Amount of one-time benefit for a newborn
In Art. 12 Federal Law No. 81-FZ dated May 19, 1995 established a payment of 8,000 rubles. But this value is growing every year. The latest indexation was established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 73 of January 28, 2021. From February 1, 2022, the benefit is 18,886 rubles. 32 kopecks From February 1, 2020 to January 31, 2022, it was 18,004.12. Indexation was 4.9%.
When calculating benefits, consider the following:
- Firstly, the size of the payment is affected by the child’s birthday, and not the day the payment is applied for. For example, if a child was born on January 31, 2022, and the mother applied for benefits on February 17, 2021, then she is entitled to a payment in the amount of 18,004.12 rubles, that is, in the amount before indexation, which is applied in 2022.
- Secondly, the amount of the benefit depends on the regional coefficient. For example, in the city of Barnaul, Altai Territory, the coefficient is 1.15. This means the payment is 18,886.32 × 1.15 = 21,719.27 rubles.
- The benefit is not subject to personal income tax and insurance premiums.
If an employee needs help financially
Many employers provide financial support to employees from time to time. Let's find out how financial assistance is processed, what is taxed and whether it is reflected in tax accounting under the simplified tax system
Financial assistance is paid to employees at the request of the employer and upon the occurrence of certain events: weddings, birth of a child, death of a relative, etc.
In other words, it is the head of the organization or individual entrepreneur who decides when, to whom and in what amount it is due. Financial assistance refers to non-production payments, is one-time in nature and is not related to the employee’s performance of work duties.
Documenting
To receive financial assistance, an employee must write an application and indicate in it the event in connection with which he expects to receive it. Documents confirming the existence of special circumstances are attached to it.
Having received the application, the manager makes a decision on payment or non-payment of financial assistance. If the answer is positive, an order to issue assistance is issued based on the application. There is no unified form of the order, so it is drawn up arbitrarily. The mandatory details of this order are the amount of money due to the employee and the deadline for its payment.
Samples of the application and order are presented in Fig. 1 and 2.
Some organizations pay financial assistance to employees using retained earnings from previous years. Let us remind you that only the general meeting of founders, participants and shareholders has the right to distribute it, including the payment of assistance (subclause 3, clause 3, article 91 and subclause 4, clause 1, article 103 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, the decision on the distribution of profits for the payment of financial assistance (directly to some employee or by creating a fund for the payment of assistance) is made by the general meeting of participants or shareholders, and it is reflected in the minutes of the meeting.
Personal income tax
According to paragraph 5 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, “simplified people” are not exempt from performing the duties of tax agents. Is it necessary to calculate and withhold personal income tax on material assistance? The amount of assistance not exceeding 4,000 rubles is not subject to personal income tax. for the tax period (clause 28 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But you will have to pay tax on the excess in the general manner. Please note: this applies even to cases where financial support is provided to former employees who left due to disability or age retirement.
Also, financial assistance paid to:
- in connection with a natural disaster or other emergency, as well as citizens - family members of persons who died as a result of these events, in order to compensate for the material damage caused or harm to their health;
- family members of a deceased employee or retired former employee;
- an employee or former employee who has retired due to the death of a member of his family;
- employees (parents, adoptive parents and guardians) during the first year after the birth (adoption) of a child, but not more than 50,000 rubles. for each child.
- citizens affected by terrorist acts in Russia, and family members of persons killed as a result of such actions.
Until 2010, the period for providing financial support in connection with the birth (adoption) of a child was unlimited. That is, whenever a payment is made that does not exceed 50,000 rubles, it is not subject to personal income tax. Now personal income tax is not withheld only from payments made within a year after birth (adoption). Such changes were introduced by Federal Law No. 213-FZ of July 24, 2009.
However, this is not all innovation. As already mentioned, personal income tax is not assessed on financial assistance issued to family members of a deceased employee or to an employee in connection with the death of a member of his family. From this year, personal income tax is also not levied on assistance paid to a former employee who retired due to the death of a member of his family or to members of his family in connection with his death (Federal Law of July 19, 2009 No. 202-FZ).
Here it is necessary to clarify who is recognized as family members. According to Article 2 of the RF IC, these include spouses, parents, children, adoptive parents and adopted children. Therefore, other relatives are not them. The Ministry of Finance adheres to the same position (letter dated 08/03/2006 No. 03-05-01-04/234).
But judicial practice on this issue is contradictory. Thus, the courts have repeatedly indicated that the family is considered as a single whole, which means that it includes both the husband’s parents and the wife’s parents.
