The balance sheet procedure has changed
In the annual reports for 2022, it is allowed not to disclose information if this would lead to losses. The changes introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 27, 2020 No. 287n came into force on February 27, 2021. Amendments have been made to a number of PBUs:
- 9/99 “Income of the organization”;
- 11/2008 “Information about related parties”;
- 2/2008 “Accounting for construction contracts”;
- 12/2010 “Information by segments”.
According to the new rules, if disclosure of information in reporting will lead to economic losses or damage to the business reputation of the organization or its counterparties, the information may not be indicated. In this case, limited information is disclosed.
Capital and reserves in the 2022 balance sheet
This section of the balance sheet (lines 1310 – 1370) reflects data on the organization’s equity capital. In 2022, there were no significant changes in the procedure for such reflection. Therefore, we recall only the most important points:
- the increase in the value of non-current assets is reflected in line 1340 “Revaluation of VA”. To do this, the results of revaluations must be taken into account separately in account 83;
- the increase in additional capital is reflected on line 1350 minus the amounts of revaluation of VA reflected on line 1340;
- We recommend reporting interim dividends paid during the year separately in a separate line. In this case, the adopted approach must be consistent from period to period;
- if during the transition to new Federal Accounting Standards it was necessary to recalculate the indicators, the results of such recalculation will adjust the value on line 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”.
Annual reporting forms
This year we will have to generate reports for 2022. The balance sheet form was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 61n dated April 19, 2019. This is a standard form of reporting that has not changed significantly for many years.
There are two documents called form number 1 Balance Sheet, but the rules for filling them out are no different.
The first document is standard. The report on this form is filled out for founders and other users of information. The second balance sheet format has only one difference: the tabular part of the document is supplemented with line codes. The report is intended for sending information to the territorial body of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Results
To compile the balance sheet for 2022, the forms of its full and simplified forms recommended by Order No. 66n are still used. From June 1, 2022, the edition dated April 19, 2019 is in effect. Entering data into the balance sheet is subject to a number of requirements for both the reporting itself and the accounting data that serves as a source of information for it.
Sources:
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Who submits the balance sheet
All Russian organizations and official representative offices of foreign companies are required to report on their financial and economic situation for the reporting year. This is regulated by the Law “On Accounting” No. 402-FZ.
The law provides “indulgences” for certain categories of economic entities that have the right to keep accounting records in a simplified form. They submit a shortened version of the balance sheet. But regardless of the method of accounting, basic or simplified, Form No. 1 is mandatory for all economic entities - legal entities.
Distinctive features of the current balance sheet
The forms of financial statements used to date are established by the current version of Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n (as amended on April 19, 2019).
The basic approach to the preparation of accounting reports corresponds to the following principles: it must be done according to accounting data, be complete, reliable, and useful for users. However, such reporting may have abbreviated versions. Recommendations for the preparation and presentation of forms are contained in the current edition of PBU 4/99.
For information on how to apply this PBU, read the article “PBU 4/99 - financial statements of an organization (nuances)” .
The full form of the balance sheet introduced by Order No. 66n (Appendix 1) is distinguished by the fact that it:
- offered only as one of the possible report options;
- assumes that the report compiler has a preferential right to independently detail the indicators;
- proposes to provide data for 3 dates (reporting date and the end of 2 years preceding the reporting year);
- provides a column for links to possible explanations by line;
- does not contain a section with information on off-balance sheet accounts.
The same document contains a simplified balance sheet form (Appendix 5), the use of which is available to persons specified in clause 4 of Art. 6 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ.
You can check whether you filled out the balance sheet correctly using step-by-step instructions from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the system, get a trial online access and go to the Typical Situation for free.
When and where to submit reports
For 2022, prepare reports in Form No. 1 to several authorities at once: to the Federal Tax Service - for all organizations, to the Ministry of Justice and (or) to the Ministry of Finance of Russia - for non-profit organizations and state employees. Upon additional request, accounting records are provided to the founders or owners of the company.
IMPORTANT!
The balance must be submitted to the tax office no later than 90 calendar days from the first day of the year following the reporting period. That is, no later than 03/31/2021.
If March 31st falls on a weekend, the transfer rule applies. This means that the deadline for submission is moved to the first working Monday. But in 2022, the delivery date is a working environment.
