1C experts remind you about the features of accounting for expenses for business trips outside the Russian Federation and talk about reflecting such expenses using the example of “1C: Accounting 8” edition 3.0, taking into account the new capabilities of the program.
Business trips abroad did not stop even under conditions of restrictions and self-isolation due to coronavirus. It is enough, for example, to recall the firefighters, virologists and epidemiologists sent to help foreign countries. And in commercial organizations, business trips outside the Russian Federation are common. At the same time, the procedure for reflecting business trip expenses in foreign currency in accounting and tax accounting, as well as settlements with accountable persons for such business trips, often raises questions. Let's consider the features of accounting for expenses for foreign business trips and their reflection in 1C: Accounting 8, edition 3.0.
Procedure for reimbursement of travel expenses
The rules for sending employees on business trips both on the territory of the Russian Federation and on the territory of foreign states are determined by the Regulations on the specifics of sending employees on business trips (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749).
The procedure and amount of reimbursement to employees for expenses related to business trips are determined by a collective agreement or a local regulatory act of the organization (clause 11 of the Regulations on Business Travel, Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if an employee is sent on a business trip, the employer is obliged to compensate him for:
- travel expenses;
- expenses for renting residential premises;
- additional expenses associated with living outside the place of permanent residence (per diem);
- other expenses incurred by the employee with the permission or knowledge of the employer. For example, telephone costs, entertainment expenses, transportation costs, etc.;
And when sent on a business trip to the territory of a foreign state, the employee is additionally reimbursed (clause 23 of the Regulations on Business Travel):
- expenses for obtaining a passport, visa and other documents;
- mandatory consular and airport fees;
- fees for the right of entry or transit of motor vehicles;
- expenses for obtaining compulsory health insurance;
- other mandatory payments and fees.
The daily allowance amount is established by a collective agreement or a local regulatory document of the organization (LND). You can set separate daily allowance rates for each country or group of countries. The maximum amounts that are not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions for compulsory pension, medical and social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity are 700 rubles. for each day of being on a business trip in the Russian Federation and 2,500 rubles. — outside the territory of the Russian Federation. There is no standard established for income tax and contributions for injuries (clause 1 of Article 217, clause 12 of clause 1 of Article 264, clause 2 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 17, 2011 No. 14-03- 11/08-13985).
Payment of daily allowances for business trips outside the territory of the Russian Federation is regulated by paragraphs 18-20 of the Regulations on Business Travel:
- for a one-day business trip, daily allowance is paid in the amount of 50% of the norm for business trips abroad;
- the dates of crossing the state border of the Russian Federation when traveling from the territory of the Russian Federation and to the territory of the Russian Federation are determined by the marks of the border authorities in the passport;
- when an employee is sent on a business trip to the territory of countries with which intergovernmental agreements have been concluded, on the basis of which marks are not made when crossing the border, the date of crossing the state border of the Russian Federation is determined by travel documents (tickets);
- when an employee is traveling from the territory of the Russian Federation, the date of crossing the state border is included in the days for which daily allowances are paid according to the norm for business trips abroad. When an employee travels to the territory of the Russian Federation - on days for which daily allowances are paid according to the norms for Russia. If an employee is sent on a business trip to the territory of two or more foreign states, daily allowances for the day of crossing the border between states are paid in foreign currency according to the standards established for the state to which the employee is sent.
Upon returning from a business trip, the employee, within three working days, is obliged to provide the employer with an advance report on the amounts spent in connection with the business trip and make a final payment for the advance payment issued to him for travel expenses, attaching documents confirming the expenses (clause 26 of the Business Travel Regulations).
The supporting documents on expenses associated with the business trip attached to the advance report must be translated into Russian (clause 9 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n). The translation can be done either by a professional translator or by a full-time employee of the organization (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 20, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/202).
1C:ITS
For more information on the procedure for reimbursing employees for travel expenses, including the calculation of daily allowances, see the “HR Handbook” in the “Legal Consultations” section.
Results
When sending an employee abroad on official business, it is necessary to issue an order indicating the purpose and timing of the trip.