Therefore, financial assistance provided in connection with the death of a father-in-law, mother-in-law, father-in-law or mother-in-law should not be subject to personal income tax (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated September 29, 2008 No. KA-A40/6198-08-O, Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Far Eastern District dated February 15, 2005 No. F03 -A37/04-2/4191 and FAS of the Ural District dated March 29, 2005 No. F09-1057/05-AK). However, it is unlikely that regulatory authorities will agree with these arguments, so we do not recommend being guided by them.
In addition, there is a court ruling containing the opposite point of view (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated December 30, 2005 No. KA-A40/13252-05).
Example 1
Vostok LLC uses the simplified tax system. In April 2010, driver V.P. Malysheva’s sister died. The HR department received an application from him for financial assistance. The manager issued an order to pay V.P. Malyshev 8,000 rubles. No other financial assistance was provided to the employee in 2010. In what amount should personal income tax be withheld and transferred, provided that standard and other tax deductions of V.P. Malyshev is not entitled to money in April?
Personal income tax is not charged on financial assistance paid to an employee in connection with the death of a member of his family (clause 8 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, as we found out, the Family Code does not classify sisters as family members, so in this case, personal income tax must be calculated in the general manner.
The amount is not taxed if it is less than or equal to 4,000 rubles. for the tax period (clause 28 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Personal income tax is paid on the excess. Thus, the accountant of Vostok LLC had to withhold and transfer personal income tax in the amount of 520 rubles. [(RUB 8,000 – RUB 4,000) × 13%]. The driver will be given 7,480 rubles. (8000 rub. – 520 rub.).
Insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds
According to paragraph 1 of Article 7 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 212-FZ), the object of taxation with insurance premiums is payments and other remunerations accrued in favor of citizens under labor, civil law, copyright and other similar agreements . Does this mean that if the payment of financial assistance is not provided for in the employment contract, there is no need to pay contributions?
Logically, yes. However, it will be quite difficult to prove that he is right to the regulatory authorities, or to an accountant who has not accrued contributions from financial assistance in favor of the person with whom the employment contract was concluded. And most likely the dispute will have to be resolved in court. But there is no arbitration practice on this issue yet. So for those who do not want to argue, it is better to still charge contributions. The amount of financial assistance not exceeding 4,000 rubles is not subject to contributions. (Subclause 11, Clause 1, Article 9 of Law No. 212-FZ). From an amount above 4000 rubles. contributions are calculated.
In addition, insurance premiums are not charged for financial assistance paid (subclause 3, clause 1, article 9 of Law No. 212-FZ):
— citizens in connection with a natural disaster or other emergency in order to compensate for material damage caused to them or harm to their health; — citizens affected by terrorist attacks on the territory of the Russian Federation; - to an employee in connection with the death of a member of his family; - to an employee (parent, adoptive parent and guardian) during the first year after the birth (adoption) of a child, but not more than 50,000 rubles. for each child.
Contributions for insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases
The list of payments for which insurance premiums are not charged to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 7, 1999 No. 765 (hereinafter referred to as the List). According to paragraphs 7 and 8 of the List, financial assistance provided to:
— employees in connection with emergency circumstances in order to compensate for harm caused to the health and property of citizens, on the basis of decisions of state authorities and local governments, foreign states, as well as governmental and non-governmental intergovernmental organizations; - employees in connection with a natural disaster, fire, theft of property, or injury that befell them; - in connection with the death of an employee or his close relatives.
At the same time, relatives in a direct ascending and descending line (parents, children, grandparents, grandchildren), as well as full and half brothers and sisters are recognized as close (Article 14 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation). As you can see, the term “close relatives” is much broader than the term “family members”. Therefore, when calculating personal income tax and insurance premiums, you need to be very careful.
For example, financial assistance provided to an employee in connection with the death of a grandmother is not subject to contributions in case of injury. However, if its amount is more than 4,000 rubles, personal income tax and insurance contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, TFOMS and FFOMS are charged on the excess.
Types of financial assistance not specified in paragraphs 7 and 8 of the List must be included in the base for calculating contributions for insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases. This is what the regulatory authorities think (letters from the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 18, 2007 No. 02-13/07-10008, dated October 10, 2007 No. 02-13/07-9665 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated September 14, 2006 No. 18-11/ [ email protected] ), as well as some judges (decrees of the FAS East Siberian District dated April 24, 2008 No. A33-8071/07-F02-1640/08, FAS Moscow District dated October 13, 2008 No. KA-A40/9447-08 and FAS Northwestern District dated December 15, 2008 No. A44-2062/2008), and it’s hard to disagree with them.
