What is a GPC agreement
The phrase “GPC agreement” stands for a civil agreement.
It is usually used as an alternative to an employment contract when it comes to hiring an individual to perform work or provide services without registering him as a member of the organization. In most cases, a GPC agreement is understood as a contract agreement (if an individual is entrusted with performing work that has a tangible result), or a contract for the provision of services for a fee (if an individual is entrusted with performing actions that do not have a tangible result). It is also possible to combine these types of contracts in one if the task involves both carrying out an activity and obtaining a specific result (clause 3 of Article 421 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT. The parties to the GPC agreement are called not “employer” and “employee”, but “customer” and “contractor” - in a work contract, or “customer” and “contractor” - in a service agreement. This must be taken into account when drawing up the contract and related documentation (applications, acts, etc.). Also, in a civil contract there should be no mention of position, working hours, bonuses for holidays and other terms characterizing labor relations. Otherwise, such a contract may be reclassified as an employment contract. And this threatens the organization with a fine of up to 100,000 rubles. (Part 4 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) and additional tax charges.
Registration under the GPC agreement in 2022
- identification data of the customer and contractor (details of the organization, full name and passport data of the individual);
- date and place of compilation;
- subject of the contract (the essence of the work or services for which the contractor will receive payment);
- amount of payment under the contract (exact amount, date of payment, attached payment schedule for partial payment);
- responsibilities of the parties (use of materials and tools, who pays for what during the execution process, the possibility of intermediate checks of completion, etc.);
- presence/absence of notarization of the contract;
- personal issues (non-disclosure of information, confidentiality, etc.);
- force majeure circumstances under which the contract becomes invalid;
- deadline for completing work or providing services;
- procedure for receiving the result (attachment of a sample acceptance certificate);
- additional conditions (negotiated individually);
- signatures of the parties with transcripts.
Contract agreement When the contractor's party undertakes to perform work assigned by the customer. The result is drawn up in an act of acceptance and transfer of work and payment is made for the work after completion in the agreed volume. GPC agreement for the provision of services. This group of agreements combines different types of agreements - an agreement of assignment or paid provision of services, a storage agreement, and others. The main idea is to provide a specific service for a pre-agreed fee.
21 Dec 2022 marketur 2139
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Failure to install a water meter
- Sponsorship refusal letter sample
- How to get rid of loans if you have nothing to pay
- 300,000 for the first child in Bashkiria, what are the conditions?
What taxes does the “employer” pay under a GPC agreement?
When paying remuneration to a contractor or performer, it is necessary to accrue and withhold personal income tax (clauses 1-4 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). According to the application of an individual who has entered into a GPC agreement, he needs to be provided with standard tax deductions, including for children (clause 3 of Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
REFERENCE. A freelance employee can receive property and social deductions only through the tax office (clause 8 of article 220, clause 2 of article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The entire amount of remuneration accrued under a “civil” contract (i.e., the amount taking into account personal income tax) is included by the “employer” on OSNO as part of labor costs (clause 21, part 2, article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The specified amount is also taken into account when calculating the single tax within the framework of the simplified tax system (subclause 6, clause 1 and clause 2, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Free accounting and preparation of income tax and personal income tax reports
Differences from taxation under an employment contract
Differences in the taxation procedure for payments under “civil” and employment contracts are related to the date of actual receipt of income.
When transferring payments under an employment contract, the following rule applies: if the employee does not quit, then income in the form of wages is considered to be actually received on the last day of each month (clause 2 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). On this day, the employer must calculate wages and calculate income tax, which must be withheld and transferred to the budget. Accordingly, when paying wages for the first half of the month, personal income tax is not calculated or withheld.
The situation is different with remuneration under a civil contract. In this case, the rule established for all other income in cash applies (subclause 1, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Such income is recognized as received on the day of payment or transfer. This means that personal income tax must be calculated and withheld under a “civil” contract for each payment. In this case, the type of payment (advance or final payment), as well as its date (beginning, middle or end of the month) does not matter.
ATTENTION. If the GPC agreement provides for the payment of an advance, then it may be necessary to adjust the personal income tax reporting for the period in which the advance payment was transferred. This can happen if the contractor returns the entire amount received or part of it due to the fact that he does not complete the work in full or on time (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 08/28/14 No. 03-04-06/43135).
Keep personal income tax records in the web service, generate and submit 6‑personal income tax and 2‑personal income tax via the Internet
Personal income tax on payments under a civil contract
If an individual entrepreneur or an organization does not have the necessary specialists on staff or it is difficult to complete the work on their own, they enter into civil law contracts with third parties. For example, a contract or service agreement.
If the person involved is an individual entrepreneur, then formalizing relations with them is no different from relations with counterparties – organizations. Those. The individual entrepreneur issues an invoice for his services or a contract is concluded, the work and services are performed, and a certificate of completion is signed. Payment is transferred to the individual entrepreneur's bank account. Individual entrepreneurs pay taxes on their income themselves.
But if you simply involve an individual who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur, then the situation will be a little more complicated.
And in this case, the customer organization will be obliged to withhold personal income tax from the income paid, because she will act as a tax agent.
In this article we will discuss how to calculate and withhold personal income tax from payments under a civil contract for the performance of work or provision of services.
articles:
1. Features of a civil contract
2. Signing the acceptance certificate for completed work
3. Obligation to withhold personal income tax from payments under a civil contract
4. Personal income tax on cost compensation
5. Two points of view on withholding personal income tax from compensation of costs to the contractor
6. Standard tax deductions
7. Professional tax deduction
8. Accounting for payments and personal income tax deductions
9. Calculation of personal income tax under a contract in 1C
So, let's go in order. If you don't have time to read a long article, watch the short video below, from which you will learn all the most important things about the topic of the article.
(if the video is not clear, there is a gear at the bottom of the video, click it and select 720p Quality)
We will discuss the topic further in the article in more detail than in the video.
Features of a civil contract
Civil contracts for the performance of work (this is a contract) and the provision of services are regulated by the Civil Code (Civil Code) of the Russian Federation.
Individuals can provide you with services (regulated by Chapter 39 of the Civil Code) or perform work (regulated by Chapter 37 of the Civil Code). An important difference between a civil law contract and an employment contract is the presence of an individual specific task. The subject of such an agreement is always the final result of the work. And it is this result that the customer pays for.
Regardless of what you have - work or services, a contract or a contract for paid services, the general rules of the relationship between the customer and the contractor will be the same, since the contract provisions apply to the service contract (Article 783 of the Civil Code).
The parties to the contract are the customer and the contractor. The one who gives the task is called the customer (this is an organization or individual entrepreneur), and the one who carries it out is called the contractor. For a service agreement, the same applies to the customer and the contractor.
Under the terms of the contract, the contractor (performer) is obliged to perform specific work (provide a service), clause 1 of Article 702 of the Civil Code.
What exactly it consists of must be described in detail in the contract, which is concluded in writing.
In addition to the type of work or services performed, the contract specifies the start and completion dates of the work, the procedure for delivery and acceptance, the cost and payment procedure, and the parties’ responsibility for violating the terms of the contract.
The final price under the contract may include two parts:
- direct remuneration for the work (service) of the contractor (performer) (clause 1, 2 of Article 709 of the Civil Code);
- the cost of compensation for the contractor's (performer's) costs.
The payment procedure under the contract may provide for the payment of an advance. This can be either a fixed amount or a percentage of the total remuneration amount. Do not forget to state that in case of failure to fulfill obligations under the contract, the contractor is obliged to return the advance received to you!
Signing the acceptance certificate for completed work
Having completed the work, the contractor is obliged to hand over the result to the customer, and the customer is obliged to accept it.
The delivery and acceptance of the work result is documented in a delivery and acceptance certificate, which must be signed by the contractor and the customer (or their authorized representatives). Based on this act, the customer makes settlements with the contractor.
When drawing up an act, do not forget to include in it all the mandatory details provided for in Article 9 of Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”.
If the contractor incurs any costs associated with the work, the company or entrepreneur can pay them. The procedure for paying such expenses is determined in the contract. More on this a little later. For now, let's look at what such an act might look like.
The act is drawn up in two copies - one for each of the parties. Based on the signed act, payment for the work is made and expenses are recognized in accounting and tax accounting.
Obligation to withhold personal income tax from payments under a civil contract
An individual who performs work or provides services for an organization receives income. And this income is subject to personal income tax (clause 6, clause 1, article 208 of the Tax Code). The organization is the source of payment of this income, and therefore is a tax agent (clause 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code). Therefore, the organization must withhold personal income tax from payments under a civil contract and pay it to the budget.
When discussing the price of the work performed with the contractor, in order to avoid conflict situations, please note that he will receive his remuneration minus the withheld tax.
You do not have the right to shift the responsibility of paying tax to an individual and thereby be released from fulfilling the duty of a tax agent. This is not provided for by law. Regardless of what you wrote in the contract.
Also, you cannot pay personal income tax at your own expense (clause 9 of Article 226 of the Tax Code), therefore the amount including personal income tax must appear in the contract.
Personal income tax rates:
- for residents of the Russian Federation - 13%;
- for non-residents of the Russian Federation - 30%.
Please see the table below for information on the date of receipt of income, withholding and payment of tax.
| Name of payment (income) | Date of receipt of income | Tax withholding date | Tax payment (transfer) date |
| Payments under a civil law agreement (contract, lease, etc.) to a contractor who is not an individual entrepreneur | Day of payment of income (clause 1, clause 1.1, Article 223 of the Tax Code) | On the day of payment of income (clause 4 of Article 226 of the Tax Code) | No later than the day following the day of payment of income from which tax was withheld (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code) |
Tax is withheld directly from the amount of remuneration upon its actual payment (clause 1 of article 223 and clause 4 of article 226 of the Tax Code).
Do not forget that the performance of the duties of a tax agent by withholding and transferring personal income tax is not limited to:
- at the end of the year, no later than April 1 of the following year, a certificate in form 2-NDFL is submitted to the tax office;
- based on the results of the quarter in which the individual (your contractor or performer) received income, and based on the results of each of the subsequent quarters until the end of the year, you will show income and personal income tax in form 6-NDFL.
If the organization cannot withhold tax (for example, if the remuneration is paid in kind), then it must inform the tax office and the contractor himself (clause 5 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Personal income tax on compensation of expenses
In connection with the execution by an individual of a civil contract, he may incur costs, for example, travel and accommodation costs, the acquisition of inventory items necessary to perform work or provide services. And the contract may provide for compensation of these actual costs by the customer (Articles 709, 783 of the Civil Code).
Compensation is paid when an individual provides primary documents on expenses incurred.
To pay expenses, you can draw up an act in any form, in which you indicate exactly what expenses were incurred, in what amount, and list the attached documents.
The act must also refer to the contract, which states the customer’s obligation to compensate for expenses incurred in connection with the execution of the contract.
The question arises: is it necessary to charge personal income tax on the amounts of such compensation? Unfortunately, there is currently no clear answer to this question.
According to Article 209 of the Tax Code, the object of personal income tax taxation is income received by the taxpayer. According to Article 41 of the Tax Code, income is recognized as economic benefit in monetary or in-kind form, taken into account if it is possible to assess it and to the extent that such benefit can be assessed. Economic benefit is determined in accordance with Chapter 23 of the Tax Code.
But even there we will not find a clear definition of income. Clause 1 of Article 210 says that when determining the tax base, income in cash and in kind is taken into account. All! No specifics, the circle is closed.
As a general rule, even compensation received to reimburse previous expenses is recognized as income. And only in situations specifically stipulated by the legislator are these incomes not subject to personal income tax. Unfortunately, compensation for actual expenses incurred by an individual under a civil contract is not included in these cases.
Two points of view on withholding personal income tax from compensation of costs to the contractor
So, two points of view:
- Opinion of the Ministry of Finance
Source: https://azbuha.ru/ndfl/ndfl-s-vyplat-po-grazhdansko-pravovomu-dogovoru/
Insurance premiums for GPC in 2022
In terms of insurance premiums, a “civil” contract turns out to be more profitable than an employment contract. Moreover, according to two parameters at once.
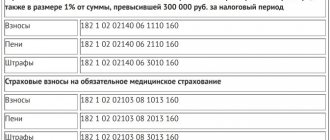
Firstly, payments under the GPC agreement do not need to be charged insurance premiums in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity (subclause 2, clause 3, article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that when using regular tariffs, the savings will be 2.9% (subclause 2, clause 2, article 425 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Secondly, as a general rule, payments under the GPC agreement do not need to be charged insurance premiums against industrial accidents and occupational diseases. Contractors and performers are recognized as insured persons only if this is expressly stated in the contract (Clause 1, Article 5 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ of July 24, 1998). If there is no such clause, then there is no need to transfer contributions “for injuries”. The amount of savings depends on the tariff established for the employer and can reach 8.5% (Article 1 of the Federal Law of December 22, 2005 No. 179-FZ).
Pension and medical contributions in respect of remuneration under civil contracts are accrued in the same manner and in the same amounts as under employment contracts (clause 2 of Article 425 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
ATTENTION. If an advance payment is provided for under a “civil” contract, insurance premiums must be calculated and paid during the period of accrual of the corresponding amount, and not after signing the act. This directly follows from the provisions of paragraph 1 of Article 421 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 1 of Article 424 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraphs 1 and 3 of Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this regard, we would not recommend following the explanations given in paragraph 2 of the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 21, 2017 No. 03-04-06/46733.
Fill out, check and submit insurance premium calculations online
RSV advance payment or final payment
And if the contractor is not an individual entrepreneur, the responsibility for calculating it, withholding it when paying income and paying it to the budget lies with the customer as a tax agent. The question is whether tax should be withheld already when paying the advance under the contract.
And if so, what to do if the work or services are never completed or provided? In general, excessively withheld personal income tax is subject to refund by the tax agent based on a written application from the taxpayer. The procedure for such a return is prescribed in Art.
231 Tax Code.
It assumes that the return of the surplus is made at the expense of personal income tax amounts subject to transfer to the budget on account of upcoming payments both for the taxpayer himself and for other individuals from whose income the tax agent withholds this tax.
The tax agent must return the excessively withheld amount of personal income tax within three months from the date of receipt of the taxpayer’s application.
Is it possible to pay an advance under a GPC agreement?
And to persons working under civil contracts, money should be given not on account, but in pursuance of a contract concluded with them (assignments, agency, etc.), for example, on the basis of their application for reimbursement of expenses for the execution of the assignment. At the same time, they do not have to prepare an advance report. They hired a person under a GPC agreement.
Sent to another city. At the same time, we will compensate for accommodation and train tickets.
Is it possible to do this: a person pays for all hotels with his bank card, then upon completion of the work he makes an advance report according to which all amounts are compensated to him? With regard to insurance premiums, the Ministry of Finance announced that remuneration paid within the framework of the specified GPA is subject to insurance contributions for compulsory pension and health insurance after the final delivery of the results of the work or its individual stages on the basis of the relevant acceptance certificates
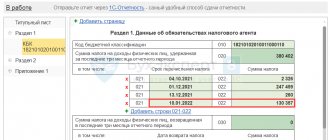
How to reflect GPC in 6-NDFL
The organization also needs to indicate the code of the municipality in which the company’s division is located. Payment for GPC in form 6-NDFL is not indicated in certain sections.
This amount must be indicated in reporting on a general basis. The first section should contain data on income and tax that was calculated and paid on an accrual basis for 1 quarter, half a year, 9 months and a year.
For each tax rate, the first section is completed. Reporting data for the reporting period are indicated in the second section.
