What an exporter of goods to Belarus needs to know: legal acts and VAT rate
Belarus is a member of the Customs Union (CU) and is subject to the rules in force on the territory of the CU member countries. When exporting goods by Russian suppliers to the territory of this republic, it is necessary to comply with the norms of the relevant legal regulations:
- Clause 1 Art. 72 of the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union (signed on May 29, 2014) - this clause determines that in mutual trade between the member countries of the Customs Union, indirect taxes are collected according to the principle of the country of destination, which provides for the application of a zero VAT rate and (or) exemption from excise taxes when exporting goods .
- Appendix No. 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) - it describes the procedure for collecting indirect taxes when exporting goods and the mechanism for monitoring their payment.
The following figure will help you become more familiar with this procedure in relation to the export of goods from Russia to Belarus:
Nuances of exporting to the Republic of Belarus
Let us briefly remind you of the peculiarities of paperwork when exporting to Belarus.
As with “regular” exports, firms that ship goods to Belarus must issue invoices with a zero VAT rate. Before sending the document to the buyer, submit an invoice to your tax office (clause 1 of Order of the Ministry of Finance dated January 20, 2005 No. 3n).
Exporters also have the right to a refund of the value added tax that was paid when purchasing exported goods. However, before receiving a refund, the right to a zero rate must be confirmed. At the same time, exporters to Belarus should be guided not by Article 165 of the Tax Code, but by paragraph 2 of Section 2 of the Regulations “On the procedure for collecting indirect taxes and the mechanism for monitoring their payment when moving goods between the Russian Federation and the Republic of Belarus” (annex to the agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Republic of Belarus ). The international agreement establishes a different procedure and time frame for confirming the zero VAT rate compared to the Tax Code (Article 7 of the Tax Code).
Within 90 days from the date of shipment (transfer) of goods to the Belarusian partner, the company must collect a package of documents and submit them to its tax office. The package of documents, instead of a customs declaration with a mark from the customs authority (as for “regular” exports), includes a third copy of an application for the import of goods with a mark from the Belarusian tax authorities. Officials from Belarus must confirm that the company, having received the goods from Russia, paid VAT in full. Or they note that the product is not subject to tax.
In addition to the import application, the following are also required (clause 2, section 2 of the Regulations):
- a copy of the contract with the buyer;
- a copy of the bank or bank statement;
- copies of transport documents;
- other documents required by law.
Let's consider what difficulties may arise with papers.
The copy will replace the original
Sometimes suppliers had to wait for a long time until their partners from Belarus sent the original application for the import of goods. But if the required document is not received on time, the company will not be able to confirm the export.
Now, instead of originals, tax officials allow you to submit copies. This applies to the entire package of documents, including the application (question 4 from the Federal Tax Service letter dated October 10, 2005 No. MM-6-03 / [email protected] ). You don't even need a notary for certification. The copies only need to be signed by the head and chief accountant of the exporting company (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 15, 2005 No. MM-6-03 / [email protected] ).
Confirm payment
The fact of receipt of proceeds from the buyer is confirmed by a bank statement or a copy thereof. If you paid in cash, you need a copy of the receipt. What if the proceeds for the exported goods did not come from the buyer, but from a third company? Can such a bank statement be included in the package of documents to confirm the zero VAT rate?
Experts from the Federal Tax Service answered this question. They believe that inspectors may refuse to confirm export VAT if two conditions are met. Firstly, the exported goods were paid not by the buyer, but by a third party. And secondly, if the officials prove that “the third party did not act in the interests of the buyer” (question 10 from the appendix to the FIS letter dated May 31, 2005 No. MM-6-03/450).
The exporter in such a situation should not wait for proceedings. It is better to immediately submit a tax document that confirms that the buyer has entrusted payment for the contract to a third company. This could be, for example, a letter from a Belarusian partner explaining the payment scheme.
Exchange goods
If the exporter works by barter, then he submits documents indicating that the goods were imported and accepted for registration (clause 2 of section 2 of the Regulations). In this case, tax authorities understand barter as “direct non-monetary exchange of goods”, which is formalized in a single agreement (question 12 from the appendix to the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated May 31, 2005 No. MM-6-03/450). Documents confirming barter can be (question 12 from the appendix to the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated October 10, 2005 No. MM-6-03 / [email protected] ):
- transport documents confirming the import of goods into Russia;
- shipping documents issued by a partner from Belarus;
- application for import of goods;
- accounting registers (if maintained), in which the company reflects the registration of imported goods.
We deliver through the warehouse
Goods sold for export to Belarus are not always delivered directly to the buyer. Intermediate warehouses are often used. Experts from the Federal Tax Service explained what to do in such a situation with transport documents. The transport documents that are needed to confirm the zero VAT rate may include information about warehouses. Then no additional documents are required. If there is no such data, then the exporting company must submit documents to the tax authorities on the transportation of goods to the warehouse and further - from the warehouse to the buyer (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated December 20, 2005 No. MM-6-03 / [email protected] ).
