Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines special rules for accounting for subsidies received by a “simplified” person. The mechanism for recognizing income in the form of subsidies and expenses made (reimbursed) at their expense, provided for by this norm, concerns, in particular, financial support funds received in accordance with Federal Law No. 209-FZ of July 24, 2007 (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 209-FZ) Federal Law). In what situations such a mechanism can fail, let's look at examples from practice.
Regulatory regulation
The subsidy received under Government Decree No. 1513 dated September 7, 2021 is taken into account by taxpayers using the simplified tax system in the following order:
- the amounts of subsidies are not taken into account in income (clause 1, clause 1.1, article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 60, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- expenses from subsidies specified in paragraphs. 60 clause 1 art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are not taken into account for tax purposes under the simplified tax system (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 48.26 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for reflecting the subsidy in the accounting system depends on the moment the expenses are incurred:
- compensation for expenses already incurred - taken into account as part of other income in account 91 “Other income and expenses”, without being reflected in account 86 “Targeted financing” (clause 10 of PBU 13/2000, clause 7 of PBU 9/99);
- when compensating for future expenses: upon receipt - on account 86 “Targeted financing”;
- as funds are spent (purchase of goods, works, services) - in account 98 “Deferred income”;
- when attributing goods (work, services) acquired through subsidies to expenses, they are included in other income in account 91 “Other income and expenses” (clauses 7, 9 of PBU 13/2000).
Organizations that received a subsidy may not be subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions (except for tax and labor taxes) on part of the salary in the amount of the minimum wage - 12,792 rubles. for each employee in the month of receiving the subsidy or the month following it (clause 89 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 17 of clause 1 of article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for reflecting payments from subsidies in personal income tax reporting is explained in Letters of the Federal Tax Service dated 02/02/2022 N BS-4-11/ [email protected] , dated 01/21/2022 N BS-4-11/592.
The benefit is provided for each employee who received income in the month of exemption, regardless of how many employees the subsidy is calculated and issued (Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated January 21, 2022 N BS-4-11 / [email protected] ).
EXAMPLE FROM JUDICIAL PRACTICE
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated July 23, 2014 No. A06-6241/2013. Although it talks about income tax, this can also serve as an example for the simplified tax system. The tax authorities considered the organization's tax base to be understated due to understatement of non-operating income and increased non-operating expenses in accordance with paragraphs. 20 clause 1 art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for the amount of fuels and lubricants acquired through subsidies and transferred free of charge to third-party organizations. The court sided with the organization, since the subsidy was allocated to it for the purchase of fuel and lubricants for its own needs on a free and irrevocable basis, in order to reimburse costs in connection with the performance of work and the provision of services, all the conditions for the provision of the subsidy were fulfilled (a report was provided on the expenditure of targeted funds, separate accounting of income and expenses was maintained). The law provides for the provision of subsidies to legal entities (including commercial organizations) on a free and irrevocable basis in order to reimburse costs or lost income in connection with the production (sale) of goods, performance of work, and provision of services. Therefore, no violations were identified on the part of the organization.
- Back
- Forward
Accounting in 1C
On December 20, a subsidy for non-working days in the amount of 25,584 rubles was received in the Organization’s bank account.
The organization decided to compensate wage costs for December 2022 using subsidies, as well as apply benefits for personal income tax and insurance contributions in December.
For December, salaries were accrued to two employees:
- Gordeev N.V. - 22,792 rubles, no deductions for personal income tax;
- Drozdov O.V. - 22,792 rubles, no deductions for personal income tax.
Let's look at the calculation procedure using one of them as an example.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C |
| KUDiR | ||||||
| Receipt of subsidies to the current account | ||||||
| 20th of December | 51 | 86.01 | 25 584 | Receipt of subsidies to the current account | Receipt to current account - Other receipt | |
| Calculation of wages and insurance premiums (costs due to subsidies) | ||||||
| 31th of December | 26 | 70 | 20 000 | Payroll | Payroll | |
| 26 | 70 | 25 584 | Payroll through subsidies | |||
| 70 | 68.01 | 2 600 | Withholding personal income tax | |||
| 26 | 69.01 | 580 | Calculation of contributions to the Social Insurance Fund | |||
| 26 | 69.03.1 | 1 020 | Calculation of contributions to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund | |||
| 26 | 69.11 | 91,17 | Calculation of contributions to the Social Insurance Fund NS and PZ | |||
| 26 | 69.02.7 | 4 400 | Calculation of contributions to the Pension Fund | |||
| Correction of the simplified tax system register | ||||||
| 31th of December | Entries in the register Expenses of the simplified tax system | Manual entry - Operation | ||||
| Reflection of subsidies in accounting revenues | ||||||
| 31th of December | 86.01 | 91.01 | 25 584 | Reflection of subsidies in accounting revenues | Manual entry - Operation | |
| Payment of salaries and transfer of contributions | ||||||
| January 19 | 26 091,17 | Consumption. Amount of salary and contributions | Report Book of Income and Expenses of the simplified tax system | |||
Who is eligible to receive a subsidy?
Let's look at which categories of businesses are eligible to receive one or both COVID-19 subsidies.
Employment Subsidy
We list the conditions that recipients of this subsidy must meet:
Subsidy for preventive measures
For this subsidy, the Russian Government has established the following recipients:
Subsidy receipt
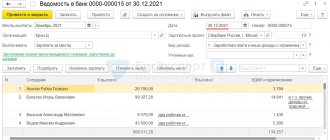
Reflect the receipt of the subsidy in the document Receipt to current account, transaction type Other receipt (Bank and cash desk - Bank statements).
Please indicate:
- The payer , the Federal Tax Service, from which the subsidy was received, is selected from the Counterparties directory;
- Settlement account - 86.01 “Targeted financing from the budget”;
- Assignment of earmarked funds - create an entry in the Assignment of earmarked funds : for example, Subsidy under Resolution N 1513 (used for internal analytics);
- Agreements - create an agreement (the basis for receiving a subsidy) with the Federal Tax Service specified in the Payer : Type of agreement - Other ;
- Type of movement - Other receipts from current transactions ;
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 51 Kt 86.01 - receipt of subsidies to the current account.
The subsidy amount does not fall into the Income of the accumulation register Book of Income and Expenses .
Individual entrepreneurs are not required to keep accounting records (clause 1, clause 2, article 6 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ), therefore they can reflect the receipt of subsidies in a simplified manner:
- Dt 51 Kt 91.01.
What documents to submit
Documents are provided to the Entrepreneurship Support Center of the region where you are registered. The composition of the package of necessary documents is established by the rules of each program. The project consists of a business plan with all attached documents. An approximate list of documents that should accompany a business plan is as follows:
- Application for a subsidy
- Copies of documents confirming the authority of the person presenting the documents
- Copy of state registration certificate
- Copy of extract from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs/Unified State Register of Legal Entities
- Certificates from regulatory authorities confirming the absence of debt
- Certificate of status of bank accounts
- Feasibility study
- Copies of the organization's constituent documents
- Copies of required licenses and permits
- Availability of necessary buildings and premises for the implementation of the business plan
The selection of entrepreneurs is carried out on a competitive basis. The formed commission evaluates it according to several criteria, among which the determining ones will be: whether your type of activity is a priority in the region, as well as what are the benefits of the project and the prospects for its development. The most significant areas of activity are considered to be social and infrastructural, and the regions also willingly support innovative and scientific and technical areas.
The most important thing is to correctly draw up a business plan and prepare the documents correctly, in accordance with the requirements, because Most refusals are based precisely on the absence of these indicators.
You will need to defend yourself before the commission meeting; if they like your report, the project will be sent for consideration to the city financial commission and after their approval, you will receive the required support.
Of course, it is worth knowing the possible size of the subsidy in advance. For example, in Moscow it is only 10,200 rubles, and in the Moscow region the maximum reaches 145,560 rubles. You can find out the amounts and conditions for receiving a subsidy on the local administration website or on the “My Business” website.
Payroll through subsidies
The 1C program implements the reflection of part of the salary paid through the subsidy in personal income tax reporting in accordance with the recommendations of the tax authorities - as a deduction with code 620 (from release 3.0.106.60).
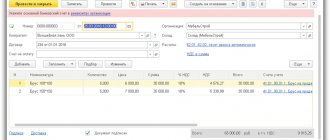
Create a new accrual (Salary and HR - Salary settings - Accruals):
Fill in all fields, taking into account the specifics:
- in the Insurance premiums : Type of income - Subsidies from the federal budget due to the coronavirus epidemic ;
- Reflection method - create a new method of accounting for salaries for each accrual account: Reflection in the simplified tax system - Not accepted .
Use this accrual (add manually) in the Payroll document for the part of the salary compensated by the subsidy.
In the Accrued , divide the accrued amount into 2 lines:
- Accrual - Payment based on salary : part of the salary minus the minimum wage (in our example, 22,792 - 12,792 = 10,000 rubles);
- Minimum wage - 12,792 rubles;
As a result, personal income tax is accrued only on the portion of income that exceeds the deduction in the amount of the minimum wage.
Insurance contributions (except for NS and PZ) are also accrued only on the part of the salary exceeding the minimum wage.
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 26 Kt 70 - salary calculation in excess of the minimum wage;
- Dt 26 Kt 70 - salary calculation due to subsidies;
- Dt 70 Kt 68.01.1 - calculation of personal income tax on the amount of salary in excess of the minimum wage;
- Dt 26 Kt 69.01 - calculation of contributions to the Social Insurance Fund from the amount of salary in excess of the minimum wage;
- Dt 26 Kt 69.03.1 - calculation of contributions to the FFOMS from the amount of salary in excess of the minimum wage;
- Dt 26 Kt 69.11 - calculation of contributions to NS and PZ from the amount of salary in excess of the minimum wage;
- Dt 26 Kt 69.11 - calculation of contributions to NS and PZ from wages at the expense of a subsidy;
- Dt 26 Kt 69.02.7 - calculation of contributions to the Pension Fund from the amount of salary in excess of the minimum wage.
Movements in the Expenses register under the simplified tax system are automatically generated incorrectly:
- Personal income tax is distributed proportionally between the taxable part of the salary and the non-taxable part;
- part of the NS and PZ contributions from wages covered by the subsidy is not accepted as expenses.
Therefore, when paying salaries and paying personal income tax and contributions, KUDIR is filled out incorrectly.
For labor costs (salary + personal income tax), the resulting amount is correct (18,858 + 1,142 = 20,000 rubles), there is no need to correct it.
For NS and PP insurance premiums, corrections must be made manually.
Before doing this, check the expenses that are not accepted using the Universal report on the Expenses register under the simplified tax system . Report settings see PDF
Let's calculate the difference between non-accepted expenses and the subsidy amount:
- 25,635.17 - 25,584 = 51.17 - NS and PZ insurance premiums for the part covered by the subsidy.
Enter the amount of insurance premiums into the Expenses register under the simplified tax system manually.
Is the subsidy considered income?
A subsidy is a non-refundable and gratuitous assistance designed to compensate for costs or supplement income that was not received for one reason or another.
It is noted separately under OSNO and simplified taxation system; in any case, these funds are taken into account and appear in the documents. Subsidies can be awarded for a variety of reasons, among which it is worth noting:
- work with regional programs;
- job creation;
- promoting employment.
Both small entrepreneurs and large businesses can take advantage of the opportunities that are opened by the state within the framework of targeted programs and other activities.
Budget funds are accepted into accounting records at the time of their provision, that is, actual receipt into the account, or at the time of allocation, which appears in the documents.
Correction of the simplified tax system register
Make the correction using the document Operation entered manually in the Operations . Create the document with the same date as the Payroll . In our example, December 31, 2021.
Click the More button - Select registers, add the accumulation register Expenses under the simplified tax system and enter two lines filled in according to the movements of the Payroll :
- 1st line with a minus: Reflection in NU - Not accepted ;
- Reflection in NU - Accepted .
After this, the expenses in KUDiR will take into account the correct amount when paying contributions.
Reflection of subsidies in accounting revenues
Reflect the amount of the subsidy as part of other income in the month of recognition of expenses (payroll) using the document Transaction entered manually (Transactions - Transactions entered manually - button Create - Transaction).
Features of filling out a document Operation entered manually according to our example:
- Debit - 86.01 “Targeted financing from the budget”, indicate the same analytics as in the document Receipt to the current account : Subconto 1 - element of the directory Assignment of targeted funds ;
- Subconto 2 - the basis for receiving a subsidy from the Federal Tax Service;
- Subconto 3 - from the closed list Movements of target funds - Other expenses ;
- Type of item - Other non-operating income (expenses) ;
Who can receive a subsidy
In order to receive a subsidy, your company must be a start-up, i.e. her age should not exceed one year, in some programs two years. The area of your activity must be a priority for the region, otherwise officials will not be interested in providing you with funds for development, and your chances will be small. A list of activities is sometimes published on the websites of territorial small business support centers.
Also, one of the significant conditions is the use of allocated funds only for their intended purpose. This means that you will not be able to manage the money you receive as you want or see fit. You will have to strictly adhere to the business plan. The period for using money is limited in time, usually one to two years.
Most subsidy programs have a condition that the entrepreneur's own investment in the project be a certain proportion of the subsidy amount. For example, the organization’s own investment in the project must be at least 60% of the amount of the requested subsidy. The percentage is set by the terms and conditions of each program.
And, of course, all documents must be prepared in accordance with the requirements.