If in one tax period personal income tax was paid at different rates, then information for each rate is entered into 6-personal income tax separately. To ensure that the tax office does not impose penalties, you must carefully check the correctness of the information entered.
Based on the specified requirements, the GPC in 6-NDFL is reflected and submitted for each reporting period no later than the last day
Advance under the GPC agreement
Any dependence between the methods of payment for work (services), the timing of their completion (rendering) and the date of inclusion of payments in the calculation base for insurance premiums Law of July 24, 2009
No. 212-FZ does not contain. Thus, neither advances for the upcoming performance of work (rendering services), nor stage-by-stage payments are no different from other payments and remunerations for which the organization is obliged to charge insurance premiums. Include the amounts of advances issued (staged payments) in the calculation base for insurance premiums on the last day of the month in which these amounts were accrued.
3 tbsp. 8 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ)
This date can be considered the earliest of the following dates: - the date of payment of the advance under a civil contract; - the date of signing the certificate of completion of work (services rendered). Such compensation payments are not subject to insurance premiums on the basis of clause "g" part 1 of Art.
9 of Federal Law N 212-FZ. The object of taxation when paying contributions is only remuneration for work (services) performed (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-05-02-04/189 dated July 14, 2006).
The organization must correctly reflect financial settlements for the results of the work done with the contractor who entered into a civil process agreement in account number 76 from the Chart of Accounts “Settlements with other debtors and creditors.”
Thus, for the employer, signing a GPC agreement brings certain advantages, but for the hired employee it often leads to negative consequences. If for employees who are paid on a time basis, the time sheet
Tax officials explained how to reflect payments under a civil contract in the RSV
September 17, 2022 September 17, 2022 The organization entered into a civil law agreement with an individual.
Do payments under this agreement need to be included in Appendix No. 2 to Section 1? No, it’s not necessary, the specialists of the Federal Tax Service of Russia answered in a letter. The authors of the letter remind that Appendix No. 2 to Section 1 of the DAM form reflects the calculation of the amount of contributions for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, based on the amounts of payments made in favor of individuals,
“who are insured persons in the compulsory social insurance system”
.
And individuals working under civil contracts are not subject to compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity (Art.
Federal Law dated December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ).
In addition, the Tax Code directly states that payments under civil contracts are not subject to insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity (subclause 2, clause 3, article 3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, in relation to an individual receiving remuneration under GPC agreements, deadlines 010-070 of Appendix No. 2 to Section 1 of the DAM are not filled out, the tax department explained.
Moreover, in line 180 of subsection 3.1 of section 3 of the DAM (
“sign of an insured person in the compulsory social insurance system”
) should indicate the value “2” - is not an insured person. Please note: when submitting calculations of premiums, those policyholders who use web services to prepare and check reports (for example, the system for sending reports “”) will feel most comfortable. There, the latest test programs are installed automatically, without user intervention.
If the data entered by the policyholder does not correspond to the current control ratios, the system will certainly warn him about this and tell him how to correct the errors. 26 530 Discuss on the forum 26 53026 530 Discuss on the forum 26 53013 11111 0609 37721 67624 8875 58180 592 Accounting news by email Also read us on Yandex.Zen and on social networks.
The Ministry of Finance explained how to calculate personal income tax and insurance premiums when paying an advance to an individual under a civil contract
August 17, 2022 August 17, 2022 Payments to an individual under a civil law agreement (CPL) are subject to both , and .
But the procedure for calculating taxes and contributions in the case of an advance payment under the GPA will be different.
Experts from the Russian Ministry of Finance draw attention to this in a letter.
For the purpose of calculating personal income tax, the date of actual receipt of income in cash is the day of their payment. This is stated in subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Accordingly, advance amounts received by an individual (who does not have individual entrepreneur status) in a tax period under a civil contract are included in the income of that tax period.
In this case, it does not matter in which tax period the final payment will be made after signing the certificate of work performed (services rendered).