Other documents
The list of documents that a company must collect to confirm the zero rate includes “other documents” (clause 2 of section 2 of the Regulations). What kind of documents these could be, Federal Tax Service specialists explained in a letter dated October 10, 2005 No. MM-6-03 / [email protected] (question 11). They examined the sale of goods using the example of a commission agreement.
The fact is that when selling goods for export to Belarus, companies do not always act independently. They often use intermediaries and enter into commission agreements. In this case, the commission agreement and the intermediary contract with the Belarusian buyer will be “other” for the exporting company.
The commission agent draws up, the owner notes
There are other issues associated with working through a commission agent. For example, about invoices for Belarusian buyers.
When exporting goods to Belarus, the company must issue an invoice to the buyer and put a mark on it in its tax office (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated January 20, 2005 No. 3n). Moreover, the owner of the goods is required to register an invoice with the inspection (clause 2 of Appendix 1 to the order).
Having concluded a commission agreement (Article 990 of the Civil Code), the exporter (committee) sells the goods through an intermediary (commission agent). In fact, the seller of the goods will be an intermediary. This means that it is he who will issue an invoice to the Belarusian buyer. However, the principal remains the owner of the goods (clause 1 of Article 996 of the Civil Code). In this case, who registers the invoice with the inspectorate?
Experts from the Ministry of Finance believe that the owner of the goods must, at the inspection office at his place of registration, put a mark on the invoice, which will be drawn up for Belarusians by the commission agent. In this case, the principal must be indicated in the line “shipper” (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated September 23, 2005 No. 03-04-08/257).
In the same letter, officials explained that the exporting company, for its part, issues an invoice to the intermediary. The VAT rate will be zero percent. There is no need to transfer this document to the Belarusian buyer.
"Belarusian" advance
When working with buyers from Belarus, companies receive an advance payment or partial payment from them. The agreement between our states makes no mention of the procedure for taxing advances. Therefore, exporters must apply the provisions of the Tax Code. Paragraph 9 of Article 154 of the Tax Code states that advances received for exports do not need to be taken into account when calculating VAT until the tax base is determined.
What date is considered such a moment when selling goods in Belarus? According to officials, this will be the last day of the month in which a package of documents has been collected to confirm the right to a zero VAT rate (question 7 from the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated October 10, 2005 No. MM-6-03 / [email protected] ). If the company does not confirm the export, then value added tax will have to be paid to the budget for the period in which the shipment occurred (clause 3 of section 2 of the Regulations). It turns out that there is no need to pay VAT on advances towards Belarusian exports (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated December 15, 2005 No. MM-6-03/1054).
Belarusians brought back marriage
Exporters may face a situation where some of the goods sold to Belarus are returned. There may be various reasons, such as defects or non-compliance with the delivery agreement.
What happens in this case? As the tax authorities explained in a letter dated October 10, 2005 No. MM-6-03/ [email protected] (question 21), the goods are being returned from Belarus, and their country of origin is Russia. This means that the agreement does not apply to him. After all, the special procedure for export operations applies only to goods whose place of production is Russia, and for imported ones - the Republic of Belarus (Law of December 28, 2004 No. 181-FZ, letter of the Federal Customs Service of January 27, 2005 No. 01-06 / 1958) .
For other goods, general rules must be applied (question 9 from the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated September 20, 2005 No. 03-04-08/247, subparagraph 1, paragraph 1, article 164 of the Tax Code).
When importing foreign-made goods, value added tax is paid at customs. It depends on the customs regime chosen by the company (Article 151 of the Tax Code).
However, in practice, for rejected Russian goods that were exported to Belarus and then returned to suppliers, the procedure defined by the agreement and described in section 1 of the annex to the agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Republic of Belarus still applies (FCS teletype message dated May 12, 2005 No. TF-1095).
The same exception is made for goods intended for display at exhibitions and fairs. And also for returned Russian packaging (FCS teleprinter dated July 4, 2005 No. TF-1500). Until further notice from customs officials, VAT on all these goods will be collected by the tax authorities.
The full text of the documents used can be found in SPS ConsultantPlus.
L. Izotova
Features of reflecting deductions in the VAT return depending on the type of goods exported
The procedure for filling out a VAT return depends on which group the exported goods belong to.
Note! From the 3rd quarter of 2022, the VAT return was updated by order of the Federal Tax Service dated March 26, 2021 No. ED-7-3/ [email protected]
You will find a line-by-line algorithm with examples of filling out all twelve sections of the report in ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the system can be obtained for free.
We are talking about dividing exported goods into raw materials and non-raw materials. The main criterion for such classification is the degree of human participation in the formation of the main characteristics of the product.