If necessary, the following are issued: a foreign passport (if you do not have one or it is expired), a visa (if it is required to enter the country), compulsory medical insurance and other documents. It is also advisable to provide the employee with instructions on what documents he should bring from the trip to justify travel expenses. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Reflection of settlements for foreign business trips
Calculations for payment and reimbursement of employee expenses related to a business trip outside the Russian Federation, including advance payment and repayment of unspent funds, can be made in foreign currency (clause 16 of the Regulations on Business Travel, clause 9 of Part 1 of Article 9 of the Federal Law dated 12/10/2003 No. 173-FZ “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control”).
The procedure for reflecting expenses and settlements with employees related to foreign business trips in accounting and tax accounting depends on the currency in which the advance for the business trip was issued and on the availability of documents confirming currency conversion.
In practice, the following options for issuing an advance to an employee are possible:
- the advance was issued in foreign currency (in cash or by transferring funds to the employee’s personal bank card in foreign currency);
- a corporate bank card in foreign currency was issued;
- the advance was issued in rubles (in cash or by transfer of funds to the employee’s personal bank card);
- A corporate bank card in rubles was issued.
Let us consider the features of accounting and reflection in the program of each of these options.
Business trip order
Before preparing an order, you need to check:
- whether the posted employee belongs to the category of persons who are prohibited from being sent on business trips;
- Are there any restrictions on sending a specific employee on a trip?
In the event of a travel ban, you must look for another candidate for a business trip. And if there are restrictions on business trips, it is necessary to inform the employee that he has the right to refuse a business trip and obtain written consent from him for the trip.
The order for a foreign business trip indicates the country and city (locality/settlement) to which the employee is sent. The receiving party is also indicated - the organization that sent the invitation or challenge.
In addition, the order can reflect at whose expense the business trip will be paid. The fact is that there are business trips, the expenses of which are paid by the host company (in whole or in part).
It makes sense in the order to reflect the type of transport on which the traveler is sent. This is especially true if the employee crosses the border in a personal or company car.
If the company’s internal regulations provide for the publication of other documents during a business trip (for example, an official assignment, an internal memorandum, etc.), it is necessary to prepare them as well.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with registering a business trip abroad using a memo in the article “What you need to know about a memo about sending you on a business trip.”
If it is customary for the company to issue only a business trip order, you only need to prepare it. There is no special form for this order. You can use the T-9 form or develop your own.
You can download the T-9 order form for free from the link below:
FORM T-9
You can also familiarize yourself with the T-9 order form in our article “Order (order) on sending on a business trip.”
If the company additionally uses its own developed document templates, you can take samples from our material “How to draw up and execute an order for daily allowance on a business trip.”
If the advance is issued in foreign currency
In accounting, currency transactions are regulated by PBU 3/2006 “Accounting for assets and liabilities, the value of which is expressed in foreign currency” (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 27, 2006 No. 154n). Transactions made in foreign currency are reflected in the currency of payment and in rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in effect on the date of the transaction (clauses 4-6, 20 PBU 3/2006, Appendix to PBU 3/2006).
Advances issued by an organization are recognized in accounting as valued in rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in effect on the date of payment of the advance. They are not recalculated due to changes in the exchange rate after being accepted for accounting (clauses 9, 10 of PBU 3/2006).
For income tax purposes, the rules are similar. Expenses expressed in foreign currency are recalculated into rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of recognition of the corresponding expense. And advances issued are converted into rubles at the official rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of transfer of the advance (clause 10 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In accounting, the date of transaction for an organization's expenses in foreign currency related to business trips is the day of approval of the advance report (Appendix to PBU 3/2006). In tax accounting, travel expenses are also recognized on the date of approval of the advance report (clause 5, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, in both accounting and tax accounting, travel expenses in foreign currency are recognized on the date of approval of the advance report:
- at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of issue of the advance - within the amount issued for the report;
- at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of approval of the advance report - in the amount of overexpenditure.
If settlements with the employee are not completed after approval of the advance report, then in accounting the resulting debt is recalculated into rubles at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the reporting dates and on the date of repayment of the debt (clauses 5-7 of PBU 3/2006). In tax accounting, recalculation is performed on the last day of each month and on the date of debt repayment (clause 10 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In “1C: Accounting 8”, the recalculation of currency balances, including the organization’s foreign currency debt to the accountable person, is performed monthly when performing the routine operation Revaluation of currency funds
included in
the Month Closing
Operations
section ). The employee’s debt to the organization in the program is considered an advance payment and is not revalued.