According to paragraph 4 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax agents are required to withhold the calculated amount of tax directly from the taxpayer’s income upon actual payment.
Therefore, in a situation where an advance is first transferred to an individual, and the final payment occurs after signing the certificate of completion, personal income tax must be calculated, withheld and transferred to the budget from both the advance and the final payment amount.
And it is necessary to transfer the amounts of calculated and withheld tax no later than the day following the day of payment of income to the taxpayer (Clause 6 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In accordance with the terms of a civil contract, an advance may be paid to the contractor or performer either for the work completely completed (service provided) or for a separate stage of it.
For the purpose of paying insurance premiums, the date of payment and other remuneration is the day of accrual of payments and other remuneration in favor of the employee - an individual (Art.
Tax Code of the Russian Federation). On this basis, the Ministry of Finance draws the following conclusion.
Remuneration paid under a civil law contract is subject to insurance premiums after the final delivery of the results of the work (provision of a service) or its individual stages on the basis of the relevant acceptance certificates for the work performed (services provided) at the time of its accrual in favor of individuals.20 266 Discuss on the forum20 26620 266 Discuss on the forum20 26613 11111 0609 37721 67624 8875 58180 593 Accounting news by email Also read us on Yandex.Zen and on social networks.
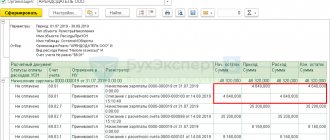
Calculation of remuneration under the GPC agreement
Several contracts may be registered for the same employee within the same organization. Contract agreements drawn up for an employee can be viewed in his card at the link GPC Agreements.
To register the terms of a GPC agreement for the performance of work or provision of services for the purpose of subsequent accrual of remuneration to an employee, the document Agreement (work, services) is intended (section Salary - Agreements (incl.
copyright) or from the employee’s card by clicking the button Execute a document - Agreements (GPC) - Agreement (work, services)) (Figure 2): In the Organization field, indicate the organization on whose behalf the agreement is concluded with the employee. In the Date field, indicate the date of registration of the document in information base.
By default, the date is filled in with the current date of the computer. The Number field is not active for the user. The program will automatically assign a number to the document after it is recorded.
When to calculate insurance premiums under GPC contracts
In the matter of paying insurance premiums under a GPC agreement, it is important that when signing such a contract, any hints of its similarity with a standard employment contract are excluded, since in judicial practice there have been cases when a GPC agreement was recognized as an employment contract, and subsequently the company was forced to pay additional insurance premiums and pay penalty for late payment.
The subject of the contract must include work, services or the transfer of rights to property, but not the performance of official functions.
The expected result of the work should be a completed project, equipment in a state of high-quality assembly, rental of premises, etc.
Insurance premiums for GPA in 2022 - 2022
Read about situations in which the courts regard GPA as a labor law in the material.
As the basis for making payment, indicate an order, act, statement (not a time sheet). An employee cannot be required to follow the company’s labor discipline, internal regulations, or subordination, which are accepted for full-time employees.
420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: Subject of the contract Is remuneration subject to insurance premiums Contract, provision of services Taxed Author's royalties Taxed, less the amount of confirmed expenses Alienation of rights to the results of intellectual activity Taxed is the amount reduced by the amount of confirmed expenses Transfer of ownership or temporary use of property (including including lease agreements, donations)
Advance payment under the GPC agreement, insurance premiums
The customer pays the physicist’s income only after the performer has delivered the results of the work and the customer has accepted them (clause.
1 tbsp. 702 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The parties may also provide for an advance payment under the contract, but the final payment occurs upon completion. The features of a civil law contract also result in its differences from an employment contract in terms of taxation and payment of insurance premiums.
According to the GPC agreement, the company must pay taxes and fees, since the individual receives income. But she doesn’t pay all the dues.
If the employee is not an individual entrepreneur, then the tax must be calculated and paid by the organization that pays remuneration for work performed.
Source: https://konsalt74.ru/rsv-avans-po-gph-ili-okonchatelnyj-raschet-67731/
Features of the GPC agreement and fines
When concluding a “civil” contract, several important nuances must be taken into account.