Enlarged groups of raw materials are listed in clause 10 of Art. 165 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
Commodity codes were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 18, 2018 No. 466.
Goods not listed in clause 10 of Art. 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, relate to non-raw materials (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 3, 2016 No. 1-4-05/0021).
For these groups of goods, the following procedure for applying VAT tax deductions is established:
- Input VAT on the value of non-commodity goods intended for export is accepted for deduction in the quarter when the goods are registered and the other mandatory conditions for deduction are met.
Find out about the conditions for applying deductions from the material “What is the procedure for applying (accepting) tax deductions for VAT: conditions”.
- Input VAT on the cost of raw materials purchased for export is accepted for deduction in the quarter when the zero tax rate is justified (clause 1, clause 10 of Article 165, clause 3 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How to apply a VAT deduction if the product is a raw material, but it is not on the government list, find out in this publication.
Issuance of export invoices in foreign currency (VAT rate 0%)
Despite the fact that a Russian invoice is not required for a foreign buyer and ownership of the products has not yet been transferred, the organization is obliged to draw up an invoice for export sales according to the general rules no later than 5 days from the date of shipment (clause 3 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , clause 17 of the Rules for maintaining a sales book, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137).
It is allowed to draw up not only the SF, but also the UPD (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 07/06/2016 N ED-4-15/12070).
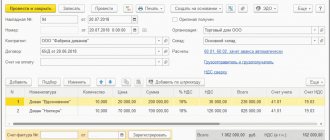
An invoice for shipped export goods is issued using the Issue an invoice at the bottom of the Sales document (act, invoice) .
The Invoice document issued is automatically filled with data from the Sales document (act, invoice) . Operation type code – “01” Sales of goods, works, services...”.
The invoice was issued in foreign currency, since the transaction is expressed in foreign currency (Clause 7, Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
If the SF is not transferred to a foreign buyer, then the Checked (transferred to the counterparty) can be left unchecked. The presence of a checkbox is for reference information; it does not affect the movement of the document and the filling out of the purchase and sales books.
SF with a VAT rate of 0% does not by default enter the sales book simultaneously with sales, as happens when shipping on the domestic market. But only at the time of determining the tax base for VAT for export, if (clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- export confirmed within / later than 180 days - on the last day of the quarter in which supporting documents were collected;
- export is not confirmed within 180 days - on the last day of the quarter in which the sale took place.
The moment of determining the tax base for VAT is not specified in the EAEU Protocol, therefore, on this issue one should be guided by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 5 of the EAEU Protocol, clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
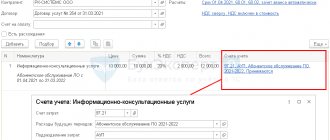
In the Northern Federation, for shipment to the EAEU, it is necessary to indicate the HS code in column 1a “Product type code” (clause 15, clause 5, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 7, 2016 N 03-07-11/58589). PDF The data will be filled in automatically if the HS code was previously indicated in the nomenclature card and in the tabular part of the Sales document (act, invoice) in the HS Code .
The document does not generate postings according to BU and NU.
Documenting
The Invoice form was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 N 1137. It can be printed by clicking the Print document Invoice or Sales (act, invoice ) button. PDF
VAT declaration for export to Belarus
Sales of goods to Belarus are reflected in the VAT return according to the following scheme:
What to do if documents confirming the zero rate are not collected in a timely manner? The answer to this question is in the ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Find out which transaction codes to use to fill out a VAT return from the diagram below:
If goods are sold to a related party or a resident of an offshore zone, special codes from the specified application are applied.
The procedure for filling out individual lines of Section 4 depends on the type of product (commodity or non-commodity):
The remaining sections of the declaration are completed in the usual manner.
A sample from ConsultantPlus will help you understand the principles of filling out a VAT return when exporting goods to Belarus in 2022, after receiving trial demo access to the K+ system. It's free.
Documents were not collected on time: what to do with VAT reporting
Exports that are not confirmed on time require the submission of an updated declaration. Such a declaration has three important nuances:
- it is rented out per quarter of export shipment;
- must contain completed section 6;
- The composition of the information in section 6 depends on the type of goods exported (raw materials, non-raw materials).
What can prevent you from confirming your export on time?
Even if the exporter conscientiously approaches the procedure for collecting documents, there is no complete confidence that he will meet the deadline allotted by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to confirm the validity of applying the zero VAT rate. This is due to the fact that the set of supporting documents includes an application for the import of goods, which the buyer must hand over to the supplier. And it is difficult to influence the actions of a buyer (especially one located abroad). At the same time, the absence of an application for the import of goods deprives the seller of a tax preference in the form of a zero VAT rate (if the buyer has not paid the tax).
