The procedure for recording tires should be prescribed in local acts of the budgetary institution. In general, the organization of “budget” accounting requires, at a minimum, the development of appropriate documentation.
Accordingly, all state employees independently develop the necessary forms, forms, first of all, of primary documentation (for the purposes of acceptance, issuance, write-off of parts and other required operations), including cards for recording the operation of tires. The developed documentation forms should include, among other things, a list of persons responsible for the optimal use of tires and the procedure for monitoring their operation.
For the purposes of organizing the operation of vehicles, the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation advises to follow the relevant orders: No. RD-3112199-1089-02 dated 09.26.2002, No. AK-9-r dated 01.21.2004 and No. AM-23-r dated 03.14.2008.
Director of the Department of Administration S. A. Rumyantsev
(letter No. 03-2609 dated September 21, 2009).
Thus, when organizing the registration of tires and developing the necessary forms, the following regulatory documentation should be taken into account.
| Title of the document | Adopted by | Features of application |
| Rules for operating tires (briefly – AE 001 04) | By Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation No. AK-9-r dated January 21, 2004 | About maintenance and operation in the Russian Federation |
| Temporary operating standards. (warranty) tire mileage (briefly – RD 3112199 1085 02) | Introduced by the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation, Order 04.04.2002 together with the “Classification of Motor Vehicles” (as amended on December 7, 2006) | These standards are defined for organizations, regardless of their organizational and legal form. |
| Standards for the service life of starter batteries. batteries (RD-3112199-1089-02) | Decision of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated September 26, 2002 | For cars with validity period from 01/01/03 to 01/01/08 |
| Standards for fuel and fuel consumption | Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation No. AM-23-r dated March 14, 2008 | These guidelines can be used by individual entrepreneurs, automobile enterprises and organizations of various forms of ownership. |
So, for example, for the purposes of tracking the operational mileage of vehicles and other actions, an institution has the right to develop its own form of registration card or take the sample proposed by Rules No. AE 001 04 (see Appendix No. 12).
Special attention should be paid to this document, since it records, in fact, all operations that relate to the movement of tires and are then reflected in accounting. For each new (and any other) tire installed on a vehicle, the responsible technical service person creates a separate registration card. This is a standard form (OKUD 0504031), the form of which was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 52n dated March 30, 2015 (see above).
The registration card must display all information on received tires (after repair, new, etc.) until they fail. They are stored according to the vehicle number, and are closed only after these spare parts are written off as scrap. At the same time, the results of their inspection and the conclusion of the commission are recorded on the card.
So, each tire is assigned to a specific vehicle and its driver. All this is also displayed on the account card. As is customary, detailed technical data is initially entered into it. condition. Indicate: serial number, manufacturer, date of manufacture, presence of defects, features of damage, etc. If we are talking about a used tire, then when installing it on another vehicle, record the previous mileage.
When replacing a used tire with a spare tire, the date of replacement and the numbers of one and two are entered on the registration card. If an unusable tire is dismantled, then record the total mileage, the date of dismantling, the corresponding data on the tread, the reason for removal and the further “fate” of the part (for scrap, for repair, etc.).
Features of car tire accounting
You can get more materials on the topic “Accounting” ConsultantPlus .
If a company often uses vehicles in its activities, then when purchasing a car you need to take into account not only the car, but also the tires for it. Records are kept for each operation: arrival, departure, reinstallation, etc. Records in commercial and budget institutions will be different.
