Procedure and timing of inventory of fixed assets
The inventory of fixed assets is carried out in the manner established by the order on the accounting policy of the enterprise, as well as in cases where its implementation is mandatory in accordance with paragraphs. 26 and 27 of the Accounting Regulations dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n, that is:
- when selling fixed assets;
- renting them out;
- acquisition of a state or municipal unitary enterprise;
- change of financially responsible persons;
- identifying facts of theft;
- the occurrence of natural disasters or fires;
- company reorganization;
- before preparing annual financial statements (at least once every 3 years, library collections - once every 5 years).
The inventory can be carried out suddenly, at the initiative of the head of the organization, to prevent theft.
In terms of the degree of coverage, it can be continuous or selective, and in terms of the method of implementation - natural (involving direct observation of the presence of accounting objects) or documentary (conducted according to the company’s accounting registers). Documentation of the inventory of fixed assets is carried out using forms unified or developed by the organization itself and enshrined in its order on accounting policies.
Each document is drawn up in two copies, one of which is transferred to the accounting department, the other to the financially responsible person.
Maintaining a book of fixed assets
Entries in the book are made on the basis of other documents:
- OS-1 (or OS-1a, b) - upon admission (the date on the papers must match);
- OS-2 - during internal movement of an object;
- OS-4 (or OS-4a, b), if there was a write-off of objects.
Important! The inventory book is kept in one copy. This is what an accountant does. After the end of the accounting period, the document is sent for storage for 5 years.
The procedure for issuing an order to conduct an inventory of OS
Inventory begins with the manager issuing an order to conduct an inventory of fixed assets. To do this, you can use the INV-22 form, approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.
Download the order form in form INV-22.
The order specifies:
- location of the inventory;
- its start and end dates;
- chairman and members of the commission;
- degree of coverage of inventory objects;
- the reason for the inventory;
- deadlines for submitting documents to the accounting department.
The commission may include a chief or other responsible accountant, a person responsible for the safety of fixed assets, shop workers, administration employees, etc. The
order is registered in the inventory order register INV-23, approved by Resolution 88 and is handed over to the chairman of the commission for signature .
Download a sample order for inventory of fixed assets.
Before checking the actual availability and condition of fixed assets, it is necessary to review the availability of:
- OS inventory cards (form OS-6), other accounting registers for OS objects and the correctness of the data entered in them;
- technical passports;
- documents for receiving or leasing OS.
If necessary, accounting documents can be supplemented or adjusted.
How to view data about an OS object for a specific date
The card reflects data about the object as of the current date. But there is a need to see what the data was before any changes, on a certain date. To do this, in the inventory card, by clicking the “More” button, select the “Change form” command.
Fig.6 Select the “Change Shape” command
Having opened the form settings, we see that among the form header details there is an unchecked “Information date” attribute.
Fig.7 Information date
By checking this box, in the form of an OS directory element we will see an additional field where we can set the date for which we want to view information about our object.
Fig.8 Setting the date
Drawing up a statement of inventory
When conducting an inventory of fixed assets, not only their availability is checked, but also other important characteristics, such as:
- appointment,
- performance,
- inventory numbers,
- external condition,
- absence of any visible defects.
During the inspection of buildings, structures and other real estate objects, the following are checked:
- main building material,
- number of storeys,
- total and usable area,
- year of construction, etc.
Natural objects are checked: length, depth, extent.
By plantings - presence and age.
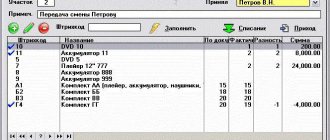
OSes of the same type received at the same time are indicated in the statement taking into account quantitative indicators.
All identified data is entered by members of the commission into the INV-1 inventory sheet, approved by Resolution 88, or an independently developed form.
What applies to fixed assets
Such funds are understood as the property of an organization used for the production of goods, works or services or for the direct functioning of the institution for a period exceeding 12 months, or a production or operational cycle exceeding 1 year.
Fixed assets include:
- buildings and constructions;
- cars and equipment;
- instruments, devices and tools;
- computer technology;
- vehicles;
- inventory and household supplies;
- breeding and working cattle;
- perennial plantings;
- roads.
Fixed assets are also various capital investments - investments for the purpose of radical land improvement and leasehold funds, plots of land, environmental management facilities.
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting only if certain criteria are simultaneously met:
- The fund is intended for the production of goods, works, services, as well as for the functioning of an institution or for the sale of funds for monetary compensation for temporary use and possession.
- The use of the product should occur over a long period, the duration of which exceeds 12 months.
- The company does not plan to further resell the fund.
- In the future, the tool may bring profit or economic benefit to the organization.
Fixed assets do not include objects recorded as finished products in the warehouses of the manufacturer or products in the warehouses of distributors. These goods will be resold, which is a failure to comply with one of the criteria for classifying products as fixed assets.
Objects that are in transit or transferred for installation are not included in this category. Capital and financial investments, with the exception of investments in leased assets and land improvement, also do not qualify as fixed assets.
Why is a matching statement needed?
After completing the inspection, the commission checks the data in the INV-1 statement with the indicators reflected in the accounting registers.
All identified discrepancies between them are entered into the comparison sheet of the results of the inventory of fixed assets INV-18, approved by Resolution 88, or a similar form developed by the organization.
All unaccounted for items are entered into accounting records by the commission, and the necessary corrective entries are made for incorrectly reflected fixed assets.
Newly identified objects are registered at current market prices. The degree of wear of an object is determined taking into account its actual condition. These changes are formalized by internal acts of the enterprise.
When facts of modernization or liquidation of fixed assets are identified that were not reflected in the accounting records, adjustment entries are made in them to reflect an increase or decrease in their book value.
For objects that, as a result of modifications, have changed their technical characteristics, new data is entered into the inventory.
For fixed assets that are out of order and cannot be restored, as well as for objects that are leased or in safekeeping, additional inventories are compiled.
Those OS objects for which no discrepancies were found are not reflected in the comparative inventories.
Form OS-6B. Sample inventory book
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
The basis for accepting a fixed asset for accounting in small enterprises is the transfer and acceptance certificate (form OS-1, OS-1a or OS-1b). One of the copies of the drawn up act is transferred to the accounting department, after which an employee of this department enters information about it into the inventory book form. Filling is carried out on the basis of the data specified in the acceptance certificate and in the technical documentation attached to the object.
Form OS-6b includes a title page and a table.
The title page contains information about the name of the organization, the time period for maintaining the inventory book, as well as the full name and position of the person responsible for filling out the form.
The fields and columns of the table serve as a place for entering data about accepted fixed assets and about all operations that are performed with the object during its use:
- Each fixed asset corresponds to a specific table row with an individual record sequence number;
- The second column is intended for the name of the fixed asset, which is taken from the transfer and acceptance certificate;
- Next, enter the inventory number of the object.
The contents of columns 4-7 reflect data on the acceptance of fixed assets for a small enterprise:
- Column 4 indicates the date and number of the act that is the basis for putting the facility into operation;
- Column 5 contains the full date (specifying the day, month and year) of acceptance of the fixed asset for accounting;
- In column 6 - the department of the organization that accepted the object;
- Column 7 contains the full name of the employee who is responsible for the safety of this fixed asset.
Also, in the inventory book, when accepting a fixed asset, you should indicate its initial cost, which is the sum of all costs of acquiring and putting the object into operation, minus VAT. This information is supplemented by the useful life established for the fixed asset. Such information is contained in the acceptance certificate.
The process of operating an object provides for the possibility of its revaluation. In this case, fill out columns 12-14 of the OS-6b form:
- Column 12 indicates the date of the revaluation;
- Column 13 indicates the conversion factor;
- Column 14 contains the updated value of the object obtained based on the results of the revaluation.
It may happen that an object is moved from one department of the company to another or leaves the organization and is deregistered (moral and physical wear and tear may be the reasons). These transactions are also subject to entry into the inventory book form OS-6b. If the object has moved from one structural unit of the enterprise to another, it is necessary to additionally issue an invoice in the OS-2 form. Next, fill out columns 10,11 and 15-18 of the inventory book:
- Column 10 is intended to account for depreciation of a fixed asset (the amount accrued at the time of disposal, relocation and write-off of the object);
- Column 11 indicates the residual value, calculated using the formula gr.8-gr.10;
- Column 15 contains the date and number of the document that serves as the basis for moving or disposing of the object. When transferring a fixed asset to another enterprise, it is necessary to draw up a transfer and acceptance certificate, and when writing off an object, fill out an act in the form OS-4, OS-4a or OS-4b;
- Column 16 reflects the internal movement of a fixed asset; it indicates the name of the company department to which the object is transferred;
- Column 17 contains the full name of the employee who will be responsible for the safety of the object in the new location;
- Column 18 is the place to enter information about the reason for the disposal and write-off of a fixed asset (for example, moral or physical wear and tear or the number of the purchase and sale agreement).
If the company receives an intangible asset, an accounting card is created for it in the form of intangible asset-1.