For public sector organizations, different deadlines for submitting reports have been established, earlier ones. This information is communicated to institutions in the prescribed manner.
IMPORTANT!
Reporting submitted to the Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Justice or the founder does not cancel the obligation to report to the Federal Tax Service within the established time frame.
Current assets in the balance sheet for 2021
Lines with codes starting with 12 are intended for inclusion in the balance sheet of data on current assets.
Let's consider those that are reflected in the balance sheet for 2022 with features.
Inventories in the balance sheet 2021
All inventories in the balance sheet for 2022 should be reflected in line 1210, taking into account the application of FAS 5/2019.
1. Raw materials, materials, fuel, spare parts, components, purchased semi-finished products are taken into account at actual cost. It is determined in the manner established by clauses 10 - 18 of FSBU 5/2019. In this case, it is permissible to accept them for accounting at the book price with the differences from the actual price reflected in account 16.
Do not reflect in line 1210 assets that are used to create non-current assets. Such accounting does not comply with either FSBU 5/2019 or FSBU 26/2020, which came into force on 01/01/2022. Such assets should be shown in the balance sheet as non-current assets.
2. Finished products are accepted for accounting at actual production costs. It is determined in the manner established by paragraphs 23 - 27 of FSBU 5/2019.
Finished products in mass and serial production can be valued in the amount of:
- direct costs (without indirect);
- planned (standard) costs.
The actual cost of finished products does not include costs that are not necessary for its production. For example, excess consumption of raw materials, losses from downtime and defects, advertising costs, etc. Accordingly, they also do not fall into line 1210.
If finished products are accounted for at the planned (standard) cost, the difference between it and the actual cost is attributed to a decrease (increase) in the amount of expenses from the sale of finished products of the reporting period in which this difference was identified (not reflected in line 1210).
3. Goods are accepted for accounting at actual cost. It is determined in the manner established by clauses 10 – 15, 17, 18 FSBU 5/2019.
Trade organizations may include in sales expenses the costs of procuring and delivering goods to central warehouses (bases), which they incurred before they were transferred for sale. Then such costs will not appear in line 1210.
Organizations engaged in retail trade can account for goods at sales price or using account 42 “Trade margin”. Goods that are accounted for in account 41 at their sales value are shown in the balance sheet minus the amount of the trade margin in account 42, which is attributable to the balance of goods not sold as of the reporting date.
Also, trading companies can reflect the receipt of goods using accounts 15 and 16 - in a manner similar to the procedure for recording transactions with materials:
- Shipped products (goods), the proceeds from the sale of which cannot be recognized in accounting for a certain time, as well as products (goods) transferred for sale to a commission agent, are accounted for on account 45 at actual or planned cost. Also, on account 45 in current assets, a real estate object that has been transferred to the buyer can be accounted for at its residual value, but the state registration of ownership does not coincide with the moment of recognition of the disposal.
- Animals being raised and fattened are accounted for on account 11. Animals purchased from other organizations and persons are accounted for at the actual cost of acquisition or accounting prices; transferred from the main herd - at residual value or initial value; offspring, weight gain and growth of animals - at the planned cost with adjustment at the end of the year to the actual cost of rearing.
At the end of the reporting period, inventories are accounted for at cost, which depends on the adopted method of calculating the cost of their movement (release of inventories into production, shipment of finished products, goods, write-off of inventories).
Work in progress (WIP) is included in inventories at actual cost. It is determined in the manner established by clauses 23 - 27 of FSBU 5/2019, similar to the assessment of finished products.
Real estate assets acquired or created (in the process of creation) for sale in the ordinary course of business are accounted for at actual cost:
- if an object is purchased, its cost is determined in a manner similar to that for raw materials;
- if created, in a manner similar to that for finished products.
Intellectual property acquired or created for sale in the ordinary course of business is accounted for at actual cost:
- if an object is purchased, its cost is determined in a manner similar to that for raw materials;
- if created, in a manner similar to that for finished products.
At the reporting date, inventories are reflected in the balance sheet at the lower of the following amounts:
- at actual cost;
- at net realizable value. It is defined as the estimated price at which an entity could sell inventories in the form in which it would normally sell them in the ordinary course of business, less the estimated costs required to produce, prepare for sale and sell them.
The excess of actual cost over net realizable value is considered impairment. In this case, a reserve is created for impairment of inventories. Account 14 is intended to account for such a reserve.