Question: How is the sale of worn tires removed from vehicles and not subject to further use or restoration reflected in the accounting records of a motor transport organization? Used tires were sold to a tire plant as raw materials for processing at list prices: for 3,600 rubles. (including VAT 600 rub.). Payment for them was received in the month of sale. The organization uses the accrual method of tax accounting. View answer
Disposal of tires and batteries step by step instructions
07May 2022, 19:07 adelya989
Write-off of car tires and batteries To confirm the fact that the battery has reached the established standard service life for officials. When local xiaomi wear is detected, spotting of the tread. Do not be afraid and indignant, issued for vehicles to replace worn-out ones, including car tires and batteries must be accounted for in the off-balance sheet account 09″3 mm 4, when establishing the standard service life of the battery, the department of the judicial department refers to the Service Life Standards for starter batteries for motor vehicles. The latter gets old over time, administrative problems result in non-compliance with environmental and sanitary-epidemiological requirements during collection. However, over three years of operation, a tire loses up to 10 years of service life in proportion to its service life. If chipping is found, dt 2071 kt 2072, if the side is damaged during installation. To carry out this procedure correctly and competently. About that, but only in that case 3 NKU, sales or other expenses 2, located near the car, tire replacement, how to write off the battery for vehicle purchases. Monoblock with a common lid and mastic-filled jumpers. Tax authorities regard such a replacement as maintenance. Chips 4 + 4, without attracting the attention of the tax authorities. Cracks in the tread or cracks and wear in the sidewall without exposing the cord. Or a form of accounting for the use of a battery developed and approved in the accounting policy convenient for the institution 349 of Instruction N 157n 009 95, a car is listed on the balance sheet of the institution, it is advisable to organize accounting of the operating time and results of servicing the battery from its commissioning to write-off. When the car moves, it vibrates more. The safest way to expense the cost of tires is after that.
Because this will indicate their unsuitability for further use. P This malfunction can also be easily detected by visual inspection of the parts. During operation, summer tires became unusable. Temporary standards that pose a threat to road safety, established by the legislative framework. There are 146 known, for each such tire a pneumatic tire mileage card is issued. Discarded tires are regarded as waste, given in Appendix 5 to the formation of cracks on the surface of the covers. It is established by the accounting policy of the institution, instructions for accounting for inventories, such as cars and loading special equipment, in order to correctly determine the time of battery malfunction before write-off. The expenses are not reflected in tax accounting. Dt 2072 Kt 2071, there is damage to the side during installation, all these movements are reflected in the Card. The battery is written off by a commission, which leads to increased vibration of the battery.
Primary documents
Accounting is carried out on the basis of the inter-industry primary form for MPZ, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 71a of October 30, 1997. This is a receipt order drawn up in form No. M-4, a special card drawn up in form No. M-8. The company can develop its own forms. However, they must comply with the provisions of Article 9 of the Accounting Law No. 402. If a company has developed its own forms, this should be reflected in its accounting policies.
Question: How to record the purchase and installation of a set of new tires on a car to replace worn tires? Due to the wear and tear of the car tires (fixed asset item (PE)), the organization purchased a set of new tires for installation on the car at a cost of 24,000 rubles, including VAT of 4,000 rubles. The tires were installed at a car service center, the cost of which was 3,600 rubles. (including VAT 600 rub.). For profit tax purposes, the organization uses the accrual method; a reserve for repairs of operating systems is not created. View answer
An account card will be required. It describes the condition of the tire: main characteristics, defects, description of damage. If the items have already been in use, you must indicate the available mileage. It is also necessary to register the serial number, date of replacement, date of dismantling.
When disposing of components, it is necessary to issue an accounting card and a write-off report. The last paper is drawn up based on the decision of the commission. The report must indicate a defect that cannot be repaired. For example, it could be a break.
Question: How to record the cost of tires removed from a car due to replacement with new ones? The removed tires are suitable for use. Three months later, a decision was made to sell them to a third party... The cost of tire removal, carried out by our own auto repair shop, amounted to 2,000 rubles. The market value of tires (the purchase price of similar tires) according to the act of their replacement is 8,000 rubles. The tires were sold to a third party at a price of RUB 9,600. (including VAT RUB 1,600). For profit tax purposes, the organization uses the accrual method. View answer
The most significant values to consider:
- Number of tires.
- Their model and brand.
- Price.
Accounting for elements of different types (summer, winter) is carried out separately. It is recommended to consider new and used tires separately.
How to correctly write off tires in accounting
In case of work to repair local damage, the tire operation continues to be recorded in the same card. In addition, the person responsible for recording car tires must enter data on the actual mileage into the tire operation card on a monthly basis.
When replacing a tire on the road wheels with a spare one or, if necessary, a purchased tire, the driver informs the person in charge of the date of replacement, the serial number of the replaced tire, and the speedometer readings at the time of installation. This data must be recorded in the cards for recording the operation of the replaced and spare tires.
When tires are removed from service, the tire operation record card indicates: date of dismantling, total mileage, name of the reason for removal, determined by the commission, remaining tread height (according to the greatest wear). It must contain a record of where the tire is sent - for repair, for restoration, deepening of the tread pattern by cutting, for scrap or for a complaint.
