Organizations working with VAT are most often faced with the need to create corrections in the invoice. The problem is that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a definition of this concept. Accordingly, accountants often make mistakes that lead to fines or other unpleasant consequences. To avoid this, it is important to understand the legal nature of this process, the difference between corrections and corrections, and the rules for processing edits in an electronic document. Let's look at these questions in detail.
What is a corrected ESF and how does it differ from an adjustment?
Let's start with the fact that the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 provides for two forms of invoices: main and adjustment. Both contain a box for making amendments.
It follows from this that the revised ESF is an original document, which, due to objective reasons, needed to be changed. Eligible criteria for making changes include:
- Technical errors;
- Incorrect amounts indicated;
- Typos.
It is important to note that only those points that actually distort the meaning of the document and lead to a change in the tax deduction are subject to correction. This is enshrined in paragraph 2 of Art. 169 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
The algorithm for working with corrected and corrective invoices does not differ for documents on paper and for electronic versions. That is, if the original document was created in electronic form, then all corrected and corrective SFs must also be in electronic form.
Corrective EFS is directly provided for by law and is necessary in situations where the objective conditions of the transaction have changed. For example, the seller and buyer signed an additional agreement to change the price. This decision assumes that the value of VAT is also subject to recalculation. Accordingly, a correction invoice is required.
It is important to note that the formation of a corrective ESF and the introduction of corrections to it or the original document is not considered a violation and does not entail liability. Naturally, if the edits were made before submitting the primary report to the Federal Tax Service.
For clarity, look at the infographic:
Fig. 1 Difference between the corrective SF and the corrected one
Accounting for an adjustment invoice when reducing the cost
Suppose the seller and buyer have entered into an agreement to change the terms of delivery, resulting in a reduction in the cost of goods shipped.
What should the seller do?
- Issue a correction invoice and register it in part 1 of the log of received and issued invoices.
- Register an adjustment invoice in the purchase book during the period when the conditions are met (the presence of primary documents (contracts, agreements) for changing delivery conditions is mandatory).
- Applies a deduction for the difference between the VAT amount before and after the adjustment.
The seller must issue an adjustment invoice no later than 5 calendar days from the date of drawing up the document on the change in value.
Here are the buyer's actions:
- Registers the adjustment invoice in part 2 of the log of received and issued invoices.
- Registers an adjustment invoice in the sales ledger. The entry is made for the period of receipt of the document.
- Restores a previously accepted deduction for the difference between the tax amount before and after the adjustment.
The parties to the transaction must include:
- original invoice;
- cost agreement document;
- adjustment invoice.
Adjustments to VAT liability where there is an agreement to reduce the cost of shipment do not affect the period of the original invoice. Everything is done during the period of issuing the adjustment invoice. No adjustments are required for the period of the original invoice.
In what cases is a corrected ESF issued?
Since the issue does not have a clear legislative regulation, it makes sense to turn to legal practice. Most often the need for changes arises in the following cases:
- A typo in the date of compilation affects the period of work with VAT and may lead to the impossibility of obtaining it;
- Incomplete or unreliable details of the parties, for example, erroneous TIN, name of the counterparty, missing last names - in fact, such an error does not make it possible to identify the parties, accordingly, from the point of view of the law, the transaction is not considered valid, VAT is not refunded;
- There is no name of the sender and recipient of the cargo in cases where they are logistics companies;
- No payment details - such an error makes it impossible to track the payment and verify its authenticity;
- The name of the currency and its code are not indicated or indicated incorrectly;
- The object of payment is incorrectly specified or missing: goods/services;
- Error in the price of a service or quantity of goods;
- The rate is indicated incorrectly, which entails the invalidity of subsequent operations for calculating taxes and the amount of VAT;
- For imported goods, the following information is missing or indicated with errors: country of origin, customs declaration number.
In other situations, an extract of the corrected ESF is not required, since the remaining information does not affect the ability to correctly interpret the information from the document and calculate tax liabilities on it.