The allowance for impairment of inventories does not reduce the value at which the inventories are recorded, but it does reduce the value at which they are recorded on the balance sheet.
If there is impairment, the formula for line 1210 is as follows:
Page 1210 = Cost of inventory according to the valuation methods used – Provision for impairment of inventories
Deferred expenses are taken into account in the amount of actual expenses incurred minus their part attributed to expenses.
Accounts receivable
To reflect receivables in the balance sheet, line 1230 is provided. When filling it out at the end of 2022, you should remember:
- The listed advances and prepayments including VAT are reflected minus VAT subject to or accepted for deduction.
- The amounts of listed advances and prepayments related to the construction of fixed assets are not reflected in line 1230 (they should be shown in the lines of the “Non-current assets” section).
- Accrued revenue not presented for payment under construction contracts, the duration of which is more than 1 reporting year or the start and end dates of which fall on different reporting years, is reflected in line 1230 - in the amount determined based on the contractual value or the amount of actual expenses incurred. , which during the reporting period are considered possible for reimbursement. At the same time, if the indicator is significant, they provide a transcript and explanation.
- Receivables expressed in foreign currency are recalculated into rubles at the Bank of Russia exchange rate on the reporting date.
- Offsetting between accounts receivable items in the balance sheet is unacceptable.
Financial investments
Line 1240 reflects short-term financial investments, with the exception of cash equivalents.
The procedure for classifying them is similar to the procedure used for long-term financial investments. The only difference is that current assets include investments with a maturity (circulation) period of less than 12 months.
Other current assets
For other current assets in the balance sheet, line 1260 is intended.
In relation to the balance sheet for 2022, the following rules should be mentioned:
- The line includes the amounts of excise taxes to be deducted in subsequent periods.
- The line includes VAT amounts on shipments for which revenue cannot yet be recognized in accounting (accounted for in account 45).
- The line includes VAT and excise taxes on exports that have not yet been confirmed, which will be deducted in the future.
- The line can take into account long-term assets for sale (see information message of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 07/09/2019 No. IS-accounting-19).
Deadlines for “special” cases
Please note that for newly formed, liquidated and reorganized enterprises the deadlines are somewhat different. Let's consider the dates for submitting Form No. 1 for the following companies:
- Creation. An organization that was formed before 09/30/2020 is required to report according to generally accepted rules, that is, before 03/31/2020. But those companies that were formed after September 30, 2020 must report not in 2022, but in 2022. That is, for the reporting period of 2021 plus the period of existence in 2022.
- Reorganization. The company is required to report three months after making the latest changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. This rule is established not only for companies that continued their activities, but also for “merged” companies that completed their activities.
- Liquidation. An institution that has officially completed its activities is required to provide reporting no later than three calendar months from the date of making the relevant entries in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
Please take into account the established guidelines for due dates. Otherwise, administrative and tax liability is provided for the organization and responsible employees.
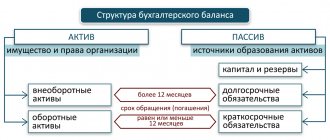
Current liabilities in the balance sheet for 2021
The same accounting and balance sheet rules apply to short-term debts reflected on lines with code 15 as to short-term liabilities of debtors.
Let us mention a few more important points:
- If borrowed funds were accounted for as long-term, but at the time of reporting the repayment period became less than 12 months, the balance of such funds should be reclassified as short-term and reflected in the balance sheet on line 1510.
- Line 1510 includes interest on long-term borrowed funds if their repayment period is less than 12 months.
- Companies determine the details for line 1520 “Accounts payable” independently, and depend on the accepted assessment of materiality.
- Those lessors who do not change the accounting for leasing agreements in connection with FAS 25/2018 reflect the difference between the amount of lease payments under the leasing agreement and the cost of the leased property as part of the indicator in line 1530 (Deferred income).