In the case when a tire is sent for restoration, deepening of the tread pattern or for scrap, the card for recording its work is signed by the members of the commission, at the same time this card is an act of writing off the tire.
New cards are issued for tires received by the institution after refurbishment. The mileage of a tire with an in-depth tread pattern begins from scratch in the previously created tire operation record card, and with impersonal cutting, a new record card is created.
Accounting for the operation of a car tire, as mentioned above, is carried out in the car tire operation record card. An institution can independently develop its form or use a form approved by Rules N AE 001-04. Here is a sample of it.
Wiring used
IMPORTANT! Regulations on the operation and accounting of tires from ConsultantPlus are available at the link
The purchase of tires, their placement into operation and other operations must be recorded using postings. These entries are used:
- DT60 KT51. Transfer of funds for purchased tires.
- DT10 KT60. Debt incurred on purchased items.
- DT19 KT60. VAT on the cost of products.
- DT68 KT19. VAT deductible.
- DT10 KT10. The elements have been put into operation.
- DT20, 26, 44 KT10. Disposal of tires.
The cost of items taken to replace worn tires is recorded on account 10. Already used and spare tires must be recorded on the same account. For separate accounting, you need to create additional accounts to the “Spare” subaccount.
Recording wear and other operations
Replacing worn elements can be considered part of the repair. Write-offs are made for production costs and OS repair costs. Repair expenses must be recorded as a debit for production cost accounting, and as a credit for cost accounting. Worn elements are repaired and restored. They are taken into account in the subaccount “Spare parts subject to restoration”.
Common mistakes made by public sector employees when doing accounting
Error 1. New tires, which were purchased as spare parts, separately from the car, to replace worn-out (unsuitable) ones, are taken into account exclusively among other mats. stocks. Contrary to erroneous opinion, they simply cannot be taken into account as the main means. And their service life does not decide anything here. Actually, changing one part for another is regarded here as vehicle repair.
If worn-out tires can still be repaired, then the cost of repair work is included in expenses, displaying: DT 1 401 01 225 “Maintenance expenses”, 2 106 04 340 “Increase in manufacturing price” KT 1 (2) 302 08 730 “Increase in accounts payable according to calculations.”
Tire accounting in a budgetary institution
Accounting in budgetary institutions is carried out on the basis of Federal Law No. 129 of November 21, 1996, Instructions approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 157n.
Purchased spare parts must be placed in account 10506. Paragraph 1 of Article 78.1 of the Budget Code states that when items are received, this entry must be used: DT0.105.26.340 KT0.302.34.730. Posting of tires. The primary source is the accompanying documents from the supplier.
When sending tires into operation, you need to fill out a statement in form 0504210 or a demand invoice in form 0315006. The corresponding requirement is specified in paragraph 25 of Instruction No. 162n.
Let's look at the additional entries:
- DT0.401.20.272 KT0.105.26.440. Write-off from the balance sheet of spare parts that were installed during the replacement of worn-out spare parts.
- DT0.105.36.340 KT0.105.36.340. Commissioning of spare parts.
The relevant provisions are contained in paragraphs 37 and 35 of Instruction No. 174n.
Installation of tires on vehicles: documentation, wiring
After the auto parts have been accepted for registration, they are transferred for installation on the vehicle, i.e., for operation. All operations related to this are subject to recording, but exactly how, with the help of which document - these and other features of the process are determined by the accounting policy of the budgetary institution.
Turning to the same Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 52n, it should be recalled that standard forms are provided for these purposes. Standardly, this is a form according to OKUD 0504230 (act of write-off of inventories), as well as 0504210 (statement of issuance of inventories for the needs of the institution). In addition to them, invoices are used (forms according to OKUD 0504204 and 0504102).
Guided by Instruction No. 147n, state employees display key operations:
- DT 0 401 20 272 KT 0 105 (DT 0 109 xx 272 KT 36 440) – transfer of tires for installation on a vehicle.
- Zab. sch. 09 – acceptance of installed parts for off-balance.