Exchange differences arising in settlements with the employee after approval of the advance report are taken into account:
- in other income and other expenses (clauses 11-13 PBU 3/2006; clause 7 PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/06/1999 No. 32n; clause 11 PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n);
- in non-operating income and non-operating expenses - for profit tax purposes (clause 11, article 250, subclause 5, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Foreign taxes
Often, employees attach supporting documents to advance reports for foreign business trips, where foreign taxes are highlighted as a separate line. According to the position of the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service, Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains a closed list of unaccounted expenses; foreign taxes are not indicated there. In this regard, taxes paid abroad can be taken into account for profit tax purposes on the basis of subparagraph 49 of paragraph 1 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as other expenses associated with production and sales.
If a corporate bank card is issued in foreign currency
If an employee is issued a corporate bank card in foreign currency, then the procedure for settlements with the employee, as well as the procedure for reflecting expenses in accounting and tax accounting, is similar to the procedure applied when issuing an advance in foreign currency.
In this case, the date of issue of the advance to the employee is the date of payment via a corporate bank card or the date of withdrawal of cash from it in foreign currency.
Let's look at an example of how to reflect expenses for foreign business trips in “1C: Accounting 8” version 3.0 if an employee receives an advance in foreign currency.
Example
Kvadrat LLC uses the general taxation system (GTS), applies the accrual method, and pays VAT. An employee of Kvadrat LLC was sent on a business trip to Munich (Germany) from 02/04/2020 to 02/07/2020 (4 days).
Business travel expenses are related to the main activities of the organization and are taken into account as part of expenses for ordinary activities on account 26 “General business expenses”.
In accordance with the organization’s regulations on business trips, the daily allowance in the Russian Federation is 700 rubles. per day, on the territory of a foreign state – 2,500 rubles. per day.
On 02/03/2020 the accountable person was issued:
- advance payment in the amount of 8,200 rubles. by transferring to the employee’s card;
- e-ticket Moscow – Munich – Moscow costs 11,393 rubles;
- corporate bank card denominated in foreign currency (EUR).
Employee:
- 02/03/2020 withdrew 500 EUR from the corporate card;
- 02/04/2020 crossed the border of the Russian Federation and arrived at the destination;
- 02/07/2020 crossed the border of the Russian Federation on the way back;
- On February 10, 2020, he submitted to the accounting department an advance report and documents confirming the expenses incurred - in total, in the amount of 8,200 rubles. and 586.20 EUR;
- On 03/03/2020 I received reimbursement for overexpenditure.
According to the terms of the Example, the employee received amounts under report both in rubles and in foreign currency (by using a corporate bank card). Therefore, to summarize information about settlements with an employee, the program automatically uses the following accounts:
- 71.01 “Settlements with accountable persons” - for settlements in rubles;
- 71.21 “Settlements with accountable persons (in foreign currency)” for settlements in EUR
.
The transfer of funds against the report to the employee’s card in the program is documented in the document Write-off from current account
with the type of transaction
Transfer to an accountable person
(section
Bank and cash desk - Bank statements
). The funds are transferred in rubles, therefore the document indicates account 51 “Current accounts” as the accounting account.
When posting a document, an accounting entry is generated:
Debit 71.01 Credit 51
— for the amount of the advance payment (RUB 8,200.00).
Hereinafter, for tax accounting purposes, special fields of the accounting register are simultaneously filled in (for those accounts where tax accounting is supported). According to the terms of the Example, there are no differences between accounting and tax accounting data.
An electronic travel ticket was purchased for the employee. Starting from version 3.0.81 in 1C: Accounting 8, electronic travel tickets can be taken into account not only as monetary documents, but also in a simplified way. For more details, see the article “Accounting for electronic travel tickets in 1C: Accounting 8”.
Let's assume that an organization uses a simplified method of accounting for electronic tickets. In this case, the purchase of a ticket for an employee when sending him on a business trip is reflected in the document Receipt of tickets
(
Shopping
). When posting a document, an accounting entry is generated:
Debit 76.14 Credit 60.01
— for the amount of the purchased ticket (RUB 11,393.00).
Let us recall that account 76.14 “Purchase of tickets for business trips” is specifically designed to account for tickets purchased by the organization for business trips in Russian currency. Analytical records are maintained for each posted employee and ticket.
