Any receipt of an object of fixed assets (F), whether it be a purchase, gratuitous transfer or acquisition in exchange, entails the mandatory determination of a depreciation group, which is assigned based on the useful life of the property. It is during this period that the cost of the property gradually becomes part of the company's costs. Write-off of accrued depreciation amounts is carried out in one of four ways that are relevant for accounting established in the accounting policy of a particular enterprise.
Shock absorption groups
When registering, PF objects are assigned to a specific depreciation group. There are 10 of them in total; they are listed in the OS Classification by depreciation groups. The main criterion for combining units of property into any of the depreciation categories is the useful life (USI) of the object. It is determined by enterprises for each PF facility, based on the expected useful period, operating conditions and regulations governing the use of the property.
SPI is the main criterion for classifying an asset into one of the presented depreciation groups.
| Group | SPI property |
| 1 | From 1 year to 2 years |
| 2 | From 2 to 3 years |
| 3 | From 3 to 5 years |
| 4 | From 5 to 7 years |
| 5 | From 7 to 10 years |
| 6 | From 10 to 15 years |
| 7 | From 15 to 20 years |
| 8 | From 20 to 25 years |
| 9 | From 25 to 30 years |
| 10 | Over 30 years |
According to the general rules, the organization depreciates the received asset over the period of fixed income, determined by the Classifier (see table). If the company cannot find an object on the list, then the deadline is set based on the specifications of the asset or the manufacturer’s recommendations. If the asset is manufactured in a company, then the company’s specialists independently develop recommendations confirming the effective life of the asset. They are drawn up in any form. This may be an order from the manager or another document defining the PPI of the asset. Let's consider the characteristic features of property classified in each depreciation group.
OKOF access control system
Healthcare institutions may well install not a complex access control system, but just ACS locks (electromagnetic locks). There is no need to register locks as a separate inventory item. This conclusion follows from paragraphs 41 and 45 of Instruction No. 157n: since after installation the locks are inseparable from the building, they do not satisfy the conditions for acceptance for accounting either as fixed assets or as materials. To control and manage access, each health worker receives an electronic key for permanent use or for a certain period of time. For example, this could be a plastic card that contains a photo, number and personal data, as well as an individual code. At the same time, patients and visitors receive a simple plastic card upon registration: - for a certain period (usually from several hours); - allowing one-time or multiple access to the territory of the institution. Let us note that at present, the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 22, 2021 N 02-06-10/1855 is still relevant, which explains what records should be used to reflect the fact of issuing key media in the accounting records of certification centers. Despite the fact that the facts of the economic life of institutions are different from those registered by certification centers, some points are still important for all institutions: - the procedure for document flow when carrying out transactions with key media for accounting purposes must be established as part of the accounting policy; - according to Article 5 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2021 N 402-FZ “On Accounting”, the objects of accounting of an economic entity are assets, which include non-financial assets, including information carriers; — objects of non-financial assets (including information carriers) and transactions with them are subject to accounting in the accounts of the Unified Chart of Accounts, intended for collecting, registering and summarizing information in monetary terms about the state of property owned by the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities , budgetary and autonomous institutions (clause 22 of Instruction No. 157n). Accordingly, you should use account 10500 “Inventories” (clause 98 of Instruction No. 157n), since electronic keys are material assets that: - acquired (created) for use (consumption) in the course of the institution’s activities; - used in the activities of the institution for a period not exceeding 12 months. It is advisable to take into account manufactured passes as part of material inventories in account 10506 “Other material inventories”. When issuing them to employees and for distribution to patients (visitors), it is necessary to use off-balance sheet accounting in account 27 “Tangible assets issued for personal use to employees (employees)” (hereinafter referred to as account 27). Note that a fingerprint can also be used for identification. Such a system is effective in restricting access to specially protected premises, for example, to a room with narcotic drugs, a storage room for donor material and other premises. In this case, cost accounting will be related to equipment and will be similar to that discussed in the next subsection.