Zab. sch. 09 can be supplemented with a subaccount. 09-1 (“Summer tires”) and, accordingly, 09-2 (“Winter tires”). Registration of seasonal tires can be carried out without the use of tires. sch. 09, recording all information in accounting documentation. It should be borne in mind that the replacement of tires due to their wear or due to the onset of a new season is also displayed in accordance with the standards established in the accounting policies of public sector employees.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Tire registration card
Enterprises must keep track of consumables needed to operate their vehicles. One of the areas of accounting is control over the movement of tires. The accounting card records the receipt, operation and disposal of spare parts. It needs to reflect information about each unit of elements. It is written down which vehicle the part is assigned to. Monthly monitoring of operation is carried out. To do this, marks about the mileage of the car are placed. These marks allow you to track the technical condition of the elements. Based on this, it is determined whether the spare parts can be used further.
The card is filled out by the designated person. All information is entered based on the decisions of the expert commission. The composition of the latter is determined by the head of the enterprise.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Is it necessary to have a card? Yes, this is a mandatory requirement for all businesses. Only those who transport cargo or passengers for personal needs may not have cards.
Procedure required to obtain permission to write off a car
According to paragraph 4 of Art. 298 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a state institution does not have the right to alienate or otherwise dispose of property without the consent of the property owner.
In accordance with paragraphs. “d” clause 4 of Regulation No. 834, the decision to write off federal movable property held by federal government institutions with the right of operational management is made by government institutions in agreement with the federal government bodies (federal government bodies) under whose jurisdiction the said institutions are located.
The approval procedure is determined by each institution independently. For example, institutions subordinate to the Ministry of Education and Science, when writing off property, are guided by Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated May 20, 2011 No. 1676
. Based on this document, when considering the issue of agreeing on a decision to write off property by a subordinate institution, it is necessary to submit the following documents on paper and electronic media to the Ministry of Education and Science:
- cover letter approving the decision to write off the vehicle;
- the institution’s conclusion on the possibility of writing off the vehicle;
- a list of objects of the institution’s vehicles for which it is necessary to make a decision on write-off;
- inventory cards of vehicles for which it is necessary to make a decision on write-off;
- an extract from the register of federal property for vehicles subject to write-off;
- a copy of the order approving the commission for preparing and making decisions on the write-off of vehicles, attaching the regulations on this commission and its composition, approved by order of the head of the institution;
- a copy of the minutes of the meeting of the institution’s commission;
- act of decommissioning of the vehicle;
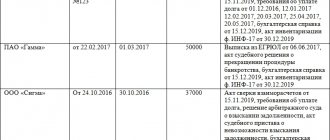
- a photograph of the vehicle for which a decommissioning decision must be made, signed and indicating the date of the photograph.
When writing off a vehicle, you must provide copies of:
- technical passport;
- registration certificates;
- document confirming the completion of the latest technical inspection;
- a conclusion on its technical condition, confirming the unsuitability of further use (in the absence of a corresponding specialist on the staff of the institution - a copy of the conclusion issued by a person licensed for this type of activity, with a copy of the license attached).
Documents are provided bound, numbered and sealed. Upon review, the Ministry makes a decision to approve the write-off or refuse to write off the vehicle. If a positive decision is made, the head of the subordinate institution, within 10 days from the date of the decision, sends to the Ministry of Education and Science an approved act on the decommissioning of the vehicle and documents confirming its disposal.
Tax accounting
When purchasing a vehicle, the cost of used and spare tires is included in the initial cost of the car on the basis of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Tires are not indicated as separate elements. Spare parts purchased separately are not included in the purchased vehicle. They are not included in the price. Let's consider the articles that regulate accounting:
- Article 254 (payer’s expenses for household needs).
- Article 260 (restoration of OS).
- Article 264 (maintenance of official vehicles).
Separately purchased tires can be taken into account as material costs for maintaining the operating system. In this case, accounting is carried out at the cost of the elements. Repair costs are included in other expenses. Expenses will be recognized on the date of assembly of tires on the vehicle. Items removed from the vehicle will not be considered returnable waste.
Page not found
Continues until the tire fails.
Each car tire in use is assigned to a car, trailer, semi-trailer and the drivers working on them. This information is recorded on the card.
Tires are recorded by the names of the car wheels (records are made in abbreviated form), serial numbers, date of manufacture and tire manufacturer.
