Accounting for business trips has a number of nuances: designation in the timesheet, payment procedure for the time spent on a business trip, calculation of average earnings, payment of travel allowances. The article examined the main nuances of accounting for business trips in 1C 8.3 ZUP:
- preliminary program setup;
- how to arrange a business trip in 1C 8.3 ZUP 3.1;
- how to calculate a business trip if it begins in the month the employee was hired;
- how to pay for work on a day off on a business trip.
Preliminary settings for travel accounting
You can register a business trip in 1C ZUP 3.1 using the documents Business trip and Group business trips (T-9a) . In order for documents to appear in the program, you will need to select the checkboxes for accounting for business trips in Setting up the composition of accruals and deductions (Settings - Payroll - Setting up the composition of accruals and deductions - Accounting for absences).
Purpose of the checkboxes:
- Business trips – connects business trip accounting in the program.
- Including intra-shift – if the checkbox is checked, it becomes possible to take into account business trips for part of the working day (intra-shift).
- Long-term business trips should be paid monthly – affects the calculation of payment for business trips that transfer to another month. It becomes possible to pay for a business trip not immediately for the entire period, but monthly.
Payment of travel allowances
If in the document 1C ZUP “Business trip” on the “Main” tab the payment “With salary” or “With advance payment” was selected, then when creating and automatically filling out a general statement for salary or advance payment, the program will include travel allowances in it.
If the payment “During the inter-settlement period” was selected, it can also be issued automatically. This can be done in two ways.
1) In the “Business Trip” document, click the “Pay” button:
The completed “Payment of accrued salary” form will open, containing data on the payment of travel allowances. It indicates the payment document - a statement to the cashier or to the bank, depending on the existing settings for the organization and for a specific employee. By clicking the “Edit” button, you can edit the statement if necessary.
By clicking the “Post and close” button, the statement will be posted.
2) Another way to reflect the payment of travel allowances during the interpayment period is to create a new statement for salary payment, select “Business trips” in the “Pay” field, and use the link to indicate one or more supporting documents – “Business trip”. The payout amounts will be filled in automatically. Then process the payment as usual.
How to arrange a business trip in 1C 8.3 ZUP
Business trip
create a new document Business trip in the section Salary - Business trips or Main - All absences of employees by command Create .
The month in the document is the month of accrual. Employee is the employee whom we send on a business trip. The period of a business trip is reflected using the details Start Date and End Date .
If the program includes maintaining a staffing table (Settings - Personnel records - Setting up a staffing table), then a temporary release of the rate can be registered in the document. To do this, there is a checkbox Free up the rate for the period of absence . The replacement of a posted worker for the period of his absence can be entered by clicking the Create based .
If intra-shift travel accounting is enabled and the document has the Part-time (intra-shift) business trip , the Start Date and End Date are not displayed. Instead, you will need to indicate the specific day you are on a business trip and the number of hours.
If monthly accounting of long business trips is enabled, for a rolling business trip (for example, from 11/29/2021 to 12/06/2021), you can select the payment method:
- Pay for the entire period of the business trip – the document will calculate the payment for the entire period of the business trip.
- Pay for a business trip at the end of each month - the document will only accrue payment for the month the business trip began (from November 29 to 30). Payment for the part of the business trip falling within the next month (from December 1 to December 6) will be calculated in the document Calculation of salaries and contributions . In our example, payment for December 1-6 will be accrued in the December document.
If in the Business Trip the Take into account minimum wage when paying according to average earnings checkbox is selected , when calculating payment, the program will compare the employee’s average earnings with the minimum wage and use the highest value in the calculation.
You can open a transcript of the average earnings calculation by clicking the button with the “pencil” sign.
Payment for a business trip can be paid not only with salary, but also with an advance or interpayment. The payment procedure can also be selected in the Business trip :
- With salary - this is the default value, the amount will be included in the statement with the operation type Monthly salary .
- With an advance - the amount will be included in the statement with the type of operation Advance .
- During the interpayment period - used if you need to pay for a business trip separately, without reference to salary or advance payment.
Details Planned payment date – the date when the accrued amount is planned to be paid.
Detailed information about accruals registered by the document can be viewed on the Accrued .
If an employee is sent on a business trip to an area with special territorial conditions, on the PFR Experience , check the box During the business trip, territorial conditions have changed . From the proposed list of codes, we will select the conditions in which the employee will be during the business trip.
If a business trip interrupts the employee’s preferential service, you will need to enable the Do not include the period in the service record for early assignment of pension .
Additional tab contains:
- props Account, subconto Method of reflecting wages in accounting – allows you to set your Reflection method (Settings - Methods for reflecting salaries in accounting) to pay for a business trip registered with a document;
- group of details Print data – additional information for printed forms.
If you need to correct a document Business trip , this can be done in two ways:
- create a patch document using the command To correct;
- make changes directly to the source document and recalculate the payment using the button with round arrows.
You can also cancel a business trip in two ways:
- on command Cancel;
- Mark the original document for deletion.
Pay button is used only for business trips with the payment procedure During the interpayment period . When you click the Pay button, Payout Statement
the Print button, you can generate the following printed forms and certificates.
Group mission (T-9a)
Group Business trip document allows you to register a business trip for several employees at once. The document can be created in the sections Salaries - Group travel (T-9a) or Main - All absences of employees. also create a group business trip in the Business Travel (Salary - Business Travel or Personnel - Business Travel) by clicking the Create T-9a .
Let's fill in the list of seconded employees using the Selection or Add .
If the business trip parameters are the same for all employees, you can first create a line for one employee, fill it in and then copy this line, changing the employee.
Group Business trip document facilitates the process of registering business trips for several employees. But it does not affect timesheets and payroll calculations - for these purposes you need to create individual documents Business trip . It is convenient to do this directly from the Group Business trip .
We will register absences for employees in one of two ways:
- selectively via link Register absence in the column Accounting for absence and accrual;
- immediately for all employees in the document via the link Register absences under the tabular part.
After registering individual Business Trips in the Timesheet (Salary – Time Accounting – Timesheets), the days of the business trip will be reflected by code K ( Business Trip ).
Reimbursement of expenses incurred by an employee in connection with a business trip
The list of expenses that the employer is obliged to reimburse to an employee sent on a business trip is established by Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and includes:
- travel expenses;
- expenses for renting residential premises;
- additional expenses associated with living outside the place of permanent residence (per diem);
- other expenses incurred by the employee with the permission or knowledge of the employer.
The procedure and amount of reimbursement of expenses related to business trips are determined by a collective agreement or local regulations of the organization. At the same time, it should be taken into account that for employees of organizations financed from the federal budget, reimbursement of expenses associated with business trips is made in accordance with the norms established by law.
For other organizations, the norms and procedures for reimbursement of travel expenses are established only for tax purposes.
Before leaving on a business trip, a posted employee is given a cash advance within the limits of the amounts due for travel, expenses for renting accommodation and daily allowance.
Within three days upon returning from a business trip within the territory of the Russian Federation (or within 10 calendar days from the end date of a business trip outside the Russian Federation), the employee is required to submit an advance report on the amounts spent in connection with the business trip and make a final payment for them.
Settlements for reimbursement of travel expenses with employees sent on business trips are not registered in the 1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8 program, since they do not relate to payroll calculations.
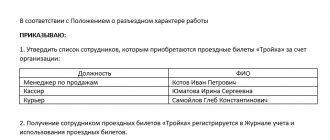
At the same time, unspent and not returned timely advances issued in connection with a business trip may be deducted from the employee’s salary. The deduction is registered in the “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8” program using the document “Registration of one-time deductions of employees of organizations” (Fig. 3). The corresponding type of deduction must be described in the plan of calculation types “Retention of organizations” with the calculation method “Fixed amount”.
Rice. 3
Business trip in the month of hiring
When sending on a business trip in the month of hiring, there is one difficulty - the program does not yet have data to calculate average earnings. Let's figure out how to get around this.
- Register your business trip. Since the employee has not yet worked for at least a month, after entering a business trip a warning will be issued:
- Click the “pencil” button to open the average earnings breakdown form and fill in the data for calculation using the Add button according to payroll data. Information for calculating the average will be filled in according to the employee’s planned accruals included in the payroll.
- After saving the changes in the calculation of average earnings, clicking OK in the document will automatically recalculate the accruals.
How to conduct a business trip on weekends in 1C 8.3 ZUP 3.1
If, while on a business trip, an employee is required to work on his day off, this must be additionally reflected in ZUP 3.1. In the Business trip , payment based on average earnings is calculated only for working days on a business trip. Let's look at how to reflect work on a day off while on a business trip.
- We will register your business trip as usual. Payment in document Business trip will be calculated only for working days.
- To register work on a day off while on a business trip, we will create a document Work on weekends and holidays (Salary – Time tracking – Working on holidays and weekends). We will indicate the days when the employee was involved in work on days off, and select the method of compensation (time off or increased pay).
- Payment for work on weekends will be calculated in the document Calculation of salaries and contributions. The calculation will be made based on the cost of the employee’s day (hour).
Taxation of travel expenses for personal income tax and unified social tax
According to paragraph 3 of Article 217 and subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 238 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, all types of legally established compensation payments related, in particular, to reimbursement of travel expenses, are not subject to personal income tax and unified social tax.
When the employer pays the taxpayer expenses for business trips both within the country and abroad, daily allowances paid within the limits established in accordance with current legislation, as well as actually incurred and documented targeted expenses for travel to the destination and back, are exempt from taxation. fees for airport services, commission fees, expenses for travel to the airport or train station at places of departure, destination or transfers, for luggage transportation, expenses for renting living quarters, paying for communication services, obtaining and registering a service foreign passport, obtaining visas, as well as expenses associated with the exchange of cash or a check at a bank for cash foreign currency.
Please note that from January 1, 2008, Federal Law No. 216-FZ of July 24, 2007 establishes daily allowance limits that are exempt from personal income tax: up to 700 rubles for each day of a business trip in the Russian Federation and up to 2,500 rubles for each day of stay on a business trip abroad.*
Note:
* Read more about these changes to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in the article by L.P. Fomicheva “The Tax Code of the Russian Federation has been corrected again” in issue 9 (September) of “BUKH.1S” for 2007, p. 6.
For the purposes of calculating personal income tax in the program “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8”, excess daily allowances, undocumented transportation expenses and expenses for renting residential premises, as well as other expenses not expressly mentioned in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, reimbursed in connection with sending on a business trip , must be accrued to the employee in the form of non-monetary income. The accrual is made by the document “Registration of one-time accruals to employees of organizations.” The types of calculations by which income is calculated must be described in terms of the types of calculation “Basic accruals of organizations” or “Additional accruals of organizations” with the checkbox “Is income in kind” checked (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4
For the purposes of calculating personal income tax, such income is accounted for under code 4800 “Other income”.
For the purposes of taxation of UST and insurance contributions to the Pension Fund for organizations that pay income tax, the accrual type form is set to the value “Not subject to taxation of UST, contributions to the Pension Fund in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 236 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (payments from profits).” For organizations that apply special tax regimes, i.e., that do not pay corporate income tax, such accruals must be subject to contributions to compulsory pension insurance. For them, as a method of taxation of UST and contributions to the Pension Fund, the value “Taxed by UST, contributions to the Pension Fund in its entirety” should be specified (in fact, in the program in this case, only contributions to the compulsory pension fund will be charged).
The accruals in question are also subject to contributions for compulsory accident insurance, which is indicated accordingly in the accrual type form.
When determining the amount of excess daily allowance, it should be borne in mind that the norms are established in the amount of payments for each day the employee is on a business trip, including the time spent on the road. The day of departure on a business trip is considered to be a calendar day (up to 24 hours inclusive) during which a train, plane, bus or other vehicle departs from the place of permanent work of the business traveler, and the day of arrival is a calendar day (up to 24 hours inclusive) during which the transport the product arrives at the place of permanent work. If a business trip lasts one day, per diem is not paid. If the place from which the vehicle departs is located outside the boundaries of the locality in which the organization is located, then when determining the days of departure and arrival, the time required to travel to the place of departure of the vehicle is taken into account. The same procedure applies if the business traveler has the opportunity to return daily to his place of permanent residence (the availability of such an opportunity is decided by the employer in each specific case).