To account for VAT calculations, use account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” and account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets”. A special subaccount 68.VAT is created for account 68. The credit of this account records accrued VAT, and the debit reflects the tax paid and amounts reimbursed from the budget. Account 19 in accounting is used to reflect input tax received from suppliers, but not yet reimbursed from the budget. Sub-accounts are also opened for account 19 “Value added tax on acquired values” depending on the type of values received.
VAT postings. Basic Rules
Enterprises in their economic activities face VAT when selling products, goods, providing services, performing work to their customers and contractors (and then it is necessary to charge VAT on their cost), as well as when purchasing goods, works, services from suppliers (taking VAT as a deduction ).
In general, VAT calculation on sales will look like this:
Debit 90 Credit 68 (if account 90 “Sales” was used when selling the asset).
Debit 91 Credit 68 (if the sale was carried out through account 91 “Other income and expenses”).
As we can see, VAT payable to the budget actually accumulates in the credit of account 68.
When we purchase a product, we have the right to reimburse the tax from the budget. In this case, the rules for accounting for VAT are as follows: the tax is allocated from the purchase amount and is accounted for in account 19 “VAT on purchased assets.” The wiring looks like this:
Debit 19 Credit 60 - VAT on purchased assets is reflected.
Debit 68 Credit 19 - VAT is deductible.
Thus, the refundable VAT is collected in the debit of account 68. And as a result, the amount of tax to be transferred to the budget is formed, defined as the difference between debit and credit turnover on account 68: if credit turnover is greater than debit, then the difference must be transferred to the budget, if vice versa - the difference is subject to compensation by the state.
We talk about typical transactions related to the deduction of VAT in the special material “Posting “VAT accepted for deduction”: how to reflect it in accounting?” .
Typical VAT entries for purchased assets
VAT on purchased assets and services is accounted for using the following entries:
Debit 19 Credit 60 - reflection of the “input” VAT on purchased fixed assets, intangible assets, materials, goods, capital investments, works, services. Posting is done based on the received invoice.
Debit 68 Credit 19 - reflection of VAT deductible on inventories and services, including in the case of confirmation of the fact of export. Posting is done on the basis of invoices, and when confirming exports, after submitting the documents listed in Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to the Federal Tax Service and receiving the appropriate decision.
See also “What are VAT tax deductions?” .
In some cases, “input” VAT cannot be deducted.
For more information about situations when VAT deduction is impossible, and how to take it into account for tax purposes, read the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the system can be obtained for free.
In accounting, tax that is not deductible is written off to cost or financial results accounts:
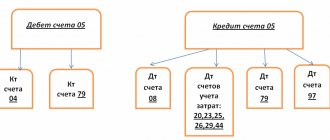
Debit 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44) Credit 19 - write-off of VAT on acquired assets and services that will be used in transactions not subject to VAT. The posting is made on the basis of an accounting calculation prepared by a certificate.
Debit 91 Credit 19 - write-off of VAT on other expenses if the invoice from the supplier was not received, lost or filled out incorrectly.
See also the material “What are the grounds and how to write off VAT on 91 accounts?” .
Debit 20 (23, 29) Credit 68 - restoration of VAT previously claimed for reimbursement of inventories and services used for transactions not subject to VAT. The basis of the posting is again a reference calculation.
For reasons for VAT restoration, see this material.
If you have made an advance payment to the supplier, you can see what transactions should be made for VAT in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus experts. Get a free trial access to K+.
Tax agent obligations for VAT from January 1, 2022
The main change of the new year was the increase in the VAT rate to 20%. In addition, the settlement rate has also increased, which is now 20/120. Innovations also include the fact that from 2022, foreign organizations that provide services in the Russian Federation electronically are required to independently organize the payment of VAT and submit the appropriate reports (rate 16.67%) in accordance with Law 303-FZ. This can be done in one of the following ways:
- when sales are carried out by an agent under a contract, the VAT report and payment are made by the representative;
- when a foreign company is directly involved in sales, it is necessary to register with the Federal Tax Service, obtain a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) in the Russian Federation, and then pay VAT independently.
In the second case, refusal to register as a Russian taxpayer does not oblige the buyer to become his tax agent and pay fines. That is, an organization or entrepreneur will not receive a VAT deduction, even if one of them decides to pay VAT on their own.
In this case, electronic services mean the following types of services provided in the customs territory of the Russian Federation:
- providing access to programs and computer facilities via the Internet;
- hosting and data storage abroad;
- advertising and promotion of goods on the Internet;
- design, support, and website administration remotely;
- access to repositories of electronic books and publications;
- search, delivery of information.
Important! It should be remembered that electronic services do not include services for ordering goods online, consultations by e-mail, software implementation, or organizing access to the Internet.
Typical entries for accounting for VAT on sales
Debit 90 Credit 68 - VAT accrual on sales of assets, works, services. The basis of the entry is the outgoing invoice.
Debit 76 Credit 68 - accrual of VAT on advances received. The basis is an advance invoice.
Debit 68 Credit 76 - reflection of the offset of VAT on advances upon completed shipment (performance of work, provision of services). The basis is the issued invoice.
Debit 08 Credit 68 - accrual of VAT on construction and installation works carried out in-house. The basis is an accounting certificate.
Debit 91 Credit 68 - VAT accrual for gratuitous transfer of assets. The posting is made on the basis of the issued invoice.
Debit 68 Credit 51 - VAT debt has been repaid. The basis is a bank statement.
If you have received an advance from the buyer, you can see what entries should be made for VAT in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus experts. Get a free trial access to K+.
How to offset VAT overpayments
The VAT offset procedure is carried out in four stages.
Step 1 - Request a tax reconciliation report
The tax office may forget to notify you about the overpayment. Then act on your own.
