VAT rate for export
There are several points of view explaining the appearance of the 0% VAT rate.
On the one hand, VAT is an indirect tax paid by the buyer. Foreign buyers are not subject to the Russian Tax Code and therefore do not have to pay Russian VAT. In this regard, the sale of Russian goods and services to foreigners should occur without tax.
On the other hand, exports are of great importance for the economic growth of the country, so the state is interested in businesses striving to develop sales not only within the country, but also abroad. To increase the interest of entrepreneurs in export operations, there are various stimulating economic instruments. One of them is the VAT rate for export transactions, equal to 0%. Against the backdrop of fairly high regular VAT rates, one of which was recently increased, the use of a zero VAT rate for exports looks very attractive.
Let us remind you what VAT rates exist in Russia in 2022:
The Federal Tax Service has introduced new forms and formats of registers for exporters to confirm the VAT rate of 0%
The Federal Tax Service has approved new forms and formats of registers provided for in paragraph 15 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The corresponding order dated October 23, 2020 No. ED-7-15/ [email protected] was published on the Official Internet Portal of Legal Information.
Let us recall that, according to the norms of paragraph 15 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, to confirm the validity of the application of the 0% VAT rate, exporters have the right to submit to the tax authority electronic registers of customs declarations (full customs declarations), registers of documents confirming the provision of services, registers of transport, transportation, shipping and other documents provided for by the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, instead of copies of documents listed in the registers.
The Federal Tax Service order introduces new forms:
- Register of customs declarations (full customs declarations) provided for in subparagraphs 3, 5 and 6 of paragraph 1, subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.2, subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.3, subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.6, subparagraph 3 of paragraph 4 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (KND 1155110);
- Register of documents confirming the provision of services for the transportation of oil and petroleum products by pipeline transport, provided for in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.2 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (in the event that customs declaration is not provided for by the customs legislation of the Customs Union or is not carried out) KND 1155119;
- Register of documents confirming the provision of services for organizing transportation (transportation services in the case of import into the territory of the Russian Federation) of natural gas by pipeline transport, provided for in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.3 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (in the event that customs declaration is not provided for by the law of the EAEU or is not performed) KND 1155121;
- Register of complete customs declarations or documents confirming the provision of services for the transportation of oil and petroleum products by pipeline transport, as well as transport, shipping and (or) other documents provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 3.2 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (KND 1155120);
- Register of customs declarations (full customs declarations), as well as transport, shipping and (or) other documents provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 3.6, subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 4 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (KND 1155111);
- Register of declarations for goods provided for in paragraph 5 of subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, or transport, shipping and (or) other documents provided for in subparagraph 4 of paragraph 1 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (KND 1155117);
- Register of transport, shipping and (or) other documents provided for in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.1 and subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.7 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (when transporting goods by rail) KND 1155112;
- Register of transport, shipping and (or) other documents provided for in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.1 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (when transporting goods by road) KND 1155113;
- Register of transport, shipping and (or) other documents provided for in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.1 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (when transporting goods by air) KND 1155114;
- Register of transport, shipping and (or) other documents provided for in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.1, subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.5, subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3.8, subparagraph 2 of paragraph 14 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (when transporting goods by sea or river vessels, mixed vessels (river-sea ) swimming) KND 1155115;
- Register of transportation documents provided for in paragraph 4.1 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (KND 1155122);
- Register of transportation, shipping or other documents provided for in paragraph 3.9 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (KND 1155123);
- Register of transportation documents provided for in paragraphs 5 (except for the fifth paragraph) and 5.1 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (KND 1155116);
- Register of transportation documents provided for in paragraph five of clause 5 and clauses 5.3, 6, 6.1, 6.2, 6.4 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (KND 1155118).
The order also contains electronic formats of the listed registers.
New forms and formats of registers will come into force on April 1, 2021. At the same time, the existing forms and formats approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 30, 2015 No. ММВ-7-15/427 are abolished.
Updating the forms and formats of registers was required due to the introduction of a number of changes to Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by Federal Laws No. 350-FZ dated November 27, 2017, No. 353-FZ dated November 27, 2017, No. 302-FZ dated August 3, 2018, and June 6. 2019 No. 123-FZ and dated September 29, 2019 No. 325-FZ. The listed laws have simplified the rules for confirming the zero VAT rate for the export of certain types of goods, works and services.