How to fill out your balance
When filling out the financial reporting form in Form No. 1, follow section 4 of Order No. 43n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 6, 1999 (as amended on January 29, 2018). Key rules that helped fill out an example of an enterprise balance sheet in Form No. 1 for 2022:
- fill out the report indicators in accordance with the actual account balances as of the reporting date, formed taking into account the requirements of PBU and the company’s accounting policies;
- reflect the indicators in monetary terms in the currency of the Russian Federation - in rubles, in thousands of rubles or in millions of rubles;
- Transactions made in foreign currency are recalculated at the rate established on the day of the transaction;
- if the company has a branch network, then at the end of the year a single balance sheet is formed (parent company plus branches);
- include indicators that exist for no more than 12 months as short-term assets and liabilities, and indicators that exist for more than one year as long-term assets;
- property and fixed assets should be reflected at “net” value, that is, taking into account depreciation and other costs provided for by PBU.
We offer a cheat sheet for filling out form No. 1.
This is what a sample balance sheet for 2020 looks like:
Non-current assets in the balance sheet
This section was entered from line 1110-1190 and the subtotal of the section (the sum of all completed lines) is line 1100.
At the same time, lines with codes 1130 (Intangible exploration assets) and 1140 (Tangible exploration assets) may not include organizations that are not engaged in the search and evaluation of mineral deposits or the exploration of new deposits.
Also, let’s immediately pay attention to the “Explanations” column in the balance sheet form: it contains indications of the corresponding section of the Explanations to the financial statements, which provides disclosure or additional information on the indicator given in the line. The “Explanations” column applies to all lines of all sections of the balance sheet, so we talk about it once in this part of the article and will not dwell on it in detail further.
We will also immediately touch on the need to decipher the summary balance sheet indicator. Decryption is needed if the data included in it is significant and without it (presented in decrypted form) it is impossible to create a reliable picture of the financial position of the company that formed the balance sheet.
The balance sheet indicator for 2022 is deciphered by introducing substrings to the corresponding line into the balance sheet and entering into them the data to be deciphered.
Intangible assets
Line 1110 of the balance sheet reflects information about intangible assets (intangible assets) recorded on account 04.
An accountant who has intangible assets often faces the question: how to report expenses on objects that will become intangible assets in the future?
Expert comments provide two points of view:
- The amount of investments in intangible assets is included in the indicator of line 1110 and is reflected separately in the transcript to line 1110. The position is based on an example of the preparation of Explanations to the balance sheet given in Appendix No. 3 to Order No. 66n. Table 1.5 to Section I of the balance sheet deciphers unfinished transactions for the acquisition of intangible assets, but in Section I itself there is no line for unfinished capital investments.
- Unfinished investments in intangible assets do not meet the requirements of paragraph 3 of PBU 14/2007 and should not be included in the indicator of line 1110. Such investments can be reflected in the section of non-current assets on a separate additional line (by decision of the reporting preparer), and if the amount of investments is not significant - it is appropriate to reflect it on line 1190 (Other non-current assets).
Which option for reflecting capital investments in intangible assets to choose for the balance sheet for 2021 remains at the discretion of the organization. The only recommendation: for all types of investments in intangible assets, it is advisable to establish and apply a unified approach.
In this article, we will not dwell in detail on what is included in intangible assets, considering that by the time the balance sheet for 2021 was drawn up, the accountant had already dealt with accounting issues.
Let us only recall that an intangible asset is accounted for in account 04 at its original cost, which is then repaid through depreciation accounted for in account 05. During the useful life of the intangible asset, depreciation is not suspended. At the same time, both the SPI and the method of calculating depreciation are subject to annual verification. The intangible asset itself must be checked annually for impairment. In addition, according to the accounting policy, intangible assets may be subject to periodic revaluation.
The results of all these actions should be reflected in the intangible asset indicator included in line 1110.
The balance sheet line indicates the residual value of the organization's intangible assets - the difference between the balance of accounts 04 and 05, taking into account revaluation and depreciation.
Intangible assets are classified at the time of their recognition based on their compliance with the established characteristics of an asset. Therefore, information about intangible assets with a private equity balance of less than 12 months as of the reporting date should not be disclosed in section II “Current assets”, but should be left in section I “Non-current assets” (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 19, 2006 No. 07-05-06/ 302).
And one more important nuance: if an organization takes into account in account 04 expenses for completed R&D, the results of which are not subject to legal protection, before being reflected as part of non-current assets, the amount of such expenses must be excluded from the balance of account 04.
Research and development results
According to Order No. 66n, a separate line 1120 of the balance sheet must reflect expenses for completed research, development and technological work (R&D), separately accounted for on account 04 (intangible assets).