We recommend reading: How to enter who issued a marriage certificate in public services
In the context of the “attractiveness” of healthcare facilities for terrorist attacks, ensuring visual control comes to the fore. This control is carried out using video surveillance systems integrated into the access control system. The video surveillance system for monitoring compliance with the regime must provide: - internal video surveillance in real time of the premises of the institution in which people are present, including wards; — permanent digital recording of the video stream coming from all video cameras. The use of video surveillance will allow you to record (and register): - movements of patients, visitors and staff within the institution; — compliance with the rules of the regime of a particular medical institution. Due to the changed requirements for anti-terrorism security, it is advisable to use video cameras with internal digital signal processing, as well as with a high level of sensitivity and resolution. For example, the use of cameras with infrared (IR) illumination provides acceptable color images during the day and black and white images at night. To carry out surveillance in the dark, it is also possible to use video cameras with the highest level of sensitivity, which will allow video surveillance without IR illumination. There are systems with functions of personal identification, sudden movements, and other things, which make it possible to identify potentially dangerous visitors to an institution. Thus, even if the territory of the institution is equipped with cameras, it is possible that their level is far from the requirements of anti-terrorism security and the accountant will again have to face accounting problems in recording video systems. Thus, an important aspect of a video surveillance system is the presence of a direct observer, that is, a security officer. To increase the efficiency of its work, a security post is usually equipped. Such a post is an integral part of video surveillance systems, since its presence provides the observer with convenience and even a certain comfort, which improves the results of: - visual control; — assessment of the situation; — checks of all security subsystems of the institution; — response to signals received from the ACS system. The security station console must have a monitor on which images from CCTV cameras located both around the perimeter and in the premises of the medical institution are displayed. Thus, the system in question is essentially a set of special equipment that must be installed. Purchased equipment is subject to accounting as part of inventories, which means it must be purchased at the expense of Article 340 “Increase in the cost of inventories” of KOSGU. Work on its installation should be paid for under subarticle 226 “Other work, services” of KOSGU. Such clarifications are given in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 16, 2021 N 02-14-10/64/944, dated June 6, 2021 N 02-05-10/27545. Equipment requiring installation is subject to accounting on account 105 04 “Building materials” (clause 118 of Instruction No. 157n). Since the installed video surveillance system is intended for use in an institution for more than 12 months, it is subject to accounting as part of fixed assets. In 2022, the video surveillance system belonged to the subsection “Machinery and Equipment”, television and radio receiving equipment (code 14 3230000 OKOF). From January 1, 2022, the old OKOF code was converted into a new one - 320.26.30.1 OKOF “Communication equipment, radio or television transmitting equipment.” This is the fourth depreciation group, the maximum service life is 7 years.
Directory "Fixed assets".
Let's start studying fixed asset accounting in the 1C Accounting 8 program with reference books. Let's go to the "Reference books" section, "OS and intangible assets" group. Let’s select the directory “Fixed Assets”.
The directory is intended to store a list of fixed assets and information about them.
Information about the fixed asset is filled in upon acceptance for accounting and may change during operation.
The directory has a multi-level, hierarchical structure. To classify fixed assets, you can create groups and subgroups.
When you enter a fixed asset, an inventory number is automatically assigned.
On the Basic Information , you can manually fill in the data:
- Full name - the name of the main tool for filling out printed forms.
- Manufacturer, serial number, passport number, date of manufacture (construction).
- Fixed asset accounting group - category of fixed asset, for example, Buildings, Structures, Transfer devices, etc.
- Type of fixed asset - type of fixed asset: direct fixed asset or capital investment in leased property.
- Depreciation group - depreciation group of a fixed asset.
- OKOF , Code according to ENAOF .
- The Motor transport checkbox is set for motor vehicles.
- Location address and region code.
The Accounting and Tax Accounting tabs contain information on accounting and tax accounting of fixed assets. This information is filled in automatically after the fixed asset is accepted for accounting and put into operation.