Let us remind you that earlier the Federal Tax Service, by its letters dated 05.15.2020 No. EA-4-15/ [email protected] and dated 08.06.2020 No. EA-4-15/ [email protected], introduced recommended forms and formats of the listed registers, which can be used up to 1 April 2021.
In “1C:Enterprise 8”, the forms and formats of registers approved by the Federal Tax Service for confirmation by exporters of the VAT rate of 0% and auto-filling of registers given in Appendices No. 1 and No. 5 to the specified order will be supported with the release of subsequent versions in accordance with the start date of exchange through channels connection given in the Directory of periods for the use of formats for submitting tax returns, calculations (updated tax returns, calculations), accounting reports and other documents used for the calculation and payment of taxes and fees (SPPFD) (approved by order No. dated 12/24/2007 MM-3-13/ [email protected] ). For deadlines, see “Legislation Monitoring.”
Zero rate
So, the subject of our article is VAT on the export of goods.
As mentioned, the VAT rate for exports is 0. Clause 7 of Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation was introduced recently and allows in some situations to refuse the 0% rate:
It is logical to ask, for what purpose or for what reasons can one refuse a preferential rate? One of the reasons is this: you cannot simply take and apply a 0 VAT rate when exporting; you need to confirm it. And confirmation of the 0 VAT rate for export requires the collection of a large amount of documentation, that is, labor and time costs.
We will tell you further what is needed to confirm the zero VAT rate for export.
Simple steps to confirm the zero VAT rate
The exporter has the right to decide for himself in what form to submit documents confirming the 0 VAT rate - on paper or electronically through telecommunication channels. On the side of electronic documents – simplicity, speed, accuracy.
It is worth remembering that the electronic format of documents is not free; registers have approved templates.
Don’t “oversleep” submitting a package of documents for 0% VAT, don’t get confused in the forms, the VLSI Electronic Reporting service can help you monitor the accuracy of your reporting.
Confirmation of eligibility for a 0 percent rate
The procedure for confirming the zero VAT rate is described in Art.
165 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. To prove the legality of applying the zero VAT rate for exports, it is necessary to generate the following package of documents:
Instead of copies of the specified documents, paragraph 15 of Art. 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows the submission of electronic registers indicating the registration numbers of the relevant declarations.
Electronic registers must be compiled in approved formats and sent to the tax authority via TKS through an EDI operator duly registered in the Russian Federation.
It must be borne in mind that during the audit, tax authorities may require the submission of documents from the electronic register.
The taxpayer is given 180 calendar days to collect documents.
If after 180 days the documents are not collected, the goods sold must be subject to VAT according to Russian rules (at the rates from paragraphs 2 and 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the taxpayer nevertheless collects the entire package of documents after 180 days and pays VAT under Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the right to submit documents to the tax office is retained. If the tax authorities come to the conclusion that the 0% rate has become confirmed, the previously paid VAT on exports will be returned to the taxpayer.
Clause 10 of Art. 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that the VAT declaration and confirmation documents must be submitted to the tax office at the same time.
Principles of using the 0% VAT rate
A 0% VAT rate is applied in certain cases, among which the prevailing situations are the export of goods/cargo from the Russian Federation and the provision of services by carriers crossing the Russian border in the process of performing these services (Clause 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, the list also includes operations occurring within the country. Using a 0% rate allows you not to charge VAT on sales and to deduct the tax imposed by suppliers of goods, works and services invested in the creation of the item of sale.
However, in order to take full advantage of such a rate, you must confirm your right to apply it. For this purpose, a legally specified set of copies of documents is collected, indicating that the operation complies with all necessary requirements. Documents are submitted to the Federal Tax Service within the established time frame.
Submitting an incomplete set of documents by the required deadline is regarded as failure to comply with the deadlines for confirming the right to a 0% rate and entails the accrual of tax in relation to an undocumented transaction at one of two main rates (20% or 10%). This accrual is carried out on the date of shipment, is accompanied by a reduction by deductions (clause 10 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and requires the payment of penalties. At the same time, the opportunity to take advantage of the 0% rate returns when a complete package of documents is generated (clause 9 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And transactions that arose during the calculation of VAT for payment on a shipment that was not confirmed on time (except for transactions for the payment of penalties) will require reverse actions.
