When the tax office asks for clarification on the submitted VAT report
The conditions regarding the provision of explanations to the tax authorities for the VAT return are set out in paragraph 3 of Art.
88 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. After the VAT payer has submitted a declaration to his Federal Tax Service, tax officials must carry out a desk audit of the document. And if during the process they have questions, the payer who filed the declaration is sent a request for clarification of points that are unclear to the tax authorities. ATTENTION! The Federal Tax Service has approved further changes to the VAT return form (order dated March 26, 2021 No. ED-7-3/ [email protected] ). The first time you will need to submit a report using this form is for the 3rd quarter of 2022. Read about changes to the form here.
The main cases when a request for clarification on a declaration will definitely be sent to the payer are:
- if errors are found in the declaration (for example, inconsistency of control values);
- if the declaration data does not coincide with the information available to the tax authority for a given payer (for example, the tax authorities have data from counter audits with the payer’s counterparties, according to which one amount of turnover is obtained, but the calculation submitted by the payer indicates another);
- based on the results of the submitted declaration, the amount of VAT to be deducted (refunded) from the budget is obtained;
- when submitting an adjusted declaration, the adjusted amount of VAT payable to the budget is less than it was in the original calculation.
There are other options available besides those listed. However, they are all combined into logical groups that are assigned a specific code.
When the inspection requires clarification
We are all already accustomed to the fact that if, during a desk audit of a VAT return, the inspectorate identifies inconsistencies or inaccuracies in the VAT return, explanations will need to be provided.
Explanations are sent in electronic form via TKS through an electronic document management operator in the format established by the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
If you provide explanations other than electronically, they will not be considered submitted.
The inspection itself draws up the request for explanations in the approved form. It is contained in Appendix No. 2.9 to the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 16, 2013 No. AS-4-2/12705 “On recommendations for conducting desk tax audits.”
But inspectors may need explanations for the VAT return not only following the results of a desk audit, but also during other control activities. In this regard, the form of the requirement has been clarified.
Previously, the form indicated that it was used only when conducting desk audits. Now mention of this is excluded. Tax authorities will compile it in the case when the taxpayer’s data does not correspond to the information available to the inspectorate, and in all other cases when they need your explanations on VAT.
The Federal Tax Service wrote about this in a letter dated February 13, 2022 No. EA-4-15 / [email protected] The changes came into force on February 17, 2022.
How is a desk audit carried out?
Read more…
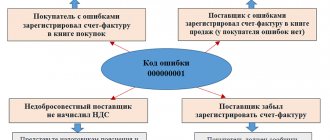
What is an error code in a Federal Tax Service request?
We present the coding and breakdown of groups of possible errors in the table.
| Code | The essence of the comment | Example situation |
| 1 | Discrepancy between the data in the payer’s declaration and the data in the declaration of his counterparty | The counterparty, the settlements with which are included in your declaration, submitted a zero report for the same period or did not submit it at all |
| 2 | Discrepancies between data from tax registers - purchase books (section and sales books (section 9) | A typical situation is the deduction of VAT on advances received for which tax was paid in earlier periods |
| 3 | Discrepancies between data from the journals of invoices received (section 11) and issued (section 10) | The intermediary has an invoice for the entire amount of the intermediary transaction |
| 4 | Other discrepancies and inaccuracies | For example, inconsistencies in indicators in the declaration columns. In this case, as a rule, when indicating code 4, the coordinates of the place of declaration in which there is ambiguity are indicated next to it in brackets |
| 5 | Errors in invoice dates in sections 8–12 | The invoice date is not specified or the invoice date specified exceeds the reporting period for which the declaration is submitted |
| 6 | VAT deduction is overdue | You claimed a deduction beyond three years |
| 7 | You have claimed a VAT deduction based on an invoice drawn up before the date of state registration | — |
| 8 | Incorrect indication in sections 8–12 of the transaction type code | More information about the codes can be found here. |
| 9 | Errors were made when canceling entries in section 9 | The VAT amount indicated with a negative value exceeds the VAT amount indicated in the invoice entry subject to cancellation, or there is no invoice entry subject to cancellation |
Indicating the error code should help the payer understand what exactly the tax office did not like in his return, as well as provide the most appropriate explanations for the situation.