Let's assume that a separate special card account is opened for a corporate bank card of an organization denominated in foreign currency (EUR), to replenish which funds are transferred from a foreign currency account. In this case, cash withdrawals using a card from an ATM are reflected in the bank’s currency statement and are registered in the program with the document Debiting from a current account
with the type of transaction
Transfer to an accountable person
. The accounting account should be account 55.24 “Other special accounts (in foreign currency)”.
When posting a document, an accounting entry is generated:
Debit 71.21 Credit 55.24
- in the amount of 500.00 EUR, the ruble valuation of which is 34,798.80 rubles. (500.00 EUR x 69.5976, where 69.5976 is the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of debiting funds from the special currency account on 02/03/2020).
The employee will have to report with two advance reports - ruble and foreign currency.
The provision of an advance report by an employee is registered with the document Advance report
(section
Bank and cash desk
or section
Purchases
).
To reflect business trip expenses in rubles, you can use both a general and a simplified form of an advance report. Let's create a simplified form of an advance report (command Create - Advance report for business trip
), Fig. 1.
Rice. 1. Simple form of expense report
In the form of an advance report with the type Business trip
When you select an employee and a business trip period, tickets suitable for the departure date are downloaded automatically and are displayed in the form of a hyperlink located next to the text
Tickets purchased by the organization
.
This hyperlink takes you to the Tickets
, where you can check and, if necessary, correct information about purchased tickets.
Advance payment documents are also selected automatically. Via the hyperlink located next to the text Advance
, you can go to the
Advances issued
to view the relevant documents.
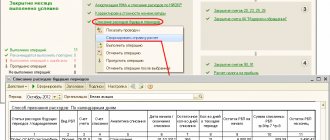
Via the hyperlink located next to the text Per Diem
, you should go to the form of the same name and fill out the business trip route, start and end dates of the business trip, including the date of border crossing (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Calculation of daily allowances
The daily allowance is calculated automatically based on the maximum amounts that are not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions. The amount of daily allowance can be changed if the collective agreement or local regulation establishes different standards. The program will remember them and substitute them into the calculation next time.
If an employee incurs additional expenses in rubles on a business trip, they should be indicated in the tabular part of the simplified form of the advance report. According to the conditions of the Example, there are no such expenses, so the tabular part is not filled in (see Fig. 1).
The default account for travel expenses is set to the main expense account specified in the organization’s accounting policy settings (section Main
).
If necessary, travel expense accounts can be changed in the Daily Subsistence
and
Tickets forms.
Mutual settlements with the accountable person are reflected in the visual form of control results, where the expenses incurred are detailed into daily allowance and other expenses of the employee (if any). According to the conditions of the Example, in the control totals line, expenses are indicated in the amount of 0.00 rubles. (see Fig. 1).
The cost of tickets purchased by the organization is accounted for separately in account 76.14, and therefore is not included in the employee’s reimbursable expenses. Also in the control totals line, the ruble equivalent of the advance received in foreign currency is indicated for reference.
When posting the document Advance travel report
accounting entries are generated:
Debit 26 Credit 71.01
— for the amount of daily allowance (RUB 8,200.00);
Debit 26 Credit 76.14
— for the cost of the ticket (RUB 11,393.00);
International transportation of passengers and baggage by any type of transport is subject to VAT at a zero rate (clause 4, clause 1, article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore no VAT entries arise.
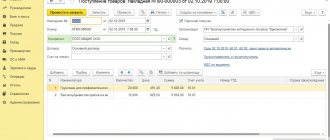
To reflect business trip expenses in foreign currency, you should use the “classic” form of an advance report with the type Purchase, expenses
(command
Create – Advance report
), fig. 3.
Starting from version 3.0.78 in “1C: Accounting 8” when posting the Advance report
You can automatically calculate the foreign currency exchange rate taking into account the exchange rate on the date of the advance payment.
To do this, follow the link located on the right above the tabular part of the document (see Fig. 3) and in the opened form Prices in the document
make settings:
- in field Currency
— select the settlement currency (EUR);
- in field Well
— set the switch to the position
Calculated automatically
. In this case, the amount of expenses within the limits of the issued advance is calculated at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of issue of the advance, and the remaining amount - at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of approval of the advance report.