The rules applied when confirming the zero VAT rate are discussed in Art. 165 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It contains:
- lists of necessary documents - in relation to the situations described in paragraph 1 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- features of the design of these papers in specific situations;
- the deadline for filing with the tax authority and the procedure for determining the day from which it begins to count in a specific situation.
The basic differences in the lists of supporting documents are due to what exactly is sold at a zero rate (goods or services), as well as through which border (requiring customs clearance or not) the export occurs. Additional nuances of confirming a 0% VAT rate arise when exporting, which is due to the linking of the rules used for it to the type of goods sold and the presence of special documents drawn up in interaction with the EAEU member countries.
Features of VAT accounting in the presence of export operations
If a company begins to export, then the question arises: what accounting features exist for this type of activity?
Let's analyze the subtleties of export in terms of VAT calculation. Let's consider the concept of export in relation to goods. When exporting services, VAT is paid in the general manner if they are provided on the territory of the Russian Federation. Services are not subject to VAT if provided outside the Russian Federation.
If an organization carries out both taxable and non-VAT-taxable transactions, then clause 4 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation requires separate accounting of such transactions, because one of the main conditions for accepting input VAT from a supplier for deduction is the condition that the purchased goods (work, service) are used for operations subject to VAT.
By analogy, we can say that when a 0% rate is applied, it becomes necessary to keep separate records of such transactions. Thus, separate accounting for VAT on exports is necessary.
Let's turn to the regulatory framework. Paragraph 3 clause 10 art. 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation prescribes separate VAT accounting according to the rules established by the taxpayer himself, if he has activities taxed at a 0% rate. However, there is an exception to this rule: when exporting non-commodity goods registered after 07/01/2016, separate accounting can be omitted and VAT can be deducted in the general manner.
Deadline for determining the tax base:
Taxpayers using the simplified tax system, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, must pay VAT when importing goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation. However, nothing is said about the need to pay VAT on exports. Thus, when exporting, simplifiers do not have any VAT obligations.
Deduction for export transactions
A pressing question is whether an organization is entitled to deduct VAT when exporting?
The answer is yes. Input VAT for export, that is, the VAT that you paid to the seller for goods used for export, is deductible. But for this there is a certain procedure, somewhat different from the general procedure for accepting VAT for deduction. Those involved in the distribution of VAT on exports need to pay special attention to the process of VAT deduction.
The procedure for applying deductions when calculating export tax is described in paragraph 3 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It states that exporters of non-commodity goods can deduct input VAT in the general manner, that is, in the same way as for ordinary non-export sales. These rules were introduced on July 1, 2016. Those exporters who refused to use the preferential rate do the same.
For commodity exporters, the process of applying deductions depends on whether a package of documents confirming the zero rate has been collected or not. In addition, if VAT was accepted for deduction earlier, VAT restoration will be required when exporting this product.
Filling out a VAT return when exporting
Let's consider what data and in what sections must be entered when filling out a VAT return for export.
Declaration for export of non-commodity goods
When exporting non-commodity goods, VAT is deductible according to the same rules as for ordinary transactions.
Line 120 of Section 3 must be completed. The fact that the collection of documents does not affect the period for recognition of the deduction does not exempt the taxpayer from collecting a package of documents confirming the zero rate. If this package is formed in the reporting quarter of shipment, the amount of the tax base falls into line 020 of section 4, and line 030 remains empty, otherwise a double deduction will result. Section 4 is completed in the same way during the period of receiving the full package of documents. An example of filling out a declaration regarding export, that is, filling out the specified lines, is shown below.
How to report VAT if you export raw materials
As already mentioned, when exporting raw materials the situation is different, which is why the declaration is filled out differently. For such exporters, there are special export sections 4, 5 and 6 in the declaration.
The completed sections of the declaration (they may be in different declarations for different tax periods) are presented below:
VAT refund on export
VAT refund when exporting is a frequent procedure.
This is due to the peculiarities of export operations, namely the fact that when a 0% rate is applied, the VAT charged to the buyer is zero. Provided that goods for export are purchased from VAT payers, that is, when input VAT exists, VAT refund on export becomes inevitable. The same situation as with the return of export VAT may arise for ordinary transactions carried out within the country. The procedure for refunding export VAT and regular VAT does not differ in any way. Only the package of necessary documents differs: as already mentioned, in order to receive a VAT refund when exporting from Russia, you must collect documents confirming the zero tax rate.