Deduction of VAT from prepayment if its amount is greater than stated in the contract
The Federal Tax Service and the Ministry of Finance insist that it is possible to deduct VAT from an advance payment only if the conditions for transferring the advance payment are contained in the contract. Implies a familiar agreement in the form of a separate document. If there is no such agreement or there is no provision for prepayment, then the tax authorities will refuse the deduction.
Arbitrators have different opinions on this matter - there are decisions in which the existence of an agreement in the form of an independent document is recognized as optional. After all, if the company made an advance payment, it means that it confirmed the conclusion of the contract.
However, the tax authorities did not refuse the contract requirement in this case. True, now they consider it acceptable to provide them with a copy rather than the original document.
Thus, if VAT is claimed on an advance payment, the Federal Tax Service may request an agreement (copy) , which must contain a condition for prepayment. Otherwise, deductions may not be recognized.
It happens that the contract specifies one advance payment amount, but in fact the buyer transfers more. The Ministry of Finance admitted that in this case, VAT can be deducted from the entire prepayment amount actually transferred. But the tax authorities nevertheless request clarification in such a situation.
You can answer something like this:
Response to request No. ___________ dated __________ for a deduction from the advance payment transferred to the supplier
Cactus LLC, in response to request for clarification No. ____________ dated _______, explains the following.
In line 150 of section 3, the deduction amount was 36,000 rubles.
In accordance with paragraph 9 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT can be deducted from an advance payment if the following conditions are met:
- the seller presented the buyer with an invoice for the amount of the advance payment, which complies with the requirements of paragraph 5.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- An agreement has been concluded between the seller and the buyer, which contains the conditions for advance payment.
These conditions are met in relation to the operation in question.
Our company transferred an advance payment in a larger amount than provided for in the contract, so we claimed a large amount of VAT as a deduction. In accordance with the explanations of the Ministry of Finance given in letter No. 03‑07‑11/8323 dated 02/12/2018, this deduction procedure does not contradict the requirements of the law. The legality of the deduction is also confirmed by arbitration practice (Resolution of the AS ZSO dated June 21, 2016 No. F04-2547/2016 in case No. A45-18969/2015).
We also inform you that the counterparty calculated VAT on the amount of the advance payment actually transferred by us and reflected it in the sales book and tax return.
How and within what timeframe do you need to send clarifications on VAT at the request of the tax authorities?
In Art. 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that clarifications on reporting requested by tax authorities should be submitted no later than 5 working days. However, the tax legislation does not specify what is considered the starting point for counting these 5 days.
According to the norms of paragraph 5 of Art. 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, almost all VAT payers submit declarations in electronic form.
IMPORTANT! If the declaration is submitted via electronic communication channels, then further interaction between the tax authorities and the payer should occur in the same way. This is stated in the order of the Federal Tax Service dated April 15, 2015 No. ММВ-7-2/ [email protected]
That is, requests for clarifications to declarations must also be sent electronically.
At the same time, in paragraph 5.1 of Art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that in the case when the tax office sends an electronic document (request) to the payer, the taxpayer confirms receipt by sending a receipt of its acceptance. The receipt must be sent within 6 days from the date of receipt of the document from the tax office.
That is, if we consider the sending of a receipt as confirmation of receipt, we can assume that the period of 5 days begins to run from the moment such a receipt is sent. Otherwise, it turns out that explanations must be submitted before a receipt confirming receipt of the request for these explanations.