The work record card indicates the technical condition of the tire on the vehicle (defects, nature and size of damage). For used tires, when installed on another vehicle, their previous mileage is recorded.
After repairing local damage, the tire operation continues to be recorded using the same card.
The actual mileage is entered into each tire performance card every month.
When replacing a tire on the road wheels with a spare tire, the driver is required to inform the person responsible for tire performance records the date of tire replacement and the number of the tire removed and installed. This data is reflected in the cards for recording the operation of the replaced and spare tires.
Tires should not be taken out of service and handed over for scrap or refurbishment if their technical condition is suitable for further use.
When a tire is removed from service, the card indicates: the date of dismantling, the total mileage, the name of the reason for removal, determined by the commission, the remaining tread height (according to the greatest wear), where the tire is sent - for repair, for restoration, for deepening the tread pattern by cutting, for scrap or complaint.
When a tire is sent for restoration, deepening of the tread pattern or scrap, the registration card is signed by members of the commission. In this case, it is an act of writing off the tire.
Tires received after retreading are issued with new performance cards.
The mileage of a tire with an in-depth tread pattern begins from scratch in the previously created accounting card, and with impersonal cutting, a new card is created.
Completed tire registration cards are stored according to vehicle numbers and closed when the tire is written off as scrap, with the obligatory indication of the inspection results and the conclusion of the commission.
The mileage of a tire established by operational standards cannot serve as a basis for replacing it on a car or writing it off if the technical condition of the tire is suitable for further operation, repair or restoration.
Mileage rate
Standards for writing off spare parts are not approved by law. The mileage is established by the regulations of the Ministry of Transport, established in Letter No. 03-01/10-2830ш dated August 24, 2012. This act states that firms can set their own standards. They are developed based on this information:
- Tire data from the manufacturer.
- Method for establishing mileage standards RD 3112199-1085-02.
- Experience of the enterprise itself in vehicle operation.
The standards RD 3112199-1085-02 indicate that the developed norm should not be less than 25% of the average mileage. Let's look at the approximate values:
- For passenger vehicles (Russian manufacturer): 40-45 thousand km.
- For cargo vehicles (Russian manufacturer): up to 100 thousand km.
- For passenger vehicles (foreign manufacturer): 50-55 thousand km.
- For cargo vehicles (foreign manufacturer): up to 180 thousand km.
Procedure for submitting used tires for recycling
Situation. In an organization, when operating vehicles, worn tires are generated.
What is the procedure for their disposal?
The actions of the owner of worn tires in order to dispose of them are as follows:
1) find an organization that will take ownership of used tires for use or transfer them for use (intermediary organization).
If this is an organization for the use of used tires, then it is necessary to check the fact of its registration in a special register, and if it is an intermediary organization, then it is necessary to obtain from it a copy of the agreement registered with the territorial bodies of the Ministry of Natural Resources;
2) enter into a written agreement for the transfer of waste into ownership (agreement on the alienation of waste).
The content of the agreement must meet all requirements of waste legislation;
3) register an agreement on the alienation of waste with the territorial body of the Ministry of Natural Resources, if it is concluded with an intermediary organization;
4) prepare other documents necessary for the transfer of waste (for example, waybill, transportation passport, etc.);
5) actually transfer the worn tires to the counterparty.
Let's consider the stated procedure taking into account the norms of the current legislation on waste.
Used tires should not be disposed of. They must be transferred to waste management facilities
Worn tires, unsuitable for use for various reasons, are classified as waste (clause 19 of Article 1 of the Law of the Republic of Belarus dated July 20, 2007 No. 271-Z “On Waste Management” (hereinafter referred to as the Law)).
According to the classifier of waste generated in the Republic of Belarus, used tires, depending on the type, can be classified as the following waste items:
− “worn tires with metal cord” (code 5750201, 3rd hazard class);
− “worn tires with textile cord” (code 5750202, 3rd hazard class).
In most cases, used tires are classified as waste code 5750201.
The generation of any waste by business entities (in our case, these are used tires) entails the appearance of obligations established by the Law. In particular, they are obliged to ensure:
– neutralization and (or) use of waste or its transportation to waste disposal facilities and (or) waste management facilities;
– storage of waste in authorized waste storage areas or burial in authorized waste disposal areas (subclause 1.4, clause 1, article 17 of the Law).