How to draw up an act based on inventory results
After inspecting all objects, compiling inventories and reflecting the identified discrepancies between the accounting and inspection data, an act on the results of the inventory of fixed assets is drawn up.
An enterprise can develop the form of the act independently or use the form approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n, form according to OKUD 0504835.
Note! Despite the fact that this form was developed for institutions and government bodies, there is no prohibition on its use by other entities.
Download the inventory list of fixed assets in the INV-1 form here.
When filling out this form please indicate:
- composition of the commission;
- financially responsible person;
- days of the beginning and completion of the inventory;
- numbers and dates of statements, acts and collating inventories.
It makes notes on the results of the work done, gives full characteristics of the detected discrepancies in quantitative and cost terms, indicating the reasons for their occurrence.
Attached to the act are: statements, collating inventories, explanatory notes from financially responsible persons.
When filling out this form please indicate:
- composition of the commission;
- financially responsible person;
- days of the beginning and completion of the inventory;
- numbers and dates of statements, acts and collating inventories.
It makes notes on the results of the work done, gives full characteristics of the detected discrepancies in quantitative and cost terms, indicating the reasons for their occurrence.
Attached to the act are: statements, collating inventories, explanatory notes from financially responsible persons.
Download a sample act based on the results of the inventory of fixed assets.
In the event that the commission has not identified any discrepancies between the accounting and actual data, an entry is made in the act about their absence.
Order of conduct
The inventory is carried out by a working commission appointed by the management of the enterprise with the obligatory participation of an accounting employee.
The start of work is preceded by the submission of invoices to the accounting department by financially responsible persons and the verification of primary documentation reflecting the movement of fixed assets. It may include:
- Inventory list (card or book) and other information media for analytical accounting;
- Technical passports for buildings and equipment;
- Documents for leased, leased or accepted for safekeeping property;
- Title documents for buildings and other real estate.
The commission, together with financially responsible employees, conducts an inventory visually, comparing numbers with inventory data. This process is all the more tedious the more objects there are in the lists, but despite all the monotony of the work, the results may be unexpected. What could happen?
- Objects were identified that were not listed in the accounting documents. In this situation, the commission receives the asset, entering into the inventory information about real wear and tear and value corresponding to the current market level.
- Signs of unaccounted capital work were found. As a result of repairs or reconstruction, the value of the object on the balance sheet increases, which must be reflected in the inventory list. The second option is when unaccounted capital work consisted of demolition (partial liquidation) and led to a decrease in the value of the property. In this case, it is necessary to draw up a separate act, which records the fact of a constructive change in the fixed asset and the reasons why it was not reflected in the accounting (with an explanatory note from the financially responsible employee attached).
- Some fixed assets are not available at the enterprise. In most cases, this situation is not an emergency. Vehicles may be away, equipment removed for repairs, etc. Comparison with inventory is delayed or made based on available invoices. If an object is missing for an unknown reason, that is, actually lost, they look for the culprits.
- The fixed asset cannot be restored. Yes, this happens too. The equipment failed hopelessly, and this happened just before the inventory. The means of production are included in a separate inventory compiled by the commission, which indicates the time of commencement of operation and the reasons that became disastrous for the objects. A search is underway for those responsible for the damage.
The result of the commission’s work is a consolidated inventory listing indicating the location of objects and their value. This document is transferred to the accounting department and serves as the basis for clarifications and changes in summary statements, inventory cards and other fixed asset accounting registers.
Important changes for 2022
On January 1, 2018, a new federal standard for fixed assets came into force. Now accounting for fixed assets in accounting must be done differently. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the key innovations shown in the table:
| Name | Content |
| Changing the grouping of fixed assets | Non-residential premises join the “Buildings and structures” group. There is no separate group for the library collection. The new grouping of objects does not directly coincide with OKOF, as before. |
| Investment property concept | This is a type of real estate that is owned by an organization and is either rented out by the owner or acts as an investment, resulting in an increase in the value of the real estate. This is a completely new group. |
| Recalculation of depreciation of some fixed assets | The limits of the initial cost of funds when calculating depreciation have been increased. Low-value property - up to 10,000 rubles. (write-off from the balance to 21 off-balance accounts). Funds from 10,000 to 100,000 rubles. upon commissioning they are depreciated at 100%. With an initial cost of over 100,000 rubles. The organization independently decides on the depreciation method. Library collection worth up to 100,000 rubles. — depreciation is charged at 100%. |
| Choosing a depreciation method | If the initial cost of the AI is 100,000 rubles. and above, then the depreciation method is selected by the institution based on the functional use of the object, that is, the method must be based on the method of obtaining economic benefits (utility potential). In 2022, the choice of institution will be made between the linear method, the method of proportional to production volume or the declining balance method. |
Also, organizations now have the right to change the method of calculating depreciation, but only from January 1. To take into account different groupings of fixed assets, you can use all 3 depreciation methods, prescribing this in your accounting policy.
Important changes also affected reporting on funds. Reports will become more detailed and transparent.
Tax accounting of fixed assets in 2022 will remain unchanged. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depreciable property is considered to be the property the owner of which is an institution and which is used to generate income. The useful life of such inventory items is more than 12 months.
From 01/01/2016, the initial cost value of the material value, at which the object is recognized as a fixed asset, increased to 100,000 rubles. This rule applies to those inventory objects that the organization puts into operation starting from 01/01/2016 (clause 7 of article 5 of the Federal Law “On Amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” dated 06/08/2015 No. 150).
On January 1, 2017, the new OKOF classifier came into force, thanks to which a new classification of fixed assets was approved (RF PP No. 640 dated July 7, 2016, Rosstandart Order No. 2020-st dated December 12, 2014). When registering an object for both accounting and tax purposes, each organization must use updated classifiers.
How to revaluate fixed assets
The institution has the right to organize a revaluation of fixed assets if necessary. Revaluation is carried out every year as of December 31 for all fixed assets grouped on a homogeneous basis.
Upon revaluation, the value of assets is revalued, that is, increased, or decreased - discounted. This cost is called replacement cost.
For revalued objects, depreciation charges are formed from the replacement cost.
Postings
1. Accounting for the receipt of fixed assets.
Accounting for the receipt of fixed assets and the commissioning of inventory objects is carried out at the original price (purchase cost) of the object. IO is accepted for accounting on the date when the initial cost is fully formed, and for tax purposes - at the time the fund is put into operation:
- Dt 08 Kt 60/10/70/69) - taking into account expenses for the acquisition or creation of fixed assets;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 - carrying out incoming VAT;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - formation of the initial cost of the inventory item.
For budget accounting, the postings will be as follows:
- Dt 110631310 Kt 130231730 - equipment has arrived;
- Dt 110434310 Kt 110631410 - commissioning of equipment;
- Dt 130404310 Kt 110404410 - depreciation calculation.
2. Accounting for the disposal of fixed assets.
Let's consider options for the sale and liquidation of the property. Accounting for the disposal of fixed assets reflects the sale price and the residual value of the investment:
- Dt 62 Kt 91 - income from sales;
- Dt 91 Kt 68 - VAT;
- Dt 02 Kt 01 - write-off of depreciation;
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - write-off of residual value.
Entries for budget accounting:
- Dt 110434 410 Kt 110134410 - depreciation write-off;
- Dt 140110172 Kt 110134410 - write-off of residual value.
Liquidation accounting:
- Dt 02 Kt 01 - write-off of depreciation;
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - the residual value is written off.
Dt 0 401 10 000 (analytics - 401 10 172) Kt 0 101 00 000 (required analytical account) - posting for partial liquidation of a fixed asset in a budget institution.
3. Off-balance sheet accounting.
Off-balance sheet accounting of fixed assets is maintained in accounts 001 and 011 (transfer or rental of inventory items), 005 (installation equipment), 010 (depreciation of some objects is reflected).
Rules for filling out the register
The OS-6b book consists of a title page and a tabular part, while there can be quite a lot of internal sheets.
The title page displays information about the owner of the OS, and also indicates the period for which the book was opened. Mandatory details are the position and full name of the employee responsible for maintaining the book.
Information about each OS object is entered in a separate line (and only in one). That is, a record about one object is made once, and as the situation with the object changes, new information is added to the line (up to and including deregistration of the object).
There are only 18 columns in a line. When revaluing an asset, information about this is entered into gr. 12–14, when moving - in gr. 15–17, and when deregistered (sale, write-off) - in gr. 18.
IMPORTANT! In the columns where the amount of depreciation should be indicated, information about the depreciation accrued for the entire period of operation should be displayed.
How to form the initial cost of fixed assets
Cost is the cost of purchasing or producing a fixed asset. The initial cost consists of the following quantities:
- amounts transferred to the seller;
- price of delivery, installation and commissioning;
- costs of construction work;
- costs of information services when purchasing a fixed asset;
- customs duties and fees paid when importing an object, state duty for the purchase;
- other costs.
At the same time, general business expenses are not taken into account as part of the initial cost, with the exception of costs associated with a specific object and VAT.
The initial cost is reflected in the accounting of the fixed asset and does not change during its operation, except in cases of modernization, reconstruction, revaluation, completion or partial liquidation of the inventory item.