Rice. 3. Advance report, “Advances” tab
When you indicate the date of the advance report and the employee in the header of the document, advances issued to him in foreign currency are selected automatically and reflected on the Advances
in the tabular part (Fig. 3).
When entering information about travel expenses in foreign currency into a document ( Other
) the amount of offset advances is calculated automatically at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of issue of the advance. According to the terms of the Example, this is 02/03/2020, that is, the date of cash withdrawal from the corporate card.
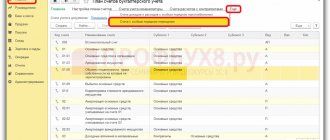
Let’s assume that the employee attached the following documents to the expense report confirming the expenses incurred in foreign currency:
- invoice for hotel accommodation in the amount of 571.20 EUR (incl. VAT 91.20 EUR);
- a certificate confirming cash withdrawal in foreign currency with an allocated bank commission amount of 15 EUR.
In accordance with the specified documents on the Other
Click the
Add
to fill out the tabular part (see Fig. 4).
Line 1 contains the details of the invoice for hotel accommodation, the name of the service, the amount excluding VAT (480 EUR), the VAT rate ( Excluding VAT
), name of the hotel service provider (for reference), invoice (26) and cost analytics for accounting and tax purposes (
Travel expenses
).
In business trip expenses, you can take into account taxes and fees paid on the territory of a foreign state, with the exception of those subject to offset when paying the corresponding tax in the Russian Federation (clause 49, paragraph 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 18, 2019 No. 03- 03-06/1/17684, dated 09/07/2018 No. 03-03-06/1/64126). Therefore, in line 2, information about paid VAT in the amount of 91.20 EUR is entered.
Line 3 contains information about the bank’s commission for cash withdrawal in the amount of 15 EUR, account 91.02 “Other expenses” and a cost item with the type of expense “Costs for bank services”.
Rice. 4. Advance report, “Other” tab
When posting a document, accounting entries are generated:
Debit 26 Credit 71.21
- for the cost of hotel accommodation in the amount of 480.00 EUR, the ruble value of which is 33,409.05 rubles;
Debit 26 Credit 71.21
- for the amount of VAT 91.20 EUR paid in Germany, the ruble value of which is 6,347.72 rubles;
Debit 91.02 Credit 71.21
- for the cost of bank services in the amount of 15.00 EUR, the ruble value of which is 1,044.03 rubles.
Let's analyze the amounts in rubles automatically calculated by the program:
- On 02/03/2020, the accountable person received an advance of 500.00 EUR; when converted into rubles, the amount of the advance is 34,798.80 rubles. (500.00 EUR x 69.5976, where 69.5976 is the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as of 02/03/2020);
- On 02/10/2020, an advance report was submitted in the amount of 586.20 EUR, while the unpaid amount in foreign currency is 86.20 EUR, in ruble valuation - 6,002.00 rubles. (86.20 EUR x 69.6288, where 69.6288 is the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as of 02/10/2020);
- the total amount of expenses in rubles is 40,800.80 rubles. (RUB 34,798.80 + RUB 6,002.00);
- the settlement rate (for reference) is 69.6022 (RUB 40,800.80 / EUR 586.20);
- the cost of hotel accommodation in ruble equivalent is 33,409.05 rubles. (480.00 EUR x 69.6022);
- the amount of foreign VAT in ruble equivalent is 6,347.72 rubles. (91.20 EUR x 69.6022);
- the cost of bank services in ruble equivalent is 1,044.03 rubles. (15.00 EUR x 69.6022).
A detailed calculation of ruble amounts is presented in the calculation certificate Ruble document amounts in foreign currency
, which is available by clicking
the Print
located on the command line (see Fig. 3, 4).
Let's assume that for some reason the overspending was not reimbursed to the accountable person by the end of February.
Therefore, when performing a regulatory operation Revaluation of currency funds
For February, an accounting register entry is generated:
Debit 91.02 Credit 71.21
- for the amount of negative exchange rate difference in the amount of 352.97 rubles. (86.20 EUR x (73.7235 - 69.6288), where 73.7235 is the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as of the revaluation date of 02/29/2020; 69.6288 is the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of the debt to the accountable entity, that is, as of 10.02 .2020 when the advance report was submitted).
In addition, foreign currency balances on foreign currency accounts 52 and 55.24 are revalued.