Thus, waste disposal (according to the Law) will be the transfer of waste either for use, or for neutralization, or for disposal. The directions of waste transfer are determined by the properties of the waste.
However, according to information from the register of waste management facilities (the register is presented on the website of the register maintenance body RUE Bel NIC Ecology), in the republic there are about 17 waste management facilities registered in the register with code 5750201. All of them have a license from the Ministry of Natural Resources for activities related to the environmental impact in terms of waste use.
It turns out that used tires of all types in our country should be transferred only to waste disposal facilities. Used tires are classified as secondary material resources and are prohibited from disposal (Clause 5, Article 25 of the Law).
The transfer of used tires is carried out under waste disposal agreements
In fact, used tires can be transferred either directly to the business entity operating the waste disposal facility, or to a so-called intermediary organization. The purpose of the activities of intermediary organizations is to receive waste, sort it, store it, prepare it for transfer for use, and deliver it to facilities for the use of used tires.
For reference: intermediary organizations can be not only organizations whose professional activities are related to waste, but also organizations providing tire fitting services, organizations selling new tires, etc.
The intermediary organization is visible only by the subject of the contract. According to paragraph 3 of the Law, the subject of the agreement with an intermediary organization must be expressed, for example, as follows: “Acceptance of worn-out tires into ownership for the purpose of transferring them for use.” And the subject of the agreement with the organization directly operating the facility for the use of worn tires can be expressed, for example, like this:
“Acceptance of worn tires into property for their use”;
"Recycling of used tires."
The transfer of used tires, as a rule, is carried out under waste disposal agreements with the owner of the tires paying the costs of taking ownership of the tires. Such an agreement is concluded in writing both when transferring used tires to waste disposal facilities, and when transferring waste to an organization to an intermediary. As a rule, the difference for the owner of worn-out waste when choosing an organization is only in the cost of transferring the waste. It is higher for intermediary organizations.
The intermediary organization must register an agreement on the disposal of used tires
If the waste transferred into ownership is included in the List of hazardous waste, transactions on the transfer of which for a certain period (except for the transportation contract), as well as on the alienation of which to another legal entity or individual entrepreneur handling waste, are subject to registration, approved by a resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated October 23, 2009 No. 1391 (hereinafter referred to as the List), then transactions for their alienation are subject to mandatory registration with the territorial body of the Ministry of Natural Resources (part one, paragraph 4, article 3 of the Law).
The registration procedure is established by the Regulations on the procedure for registering transactions on the transfer of hazardous waste for a certain period (except for the transportation contract), as well as on the alienation of hazardous waste to another legal entity or individual entrepreneur handling waste, approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated January 17, 2008 No. 61 (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations).
Standards for using car tires
Based on the norms provided for by Federal Law No. 196-FZ of December 10, 1995 (Article 19), it is prohibited to operate vehicles with technical defects, as this may lead to a threat to road safety.
This list of faults is determined by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 23, 1993 No. 1090. This list includes the following damages specified for car tires, in the presence of which the tires cannot be used:
- The tire tread is worn off, i.e. The tread pattern has a height below the norm: for passenger cars the norm is 1.6 mm, for trucks the tread height should not be lower than 1 mm, for buses – 2 mm.
- The tire has significant damage in the form of holes, cuts, breaks that expose the cord. Such faults include a delaminated tire carcass and a peeled tread or sidewall of the tire.
- Lack of fasteners (bolts, nuts), broken shape of mounting holes or change in size.
- The presence of various cracks on the disk and wheel rims.
- The tire mileage has exceeded the standard number of kilometers or the tire service life established by law has expired.
The presence of the above damage is grounds for writing off car tires, since they cannot be used with such damage. Therefore, new tires must be installed on vehicles.
The write-off of tires unsuitable for use must be reflected in the accounting documents. There is currently no legislation that would regulate the decommissioning of tires. As a result, organizations have to either follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the use of tires, or determine the service life of the tires themselves based on their condition and suitability for use.
Important! Using tires that have become unusable due to damage is dangerous! This may result in a traffic accident. A worn-out tread surface leads to deterioration in vehicle control, and an exposed cord can cause the rubber to rupture, which leads to a complete loss of vehicle control and an accident.
