countries.
Since two-way electronic exchange of data on the import/export of goods has been established between the customs and tax services, the presentation of paper documents is not necessary. It is enough for an exporting company to create a register of necessary documentation in electronic form and submit it to the tax office.
Export to other foreign countries
When exporting goods to countries outside the EAEU, you can confirm the application of a 0% VAT rate with the appropriate documents:
- a copy of the foreign trade contract or, in its absence, an acceptance or offer;
- agreement for the provision of intermediary services - if the export is carried out through a third party (attorney, agent, intermediary);
- customs declaration (copy or register in electronic form);
- commodity and transport documents (bill of lading, CMR waybill, air or combined waybills).
All documents presented must have official marks from customs services, indicating the actual export of goods from the territory of Russia.
During a desk audit, tax authorities may request bank statements or invoices for an export transaction, so it is advisable for the seller to prepare copies of documents to be attached to the VAT return.
Mandatory transition to electronic document management
Under the National Product Traceability System, organizations on the simplified tax system, when working with such goods, are required to assign them registration numbers, as well as record tracking details in the primary documentation and submit reports to the Federal Tax Service on all operations with traceable products.
These responsibilities are performed when using electronic document management, for example, they include:
- sending notifications about the import and export of traceable products;
- receiving information about tracking details assigned to goods;
- transfer to buyers of primary documents in electronic form confirming the fact of sale of traceable products;
- Submitting reports to the Federal Tax Service on transactions with traceable products.
Thus, if a company using the simplified tax system decides to work with traceable products, it must organize electronic document flow, for which it must enter into an agreement with an e-document flow operator.
Deadline for confirming the legality of applying the zero rate and desk audit
Tax legislation requires the exporting seller to generate and submit a package of necessary documents to the tax service within 180 calendar days after the cargo leaves Russia.
After successful confirmation by the taxpayer of the right to apply the 0% VAT rate, the Federal Tax Service begins a desk audit. It should be borne in mind that the fiscal authority does not control the correctness of a separate export transaction - the entire tax period during which the transaction was completed is subject to verification.
During the desk audit the following is subject to analysis:
- the exporter has the resources necessary for international trade - office, warehouses, staff;
- presence of licensing and permitting documentation;
- timely conclusion of agreements with transport and logistics companies transporting export cargo.
Tax inspectors will most likely conduct counter audits by requesting invoices and invoices from suppliers of goods exported abroad.
If the exporting company has undergone reorganization changes over the past 6 months (change of legal address, merger or incorporation procedures), then the attention of the tax inspectorate to its foreign trade activities will be especially close.
Help SB Cargo
helps to carry out customs clearance of imported and exported goods according to two main schemes: for your own contract and for the client’s contract. We can completely take care of customs clearance, including preparing a package of documents: necessary certificates, declarations, permits. We can enter into an agreement directly with the supplier and bring the cargo to Russia, subsequently transferring it to the client under a commission agreement or a purchase and sale agreement.
We are competent in international transportation and customs clearance of any categories of cargo, including valuable, dangerous, and perishable. Cooperating with us is convenient and profitable. To use our services, prepare an invoice, packing list and foreign trade contract. These are the main documents that we will need for settlements and concluding an agreement. We remind you of our telephone and email
Consequences of non-compliance by the exporter with the prescribed regulations
The absence of a complete package of documents or failure to submit them to the tax authority results in the following sanctions for the exporter:
- additional VAT at a rate of 18% (10% when exporting goods from the relevant list);
- the tax base is determined by the moment the cargo actually crosses the border of the Russian Federation;
- calculation of penalties from the date of shipment of goods.
If the exporter is late in providing documents, he can count on a VAT refund in the next tax period. After the full list of documents is submitted to the Federal Tax Service, the supervisory authority decides to conduct a desk audit. However, this procedure will begin only from the beginning of the next quarter and will last three months.
Registration of foreign trade participants
Previously, registration of foreign trade participants was a complex procedure, but now, with the introduction of electronic declaration, this process has been simplified.
All that is required of the importer, when first applying to the customs authorities as a declarant, is to submit documents confirming the status of an individual entrepreneur and providing customs with certain information about him.
The list of documents includes:
- Full name IP;
- TIN, OGRNIP certificates;
- OKPO and OKVED codes;
- bank details of the individual entrepreneur;
- registration address at the place of residence;
- certificate of registration of individual entrepreneurs (USRIP).
Voluntariness in applying a zero VAT rate
The use of any benefits for the taxpayer is entirely voluntary. Quite often, organizations do not take advantage of the required concessions if they are not sure that they can reliably and reasonably confirm their right to the benefit.
In contrast to tax privileges established by law, the use of a zero VAT rate for export transactions is a mandatory condition. The taxpayer is not exempt from paying tax; he must, as a general rule, keep records of taxable transactions and submit a VAT return to the tax authority.
In addition, the taxpayer must separate the accounting of transactions at standard rates (10% and 18%) and at the zero rate. “Input” VAT on goods/services subsequently used in export transactions must be accounted for separately. This includes costs for the purchase of materials and raw materials, goods for sale, transport services of third-party companies, rental of warehouses, etc. The entire amount of tax on purchased resources used to ensure exports is subject to reimbursement from the budget, therefore, in order to avoid tax disputes, strict accounting is necessary.
Remember: export transactions are subject to a mandatory invoice with a highlighted zero rate. The document must be issued no later than five days after shipment.
Tax registration
Tax registration of exports is also inextricably linked with VAT. The tax is calculated and paid by the exporter when goods cross the border of the Russian Federation. The tax base includes the cost of exported products, excise tax, and customs duties. Didn't pay VAT on time? The goods will not leave the temporary storage area. In addition, late payment leads to the accrual of penalties. Accordingly, the costs of tax registration of exports increase.
If all conditions stipulated by current legislation are met, the VAT paid is accepted for deduction. To do this, the proceeds from the transaction must be taxable. Also, the main conditions are payment of export VAT in full, submission of all supporting primary documents and timely receipt of goods and their reflection in accounting.
Under the simplified export taxation system, VAT is not deductible. With the “Income” SSC, the tax is included in the cost of the goods. If expenses incurred are taken into account when determining the taxable base, VAT must be included as part of the expenses.
The specifics of export accounting are also determined by where the goods are exported. The preparation of accounting documents when a company cooperates with counterparties from the EAEU has its own characteristics. One way or another, export accounting must be continuous and professional. Contact the specialists!
When can an exporter receive budget money?
Upon completion of a three-month desk audit, the tax service makes a decision in which it orders the exporting company to fully or partially reimburse the “input” VAT paid. The law allocates the supervisory authority no more than 7 calendar days to make a decision.
The taxpayer may declare his intention to use the refund amount to cover the existing arrears on mandatory payments. If such an application is not received by the Federal Tax Service, the compensation amount must be received in the exporter’s current account within five banking days.