This allocation of R&D again creates a dilemma for accountants:
- On the one hand, the amount of costs for unfinished R&D participates in the formation of the indicator of line 1120 and is reflected separately in one of the lines deciphering the indicator of line 1120. This position is based on the same Example from Order No. 66n as for line 1110.
- On the other hand, the amount of costs for unfinished R&D should not be included in line 1120 for the reason that, according to clause 16 of PBU 17/02, in the section “Non-current assets”, a separate group of items reflects information about R&D costs. At the same time, PBU 17/02 does not apply to costs of unfinished R&D. Thus, these expenses must either be reflected on a separate line entered independently by the organization, or if they are insignificant, they can be included in line 1190 (Other).
The company must decide on the reflection of expenses for incomplete R&D independently - with the same recommendation for uniform reflection of all such expenses as for capital investments in intangible assets.
For the indicator of line 1120, by analogy with line 1110 (intangible assets), the requirements are valid for the exclusion of expenses, the results of which are not protected by law, and for the reflection in it of assets whose PPI expires less than 12 months after the reporting date.
Fixed assets in the balance sheet 2021
Line 1150 to reflect the organization's fixed assets is usually filled out in four out of five balance sheets. Therefore, let's look at it in detail. Here, in the balance sheet for 2022, there was also a dual approach in terms of reflecting capital investments in unfinished fixed assets.
Proponents of the first approach believe that the amount of unfinished capital investments in objects, which will then be accounted for in account 01, is included in the indicator of line 1150 and reflected separately on one of the decoding lines. The opinion is based on the fact that the form of the Balance Sheet, approved by Order No. 66n, does not provide separate lines for reflecting investments in unfinished fixed assets. In this case, for example, the article “Unfinished capital investments”, according to the same order and the example to it, is included in the group of articles “Fixed assets”.
The second approach is that information about unfinished capital investments is not reflected in line 1150 “Fixed assets”. Those who are in favor of this accounting option draw a conclusion from the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting, in which in the section “Rules for the evaluation of items of financial statements” the subsection “Unfinished capital investments” is present along with the subsection “Fixed assets”.
As a result, how to reflect capital investments in unfinished fixed assets will have to be determined by each reporting preparer, while ensuring a uniform approach for all their types.
Important nuances in the formation of the “Fixed Assets” indicator arise in connection with the mandatory application of new Federal Accounting Standards from 01/01/2022:
1. There are two possible options for reflecting the right to use the asset (ROU) of the tenant (lessee):
- on line 1150 - if the received object meets the criteria for recognition of OS, with a decryption of information and disclosure in the Explanations;
- on a self-entered separate line.
If there are several options for accounting and reporting, the chosen one must be fixed in the accounting policy.
2. Nuances have emerged for the lessor (lessor) to reflect items transferred to the recipient:
- when applying FAS 25/2018, only fixed assets transferred for operating lease should remain on account 01(03), which forms line 1150;
- leased (financial lease) are subject to transfer into leased investments and should not be reflected in the fixed assets accounting accounts included in line 1150.
3. If the balance sheet compiler established from 01/01/2022 (according to FAS 6/2020) a different value limit for recognition as an asset than in previous years, then in order to correctly reflect the item “Fixed Assets” in the balance sheet, adjustments must be made: add to account 01 objects that began to meet the recognition criteria, or remove from account 01 objects that no longer meet these criteria.
4. If you use the retrospective option of switching to new Federal Accounting Standards, it is necessary to recalculate comparative indicators on line 1150 for previous years.
The fixed asset is accepted for accounting on account 01 at its original cost, which is then repaid through depreciation accounted for on account 02. A non-depreciable amount (liquidation value) can be established for the fixed asset. During the SPI of an object, depreciation is not suspended until the moment when the depreciable value becomes equal to or less than the liquidation value. At the same time, both the SPI, the method of calculating depreciation, and the value of the liquidation value are subject to annual verification.
Assets must be tested annually for impairment. In addition, according to the accounting policy, fixed assets may be subject to periodic revaluation.
The results of all of the above actions for the year should be taken into account in the OS indicator included in line 1150.
If during the reporting period the organization assessed fixed assets for the purpose of transferring them as collateral (or for other purposes), then such an assessment is not taken into account when preparing reports. And only the revaluation made in accordance with the accounting rules and accounting policies matters.