Documents to confirm 0% VAT on export
Export of goods is subject to VAT at a rate of 0%. To use the zero rate, the company must confirm the fact of export.
To confirm the fact of export and reimburse the “export” VAT from the budget, it is necessary to fulfill certain requirements:
- you need to collect documents confirming that the exporter actually exported the goods abroad to Russia. Lists of documents are contained in Art. 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in relation to the situations given in paragraph 1 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- you need to fill out a VAT return and submit it to the tax office along with documents confirming export.
What documents are needed
To recover VAT, you must submit a package of documents to the tax office. Here is a list of them.
- Foreign economic contract (copy of the contract) with a foreign partner for the supply of goods outside Russia. That is, a document reflecting information about the parties and the subject of the transaction, as well as the conditions for its implementation.
- Customs declaration (CD) or a copy thereof.
The DT must have:
- mark of the customs office that carried out the customs operations;
- mark of the border customs office through which the goods were exported from Russia.
If a company submits a customs declaration in electronic form, then it is sufficient to submit it in the form of information about the release of goods. Such a mark will appear in the document automatically when the customs authority finishes checking the declaration and sends a corresponding message to the customs declaration service.
If the export of goods was carried out through the territories of the member states of the EAEU Customs Union, where customs control has been abolished (Belarus, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan or Kazakhstan), it is sufficient for the DT to indicate the customs office that carried out customs operations with the goods.
O must be obtained in the form of an original stamp only if the exporting company will submit documents confirming zero VAT to the tax office on paper. The stamp is affixed to the customs declaration and transport document by the customs authority at the border crossing point.
Until 2022 (more precisely, until October 1, 2022), the exporter also had to submit to the Federal Tax Service copies of transport or shipping documents with a mark from the customs authority on the export of goods. Now these documents are submitted only upon request from the tax authorities. The Ministry of Finance of Russia reminds us of this in letter dated August 27, 2019 No. 03-07-08/65684.
Registers of documents
If there is a large volume of documents, it is possible to submit registers based on them (Clause 15, Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This applies to shipping, transport, shipping and other documents, as well as customs declarations. The Federal Tax Service has the right to request for control any of the documents included in such a register.
These registers are presented exclusively in electronic form via telecommunication channels through an electronic document management operator. The forms of these registers and the procedure for filling them out, as well as the formats and procedure for submitting them in electronic form, were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 30, 2015 No. ММВ-7-15/427.
Deadline for collecting supporting documents
The period for confirming the legality of using a 0% rate is a single 180 days and does not depend on the specific situation for which such a rate is applied.
The generated set of documents must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service along with the tax return issued for the period in which this set was collected (clause 10 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Documents to confirm zero VAT must be submitted to the tax office at the place of registration of the company. This can be done on paper or in the form of electronic registers.
Simplified export confirmation procedure
According to the current rules, you can claim VAT deduction on goods, works and services purchased for export operations in the generally established manner before you have collected a package of documents confirming the zero VAT rate. That is, at the moment of acceptance of these goods for accounting and receipt of invoices from suppliers.
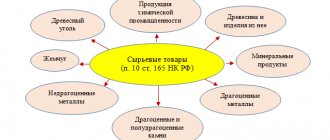
An exception to this rule is the export of primary goods, which include: mineral products, chemical products and other related industries, wood and wood products, charcoal, pearls, precious and semi-precious stones, precious metals, base metals and products of them.
Differences between exports to the EAEU and other countries
Many Russian companies work with neighboring countries, so questions often arise about the specifics of paying VAT when exporting to Uzbekistan from Russia or about VAT reimbursement when exporting to Kazakhstan.
Peculiarities of trade in terms of VAT with close neighbors do exist, but not with all of them. Countries that are part of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) are subject to special conditions:
So, what are the features of accounting for VAT when exporting to Belarus and other EAEU countries?
Despite the fact that VAT for exports to Kazakhstan and other EAEU states is zero, since in any case a zero tax rate is applied, an invoice must be drawn up. Indication of the zero VAT rate and the code of the type of goods according to the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity is mandatory. Here is an example of filling out an invoice indicating the zero VAT rate when exporting to Belarus in 2022: