Special sections of the declaration
For exporters, the VAT declaration provides:
- section 4 – to reflect the tax in the case where the zero rate is confirmed;
- section 5 – to reflect tax deductions;
- Section 6 – to reflect tax when the zero rate is not confirmed.
In the same sections, report on exports to member states of the Customs Union. For the purposes of calculating VAT for Russian organizations, the following is equivalent to the export of goods:
- manufacturing of goods intended for export to countries participating in the Customs Union (clause 9 of Appendix 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union);
- transfer of goods under a leasing agreement, which provides for the transfer of ownership to the lessee, as well as under trade credit or trade loan agreements (clause 11 of Appendix 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union).
Construction and installation work Subtleties of design when exporting
May 21, 2021
Now let's talk about the second very important and mandatory shipping document for export deliveries - construction and installation work.
Construction and installation work (CMR) is a document reflecting basic information regarding the movement of goods across the border. In simple terms, construction and installation work is a consignment note only for international deliveries. By the way, very often it is precisely because of filling out construction and installation work that many foreign counterparties turn to our company with a request to accompany the transaction. It’s not a rare case: a supplier who has never worked for export before claims that he can make a UTD (universal transfer document), setting a 0% rate there as required by the counterparty and then reimburse it from the budget (or set a “pseudo-zero” and not reimburse anything , after all, he has already received his profit), but this is how the question of formalizing construction and installation work arises - here a “dead end” awaits him. After all, this document contains many more columns than the usual consignment note and has its own nuances of filling out. And if the registration is incorrect, the tax authorities will, of course, issue a fine for a decent amount.
So, what should you pay attention to when filling out construction and installation work? In this article, in addition to characterizing the graphs and describing the filling, we will indicate which graphs are required and which are not. In practice, we know for sure that not everything in construction and installation works has to be recorded, but this saves a lot of time for the foreign trade participant.
Let's start with the column without a number - the upper right side of the document. Here the exporter manually enters the Construction and Installation No. Every company chooses a different numbering. Very often, when exporting deliveries, the selected transport company asks for a specific number corresponding to their internal documentation. The exporter has the right to refuse and appropriate his own, or use their procedure. In our company, to simplify the accounting system, we assign a construction and installation work number the same as the number of the universal transfer document in the shipment. Visually, it is much easier to perceive the document flow; it looks, for example, like this: UPD No. 060502 dated May 6, 2022, construction and installation work No. 060502 dated May 6, 2022.
This way, supplies do not get confused with each other and it is always easy to find the corresponding UPD for the corresponding construction and installation work. Many people simply number in order, but there is a nuance here: the manager can prepare the documents “in advance,” but the delivery will never take place and “gaps” will appear in the overall numbering.
After the construction and installation work number, fill in the “Sender” and “Recipient” columns. Everything is simple here: the name (the organizational and legal form can be indicated abbreviated so as not to take up space in the column) of the company of the seller and the buyer, the full address (don’t forget the zip code and country) and Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN). These columns correspond to the names in the UPD. The columns below are “Place of unloading” and “Place and date of loading of cargo.” We put down the city, and be sure to put the country again in both columns. In column No. 4 we also indicate the date. This is the day when the cargo is accepted by the transport company or driver for transportation. We cannot put a date in column No. 3, because... We don’t know how long the cargo will be on the way. The arrival date is entered in column No. 24 directly by the buyer upon receipt.
Column No. 5 – “Attached documents.” Here we register the export documentation, but it is not necessary to indicate the complete set of documents. Required are the UPD No. and date, as well as the contract No. and its date. If desired, you can indicate: specification, invoice, packing list, cargo customs declaration number. But this takes time and increases the size of the document (it may not fit on one page).
Columns No. 6-9. It is mandatory to fill in completely if exporting outside the EAEU. That is, signs and numbers are affixed, the number of pieces, type of packaging and name of the cargo, for example:
1. 2 places football goal boxes
The information must match the data on the packing list!
If the export is to the EAEU countries, then there are no such strict requirements; in practice, we found out that only the name of the cargo is enough. And even the name can be abbreviated. If in the UPD the cargo is named with all brands, GOSTs, sizes, etc., then in the construction and installation work you can put a short name, for example:
In the UPD: “net for football goals 7.5x2.5x1x2 m 100x100 mm knotless 2.8 mm, white/green”
In construction and installation work: “net for a football goal.”
The required column for any deliveries is HS code. Here we put a ten-digit code that matches the code in the UTD and the cargo customs declaration.
Columns No. 11 and 12 – weight and volume are filled in for deliveries outside the EAEU. We put down the values of our cargo in numerical format. When exporting to the EAEU, it is permissible to leave these fields blank, but sometimes transport companies accepting cargo for transportation insist on filling them out.
In column No. 13 we fill in only the full cost of the cargo, always indicating the currency, for example:
“1,090,000.00 Russian rubles” or “490.12 euros”
We leave column No. 14 empty.
Column No. 15 “Terms of payment”. As a rule, the designation “free” is marked with “Incoterms – 2010” automatically. But some companies have already switched to the new Incoterms and are affixing them. Accordingly, we put down “Incoterms – 2020”.
Column No. 16. Here, either the exporter manually writes down the name of the transport company, or the company itself affixes its own stamp. The column is not filled in if the cargo is accepted for transportation not by a transport company, but by a private driver. He will sign in the appropriate box, more on that below.
Columns No. 17,18,19, 20 are usually empty. But there are special cases of filling.
Column No. 21 is filled in. Here we put the name of the city. Intermediary exporters (such as the UVTC company) can register here both the city of shipment and the city that is the legal location of their office. After all, the column is called “compiled in”. Accordingly, you can draw up construction and installation work both in the city of shipment and while in the office, sending documents electronically from any city. This will not be considered an error. Cell “Date” - enter the construction and installation date (coincides with the UPD date).
Columns No. 22-24 are filled in with the corresponding signatures and seals of authorized persons. The exporter's representative, the driver and the buyer's representative put down their designations. The exporter at the time of shipment, the driver when accepting the cargo and its transportation, and the buyer when receiving the goods. By the way, time is not required to be filled.
Columns No. 25 and 26 – state numbers of the car and trailer (if any), as well as their names, for example:
“U500KR777 Hyundai Porter” – car only
“50A940OA 507190AA / DAF KRONE” – vehicle with trailer.
Columns No. 27, 28 and 29 are often empty.
This is how an international transport document is filled out. Of course, these are general recommendations. Filling always depends on many factors and, first of all, on the nature of the cargo. The main thing to remember is that the data entered into the package of documents must match. The information in the packing list reflects data from construction and installation work, construction and installation work from the UPD, UPD from the invoice, invoice from the invoice, invoice from the contract, etc. Check the documentation carefully and you won’t be afraid of tax audits, but it’s better to contact the company
UVTK and we will take care of your cargo!
Author - Foreign Trade Manager, Anastasia Rozvazhaeva
Section 4
In section 4, reflect export transactions for which the right to apply the zero rate has been confirmed. Indicate in it:
- on line 010 – transaction code;
- on line 020 – for each transaction code, the tax base for confirmed export transactions;
- on line 030 – for each transaction code, the amount of deductions of input VAT on goods (work, services) used to conduct confirmed export transactions;
- on line 040 - for each transaction code, the amount of VAT previously calculated for these transactions when the export had not yet been confirmed;
- on line 050 – for each transaction code, the recoverable amount of input VAT previously accepted for deduction when the export had not yet been confirmed.
Lines 040 and 050 of Section 4 must be completed if the organization was previously unable to confirm the export on time.
Fill in lines 070 and 080 when returning goods for which the right to apply a zero rate has not been confirmed. On line 070, reflect the amount of adjustment to the tax base, and on line 080, the amount of adjustment of tax deductions. These lines must be completed in the tax period in which the exporting organization recognized the return of goods (the parties agreed on the return).
If the price of exported goods for which a zero rate was confirmed has changed, indicate the adjustment amounts on lines 100 (if increasing) and 110 (if decreasing). Reflect the adjustment in the tax period in which the exporting organization recognized the price change.
On line 120, reflect the amount of tax to be reimbursed:
| Line 120 = (Lines 030 + Lines 040) – (Lines 050 + Lines 080) |
On line 130, reflect the amount of tax payable:
| Line 130 = (Lines 050 + Lines 080) – (Lines 030 + Lines 040) |
This is stated in section IX of the Procedure, approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/558.
Situation: how to reflect in section 4 of the VAT return the amount of VAT on the cost of services of a customs broker who carries out customs clearance for the export of goods? The broker works under a fee-based service agreement. Different VAT rates are established for exported goods
The amount of tax deduction for brokerage services must be distributed.
Customs brokerage services may be subject to VAT either at a zero rate or at a rate of 18 percent. The zero rate can only be applied if the broker provides services under a transport forwarding agreement when organizing international transportation. This was stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 14, 2015 No. 03-07-08/46977. In the situation under consideration, there is no such agreement, so the tax rate of 18 percent applies. Since the input tax presented by the broker simultaneously applies to goods subject to VAT at different rates, when filling out section 4, its amount must be distributed.
The fact is that section 4 reflects:
- with code 1011410 – operations for the export of goods for which the VAT rate is set at 18 percent;
- with code 1011412 – operations for the export of goods for which the VAT rate is set at 10 percent.
Transaction codes are indicated on line 010 of section 4 of the VAT return. Line 020 of this section reflects the tax base for confirmed export operations, and line 030 - the amount of tax deductions for goods (work, services) used to carry out these operations.
Such instructions are contained in paragraphs 41.1–41.3 of the Procedure approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/558.
Nothing is said about the reflection of tax deductions for goods (work, services) that simultaneously relate to transactions with codes 1011410 and 1011412 in the Procedure approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/558. However, in order to correctly fill out the declaration, the amount of such tax deductions should be distributed proportionally to the tax bases for transactions with codes 1011410 and 1011412. To do this, use the following formulas:
| The amount of tax deduction for goods (work, services) used in the sale of goods for export, not specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | = | The amount of tax deduction for goods (work, services) used in the sale of goods for export, specified and not specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation __________________________________________ | × | The cost of goods sold for export not specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| The total cost of goods sold for export, specified and not specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| The amount of tax deduction for goods (work, services) used in the sale of goods for export, specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | = | The amount of tax deduction for goods (work, services) used in the sale of goods for export, specified and not specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | – | The amount of tax deduction for goods (work, services) used in the sale of goods for export, not specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
The amounts of tax deductions received after distribution should be reflected on line 030 of section 4 of the VAT return according to the corresponding transaction code.
An example of reflecting in section 4 of a VAT return the amount of VAT on the cost of brokerage services related to the export of goods specified and not specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Alpha LLC entered into a contract for the supply to Finland of:
- children's clothing made of natural sheepskin and rabbit (the VAT rate is set at 10% (paragraph 3, subparagraph 2, paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation));
- products made of genuine leather and natural fur (VAT rate is set at 18%).
The total cost of the export contract is 16,000,000 rubles. At the same time, the cost of children's clothing is 3,200,000 rubles, the cost of products made from genuine leather and natural fur is 12,800,000 rubles.
For customs clearance of goods, Alpha used the services of a customs broker. The cost of brokerage services amounted to 118,000 rubles, including VAT - 18,000 rubles.
Within the prescribed period, the organization collected all the necessary documents confirming the right to apply the zero tax rate. The amount of VAT on the cost of brokerage was distributed in proportion to the cost of children's clothing and products made from genuine leather and natural fur.
In section 4 of the VAT return, Alpha’s accountant indicated:
1) on the line with code 1011410 (sales of goods not specified in clause 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- on line 020 (tax base) – 12,800,000 rubles;
- on line 030 (tax deductions) – 14,400 rubles. (RUB 18,000: RUB 16,000,000 × RUB 12,800,000);
2) on the line with code 1011412 (sales of goods specified in clause 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- on line 020 (tax base) – RUB 3,200,000;
- on line 030 (tax deductions) – 3600 rubles. (RUB 18,000 – RUB 14,400).
If the deduction is claimed after confirmation of the right to a zero rate
Input VAT on purchased goods (works, services, property rights) that are purchased for the export of non-commodity goods is deductible in the general manner, subject to compliance with the requirements specified in clause 2 of Art. 171, paragraph 1, art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 13, 2016 No. 03-07-08/41050). According to clause 1.1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, this tax deduction provided for in paragraph 2 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, can be declared in the following tax periods within 3 years from the date of acquisition of goods (work, services, property rights).
Thus, if the input invoice for goods (works, services, property rights) purchased for export operations was received after the zero rate for the export of non-commodity goods was confirmed, then submit an updated declaration for the period when the tax base was formed for such export shipment, it is not necessary. The deduction will be reflected in line 140 of section 3 of the VAT return.
If an invoice for goods (works, services, property rights) used to export raw materials was received after confirmation of the fact of export, then the question often arises: in what period should the deduction be declared?
There are two points of view on this issue.
According to one of them, the deduction must be declared in the period when the application of the 0% VAT rate is confirmed. This position is substantiated in detail in the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated November 8, 2006 No. 6631/06. The same conclusions are contained in the resolution of the FAS Moscow District dated November 7, 2008 No. KA-A40/9059-08-P, the FAS North Caucasus District dated December 19, 2008 No. F08-7571/2008 in case A22-487/2008/12-29 and etc. The arbitrators emphasized that for transactions with a zero VAT rate, deductions should be made in the declarations of the tax period when the right to deduction arose.
How to confirm a zero rate, read the article “What is the procedure for refunding VAT at a rate of 0% (receiving confirmation).”
Another point of view is that the deduction can be claimed not in the period of confirmation of the 0% rate, but in the period when documentary evidence of deductions was received. In the decisions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated 02.02.2009 No. F04-509/2009(20394-A70-25) in case No. A70-665/13-2008, dated 22.12.2008 No. F04-7498/2008(16935-A70- 14), F04-7498/2008(20016-A70-14) in case No. A70-37/13-2008, FAS North-Western District dated 08.08.2008 in case No. A52-154/2008, the judges came to the conclusion that the deduction input VAT must be declared in the tax period when the conditions defined by clause 1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. That is, there is no need to submit an updated declaration for the period when the zero rate was justified. It should be noted that this point of view is also confirmed by the procedure for filling out the VAT return. From the analysis of clause 42.6 of the Procedure for filling out the declaration, approved. by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/, we can conclude that the deduction of input VAT in the event of receipt of a late invoice for purchased goods (works, services, property rights) relating to previously confirmed exports of raw materials (works, services), is reflected in line 050 of section 5 of the VAT return for the quarter in which the right to deduction arose (that is, in the period of receipt of the invoice).
Confirmation of this position can also be found in the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 30, 2009 No. 692/09. The higher court ruled that the taxpayer was entitled to claim the export deduction on a later tax return.
In circumstances in which documents confirming the right to apply a zero rate on the export of raw materials are not submitted to the Federal Tax Service within 180 calendar days, the taxpayer must declare a deduction for purchased goods (work, services, property rights) in the generally established manner on the date of shipment (para. 2 clause 9 article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The deduction of input VAT on unconfirmed exports is reflected in line 040 of section 6 of the VAT return drawn up for the period in which the goods were shipped.
See also “What to do if the export is not confirmed within the specified time frame.”
In case of receipt of a late invoice for purchased goods (works, services, property rights) relating to a previously unconfirmed export of raw materials, the VAT deduction is reflected in line 070 of section 5 of the VAT return for the quarter in which the right to deduct arose ( that is, in the period of receipt of the invoice). This conclusion can be drawn from the analysis of clause 42.9 of the Procedure for filling out the declaration.
ConsultantPlus experts spoke about the nuances of filling out a VAT return if the zero export rate could not be confirmed on time. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Section 5
Section 5 should be completed in the declaration for the period when the right to deduct VAT on export transactions (previously confirmed and not confirmed) arose. For example, if you previously collected documents and confirmed the zero rate, but did not fulfill the conditions for applying the deduction.
On line 010, indicate the year in which the declaration was submitted, which reflected transactions for the sale of goods. On line 020 - tax period code in accordance with Appendix No. 3 to the Procedure, approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/558.
Fill out Section 5 separately for each tax period, information about which is reflected in the indicators on lines 010 and 020.
Please indicate:
- on line 030 – transaction code;
- on line 040 - the tax base relating to already confirmed export transactions (i.e. for which Section 4 was submitted to the tax office, but which could not be accepted for deduction at that moment);
- on line 050 – the amount of input VAT related to confirmed exports;
- on line 060 - the tax base related to unconfirmed exports (i.e. for which Section 6 had already been submitted to the tax office, but which could not be accepted for deduction at that moment, for example, in the absence of an invoice);
- on line 070 – the amount of input VAT related to unconfirmed exports.
Such instructions are contained in section X of the Procedure, approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/558.
On deducting VAT on non-commodity goods
The period when you can deduct “input” VAT on expenses associated with the export of non-commodity goods depends on when the goods were accepted for accounting. The Russian Ministry of Finance explains this in letter dated May 28, 2020 No. 03-07-08/44851.
When were the goods received: July 1, 2016 and later?
From July 1, 2016, the procedure for deducting “input” VAT from the cost of purchased goods (work, services, property rights) that are used in the sale of non-raw materials for export was changed (subsection 1, clause 1, article 164, clause 3, art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From this date, you can apply for VAT deduction on goods, works and services purchased for export operations in the generally established manner before you have collected a package of documents confirming the zero VAT rate. That is, at the moment of acceptance of these goods for accounting and receipt of invoices from suppliers.
There is no need to wait until the organization ships goods for export and collects documents confirming the zero VAT rate to deduct VAT. The amendments were adopted by Federal Law No. 150-FZ of May 30, 2016.
The exception to this rule is the export of primary goods.
Goods were received before July 1, 2016
In this case, the old rules apply.
Export sales are subject to VAT at a rate of 0 percent, so previously, deduction of “input” VAT on goods purchased for sale for export was required at the time of determining the tax base - on the last day of the quarter in which the full package of supporting documents was collected (clause 9 of Art. 167, paragraph 3 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, input VAT on goods registered before 07/01/2016 must be deducted in the quarter in which the organization determines the tax base for export supplies.
Commodities
For these goods, the procedure for deducting input VAT remains the same. The list of raw materials is in paragraph 10 of Article 165 of the Tax Code:
- mineral products;
- products of the chemical industry and related other industries;
- wood and wood products;
- charcoal;
- pearl;
- precious and semi-precious stones, precious metals;
- base metals and products made from them.
Specific codes of goods that are classified as raw materials are approved by Government Decree No. 466 dated April 18, 2018.
Clause 3 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for a special procedure for deducting VAT in relation to raw materials subject to VAT at a tax rate of 0%. VAT deduction on purchased goods, works, services, property rights related to such sales is made at the time of determining the tax base established in Art. 167 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What documents need to be collected to confirm export
To refund VAT, you need to submit a package of documents to the tax office (Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Here is a list of them.
1. Foreign economic contract (copy of the contract) with a foreign partner for the supply of goods outside Russia.
If the contract contains information that constitutes a state secret, then you can submit an extract from it. It must contain information about the conditions, delivery times, and price of goods.
Please note: contracts (agreements) can be presented in the form of a single document drawn up in writing, signed by the parties, or documents indicating that agreement has been reached on all essential terms of the transaction and containing the necessary information about the subject, participants and conditions of the transaction, including price and timing of its execution (clause 19 of article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
2. Customs declaration (CD) or a copy thereof.
The DT must have:
- mark of the customs office that carried out the customs operations;
- mark of the border customs office through which the goods were exported from Russia.
If the export of goods was carried out through the territories of the member states of the Customs Union, where customs control has been abolished (Belarus, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan or Kazakhstan), it is sufficient for the DT to indicate the customs office that carried out customs operations with the goods.
3. Copies of transport and shipping documents.
Transport and shipping documents must bear the mark “Goods Exported” from the border customs office. If the goods were exported through the territories of the member states of the Customs Union, where customs control has been abolished (Belarus, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan or Kazakhstan), then on the transport documents it is sufficient to indicate the Russian customs office that carried out customs operations with the goods.
Please note: if the goods were placed under the free customs zone procedure, the list of documents provided will be slightly different:
1. Contract (its copy) with a resident of the special economic zone.
2. A copy of the person’s registration certificate as a resident of the special economic zone.
3. Customs declaration (its copy) with notes from the customs authority on the release of goods in accordance with the free customs zone procedure.
Register of customs declarations
In accordance with paragraph 15 of Article 165 of the Tax Code, you can submit:
- register of customs declarations (full customs declarations) indicating in it the registration numbers of the relevant declarations instead of their copies;
- register of customs declarations (full customs declarations), as well as transport, shipping or other documents instead of their copies.
These registers are presented exclusively in electronic form via telecommunication channels through an electronic document management operator. Let us note that the Federal Tax Service of Russia developed in its letter dated May 15, 2020 No. EA-4-15/ [email protected] recommended forms and formats of registers, procedures for filling them out and submitting them to the tax authorities in electronic form, as well as XSD schemes. Previously, they were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 30, 2015 No. ММВ-7-15/427.
Section 6
Section 6 is intended to reflect transactions for which the deadline for submitting documents confirming the right to apply the zero VAT rate has expired.
The duration of this period is 180 calendar days. For exported goods, the 180-day period is counted:
- from the date of shipment (for deliveries to countries participating in the Customs Union) (clause 5 of Appendix 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union);
- from the date of placing goods under the customs export procedure (for deliveries to other countries) (clause 9 of article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In relation to work (services) related to the export of goods (import of goods into Russia), the procedure for determining the 180-day period depends on the type of work (service).
On line 010, enter the operation code. For each transaction code, fill in lines 020–040.
On line 020 reflect the tax base.
On line 030, indicate the amount of VAT calculated based on the tax base on line 020 and the VAT rate (10 or 18%).
Line 040 reflects the amounts of tax deductions:
- input VAT paid to the seller;
- VAT paid when importing goods into Russia;
- VAT paid by the tax agent when purchasing goods, works, services.
Fill in lines 050–060 only on the first page, and put dashes on the rest.
On line 050, reflect the total amount of VAT (the sum of all lines 030 for each transaction code).
For line 060, enter the summed indicator of lines 040 for each transaction code.
If the buyer returned some of the goods to the exporter, fill in lines 080–100:
- on line 080 – the amount by which the tax base is reduced;
- on line 090 – VAT adjustment (the amount by which the calculated VAT is reduced);
- on line 100 – the amount of VAT that needs to be restored (previously accepted for deduction).
If you increase or decrease the price, fill in lines 110–150:
- on line 120 - the amount by which the tax base is increased;
- on line 130 – the amount by which VAT is increased;
- on line 140 – the amount by which the tax base is reduced;
- on line 150 – the amount by which VAT is reduced.
Calculate the amount of VAT payable to the budget for line 160 as follows:
| Line 160 = (line 050 + line 100 + line 130) – (line 060 + line 090 + line 150) |
Calculate the VAT refund amount for line 170 as follows:
| Line 170 = (line 060 + line 090 + line 150) – (line 050 + line 100 + line 130) |
Please take into account the amounts of VAT payable (reduced) reflected in sections 4–6 when filling out section 1 of the VAT return (clauses 34.3, 34.4 of the Procedure approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/558) .
Registration of SF supplier
To register a supplier invoice (SF), you must indicate its number and date at the bottom of the Receipt document form (act, invoice) and click the Register .
The Invoice document received is automatically filled with data from the Receipt document (act, invoice) . Operation type code – “01” Receipt of goods, works, services.
If the document has the Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt checkbox , then when it is posted, entries will be made to accept VAT for deduction.
VAT is deductible in the general manner, i.e. if the conditions are met (clause 2 of article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the goods must be used in activities subject to VAT;
- a correctly executed SF (UPD) is available;
- goods are accepted for accounting (clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Separate VAT accounting is not maintained. The right to accept VAT as a deduction will arise for purchased goods, works, services, regardless of confirmation or non-confirmation of the 0% rate for the export of non-commodity goods (Clause 10 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Postings according to the document
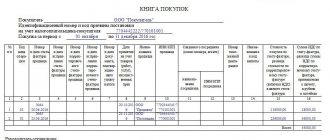
Purchase Book report can be generated from the Reports – VAT – Purchase Book section. PDF
How to reflect exports in VAT returns in 1C 8.3
The VAT return reflects the amount of VAT deducted:
In Section 3 page 120 “Amount of VAT to be deducted”: PDF
- the amount of VAT accepted for deduction.
In Section 8 “Information from the purchase book”:
- invoice data, transaction type code "".
Sections 8 and 9
In section 8, enter information from the purchase book for those transactions for which the right to deduction arose in the reporting quarter.
In section 9 of the declaration, indicate information from the sales book. For more information on the procedure for filling out sections 8 and 9, see How to draw up and submit a VAT return.
If changes have been made to the purchase book or sales book, you will need to fill out Appendix 1 to sections 8 and 9.
An example of filling out a VAT return for export transactions
Alpha LLC is registered in Moscow and is engaged in the production of furniture (OKVED code 36.1). The organization did not carry out any transactions on the domestic market that should be reflected in the VAT return for the first quarter of 2016.
Alpha has a long-term contract for the supply of furniture of its own production to Finland.
In January 2016, under this contract, Alpha supplied:
- children's beds (VAT rate - 10%) (paragraph 5, subparagraph 2, paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - in the amount of 7,800,000 rubles;
- wooden cabinets (VAT rate - 18%) - in the amount of 10,000,000 rubles.
The total cost of the export contract was 17,800,000 rubles.
For customs clearance of goods, Alpha used the services of a customs broker. The cost of brokerage services amounted to 141,600 rubles, including VAT - 21,600 rubles.
In February 2016, the organization collected all the necessary documents confirming the right to apply a zero tax rate, and accepted for deduction the amount of input VAT presented to it when purchasing materials for the manufacture of export products:
- from the cost of materials for children's beds - 57,800 rubles;
- from the cost of materials for wooden cabinets - 89,350 rubles.
The amount of VAT on the cost of brokerage was distributed in proportion to the cost of children's beds and wooden cabinets. The amount of VAT accepted for deduction for each product item is:
- for cabinets - 12,135 rubles. (RUB 21,600 × RUB 10,000,000: (RUB 7,800,000 + RUB 10,000,000));
- for beds – 9465 rub. (RUB 21,600 × RUB 7,800,000: (RUB 7,800,000 + RUB 10,000,000)).
In February 2016, Alpha received an invoice for transportation costs (cost - 118,000 rubles, including VAT - 18,000 rubles) for an export transaction completed in November 2015. Then the organization sold products worth RUB 2,360,000. (including VAT – 360,000 rubles). A package of documents confirming the application of a 0 percent rate for this operation was collected in December 2015; the amount of deduction for raw materials and supplies spent on the production of export products is reflected in the VAT return for the fourth quarter of 2015.
In addition, in February 2016, Alpha expired the period (180 calendar days) allotted for collecting documents confirming the application of the zero VAT rate for the export transaction completed in the third quarter of 2015. The organization’s accountant charged VAT at a rate of 18 percent on unconfirmed export proceeds. At the same time, he prepared an updated VAT return for the third quarter of 2015. In addition to the information previously reflected in the declaration, the accountant filled out section 6. In it, for the transaction with code 1010401, he showed the tax base (912,300 rubles), the accrued amount of VAT (164,214 rubles) and the amount of tax deduction (90,000 rubles).
The Alpha accountant began filling out the VAT return for the first quarter of 2016 with the title page. On it he indicated general information about the organization, as well as the tax office code and the code for the location of the organization - 214.
Then the accountant filled out section 4, in which he indicated:
1) according to code 1010410 (sale of goods not specified in clause 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- on line 020 (tax base) – 10,000,000 rubles;
- on line 030 (tax deductions) – 101,485 rubles. (RUB 89,350 + RUB 12,135);
2) according to code 1010412 (sales of goods specified in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- on line 020 (tax base) – RUB 7,800,000;
- on line 030 (tax deductions) – 67,265 rubles. (RUB 57,800 + (RUB 21,600 – RUB 12,135));
3) on line with code 120:
- RUB 168,750 – the amount of tax calculated for reduction under this section.
After this, the accountant filled out section 5. In it, he indicated the amount of VAT accepted for deduction on transport services in the amount of 18,000 rubles.
The accountant finished drawing up the declaration by filling out section 1. In it, he indicated the total amount of tax to be reimbursed under the declaration - 186,750 rubles. (RUB 168,750 + RUB 18,000).
The VAT return for the first quarter of 2016, signed by the General Director of Alpha Lvov, was submitted by the organization to the tax office on April 22, 2015.
Situation: when do you need to submit a VAT return for export transactions?
Submit sections of the declaration provided for export operations as part of the general tax return.
Starting from January 1, 2015, submit VAT returns to the inspectorate no later than the 25th day of the month following the expired tax period (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The expired tax period should be understood as the quarter in which the organization collected documents confirming the right to apply the zero tax rate. Submit supporting documents at the same time as your declaration.
To collect documents confirming the right to apply the zero VAT rate, the organization is given 180 calendar days:
- from the moment of release of goods in the export procedure to countries that are not members of the Customs Union;
- from the moment of shipment of goods to a country that is a member of the Customs Union.
This period is established by paragraph 9 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 5 of Appendix 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union.
The end of the 180-day period allotted for collecting documents is not associated with the established deadline for filing the declaration, but with the tax period in which this period expires. If the complete package of supporting documents is collected by the organization within a period not exceeding 180 calendar days, reflect export transactions in section 4 of the VAT return for the tax period in which the day the documents were collected falls. Regardless of the fact that this day is not the end of the tax period.
For example, the 180-day period allotted for collecting documents expires on November 20, 2015. In fact, the documents necessary to confirm the right to a zero VAT rate were collected on October 15, 2015. In this case, the right to apply a zero tax rate must be declared in the VAT return for the fourth quarter of 2015, which must be submitted no later than January 25, 2016. If the documents had been collected at least a day later (November 21, 2015), then the organization would not have had any grounds to reflect the export operation in the declaration for the fourth quarter.
This conclusion is confirmed by letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 17, 2012 No. 03-07-08/108, dated October 6, 2010 No. 03-07-15/131 and dated June 3, 2008 No. 03-07-08/137 .
The deadline for collecting documents has been missed: fill out section 6
If you have not collected the necessary documents on time, you will have to calculate VAT on export proceeds at a rate of 10% or 18% depending on the type of goods (Clause 9 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The calculated tax must be reflected in section. 6 declaration for the quarter when the goods were shipped, that is, it will be necessary to submit an update (Article 81, clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 3 of the Procedure for filling out the declaration). Although there is an opinion that the declaration must be submitted for the quarter when 180 days have expired. And there are even court decisions supporting this position (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region dated December 22, 2010 N KA-A40/15981-10). We decided to clarify this issue with specialists from the Russian Ministry of Finance. And this is what they answered us.
From authoritative sources Lozovaya A.N., Ministry of Finance of Russia “Since in the initial declaration there is a “non-reflection or incompleteness of the reflection of information”, which led to an “understatement of the amount of tax payable”, on the basis of clause 1 of Art. 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for the tax period in which the date of shipment of exported goods falls, an updated tax return must be submitted.”
Most likely, after submitting an updated declaration, the tax authorities will charge you penalties starting from the 21st day of the month following the quarter in which goods were shipped for export, until the day the tax is paid or a declaration is submitted with data on the export transaction with supporting documents (Letter from the Ministry of Finance Russia dated July 28, 2006 N 03-04-15/140). But the obligation to pay VAT arises only on the 181st day; accordingly, penalties in case of non-payment should be accrued from the same date. And the courts confirm this (Resolutions of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 16, 2006 N 15326/05; FAS VVO dated October 7, 2010 in case N A43-40137/2009). Therefore, it is better to pay VAT on unconfirmed exports directly on the 181st day, then penalties can be avoided altogether.
Example 2. Procedure for calculating VAT on exports if the deadline for collecting documents is missed
Condition
Let's take the data from example 1, changing them as follows: documents were not collected within 180 days (that is, until March 28, 2011 inclusive). Similar goods sold in the Russian Federation are taxed at a rate of 18%.
Solution
The procedure will be as follows. Steps 1 - 3. Will be the same as in example 1. Step 4. 03/29/2011 (on the 181st day) we recalculate the proceeds into rubles at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of shipment (Subclause 1, clause 1, clause 9, art. 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Export revenue is 618,330 rubles. (15,000 euros x 41.2220 rubles/euro). We make changes to the previously issued invoice: we change the rate from 0% to 18% (Clause 2, 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of calculated VAT is RUB 111,299.40. (RUB 618,330 x 18%). Step 5. We register the invoice in the sales book for the third quarter of 2010 (the quarter in which the goods were shipped for export) (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 5, 2007 N 03-07-08/180). To do this, we draw up an additional sheet for the sales book (Clause 16 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase book and a sales book). Step 6. 03/29/2011 an invoice in the amount of 413,000 rubles, including VAT - 63,000 rubles, received from organization B, is registered in the purchase book for the third quarter of 2010 (the quarter in which the goods were shipped) (Clause 8 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book and sales book). To do this, we draw up an additional sheet for the purchase book (Clause 7 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book and sales book). Step 7. Fill out section. 6 of the updated VAT return for the third quarter of 2010.
Step 8. We transfer to the budget the amount of VAT calculated for this operation, 48,299 rubles. (RUB 111,299 - RUB 63,000). Step 9. Submit the updated declaration to the Federal Tax Service. In this case, you are only supplementing the previously submitted declaration, Section. 6, and all other sections except Sect. 1 (it is adjusted taking into account Section 6), are transferred to the clarification without changes. There is no deadline for submitting updated returns, so you can submit it on the day of VAT payment or later, the main thing is to pay the tax on time. In accounting, the entries on the date of purchase of goods (09.24.2010), on the date of sale of goods for export (09.28.2010) and on the date of receipt of payment from a foreigner (01.10.2010) will be the same as in example 1.
| Contents of operation | Dt | CT | Sum |
| On the 181st day from the date of shipment (03/29/2011) | |||
| VAT has been charged on unconfirmed exports (15,000 euros x 41.2220 rubles/euro x 18%) | 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount “Other expenses” | 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount “VAT” | 111 299,40 |
| Accepted for deduction of input VAT | 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount “VAT” | 19 “VAT on acquired assets”, subaccount “VAT on unconfirmed exports” | 63 000,00 |
VAT declaration for export: features of 2021
For 3 sq. 2022 VAT transactions are declared in an updated report form (by Order of the Federal Tax Service No. ED-7-3 / [email protected] dated March 26, 2021, changes were made related to the implementation of a goods tracking system).
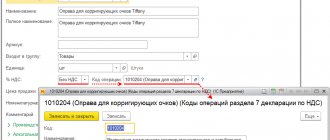
Exporters fill out the declaration according to the general rules, including the title page and sections 1, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9. The amounts in the report are indicated without kopecks, rounded according to mathematical rules to the full ruble. To identify transactions, use the codes listed in Appendix 1 to the Procedure for filling out the declaration, approved. Order No. ММВ-7-3/558 dated October 29, 2014.
In section 4 of the VAT declaration for export, the codes of transactions (page 010) carried out at a rate of 0% are indicated, and for each of them - the size of the base (page 020), the amount of deductions on it (page 030), as well as VAT , calculated for transactions for which the validity of the zero rate was not confirmed (line 040), and subject to restoration (line 050). Blocks of these lines are formed for each type of operation.
The remaining lines are used to record information:
- for tax subject to restoration (lines 060, 070,080). Fill in the period when the exporter or both parties to the transaction accepted the return of the goods;
- when transforming prices (pages 100, 110): on page 100 they reflect its increase, on page 110 – a decrease. The data is corrected during the period of recognition of this fact;
- by the amount of VAT refund per section (p. 120). Calculated as the difference between the sums of the lines (030 + 040) and (050 + 080);
- amount of VAT payable (p. 130). It is calculated as the difference between the sums of the lines (050 +080) and (030 + 040).
In section 5 they record in the lines:
- 030–050 - the amount of the base and deductions by transaction codes based on received confirmation of the use of the benefit;
- 060, 070 - unconfirmed amounts of base and deductions;
- 080, 090 - the results obtained for the section.
Section 6 contains information about export transactions with a “justifying” set of documents that has not yet been collected. The data is grouped similarly to section 4, distributed by transaction codes.
Let's consider filling out a VAT return for exports for the 3rd quarter of 2022.