A detailed calculation of exchange rate differences can be analyzed in the Help-calculation of currency revaluation
for February 2022.
Reimbursement of overexpenditure to the accountable person can be formed on the basis of an advance report. If overexpenditure is paid by bank transfer to an employee’s foreign currency account, then you should use the document Write-off from current account
with the type of transaction
Transfer to an accountable person
. The funds are transferred in foreign currency, so account 52 is indicated in the document as the accounting account.
When posting a document, accounting entries are generated:
Debit 71.21 Credit 91.01
- for the amount of positive exchange rate difference in the amount of 26.36 rubles. (86.20 EUR x (73.7235 - 73.4178), where 73.7235 is the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of the last revaluation 02/29/2020; 73.4178 is the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of transfer of funds 03/03/2020);
Debit 71.21 Credit 52
- for the amount of compensation for overexpenditure in foreign currency (86.20 EUR), the ruble value of which is 6,328.61 rubles. (86.20 EUR x 73.4178, where 73.4178 is the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as of the date of transfer of funds 03/03/2020).
In addition, currency balances on account 52 are revalued.
You can analyze the status of settlements with an accountable person for settlements in rubles and in foreign currency using standard reports, for example, using the account balance sheet
for accounts 71.01 and 71.21 (section
Reports
).
As of 03/03/2020, settlements with the employee in rubles and foreign currency were completed.
If the advance is issued in rubles
If an advance payment for a business trip abroad is issued to an employee in rubles, and expenses on a business trip abroad are incurred in foreign currency, then in this case the procedure for accounting for foreign currency expenses is different. According to the Russian Ministry of Finance (see, for example, letters dated June 19, 2020 No. 03-03-06/1/52967, dated January 21, 2016 No. 03-03-06/1/2059), travel expenses in foreign currency are recognized on the date of approval advance report:
- at the conversion rate on the date of the transaction (on the date of purchase of currency by the employee or the date of debiting funds from his bank card), confirmed by a certificate or bank statement;
- at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of issue of the advance, if the conversion rate is not documented;
- at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of approval of the advance report - in the part not covered by the advance payment).
In this case, exchange rate differences on advances in rubles do not arise.
If a corporate bank card is issued in rubles
When issuing a corporate bank card to an employee in rubles, the procedure for recording expenses and settlements with the accountable person is similar to the procedure used when issuing an advance in rubles. Travel expenses are recognized on the date of approval of the advance report at the conversion rate on the date of the transaction, that is, on the date of purchase of currency by the employee or on the date of debiting funds from the corporate bank card.
If an employee received an advance in rubles (from the cash register in cash, by transferring funds to a personal bank card or by making a transaction with an organization’s corporate card), then he should report on foreign currency expenses on a foreign business trip only with a ruble advance report. In the document Advance report
ruble amounts will have to be calculated manually, guided by the explanations of the Russian Ministry of Finance given above.
1C:ITS
In the Directory of Business Operations. 1C: Accounting 8” section “Instructions for accounting in 1C programs”, see in more detail: about paying with a corporate card for goods (work, services); on settlements with accountable persons, including when sent on a business trip abroad.
From the editor.
1C experts spoke about settlements with accountable persons in “1C: Accounting 8” edition 3.0 on July 30, 2020 at a lecture in 1C: Lecture Hall.
The video is available on the 1C:ITS website on the 1C:Lecture .
Transferring the accountable amount in euros to the employee’s card
To issue accountable amounts, the organization has the right to use:
- cash;
- corporate card;
- employee card, including salary card.
Read more Procedure for recording settlements with accountable persons: legislation
When filling out a payment order, select the transaction type Transfer to an accountable person . The income type code will be filled in automatically.
- Deduction under a writ of execution - 2 - prohibited (without reservations) .
More details Codes of salary payments in payment documents
Conduct the transfer of the accountable amount in foreign currency using the document Write-off from the current account transaction type Transfer to an accountable person (Bank and cash desk - Bank statements).
When filling out, check:
- Bank account - foreign currency account must be selected from the Bank Accounts ;
- Accounting account - “Currency accounts” - in this case the account will be entered automatically;
- Type of transaction - Transfer to an accountable person ;
- Expense item - Issuance of accountable amounts - this is a predefined item and is filled in automatically.