No labor discipline and personnel records
Persons working under a GPC agreement are not full-time employees and are not required to obey internal labor regulations. This means, in particular, that they do not have to come “to work” every day, or at a certain time. They can also finish performing work or providing a service at any time and go about their business. For such “workers” there are no lunch breaks, vacations or sick leave.
The organization, in turn, should not fill out a time sheet for freelance employees. Also, you should not draw up personnel documentation on them, including orders and work books. All this significantly reduces the non-productive burden on the “employer”.
Compose HR documents using ready-made templates for free
Payment of remuneration and fines
The freelance status of persons with whom GPC agreements have been concluded means that remuneration is paid to them not for their labor function, but for the fact of performing work or providing a service. Therefore, if the work or services are not performed in full, of poor quality or in violation of the deadline, the advance amount paid is subject to return.
The lack of the right of the performer (contractor) to a monthly salary also means that the customer does not have the obligation to transfer remuneration strictly every half month.
The fact that the relationship between a company and an individual is formalized by a GPC agreement makes it possible to have a flexible approach to the issues of establishing and paying appropriate remuneration. All these issues are resolved exclusively on a contractual basis. Therefore, various fines can be included in a civil contract if the work is completed in violation of the deadline or of poor quality.
For example, it is permissible to establish a condition on reducing remuneration for each day of delay in delivering the work. Or determine that the payment is reduced if the work is performed poorly. However, it is impossible to fine an “employee” under a GPC agreement for lateness, absenteeism and other labor violations. After all, as we have already said, the work regime does not apply to freelance employees. At the same time, a fine for untimely start of work or provision of a service, if the start date (time) is directly indicated in the contract, is quite legal (clause 1 of article 708 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, article 783 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1 of article 330 of the Civil Code RF).
Termination of an agreement
When terminating a civil contract, the protective mechanisms provided for by the Labor Code do not apply. And the Civil Code allows the inclusion of any termination rules in a civil contract (subclause 2, clause 2, article 450 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, the possibility of unilateral refusal to fulfill a contract for the provision of services at any time and without explanation is directly stated in Article 782 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, there are usually no problems with “dismissal” under a GPC agreement.
IMPORTANT. These rules apply in both directions. This, in particular, means that the “employee” can refuse further cooperation at any time without notifying the customer two weeks in advance. True, in this case, it will be possible to deduct losses incurred due to the early termination of the contract from the amount of remuneration (clause 2 of Article 782 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In conclusion, we note that any contract or service agreement that an organization has concluded with a non-entrepreneur individual may come under the close attention of regulatory authorities. If inspectors find signs of an employment contract, this will result in a fine and arrears for insurance premiums for the “employer”. To prevent this from happening, you need to correctly draw up the GPC agreement in 2022 and not include unacceptable conditions in it.
Sample GPC agreement with advance payment
- Refund of unearned advance payment. If an advance payment was made under a contract, but the contractor did not fulfill it, then the customer may request a refund of the amount he paid. In addition, penalties for late completion of work may also be added here.
- Reducing the amount of advance payments.
Insurance premiums Insurance premiums are paid on GPC agreements. But only pension contributions and compulsory health insurance contributions are paid. As for 4-FSS reporting, in civil law relations the customer does not pay contributions for occupational diseases and industrial accidents, unless this is expressly provided for in the contract. Insurance premiums are calculated using the same rates as under employment contracts: 22% In the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation 5.1% In the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund If the customer has the right to benefits expressed in reduced rates, then he has the right to use them in relation to payments for civil contracts. Moreover, if the work is performed (services are provided) on the basis of full or partial prepayment, according to representatives of the Ministry of Finance, then the tax is subject to withholding upon transfer of such (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 28, 2014 N 03-04-06/43135, dated 26 May 2014 N 03-04-06/24982, dated January 13, 2014 N 03-04-06/360). This position in itself is by no means indisputable.