You can find detailed explanations on these errors in the letters of the Ministry of Finance dated 08/02/2019 No. 03-07-11/58375, dated 04/19/2017 No. 03-07-09/23491, dated 09/18/2014 No. 03-07-09/46708, dated 04/25/2011 No. 03-07-08/124, dated 03/11/2012 No. 03-07-08/68, as well as in the resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated 02/25/2009 No. 13893/08.
A significant error on an invoice will not invalidate the deduction if corrected.
Errors in invoices may or may not be significant. If the error is material, the seller must issue a corrected invoice and record it in the sales ledger. If he does not do this, the buyer will lose the right to deduct VAT.
An invoice is a document that serves as the basis for accepting the VAT amount for deduction. According to paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an invoice is issued:
- taxpayers for transactions carried out in relation to the object of taxation (Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- persons exempt from VAT under Articles 145 and 145.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- tax agents for purchases on the territory of Russia from foreign suppliers (subclauses 1 and 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or when using state property (clause 3 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- VAT payers on received advances and when changing the price or volume of shipments already made (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- non-payers of VAT when selling on their own behalf or when re-issuing invoices (subclauses 1 and 3.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The established forms of the invoice form and the procedure for filling it out are contained in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 (hereinafter referred to as the Rules).
Mandatory information
The information required to fill out an invoice consists of a certain set of indicators (subclauses 5, 5.1, 5.2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- details (number and date);
- information about the seller and buyer;
- the currency in which the numerical data of the document is reflected;
- unambiguous name of the object of sale;
- the total sale price without taxes and with taxes, the amount of taxes, the VAT rate, if there is a tax;
- signatures of persons entrusted with this right.
Significant errors in the invoice
An invoice in which (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) is completely unsuitable for deduction:
- there is no information about individuals or this information is fundamentally incorrect;
- it is impossible to unambiguously determine the object of sale;
- the sales price, rate and amount of tax are missing or given with errors (see, for example, the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 19, 2017);
- the currency is missing or incorrectly indicated (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 2012 No. 03-07-08/68).
These defects prevent a reliable determination of the basic data included in the invoice. Therefore, tax deduction based on documents with such errors is impossible.
This means that if in the invoice the cost of the purchased goods and, accordingly, the amount of VAT are indicated incorrectly (including with arithmetic and technical errors) or their indicators are missing, then a deduction on such an invoice is not provided.
Please note that some courts (see Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service No. F03-2116/2014 of June 10, 2014 in case No. A51-17093/2013) believe that the signing of invoices by unidentified persons is an independent basis for refusing to accept tax deductions for VAT. However, there are also opposing court decisions in which the arbitrators recognized the signing of invoices by an unidentified and unauthorized person as an insignificant circumstance (see Resolution of the AS SKO dated June 11, 2015 No. F08-3452/2015 in case No. A32-26952/2012).
Minor errors in the invoice
Some errors in the invoice are not grounds for denial of the VAT deduction highlighted in this document. These are errors that do not prevent inspectors from identifying during a tax audit (Clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- seller, buyer of goods (works, services), property rights;
- name of goods (works, services), property rights;
- their cost;
- tax rate;
- the amount of VAT charged to the buyer.
Such “non-critical” defects include, in particular, the date the invoice was issued by the seller, as well as obvious typos in information about the supplier and buyer, the absence of a number, the inclusion of additional details in the invoice, etc.
Thus, with regard to such details as the address, officials are not very strict. It can be written in the invoice with abbreviations (partly in capital letters and partly in small letters), since such address abbreviations are not prohibited in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 11, 2017 No. 03-07-09/66329).
If the address of the seller and buyer from the register does not indicate a country, the seller can independently add the words “Russian Federation”, “Russia” or “RF” to the address.
Also, if the words “district”, “street”, “house” are not written in the address, or the words “city” and “street” are written in abbreviated form, this will not be considered an error due to which the tax office will refuse to deduct VAT. The deduction of VAT is also not prohibited when replacing the word “premises” with the word “office”. After all, inspectors will still be able to identify the seller or buyer using such a document (see letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 08/17/2018 No. 03-07-14/58351, dated 02/06/2018 No. 03-07-09/6850, dated 01/29/2018 No. 03 -07-09/4545).
