Selling costs are NOT directly related to production
,
provision of services, performance of work
and are NOT included in the cost of products, work, services:
- storage costs (clause “e”, clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019);
- expenses for advertising and promotion of products (clause “e”, clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019);
- and other costs, the implementation of which is not necessary for the production of products, works, clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019).
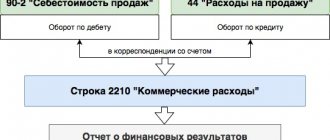
In the working Chart of Accounts 1C, account 44 “Sales expenses” provides subaccounts for accounting for sales expenses for:
- trade organizations,
- production organizations,
During the month, costs are accumulated according to Dt 44, and at the end they are recognized as expenses in full Dt 90.07 “Sales expenses”.
Commercial expenses in UE
establishing the procedure for accounting for commercial expenses
– what will relate to such costs:
How does accounting take into account the costs of delivering goods to the buyer?
The costs of delivering goods to the buyer are included in distribution costs and are expenses of the current period:
- document Receipt (act, invoice, UPD) type of operation Services – Cost item of the type other expenses
Costs will be fully written off on Dt 90.07 at the end of the month.
The company produces products and delivers them to wholesale buyers. Products are accounted for in several product groups and produced by different divisions. Which document and on which account should be used to correctly reflect the costs of delivering products so that the costs increase the cost of production? Products from different product groups are delivered at the same time.
Delivery of finished products cannot be included in the actual cost of production (clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019). Delivery costs should be charged to account 44 “Sales expenses”.
Selling expenses in cost
Selling expenses are the cost:
- goods along with the purchase price;
- products produced along with the cost of production.
They enter the cost price by transferring from account 44. Postings can be as follows:
- Debit 44 credit 10
- expenses for packaging materials and containers are reflected;
- the cost of delivering goods to customers' warehouse facilities or to intermediate departure points is taken into account;
- paid for third party services (delivery, packaging, sale of finished products);
- salaries were accrued to sellers, sales department employees, workers involved in packaging, loading and selling products, etc.
Business expenses must be written off by the end of each reporting period. The wiring is like this:
- Debit 90-2 Credit 44
- expenses for the sale of products (goods, works, services) are written off.
Costs for storing raw materials and GP
In what account should the costs of renting a warehouse for storing raw materials and finished products be reflected? We keep records on account 25, the situation is confusing that storage services are not included in the cost of production from 2022, but with such accounting they will get there.
In accordance with paragraphs. “d” clause 26 FSBU 5/2019 storage costs, if this is not part of the technological process, are not included in the cost of production, works, services. If we take into account such costs for Dt 25, then 1C will distribute them in Dt 20 in proportion to the distribution base established in the UE. Even if there is no database, 1C will automatically select another one. Consider storage costs in Dt 44.02 - as costs for the sale of production organizations.
See also:
- Actual cost of inventory
- Transportation and procurement costs when purchasing materials: legislation and 1C
- Accounting for the costs of delivery of goods during their sale
- [06/08/2021 entry] Practice of application of FSB 5/2019 Inventories in 1C - Part 3
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Direct production costs (account 20) from 2022 ...
- Indirect production costs (account 25) from 2022 ...
- Management costs (account 26) from 2022 ...
- Inventory storage costs according to FAS 5/2019...
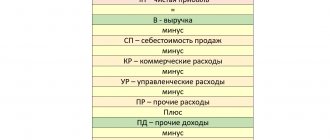
What costs can be included in business expenses (line 2210)
Depending on whether the enterprise is a trade (wholesale, retail) or manufacturing enterprise, the list of business expenses may vary:
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
| Kind of activity | What are the costs involved? | additional information |
| Production | Includes any costs associated with sales: — entertainment expenses; — costs of advertising the product; — depreciation costs (wear and tear of office and commercial equipment); — payment for security services; — salaries of employees (including office workers) engaged in sales; — costs of maintaining an office and warehouse space. | Any other expenses reflected in the debit of account 44 and related to distribution costs are also taken into account. |
| Trade (retail, wholesale) | Costs of selling manufactured products: — entertainment expenses aimed at promoting the product; — advertising costs; — costs of maintaining warehouses with goods ready for sale; — commission fees; — transportation costs (delivery to the place where goods are sent); — packaging costs; - other similar expenses. | If we are talking about a manufacturer (processor) of agricultural products, in addition to commercial expenses include: — costs of maintaining reception and procurement points (including caring for poultry and livestock there); — general procurement costs; - other similar costs. |
| Business valuation | Financial analysis according to IFRS | Financial analysis according to RAS |
| Calculation of NPV, IRR in Excel | Valuation of stocks and bonds |
To what account should transport costs and costs associated with the movement of fixed assets be attributed?
In accordance with the provisions established within the eighth paragraph of the Rules defining the accounting procedure, this category of expenses is equated to the acquisition or creation of products by the enterprise. This approach applies to the following types of OS:
- Created directly by the organization.