Submit an application for reconciliation to the Federal Tax Service in person or through electronic communication channels. Within 5 days the tax office will send you a report. Check it with your data. If there are no objections, sign and give one copy to the tax office. If you disagree with something, write “the act was signed with disagreements” at the end of section 1.
Instead of an act, you can request a certificate about the status of settlements with the budget. It will arrive in 5 working days.
Step 2 - Select the tax to offset the overpayment
For example, in a deed or certificate you saw an overpayment of VAT. It can be used to pay off any federal, regional or local tax. You can also pay off fines and penalties. There are no restrictions.
Step 3 - Apply for Credit
Do this in free form or according to a template. Based on one application, the overpayment is offset to pay off one tax. If the overpayment amount is enough to pay another tax or fine, prepare a second application.
You can offset the overpaid tax against your debt or future payments. Often, the tax office automatically counts an overpayment on one tax against the debt on another. But you will still be charged penalties on the debt from the moment the debt arises until the day the decision on offset is made. Therefore, submit your application in advance.
With your application, submit documents that confirm the overpayment: a certificate of the status of settlements with the budget, a reconciliation report, a payment order, a declaration, and so on.
You can submit your application in person, by mail or electronically.
Stage 4 - Wait for the inspection's decision
The Federal Tax Service has 10 days from the date of filing the application to make a decision. In this case, the inspection may ask you to sign a reconciliation report if you did not do this at the first stage. Then the 10-day countdown will begin from the moment the document is signed.
You will have to wait longer if the overpayment occurred due to the submission of an amendment along with the application. Then the decision on offset will be made within 10 days after the desk audit of the new declaration, which lasts 3 months.
The cloud service Kontur.Accounting fills out tax returns without errors. We have a built-in verification system that automatically checks all control ratios and makes recommendations to avoid fines and legally reduce the amount of VAT payable. We give all newcomers a free trial period for 14 days.
If VAT is calculated by tax agents
Example 1. Lease of state property:
Debit 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) Credit 60 (76) - accrual of costs for renting state property.
Debit 60 (76) Credit 68 - VAT accrual from the tax agent.
Debit 19 Credit 60.76 - accrual of input VAT specified in the agreement.
Debit 68 Credit 51 - reflection of VAT transferred to the budget.
Debit 68 Credit 19 - VAT on rent to be refunded at the time of tax payment.
See the material “ Tax agent for VAT in transactions with state property ” for more details.
Example 2. Services provided by a foreign company on the territory of the Russian Federation:
Debit 44 (20, 25, 26) Credit 60 (76) - a reflection of services provided by a foreign company to a Russian organization in the Russian Federation.
Debit 19 Credit 60 (76) - accounting for VAT paid on the income of foreign legal entities.
Debit 60 (76) Credit 68 - VAT withholding from a foreign partner.
Debit 68 Credit 51 - VAT paid by the tax agent.
Debit 68 Credit 19 - VAT of the tax agent to be deducted after its payment.
See also the material “ How can a tax agent deduct VAT when purchasing goods (work, services) from a foreign seller .”
Responsibility for failure to fulfill obligations
If a tax agent untimely or intentionally fails to withhold VAT from remuneration to a supplier who is not registered with the Federal Tax Service and does not have resident status, then he is subject to the following penalties:
- 20% of the amount of unwithheld and unpaid tax (123 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- penalties for each day of delay (75 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- 200 rubles for failure to submit a VAT return on time upon fulfillment of the duties of a tax agent (126 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- 5% of the amount of the unpaid obligation for each month of delay in case of failure to submit or late submission of the declaration, but not less than 1000 rubles and not more than 30% (119 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From the point of view of tax legislation, it is considered incorrect if the unrecovered VAT is paid at the expense of the buyer. In this case, a fine of 20% will be charged, as well as penalties for the entire time of non-payment of the obligation. In this case, the agent must withhold VAT from the remuneration amount for the subsequent delivery and transfer the non-payment to the budget. If the transaction was a one-time transaction, then the law does not explain further actions in such a situation. That is, repaying the debt with the buyer’s funds will still be preferable. Bring the tax agent to criminal liability under Art. 198 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation should not, since this measure provides for fairly large amounts of fines, forced labor, as well as imprisonment for repeated intentional violations on a large and especially large scale.
Typical VAT transactions when returning goods
From 2022, postings for returning goods depend on how the return occurs: within the framework of the original contract or as a resale under another contract, and does not depend on whether the goods returned are of high quality or defective.
If the item is returned under the original contract, the postings will be as follows.
Important! ConsultantPlus warns If you are returning a product for which “input” VAT was previously deducted, the tax must be restored. This is done on the basis of the seller's adjustment invoice or primary documents on the reduction in the value of goods shipped, whichever came first. See K+ for more details. Trial access is available for free.
From the buyer:
Debit 60 Credit 76 - adjustment of settlements with the seller.
Debit 76 Credit 41 - return of defective goods to the seller.
Debit 76 Credit 68 - restoration by the buyer of VAT previously accepted for deduction, attributable to the cost of the return.
From the seller:
Debit 62 Credit 90.1 - reversal of revenue.
Debit 90.2 Credit 41 - reversal of cost.
Debit 90.3 Credit 19 - reversal of accrued VAT on returned goods.
Debit 68 Credit 19 - deduction by the seller of VAT on the returned goods.
In case of reverse sale, taxation will be the same as for a regular sale, only the buyer and seller change places.
Example. Postings when returning goods of proper quality from ConsultantPlus The organization received 100 units of goods worth 120,000 rubles, including VAT - 20,000 rubles. Of these, 10 units were returned to the supplier for 12,000 rubles, including VAT - 2,000 rubles. You can view the entire example in K+, getting free full access.