You can register the acceptance of a fixed asset for accounting on the Accounting using the hyperlink Enter a document of acceptance for accounting .
An inventory card of a fixed asset (form OS-6) can be generated by clicking the Form OS-6 .
You can add a group of fixed asset objects of the same type, differing only in inventory numbers, to the directory by clicking the Group addition .
In the form that opens, you must indicate:
- The code from which numbering will begin is
- Number of elements created,
- Name of fixed assets.
You can also fill in other information that is common to the objects you are adding.
The number of added objects is limited by the bit depth of the code. For example, specifying the start code 01 means that no more than 99 directory entries can be added automatically. If you want to add more elements in batches, you must add enough bits to the initial code.
Group addition of directory elements is done by clicking the Add . All elements will have the same names and contain the information specified in the fields of the group addition form.
To quickly fill out documents with similar fixed asset objects that have the same names, you need to enter at least one such object into the tabular section. The list of fixed assets will be filled with objects that have the same name as the one originally entered, by clicking the Fill - By name command panel of the tabular section.
Receipt of fixed assets
Let's move directly to accounting for fixed assets and create the first document related to the receipt of fixed assets in our company.
Go to the “OS and Intangible Materials” section of the “Equipment Receipts” magazine. Let's create our first document:
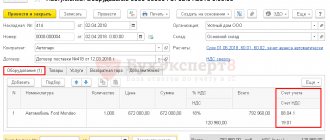
We receive equipment from the supplier:
- Invoice 1501 dated 01/15/2015, invoice 1501 dated 01/15/2015
- Supplier LLC "KVADROKOM" INN/KPP: 5027147377/ 770301001
- OGRN: 1095027003367
- Address 123242, Moscow, Sadovaya-Kudrinskaya street, building No. 11, building 1, apartment Room 2P-14
- Automatic striping machine. EXS 108 1 pc. RUB 1,180,000.00 each
Total: RUB 1,180,000.00 incl. VAT 180,000.00
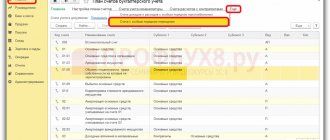
Directory "Methods of reflecting expenses."
The directory is located in the “Directories” section, the “Income and Expenses” group.
The directory is intended to store a list of possible ways to reflect depreciation expenses (repayment of cost) in the costs of the enterprise.
The method of reflecting depreciation expenses is indicated when accepting a fixed asset for accounting, when accepting an intangible asset for accounting, when indicating the purpose of use of work clothes and special equipment.
When entering a method for reflecting depreciation expenses, you must specify the accounting and tax account and the corresponding analytics according to which the depreciation amount should be distributed.
Depreciation costs can be distributed in a certain proportion across several cost items and analytical objects, for example, across several divisions of the organization. To do this, you need to set the values of the distribution coefficients in the K . When calculating the amount of depreciation, the values of the specified coefficients are summed up, and then the amount of depreciation is distributed proportionally to the value of each coefficient.
By default, several elements have already been created in it and note that they are called Depreciation (account 20.01), Depreciation (account 26), Depreciation (account 44).
What is an OS classifier?
The 2016 classifier of fixed assets used when searching for depreciation groups is provided by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups” dated 02/01/2002 No. 1 with the latest amendments established by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On amendments to the classification of fixed assets” dated 07/06/2015 No. 674. The classification of depreciation groups is formed according to information from the All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets (abbreviated as OKOF) OK 013-94, established by Decree of the State Standard of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 1994 No. 359.
IMPORTANT! From January 1, 2022, the OK 013-2014 classifier, approved by the order of Rosstandart “OK 013-2014 (SNS 2008), begins to function. OKOF" dated December 12, 2014 No. 2018-st. Classifier OK 013-94 will become invalid.
Replacing the old OKOF with a new one will entail reforming the classifier of fixed assets by depreciation groups.
See “The classification of fixed assets by depreciation groups has been updated.”