The main difficulty in obtaining such a document is that the Belarusian buyer must pay the tax, put a stamp on the application with his tax authorities about payment and, with such a mark, transfer the application to the supplier.
It happens that the export seller was unable to receive an application because the buyer:
- for some reason I did not send the application, although I paid the tax;
- did not pay the tax and did not send anything to the seller;
- I sent the application, but without a tax payment mark.
There are two possible scenarios here:
- If the Belarusian buyer has paid the tax, the situation is not hopeless - Russian tax authorities can check the fact of tax payment in their database (within the framework of electronic information exchange), and the supplier himself can check in a special electronic service on the Federal Tax Service website.
- If the tax is still not paid, the Russian export seller will not be able to confirm the zero rate.
We will tell you in the next section what a supplier can do to protect itself from possible material losses due to unscrupulous buyers.
Confirmation of the validity of applying the zero VAT rate
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 1 of the Protocol on Goods, to confirm the validity of the application of the zero VAT rate by the taxpayer of the CU member state from whose territory the goods were exported, the following documents (copies thereof) are submitted to the tax authority simultaneously with the tax return:
- agreements (contracts) with amendments (additions and annexes) to them, on the basis of which the export of goods is carried out;
- application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes, drawn up in the form established by the Protocol on the exchange of information in electronic form between the tax authorities of the member states of the Customs Union on the paid amounts of indirect taxes dated December 11, 2009 (Appendix 1), with a mark from the tax authority of the state — a member of the Customs Union into whose territory goods are imported, on the payment of indirect taxes (exemption or other procedure for fulfilling tax obligations). It should be noted that by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 30, 2012 N ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] , the electronic format of the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes by Russian taxpayers was approved;
- transport (shipping) documents provided for by the legislation of the CU member state, confirming the movement of goods from the territory of one CU member state to the territory of another CU member state.
- other documents provided for by the legislation of the CU member state from whose territory the goods were exported. Such documents may be required, for example, in the case of selling goods through an intermediary (Clause 2 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). They can be a commission agreement, a commission agreement or an agency agreement, reports from the intermediary on the performance of his duties, etc.
The exporter must provide the above documents to the tax authority within 180 calendar days from the date of shipment (transfer) of goods.
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 1 of the Protocol on Goods, the date of shipment is the date of the first drawing up of the primary accounting document issued to the buyer of goods or the first carrier, or the date of issuance of another mandatory document provided for by the legislation of the CU member state for VAT payers.
REGISTRATION AT CUSTOMS
If documents are not submitted within the prescribed period, VAT is payable to the budget for the tax (reporting) period in which the date of shipment of the goods falls. Further, if the taxpayer collects and submits the appropriate package of documents confirming the fact of export to Belarus, the paid VAT amounts are subject to deduction (offset) or refund.
In accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 166 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxpayers are required to keep separate records of transactions for the sale of goods to Belarus, subject to VAT at a rate of 0%, and other transactions.
It should be noted that in addition to the above documents, tax authorities, in order to confirm the validity of VAT refunds on export transactions, require taxpayers to fill out the “VAT Refund: Taxpayer” program (version 3.0.8.2.).
Contractual insurance against unscrupulous buyers
In order to somehow protect yourself from careless buyers from the EAEU, provide special conditions in your contracts with them. For example:
- The buyer's obligation to pay a fine (compensating for the seller's losses from paying VAT and penalties on it) if the import application is not received from him within the agreed period (for example, no later than 160 days from the date of shipment).
- An indication of the judicial authority (Russian or Belarusian) in which the dispute will be heard if the buyer refuses to pay penalties. It is no secret that it is better to protect your interests on your own territory with the participation of competent lawyers.
The “penalty” element of the contract may look like this:
Export to Belarus | What changes await us?
At the legislative level, there have been no changes in the export procedure in 2022. Today, the same package of documents is required no later than 180 days from the date of shipment. If it was not possible to confirm the zero rate on time, and you paid VAT on the export transaction, you can take into account the paid VAT for income tax - based on subclause. 1 clause 1 art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 27, 2015 No. 03-03-06/1/42961).
Independent registration of exports from the Russian Federation to Belarus does not always lead to a positive result. Often, VAT refunds are delayed by tax authorities or the refund is refused altogether. The buyer’s failure to provide an application for payment of indirect taxes, failure to pay VAT by the supplier - all this is also a reason for refusal.
We offer VAT refund on the day of shipment, regardless of the tax authorities' decision. This speeds up the turnover of funds for our clients and removes all risks in the export transaction.
Results
Exports of goods from Russia to Belarusian buyers are taxed at a rate of 0% if the supplier submits a set of supporting documents to the tax authorities along with the VAT return. If the documents cannot be collected on time, the supplier must submit an updated VAT return for the period in which the export shipment occurred.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union (signed on May 29, 2014)
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 18, 2018 No. 466
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.