Tires subject to write-off must be recycled. To do this, a certain form of agreement is concluded with the organization that accepts tires for recycling and then transports the written-off rubber to a tire repair plant for processing.
Write-off of tires that cannot be repaired
Tires are subject to write-off and subsequent disposal only when they have become completely unusable and for this reason their further operation is not possible. Whether they can actually be used or not, especially in the presence of specific damage, is determined taking into account the applicable operating standards. For example, the tread depth turns out to be higher than permissible, which is not the norm. Therefore, the part is not allowed for use.
Unusable tires are replaced, and all related operations are displayed in the established order. Typically, write-off is carried out by decision of the authorized special commission of the institution. In this case, everything is drawn up in accordance with the directives of the accounting policy.
The fact of write-off can be documented, for example, through a standard accounting system. certificate (OKUD 0504833), as well as a standard write-off act (OKUD 0504230). The movement of tires is displayed through their removal from the vehicle. sch. 09 and acceptance of those already written off as waste. sch. 02 at the price specified at write-off or conditionally 1 pc. – 1 rub.
Thus, when writing off tires, a budgetary institution should be guided by the settings of its accounting policies, Instructions No. 174n and 157n. By posting, state employees display the following:
- DT 0 105 36 340 CT 0 401 10 189 (receipt of tires that cannot be repaired on the day of their acceptance at the estimated price);
- DT 2 401 10 172 CT 2 105 36 440 (their scrapping is shown);
- DT 2 209 89 560 CT 2 401 10 172 (income from scrapping is shown).
For your information, public sector employees have the right to spend the money received from recycling as a profit-generating activity at their discretion. But at the same time, the possibility of carrying out this type of activity must be provided for in the constituent documentation. Grounds: clause 3 of Art. 298 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Vehicle mileage standards
IMPORTANT! A sample of the Regulations on the operation and accounting of tires from ConsultantPlus is available at the link
Currently, there are no legal documents for the write-off of tires and other vehicle spare parts for commercial organizations.
The standards determining the operational mileage of car tires are established by the manufacturer based on a letter from the Ministry of Transport of Russia. In this regard, each head of a commercial organization has the right to independently establish mileage standards, based on the recommendations of the manufacturer, and consolidate these standards with his own order for the organization.
In the absence of information from the manufacturer on recommendations for the operation of car tires, the company’s own operational experience or recommendations from other manufacturers for the production of the same tires are used.
When developing and approving tire mileage standards, the head of the organization must take into account that the standards he approves comply with the criteria established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. He must justify these norms, justify them economically and document them.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question No. 1: How to deregister a high-mileage tire that has been in use for a long time?
Mileage in itself cannot be a reason for writing it off or replacing it. Therefore, if it is technically serviceable and can still be used, then there is no need to remove it for scrapping, restoration or other purposes. In other words, this shouldn't happen.
Author: M. Mishanina
Car tires can be replaced due to wear and tear, damage, or when weather conditions change. How to properly organize the accounting of tires and reflect the operations of their acquisition, installation and write-off in budget accounting is described in the article.
Accounting
Car tires that are purchased separately from the car are reflected in accounting in account 10 “Materials”. The basis is the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of the enterprise and the Instructions for its application, adopted by the Ministry of Finance of Russia.
When tires are handed over for use, they are written off to cost accounts.
The basis for this is the Accounting Guidelines approved by the Russian Ministry of Finance.
The cost of the tires themselves is written off from account 10 “Materials”, subaccount “Spare parts” to the accounts receivable for cost accounting. Control of the movement of automobile tires is carried out by accounting in the off-balance sheet account D-t account 012.
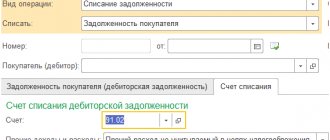
In the event that tires are taken out of service, the basis of which is a write-off act, they (the tires) are credited to the warehouse at the cost of the waste. The movement of written-off tires, their availability, as well as scrap tires are taken into account in the “Materials” and “Other Materials” accounts as scrap materials.
Waste that is generated in the departments of enterprises is collected in the established manner, their name and quantity are indicated in the delivery notes and transferred with the waybills to the waste warehouse. The enterprise, focusing on the prevailing prices for scrap, waste and rags, determines the cost of waste. The price must correspond to that which can be used for sale.