- Purchased on the basis of an appropriate agreement (including in relation to barter-type agreements, when mutual settlements do not involve the transfer of funds).
- Received free of charge.
All of the above options for transportation costs in the accounting policy are considered as capital investments, which actually increase the base cost of commodity units. For reflection, the corresponding debit accounts are used, and within the framework of correspondence, expense accounts are used.
It is important to consider that this procedure is not relevant for all situations. Thus, expenses associated with the movement of objects within the territory of an enterprise that do not require installation work for subsequent operation are classified as production. This is true not only for vehicles, but also for various types of equipment, including large equipment used in construction work - from excavators and bulldozers to concrete mixers and rollers for laying asphalt. In the case of transportation of equipment that involves installation and dismantling, the costs incurred are considered as operating costs.
Calculation of TR in tax and accounting
Now let's look at the methods used for each type of cost.
Property acquisition costs
In such situations, expenses are considered by the legislator as falling into the direct category, which necessitates distribution between already sold and other products - instead of including the full amount in the cost structure. The provisions enshrined within Art. 320 of the Tax Code, provide for the use of an average indicator determined for a specific period, and also indicate how to calculate the percentage, calculate and write off transportation costs for the delivery of goods.
For calculation you will need to perform the following steps:
- Clarify the amount of costs in relation to unsold balances as of the starting date of the calendar period, as well as the total amount of sales.
- Determine the purchase price of the goods sold and the inventories available to the company.
- Calculate the average percentage, which is the ratio of total direct expenses and commodity value.
- Find the amount of costs related to balances, equal to the product of two factors: the found percentage and the actual balances at the end of the reporting time period.
It is important to consider that transportation costs include all direct costs associated with inventory that is the property of the organization. This category includes, among other things, objects that at the time of settlement are in the process of being transported to the final recipient.
Delivery of goods to customers
The specifics are directly related to the core activities of the enterprise. Firms specializing in production classify logistics as indirect material costs, which are an integral part of the work cycle. In turn, for companies engaged in commercial transactions, shipping costs are indirect - and trade transactions are processed accordingly. Without exception, all organizations that ship products are required to ensure the availability of goods and waybills.
Costs associated with maintaining a vehicle fleet
This expense item combines such types of costs as:
- Purchase of fuels and lubricants.
- Purchase of components for repairs and scheduled maintenance.
- Vehicle insurance, as well as payment for parking spaces and fines for traffic violations.
Let's take a closer look at each of these points.
In the case of fuels and lubricants, as a rule, categories of technical regulations related to ensuring production or sales are applied. The exception is situations when costs are taken into account as direct - based on the corresponding letter from the Ministry of Finance of 2011. For example, accounting for transportation costs for delivery from a supplier using your own transport can be attributed to material costs - however, to write off fuel, you will also need to issue waybills.
The purchase of spare parts and the organization of repairs are operations related to indirect expenses and are subject to complete write-off within the reporting period during which they arose. Do not forget about the economic justification - maintenance designed to improve the performance of the car will be considered a reasonable necessity, while expensive, but useless from a functional point of view, tuning may give rise to questions from the tax authorities.
In the case of insurance, a mandatory condition is the presence of compulsory motor liability insurance. The costs associated with its execution are also considered indirect, and are included in equal shares in the structure of other technical regulations of the enterprise during the validity period of the concluded agreement. But the increase in transportation costs in connection with the acquisition of Casco, which is a voluntary option, will be considered within the category of other costs, and cannot be taken into account in situations where a simplified taxation system is applied.
Parking, cash and sales receipts are used as the basis for writing off expenses incurred when paying for a parking space - if it is not located on the territory owned by the organization. When registering a long-term lease, the basis document can also be an act on the provision of relevant services. In both cases, transportation costs are indirect, which under no circumstances can be considered administrative fines issued for violations of traffic rules. In case of non-compliance with the requirements of the traffic police, it is either collected from the entity guilty of committing the offense, or written off in a non-sales form - from the company’s own funds.
How are business expenses written off?
Enterprises are allowed to independently decide on the procedure for writing off business expenses (the rules are not approved by legislative and regulatory acts). At the same time, companies are required to consolidate the write-off method they have chosen in their accounting policies.
Important! For manufacturing companies, there are recommendations for writing off business expenses, which are given in the text of the Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts.
Product manufacturers are recommended to write off sales costs as a debit to their account. 90 “Sales” s/ac. 2 “Cost of sales”. The costs of a manufacturing company for transportation and packaging should be distributed among the varieties of shipped goods based on considerations of an independently selected indicator (cost of ready-to-sell products, volume, weight, quantity).
To calculate the amount of business expenses to be written off, you must first calculate the value of the special coefficient using the formula below:
Knowing the value of this coefficient, you can proceed to calculating the volume of business expenses of the enterprise to be written off: