The Essence of Balance
The BB is a special document intended for general recording and grouping of finances according to their structure, sources and purposes. A BB item is an autonomous line containing information about an enterprise’s money. The list of similar articles forms sections and subsections.
How to disclose information about receivables and payables in notes to the balance sheet ?
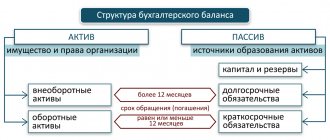
BB is divided into two parts:
- Assets. It contains information about funds, the source of which is various business transactions.
- Liabilities. Information about the organization's equity and liabilities is recorded here.
BY THE WAY! The same funds can appear in both the right and left columns. This means that assets equal liabilities.
Balance sheet - what is it?
Such a reporting form as the balance sheet in accounting is considered as one of the main reports on the activities of any organization. With its help, you can quickly assess the financial position of the company.
The very name of the document “balance sheet” suggests its form. It consists of two equal parts - an asset and a liability. Information in both parts is entered in monetary terms.
The asset is formed from data on the property of the enterprise, which is divided into two groups - non-current and current. Non-current assets represent everything with the help of which the company's activities are carried out. They can also be called long-term (used in the company’s activities for 1 year or more). This:
- real estate;
- equipment;
- transport;
- software systems;
- structures;
- long-term investments in other companies;
- scientific and technical developments, etc.
Over time, the value of this group of assets changes. Tangible property is depreciated and included in the balance sheet at its residual value, and financial investments increase.
The second group of company property as part of the balance sheet asset is called current assets. They are actively involved in the process of economic activity and are updated. Another characteristic of this group of property is its fairly high liquidity. These assets are usually short-term (turnover up to 1 year). These include:
- raw materials;
- materials;
- tools;
- accounts receivable;
- finished products in warehouse;
- money in accounts and in the cash register, etc.
Types of balances depending on the user
The structure of the balance sheet may differ depending on which entity the document is being drawn up for:
- For commercial companies. This is the most used form of BB. Differs in versatility. Relevant for organizations with any form of ownership. An enterprise may also engage in various forms of economic activity. The specifics of the economic activity of the subject primarily influence the composition of the asset. If it is a trading company, most of its finances will be concentrated in inventory.
- For insurance organizations. The majority of the asset is receivables generated as a result of insurance operations. Most of the liabilities are insurance reserves and accounts payable.
- Banks and credit entities. There are no inventories or finished products in the assets, since institutions work with finances, not products. Instead of goods, assets include precious metals, money, loans provided to clients, and money held in other financial institutions. Liabilities reflect funds from the Central Bank, government loans, money from clients and banking institutions. The balance sheet of credit institutions reflects the peculiarities of the turnover of funds in them.
- For budgetary institutions. The balance sheet of these entities includes three areas: supply, financing and consumption. Most of the liability is financing and related payments.
Should an organization prepare a balance sheet ?
Question: How long should the balance sheet statement have? View answer
Balance sheets differ depending on the specifics of the activity. Therefore, they distinguish between types of BB depending on for which institution the document is being drawn up.
Assets and liabilities in the balance sheet
The preparation of financial accounting statements is the direct responsibility of all economic entities conducting accounting. Some companies and organizations are entitled to keep records in a simplified form, and some are completely exempt. For example, individual entrepreneurs have the right to refuse accounting altogether. But if the enterprise maintains accounting, then reporting becomes inevitable.
Reporting is necessary to obtain up-to-date information about the activities, property status and obligations of the entity. Analysis of the information received allows you to quickly and timely make the right management decisions, thereby allowing the enterprise to function smoothly, make a profit, and perform the functions and powers for which it was created.
In essence, reporting is a reflection of property and capital, as well as the sources from which they were obtained, only in monetary terms. The key form of financial reporting is the balance sheet, the unified form of which is approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n. For public sector institutions, other forms of reports apply: Orders of the Ministry of Finance No. 33n and 191n. However, regardless of the type of organization, the structure of the balance sheet is practically the same, that is, the forms include the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet.
The typical structure of the balance sheet contains the following numerical indicators.
Assets. Section 1. Non-current assets.
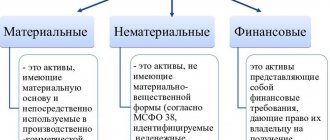
- Intangible assets: rights to intellectual property; patents, trademarks, service marks, organizational expenses; business reputation of the organization.
- Fixed assets: land plots and environmental management facilities; buildings, machinery, equipment, construction in progress.
- Profitable investments in material assets: property for leasing, provided under a rental agreement.
- Financial investments: investments in subsidiaries, dependent companies; loans provided to an organization for a period of more than 12 months; other financial investments.
Section 2. Current assets.
- Inventories: raw materials, supplies and similar valuables; costs in work in progress; finished goods, goods for resale and shipped; Future expenses.
- Accounts receivable: buyers and customers; bills receivable; debt of subsidiaries and dependent companies; debt of participants on contributions to the authorized capital.
- Financial investments: loans provided by the organization for a period of less than 12 months; own shares purchased from shareholders; financial investments.
- Cash: current accounts; foreign currency accounts; cash.
Passive. Section 1. Capital and reserves.
- Authorized capital.
- Extra capital.
- Reserve capital: reserves formed in accordance with legislation and constituent documents.
- Retained earnings.
Section 2. Long-term liabilities.
- Borrowings: loans due to be repaid more than 12 months after the reporting date; loans due to be repaid more than 12 months after the reporting date.
- Other obligations.
Section 3. Short-term liabilities.
- Borrowings: loans due to be repaid within 12 months after the reporting date; loans due to be repaid within 12 months after the reporting date.
- Accounts payable: suppliers and contractors; bills payable; debt to subsidiaries and dependent companies; to the organization's personnel; before the budget and state extra-budgetary funds; to participants in the payment of income; advances received.
- Deferred income: reserves for future expenses and payments.
The balance is always drawn up on a certain date, that is, on the first day following the reporting date of the month, quarter, or year. The balance sheet shows the state of funds and their sources at the end of the reporting period. The assets and liabilities of the balance sheet are items grouped into sections, that is, each line of the balance sheet is a balance sheet item.
Balance Sheet Classification
BBs are classified according to characteristics. Let's look at these features and the type of document:
- According to the formation method. This is a balance BB, which is formed based on account balances. This is also a balance sheet balance sheet, which includes information about the movement of money during the reporting period.
- By frequency of creation. BB can be created at different intervals: once a year, a month, a quarter. The introductory document is drawn up after the registration of the company, the final document is a report for a specific period of time. The annual BB is the basis for creating accounts in the new year. The interim document is a condensed form of the annual BB. A sanitized balance sheet is needed if there is a threat of bankruptcy. A liquidation BB is needed upon completion of the activities of a legal entity.
- According to the degree of readiness. The preliminary document is prepared in advance. In this case, predicted adjustments are taken into account. The final BB is formed based on real information.
- According to the degree of consolidation. An individual BB records the results of the economic activities of one company. The consolidated document combines the values that arise through the summation of balance sheet items of several institutions. A consolidated BB is needed to combine the balance sheets of independent companies that are interconnected. A separating BB is created when one organization is divided into several legal entities.
- According to sources. BBs are divided into types depending on the sources on which they are compiled. There are inventory balances drawn up on the basis of information about the inventory of property. There are also book BBs drawn up on the basis of accounting.
- By including regulatory articles in the document. The gross balance sheet includes items that regulate the values of other items. For example, this is depreciation of intangible assets. This is also a net balance created on the basis of gross balance information. Its main difference is the absence of regulatory articles.
BB is a fairly broad concept. A balance sheet can mean a variety of documents.
Types of balance sheet
Equity agility ratio: balance sheet formula
The purpose of compiling the balance sheet determines its type. Types of balance sheets are classified into several types of different economic content.
- Balance sheet time. Depending on the period of activity in which the balance is formed, it can be one of the following types.
- Opening. This balance is drawn up immediately after the registration of the enterprise. Its data reflects the company's starting capital.
Current. Such a balance is drawn up at the end of a certain period in the organization. In common practice, these are periods: quarter, year. However, in companies it can be compiled monthly, depending on the need to obtain information from the balance sheet.
- Sanitable. Such a balance is drawn up in anticipation of the possible bankruptcy of the enterprise. Its compilation helps to understand how realistic the state of solvency of the enterprise is.
- Liquidation. Such a balance sheet is drawn up in the event of liquidation of the organization.
- Unifying. Such a balance is drawn up in cases of merger of several organizations into one legal entity.
- Dividing. Such a balance is drawn up in cases of division or separation of individual enterprises from one large enterprise.
- Form for presenting information.
According to the form of presentation of indicators in the balance sheet, they can be as follows.
- Static. This is a standard balance sheet, which reflects indicators valid at a certain moment.
Dynamic. This is a special type of balance sheet that reflects indicators in motion. Such a balance can be a balance sheet or a checkerboard balance sheet.
- Sources of compilation
Based on the sources of data generation, the balance can be of the following types.
- Inventory. This type of balance sheet is compiled after an inventory of any property or liabilities.
Book. This is a standard balance sheet that reflects the actual indicators currently in effect.
- General. This is a type of final balance sheet that contains actual data based on inventory results.
- Amount of information.
Based on the amount of information reflected in the balance sheet, it can be one of the following types.
- Unit. This type of balance sheet reflects the indicators of only one company.
Consolidated. This type of balance sheet reflects the indicators of only a few companies.
- Consolidated. This type of balance sheet reflects the indicators of only several companies that are legally separate, but are connected by economic operations.
- Method of "cleaning".
Classification of the balance according to the cleaning method can be of two types.
- Gross. This balance includes regulating items of certain indicators (depreciation, reserves, markup).
Net. This balance accordingly excludes the above indicators.
All of these six types of balance sheets are compiled according to the general rule - that is, according to the rule for grouping balances on accounting accounts.
Note 1
These five characteristics of balance sheet classification are the main ones used in accounting.
Types of balance sheets
Let's look at all types of balance sheets with a brief description of the document:
- Balance of income and expenses. It is a document of a financial nature that is created for a year or quarter. The purpose of its formation is the consistency of the movement of funds, the ability to make a forecast about the development of the company. Using this document, you can track the financial relationship of the company with its creditors. It includes the calculation of income and expenses, tax payments, and the creation of funds.
- Gross balance. This document is distinguished by the presence of regulatory articles. It is needed to conduct scientific research and improve balance functions.
- Net. There are no regulatory clauses in this document. Such a balance is needed to establish the real value of the company's property.
- Introductory BB. This balance is formed immediately after the company is registered. The document contains a minimum of information, since the company is just starting to operate. Assets indicate the composition of available property. The liability serves to reflect the sources of capital and property formation. As a rule, before creating such a BB, you need to perform an inventory.
- Final BB. It is a reporting paper on the financial performance of the company for a specific period. It is drawn up on the basis of accounting information that has been previously verified.
- Consolidated BB. Represents consolidated reporting on the work and financial results of parent and subsidiary entities. This is common reporting for several interconnected organizations. A BB of this type does not include mutual turnover of subsidiary entities.
- Liquidation BB. This is a reporting BB from which you can obtain information about the property status of the company as of the date of completion of its activities. Displays the amount and sources of funds, the status of settlements after the end of the liquidation period.
- Reverse BB. This document sets out information about the movement of property over a certain time. It contains information on turnover for the reporting period and fund balances. Such a BB is an intermediate paper used in the formation of the initial, liquidation and closing balance sheet.
- Preliminary BB. The document is drawn up in advance for the end of the reporting period, taking into account predicted corrections. The compilation involves already existing and forecast information about operations.
- Trial BB. Needed to check the accuracy of money accounting.
- Intermediate. Formed before the end of the year.
- Interim liquidation. The paper includes data on the structure of the property of the legal entity that is being liquidated. It indicates the requirements from creditors and the results of their satisfaction. Issued by a commission.
- Dividing. Based on this paper, the legal entity is divided. The balance records the fact that the rights of one legal entity are distributed among several entities. The document contains information about the succession of obligations of the reorganized legal entity.
- Baldovy. The document records the company's property and the sources of its appearance on a given date. It is formed based on the calculation of account balances.
- Consolidated. It is issued through the association of BB of persons who are connected. Such documents are usually created by holding companies.
- Consolidated. Formalized through the combination of different closing balances. Such balances are compiled by ministries and statements.
At the moment, commercial firms use mainly net balance sheets.
Contents of the balance sheet
According to the location of the asset and liability of the balance, the arch is divided into:
- balance in the figure - to the synchronous location of notes and areas of active and passive;
- balance in the figure of the report - on the alternate location of assets and liabilities (balance sheet).
Types of balance by expression display type:
- the balance sheet is drawn up by counting fragments (remainder), according to the accounts;
- the reverse balance, in addition to fragments (balance), includes information about their movement (debit and credit expressions) and for the past period.
Each accounting code is subject to the following certain conditions: honesty (truthfulness), validity, integrity, continuity, clarity.
It seems true that the balance was drawn up in accordance with the records made on the basis of the information in the papers. The papers, in turn, display the data of the institution’s work for a specific period of time.
The balance sheet, the types of balance sheets discussed above, proves and defines accounting data.