At the same time, the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated November 6, 2015 No. ED-4-15/19395 states that 5 days for preparing explanations should be counted from the date of receipt of the request. Let us remind you that in accordance with paragraph 4 of Art. 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the day of receipt of the request is considered to be the day following the day the request is posted in electronic access for the payer (for example, in the payer’s personal account on the Federal Tax Service website).
Thus, the question of when to start counting the days for providing explanations after a tax office request is not clearly defined by law. If the request came in electronic form, we recommend that when determining the deadlines, rely on the explanations of the Federal Tax Service, namely: count 5 working days from the working day following the day when the corresponding message from the Federal Tax Service appeared on your electronic resource.
IMPORTANT! In accordance with Art. 129.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the fine for explanations not submitted or submitted on time is 5,000 rubles. for the first violation within a year and 20,000 rubles. - if repeated.
We respond to the demand
Explanations must be given electronically. If you provide explanations other than electronically, they will not be considered submitted. Apparently everyone has already gotten used to this.
Further actions are as follows.
Having received a request to provide explanations on the TKS, you must submit to the inspection a receipt of acceptance of the request in electronic form through the EDF operator. You need to do it within 6 days from the day the inspection sent you the request. If you are late, inspectors may block your bank accounts within 10 days after the deadline for transmitting receipts.
Then check the factual part to see if your return is completed correctly. Carefully check the information for which discrepancies have been established: dates, document numbers, amounts depending on the tax rate and the cost of purchases (sales).
Separately, check whether VAT deductions claimed in parts correspond to the total tax amount. To do this, you may have to check previous quarters as well.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Typical errors that tax authorities identify when checking VAT returns
In what format should explanations be submitted?
Let us immediately clarify that the response to the tax office’s request for clarification on the VAT return can be in 2 options:
- Option 1. If the declaration initially contained an error when filling it out, which affected the amount of VAT payable, then in response to a request from the Federal Tax Service, an updated declaration should be submitted.
Read more about this in the article “How to make an updated VAT return in 2021?”.
- Option 2. If the data in the declaration will not change, but it needs to be deciphered for tax authorities, you need to create explanations and send them to the tax office.
ConsultantPlus experts will help you correctly draw up explanations for your VAT return. Get trial access to the system for free and go to the Ready-made solution.
The format of explanations for VAT is electronic only (unlike explanations for other taxes, which can be submitted both electronically and in paper form). The mandatory electronic format of this document is established by order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 16, 2016 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected] The document is a set of electronic tables that should be filled out by the payer for each figure in the declaration that raised questions.
Transfer of deductions
Fearing in-depth “camera chambers”, many companies transfer VAT deductions to future periods in order to comply with the standard, despite the fact that it is not mandatory for taxpayers.
The possibility of transferring deductions is provided for in clause 1.1 of Art. 172 Tax Code of the Russian Federation . In this case, you can only transfer deductions that are listed in clause 2 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ( paragraph 1, clause 1.1, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). In these cases, the company has the right to apply a VAT deduction within three years after the goods (work, services) are accepted for accounting. The last date of the quarter in which the deadline falls is the deadline for deducting VAT ( Definition of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated March 24, 2015 No. 540-O ).
As a result of a discrepancy between the invoices in the company's purchase book, reflected in the IR ASK VAT-2 database, and the counterparty's invoices reflected in the sales book, the tax authorities send requests for explanations.
Response to requirement No. 5/54 dated 08/06/2018 on the reasons for discrepancies in the VAT return
The company, in response to message (requesting presentation) No. 5/54 dated 08/06/2018, explains the following. The amount of tax and deductions in the declaration for the second quarter of 2022 is indicated correctly: on line 190 of section 3, the amount of deductions amounted to 5,200,100 rubles.
The discrepancy with the data of the counterparty LLC “Lutik” arose due to the transfer of VAT deductions in the amount of RUB 515,000. from the second quarter of 2018 to the third quarter of 2022.
The counterparty LLC "Lutik" presented the tax amount in invoice No. 4512 dated June 29, 2018 and included it in the tax base in the second quarter of 2018.
The company, using the right granted by clause 1.1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, will declare a deduction on the specified invoice in the third quarter of 2018.
When transferring company deductions, you need to keep in mind that you cannot transfer:
– deduction from an advance (“spent” advance, return of advance);
– “travel” deductions;
– deductions of the buyer acting as a tax agent;
– deduction for property received as a contribution to the authorized capital ( letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 01/09/2017 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] , Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 17, 2016 No. 03‑07‑08/67622 , dated 10/09. 2015 No. 03-07-11/57833 , dated 07/21/2015 No. 03-07-11/41908 , dated 04/09/2015 No. 03-07-11/20290 ).
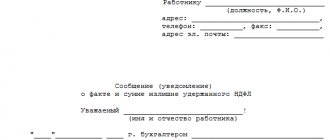
Form of explanations for the VAT return: sample
Since VAT explanations must now be submitted strictly via electronic communication channels in the form established by the Federal Tax Service, samples of paper explanations previously presented on professional websites on the Internet have lost their relevance.
The ability to prepare electronic explanations in the required format is implemented in the “Legal Taxpayer” program.
See more details here.
In addition, if you use the services of electronic document management operators, they also allow you to send explanations. For example, if the Federal Tax Service sends a request through “Kontur”, an xml file is attached to the message, using which you can generate a tax response. To clarify how to respond to the tax authorities, please contact the operator through whose system you received the request.
This feature has been implemented in 1C. The form of explanations in 8 should be looked for as follows: Directories - VAT reporting - Clarification of declaration indicators - Submission of explanations at the request of the tax authority.
What documents must be attached to the explanations?
The form of explanations does not imply the submission of additional documents (copies) along with it. The tables are designed in such a way that if they are filled out correctly, tax authorities will see all the information they need:
- information from primary accounting documents (invoices);
- details of primary documents;
- data from tax registers - sales books and purchase books;
- the amount of identified discrepancies in relation to the primary data and registers;
- the amount of adjustments made;
- Payer comments on discrepancies.
Therefore, there is no need to provide documentation along with explanations. However, it should be borne in mind that in some cases, during the audit, the tax office has the right to request documents.
There is a lot of interesting information about documentary tax audits here.
Explanations are provided: how to find out about the results
After sending explanations to the Federal Tax Service, taxpayers have questions:
- How to confirm the fact that the tax office has received clarifications?
- How can I find out the results of reviewing the explanations?
The answer to the first question is related to the system for sending explanations via electronic communication channels. Upon receipt of a tax document, the taxpayer receives an electronic notification about this, certified by the electronic signature of an authorized person. Or, if the explanations are not accepted, a refusal will be issued in the same way. Refusal is possible only in one case - if the explanations are sent in the wrong format.
As for the results of checking the explanations at the tax office, the current provisions of the law do not provide for the obligation of the Federal Tax Service to specifically inform payers about the results of consideration of their explanations.
So the results can only be learned in indirect ways:
- Conduct a reconciliation with the tax office some time after submitting clarifications and explanations. If the accruals on the personal account coincide with the updated (explained) data, then the explanations have “passed”.
- Receive a repeated request for clarification or a document verification order. From which it can be concluded that the explanations presented “did not pass.”
- There is also the option to contact the contractor who sent the request. However, today this method may not be justified. On the one hand, the operating procedure of the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate itself is aimed at minimizing personal communication between employees of the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate and payers. On the other hand, as we noted above, the employee you contact has the right to refuse to inform you about the results of the check.
Results
The procedure for submitting clarifications on VAT is now in effect, established by Order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 16, 2016 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected] According to this procedure and the requirements of the Tax Code, clarifications are submitted strictly in electronic form. Explanations are created by filling out tables according to the forms and format established by the Federal Tax Service.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 16, 2016 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.