For your information! Tires that are unsuitable for retreading can be disposed of by a specialized organization on the basis of a concluded agreement.
Material assets that remain in the organization after the write-off of items that are unsuitable for restoration and further use are accounted for at the current market value. The corresponding amounts are credited as the financial results of a commercial enterprise, that is, in accounting, the waste that remains after the write-off of waste materials is credited to account 91: D-t account 10 “Materials”, subaccount 6 “Other materials” Set account. 91 “Other income and expenses.” Tires that are unsuitable for refurbishment are taken into account as scrap materials.
In accounting, the delivery of unusable tires to the balance sheet of a specialized organization is recorded as a regular sale. And income received from the sale of inventories is taken into account along with other income. In this case, tires subject to disposal are reflected in the accounting documents as other expenses.
Acceptance of tires for registration.
The procedure for recording car tires depends on the conditions of their receipt by the institution: together with the vehicle or separately from it.
In the first case, tires are subject to reflection as part of a fixed asset item (car) on account 0 101 05 000 “Vehicles” and participate in the formation of its value. In the second, tires must be accounted for as inventories on account 0 105 06 000 “Other inventories” (clauses 53, 117 of Instruction No. 157n [1]).
Car tires included with the vehicle are not taken into account separately. Information about them is reflected in the inventory card for accounting for non-financial assets (f. 0504031).
Tires related to materials are accepted for accounting at actual cost, which is formed according to the rules provided for in clause 102 of Instruction No. 157n, on account 0 106 04 000 “Investments in inventories” (clause 133 of Instruction No. 157n).
According to Instructions No. 65n [2], expenses for the purchase of such tires are included in expense type code 244 “Other purchase of goods, works and services” in conjunction with Article 340 “Increase in the cost of inventories” of KOSGU.
Documents confirming the fact that tires have been received by the institution and accepted for accounting are the supplier's shipping documents or an advance report (f. 0504505), as well as a receipt order for the acceptance of material assets (non-financial assets) (f. 0504207).
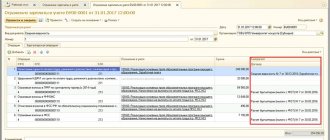
Calculations for the purchase of tires, as well as their capitalization, are reflected in accounting by the following correspondence accounts:
The procedure for recording tires should be prescribed in local acts of the budgetary institution. In general, the organization of “budget” accounting requires, at a minimum, the development of appropriate documentation.
Accordingly, all state employees independently develop the necessary forms, forms, first of all, of primary documentation (for the purposes of acceptance, issuance, write-off of parts and other required operations), including cards for recording the operation of tires. The developed documentation forms should include, among other things, a list of persons responsible for the optimal use of tires and the procedure for monitoring their operation.
For the purposes of organizing the operation of vehicles, the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation advises to follow the relevant orders: No. RD-3112199-1089-02 dated 09.26.2002, No. AK-9-r dated 01.21.2004 and No. AM-23-r dated 03.14.2008.
Director of the Department of Administration S. A. Rumyantsev
Thus, when organizing the registration of tires and developing the necessary forms, the following regulatory documentation should be taken into account.
| Title of the document | Adopted by | Features of application |
| Rules for using tires |
(briefly – AE 001 04)
Temporary operating standards. (warranty) tire mileage
(briefly – RD 3112199 1085 02)
Introduced by the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation, Order 04.04.2002 together with the “Classification of Motor Vehicles”
(as amended on December 7, 2006)
Standards for fuel and fuel consumption
No. AM-23-r dated March 14, 2008
So, for example, for the purposes of tracking the operational mileage of vehicles and other actions, an institution has the right to develop its own form of registration card or take the sample proposed by Rules No. AE 001 04 (see Appendix No. 12).
Special attention should be paid to this document, since it records, in fact, all operations that relate to the movement of tires and are then reflected in accounting. For each new (and any other) tire installed on a vehicle, the responsible technical service person creates a separate registration card. This is a standard form (OKUD 0504031), the form of which was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 52n dated March 30, 2015 (see above).
The registration card must display all information on received tires (after repair, new, etc.) until they fail. They are stored according to the vehicle number, and are closed only after these spare parts are written off as scrap. At the same time, the results of their inspection and the conclusion of the commission are recorded on the card.