Profitable investments in material assets
On line 1160, intended for inclusion in the balance sheet of data on fixed assets accounted for in account 03 “Income-generating investments in tangible assets,” there are also changes in connection with the new Federal Accounting Standards, effective from 2022.
But before we talk about them, we note that in terms of reflecting capital investments in unfinished fixed assets, the situation is similar to that described in the previous subsection “Fixed Assets”. Here too, the balance sheet compiler needs to make a choice of the option for reflecting capital investments and consolidate it in the accounting policy.
From January 1, 2022, leasing (financial lease) transactions are accounted for in accordance with FAS 25/2018. Previous documents regulating leasing accounting have been cancelled. Thus, if an organization uses account 03, then from 01/01/2022 it can continue to account on it only fixed assets transferred for operating lease (clause 41 of FSBU 25/2018).
Accounting for fixed assets on account 03 and reflected in line 1160 of the balance sheet is carried out according to the same rules as for account 01 and line 1150.
Financial investments
In line 1170, as part of non-current assets in the balance sheet for 2022, the amount of financial investments whose maturity (circulation) period is more than 12 months from the reporting date should be reflected.
Without dwelling in detail on what constitutes financial investments and by what criteria they are recognized, we note several important points:
- Issued interest-free loans, interest-free bills received from buyers, accepted for accounting at face value, as well as similar assets are not financial investments (included in accounts receivable).
- Financial investments for which the current market value is determined (which are traded on the ORS) are reflected in the balance sheet at the end of the reporting year at the current market value by adjusting their valuation as of the previous reporting date.
- Financial investments for which the current market value is not determined (are not listed on the securities market) are subject to reflection in the balance sheet at their original cost (clause 21 of PBU 19/02). At the same time, for such financial investments, the organization is obliged to test for impairment and create an impairment reserve.
Companies that have the right to use simplified accounting methods may not comply with paragraphs 2 and 3 and account for financial investments at their original cost.
Basically, investments reflected on line 1170 are taken into account in account 58 in analytics, which allows them to be divided into long-term and short-term. However, line 1170 may also include debit balances on accounts 55 (deposits), 73 (interest-bearing loans issued to personnel), 59 (reserves for impairment of financial investments).
Deferred tax assets
Line 1180 of the balance sheet shows deferred tax assets as of the reporting date.
Those who can conduct simplified accounting and not apply PBU 18/02 may not fill out this line.
The rest, in general, are given the right to reflect in the balance sheet the condensed amount of ONA and ONO (clause 19 of PBU 18/02). The company itself can decide on a detailed reflection of deferred taxes in the balance sheet.
Any chosen option should be fixed in the accounting policy. And reflected for users in the Explanations.
If in previous years a different method was chosen for reflecting IT and IT in the balance sheet - for example, in 2022 and 2022 they reflected it on a collapsed basis, and in 2021 they decided to “expand” it - then the comparative data on line 1180 also needs to be recalculated.
Other noncurrent assets
Line 1190 reflects assets whose shelf life is more than 12 months from the reporting date, but at the same time:
- they did not fall into the lines presented above;
- their magnitude is not so significant as to warrant disclosing them in a separate line.
General provisions on accounting
Standard financial reporting is mandatory for all Russian organizations. Even small businesses are no exception. They also have to report on financial indicators, although simplified accounting and reporting are provided for small businesses.
More information about filling out unified reports for small businesses: simplified financial statements
Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n dated July 2, 2010 explains that reporting on F1 and F2 are two main accounting reports:
- Form No. 1 (OKUD 0710001) - balance sheet;
- Form No. 2 (OKUD 0710002) - statement of financial results.
The accounting records also include other reports - on changes in capital (OKUD 0710004), on cash flows (0710005), on the intended use of funds (0710003) and explanations to the balance sheet (Form 5).
Read more about the structure of financial reporting: composition of accounting reports 2021
Companies annually submit financial reports to the Federal Tax Service. But for some entities there are obligations to submit interim reports. For example, public sector employees and some insurers are required to submit financial reports monthly or quarterly. Special reporting forms have been approved for them. Interim financial reports are required to be prepared by accountants of organizations in which management or founders have decided to receive them monthly.
ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to fill out the balance sheet and financial financial statements. Use these instructions for free.