As for such details as checkpoint, unlike the TIN, which is indicated here, it is not included in the mandatory invoice details listed in paragraph 5 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. That is, these are defects that will not lead to denial of deduction.
Errors in buyer details
To avoid any doubt about the identification of the buyer who will accept the amount of “input” tax for deduction, information about him must be correctly indicated in the invoice. We are talking about the following details:
- name (line 6);
- address (line 6a);
- taxpayer identification number (line 6b).
Let us remember the rules by which these details are filled out.
On line 6 indicate the full or abbreviated name of the buyer in accordance with the constituent documents.
If the goods are supplied to separate divisions of buyers, then line 6 indicates the name of the parent organization (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 04.05.16 No. 03-07-09/25719).
Minor typos (capital letters instead of lowercase letters and vice versa, extra dashes, commas, etc.), which do not interfere with the identification of the buyer, are not grounds for refusal to deduct (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 2, 2012 No. 03-07-11/130).
But if instead of the name of the organization the full name of the employee is indicated, the buyer is deprived of the right to deduction (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 01/09/17 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] ).
The location of the buyer is indicated on line 6a in accordance with the constituent documents.
If the invoice indicates an outdated legal address of the buyer, the right to deduction is retained (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 08.08.14 No. 03-07-09/39449).
The actual address, which differs from the legal address, can be indicated additionally (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 2017 No. 03-07-09/85517).
Abbreviations, replacing capital letters with lowercase letters, and rearranging words in street names are minor changes. They do not prevent deductions (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 17, 2018 No. 03-07-09/1846).
If the goods are supplied to separate divisions of buyers, then line 6a indicates the location of the parent organization (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 04.05.16 No. 03-07-09/25719).
If the goods are delivered to separate divisions of the buyer, then in line 6b you must indicate the TIN of the parent organization and the checkpoint of the division (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 05/04/16 No. 03-07-09/25719).
If the buyer's TIN and KPP are indicated incorrectly or not indicated at all, tax authorities will try to deprive the buyer of the right to deduction.
The courts have a different opinion. The buyer’s right to deduction is retained, since the buyer’s TIN is known to the tax authorities (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated September 28, 2010 No. KA-A40/11365-10), and the checkpoint is not a mandatory requisite mentioned in paragraph 5 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated February 27, 2010 No. KA-A40/1164-10).
Invoice: adjustment or corrected?
If there are significant errors in the original invoice, a corrected document is drawn up. Significant errors prevent the buyer from exercising the right to deduct “input” VAT. If the error is not recognized as such, changes may not be made to the invoice (clause 7 of the Rules).
Let us remind you that an adjustment invoice is issued when the cost of goods already shipped, work performed, services rendered, or transferred property rights is changed. A price change is possible if:
- after the goods are shipped, their price is changed;
- specify the quantity of goods shipped.
In addition, before issuing an adjustment invoice, the seller must:
- notify the buyer of changes in the cost of shipped goods;
- receive from the buyer a document as a fact of notification of a change in the terms of the transaction, confirming his consent. This could be a contract, agreement or any primary document.
As a rule, in the event of a technical error, such documents are not issued. And since the supplier will not have a single document confirming the change in the price of the goods, he cannot issue an adjustment document. He will have to issue a corrected invoice.
Can I get a deduction on a corrected invoice?
In the corrected invoice, which the seller draws up in case of detection of significant errors, indicate the serial number and date of the invoice drawn up before the correction was made to it (clause 1, 7 of the Rules).
Therefore, the corrected invoice must be prepared using the form in effect on the date of the original invoice. The corrected invoice drawn up by the seller upon discovery of a significant error and issued to the buyer must be registered in the sales book in the manner prescribed by paragraph 11 of the Rules.
If the seller does not do this, then the information from this invoice will not be included in the VAT return. Accordingly, the buyer will have no grounds for applying tax deductions.
If a corrected invoice is drawn up by the seller when errors are discovered that do not prevent the tax authorities from identifying the buyer, then such an invoice is not recorded in the sales book.
Thus, the Ministry of Finance once again confirmed its position: those errors in invoices that do not prevent tax authorities from identifying the seller of goods (works, services, property rights) are not grounds for refusal to deduct VAT (Clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code RF).
How to write out a corrected ESF?
Fig. 2 General scheme of working with a corrected invoice
The legislation does not establish restrictions or specific requirements regarding how the corrected electronic invoice is issued. This means that you can make edits an unlimited number of times.
For example, instead of . After identifying this error, a new form of the original document is created independently or by the counterparty and issued to the other party. Simply put, if an error is not detected by the tax authorities, the document is simply redone.
Required documents
If errors are identified after registration of the invoice, in order to make changes, the buyer must contact the seller in writing with a statement about the need to correct the document.
The seller corrects the invoice in accordance with the procedure provided for in subclause. “b” clause 1, clause 7 of the Rules for filling out an invoice. The algorithm is as follows:
- Create a new ESF document;
- Indicate in line 1 the date and number of the ESF entered with an error;
- In line 1a – registration data of the new document;
- Make any necessary edits.
Applying the rules for filling out an invoice is appropriate only if the document has already been officially registered; in all other cases, issue a new invoice without reference to the version with typos.
Features of filling out and registering the corrected ESF
It is impossible to issue a revocation of an erroneous invoice if the document is listed in the registration journals. Therefore, you will have to not only submit new documents, but also add cancellation of the incorrect ESF. Accounting departments should also take into account that there are clear criteria for registering an amended invoice. This is important to consider for the possibility of obtaining VAT.
A typical situation is when the ESF with amendments is received in the same quarter as the original document. In this case, the service or product provider records the corrected and erroneous invoice. The primary document is entered with a minus sign.
For example, on 02/02/2020, enterprise “K” sold a batch of goods. A week later, it was discovered that the recipient's TIN was incorrect on the invoice. Accordingly, Enterprise “K” issued a corrected ESF and registered it on 02/19/2020. The primary document is also registered on the same date, but in a negative value. Accordingly, the balance in the sales book for the erroneous document is reduced to zero, and only the new, corrected ESF remains. For the buyer or recipient of services, the procedure is similar, but if an error is detected before the incorrect invoice is registered, only information about the correct ESF is entered into the purchase ledger.
Let's look at another example. The buyer received an invoice in the first quarter of 2022, but discovered the error only in the second. In this case, information about the documents is recorded in an additional sheet of the purchase book.
As in the previous case, the corrected and original document is registered with a minus sign. It is extremely important to cancel the balance, since in the future this will have a direct impact on the calculation of VAT.
Although the law allows you to send an invoice with typos to your counterparty, in practice it is better to double-check the document in advance. The implications are purely technical and add unnecessary work. In addition, if the error is discovered late, problems may arise with the tax authorities. For example, if the cost of a product was underestimated relative to the market value, this fact may be considered as an attempt to illegally reduce the amount of taxation. This involves administrative and, in some cases, criminal liability.
We will quickly implement EDI for the exchange of electronic invoices
Corrective invoices in 1C: Accounting - reflection rules
Published 10/22/2018 11:11 Author: Administrator An error in accounting and reporting is the incorrect reflection (non-reflection) of the facts of economic activity. Identified errors and their consequences are subject to mandatory correction (PBU 22/2010). Corrections to sales documents are necessary if errors are found in them that do not allow the tax authorities to unambiguously identify the seller, buyer, name of goods (work, services) and their cost; tax rate and VAT amount.
Distinctive features of correction invoices:
- corrections to the price are made in case of arithmetic or technical errors, they are not agreed upon by any documents;
- the mechanism for recording in the seller’s sales book and the buyer’s purchase book does not depend on whether the VAT amount in the corrective invoice has increased or decreased.
Regardless of the date of correction, rights and obligations to the budget relate to the period when the original invoice was issued.
The numbering of invoices within one period is continuous, and the numbering of corrections within one invoice always starts from No. 1, the number of corrections is not limited. The corrective invoice reflects the completely correct data of the primary invoice and the corrected data instead of the erroneous data.
Anatomy of a vendor fix
Correcting errors of the current tax period
The corrected invoice has the same serial number and date, the correction is recorded under serial number 1, the current date of the quarter.
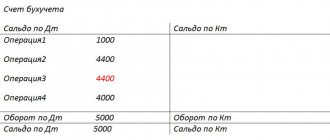
Reversing entries are generated for the difference in the cost of sales and the difference in the amount of VAT.
In this case, two entries are generated on the “VAT Sales” tab (accumulation register): reversing the primary sale and corrective sale.
In the sales book of the current period, three entries are formed: primary, cancellation of the primary and corrected.
We compare similar indicators in accounting and tax accounting.
Correcting errors from the previous tax period
Corrections are reflected in the additional sheet of the sales book, and, accordingly, in Appendix 1 of Section 9 of the corrective VAT Declaration.
We compare accounting and tax accounting data. Please note: corrective data in accounting is reflected in the current period, and in tax accounting - in the period of initial sales.
The buyer's received correction documents are registered in the same way:
- if the seller changed the data before the end of the tax period - using “three entries” in the purchase book (primary, canceling the primary and corrective);
- if the seller “changed the testimony” after the end of the tax period - using “two entries” of an additional sheet of the purchase book (cancelling and correcting).
If the amount of the discrepancy declared by the seller is significant, the buyer finds himself in a disadvantageous situation with any correction option: if the amount of the tax deduction is reduced, this will lead to additional payment of VAT and the payment of penalties; if the amount of the tax deduction is increased, this may lead to a refund from the budget, which is also undesirable.
And a little about other rules: “The feeling of fullness in life depends on your worldview, and not on momentary success. We move forward to make our way, not to find a way out. Working and interacting with other people, we are always stronger than I am.”
Author of the article: Irina Kazmirchuk
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the newsletter for new materials
Add a comment
JComments
How to take corrected ESF?
Making changes to an invoice is not a problem, but each additional ESF involves wasting time and unnecessary entries. Practice shows that accounting books full of corrections are of particular interest to inspection authorities. Also, although these are small, they are still unnecessary expenses. Therefore, when accepting an invoice, especially after corrections, it is recommended to carefully check all document details. Moreover, the information should not only be in its place, but also correspond to reality.
At the same time, no one can work without making a single mistake. With digital document management, it is much easier to make changes to documents. In addition, the speed of data exchange increases significantly. This allows you to quickly identify errors and correct them immediately. Our company specializes in the development and implementation of paperless technologies and the implementation of EDI for the exchange of documents with counterparties. If you are interested in their capabilities, contact us by leaving a request on the website or by phone. We will be happy to advise you and offer the best option for cooperation.
Let's sum it up
It is not always possible to draw up an invoice correctly the first time. This is due both to the characteristics of the specific field of economic activity in which the company operates and to the human factor. Moreover, there are often cases when a seller or supplier makes mistakes due to the fault of the counterparty. For example, the buyer made a mistake when entering bank details or missed a number in the tax ID.
Therefore, the legislator is loyal and gives the opportunity to business entities to make amendments on their own. For this purpose, either an adjustment invoice or a corrected one is used. These two types of documents should not be confused, since their purpose is radically different. It is impossible to reflect a change in the price of a product in the form of a correction if it occurred in connection with the signing of an agreement between the seller and the buyer. To do this, you should use a correction invoice, otherwise it is contrary to current legislation. But if we are talking about real corrections of errors, then it is necessary to prepare a corrected invoice.
In addition to the instructions and recommendations described in the article, remember one more rule: each ESF is signed with a qualified digital signature. No matter how many changes you make to the same document, each time it must be endorsed using the CEP.