However, there is also an opposite opinion. Insurance premiums are calculated for wages (income) of employees, as well as for remuneration under civil contracts (clause 3 of the Rules for the accrual, accounting and expenditure of funds for the implementation of compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 02.03 .2000 No. 184). On this basis, some judges come to the conclusion that any one-time financial assistance (for marriage registration, birth of a child, anniversary, etc.) not specified in an employment or collective agreement is not related to wages and should not be subject to contributions (rulings FAS of the East Siberian District dated 02/03/2009 No. A58-3247/08-0327-F02-76/09 and the West Siberian District dated 07/27/2009 No. F04-3501/2009(11928-A27-41)).
However, we do not recommend being guided by these arguments. The position of the regulatory authorities is different, which means that you will have to defend your case in court. And arbitration practice, as we see, is both positive and negative.
Tax accounting
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system with the object of taxation being income minus expenses, take into account expenses from the list of paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Subclause 6, in particular, indicates labor costs. These include payments listed in Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There is no financial assistance among them. At the same time, the article contains paragraph 25, which talks about other payments provided for in the employment contract, but in this case it is not suitable. The amounts allocated by the employer are not included in the remuneration system and are not stimulating or rewarding in nature. These expenses cannot be called justified, since they are not aimed at generating income, therefore, the conditions necessary for accounting for expenses (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) are not met. Therefore, paid financial assistance is not taken into account in expenses under the simplified tax system. By the way, under the general regime the situation is similar: reducing the income tax base for issued material assistance is also not allowed (Clause 23, Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If financial assistance is not included in the list of non-taxable payments, then insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds are charged for an amount exceeding 4,000 rubles. And, despite the fact that the material assistance itself is not included in expenses, the contributions transferred from it will reduce the tax base on the basis of subparagraph 7 of paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, since they were paid in accordance with the law.
Example 2
Tornado LLC applies the simplified tax system with the object of taxation being income minus expenses. The director, having received a statement from Secretary I.E. in April 2010. Golubkina, issued an order to provide the employee with financial assistance in connection with the registration of marriage in the amount of 10,000 rubles. Golubkina is not entitled to standard or other tax deductions. When calculating contributions for insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases, the organization adheres to the point of view of the regulatory authorities. We will reflect the payment in tax accounting.
Since the material assistance paid is not related to the wage system, it cannot be taken into account in expenses that reduce the base for the single tax under the simplified tax system. However, it must be subject to personal income tax, pension contributions and contributions in case of injury (assume the insurance rate is 0.2%).
Personal income tax and pension contributions are calculated on amounts exceeding 4,000 rubles. The tax will be 780 rubles. [(10,000 rubles – 4000 rubles) × × 13%], and contributions - 840 rubles. [(RUB 10,000 – RUB 4,000) × 14%]. Contributions in case of injury will be 20 rubles. (RUB 10,000 × × 0.2%). After paying insurance premiums (let's say it was May 5, 2010), they can be taken into account as expenses. Personal income tax is withheld from payments to the employee, but since the material assistance itself is not an expense, the tax amount will not be either. The completed fragment of the Income and Expense Accounting Book is presented in the table.
Note that profit for distribution is determined according to accounting data, so an organization that wants to pay financial assistance to employees at the expense of profits from previous years will have to keep accounting records in full
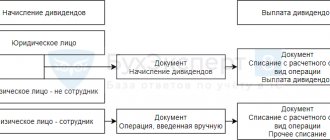
Rice. 1. Sample application for financial assistance
General Director of Coral LLC A.N. Romanov from accountant Shmeleva N.E.
Statement
In connection with the birth of a child in my family on April 2, 2010 (Dmitry Petrovich Shmelev), I ask you to provide me with financial assistance.
Attachment: copy of the child's birth certificate
Shmeleva May 11, 2010
Rice. 2. Sample order for financial assistance
Order No. 23-K
Moscow May 11, 2010
About payment of financial assistance
According to paragraph 21 of the collective agreement
I ORDER
provide one-time financial assistance to accountant Shmeleva N.E. in the amount of 40,000 (Forty thousand) rubles in connection with the birth of a child. Payments must be made from the cash desk before May 17, 2010.
Reasons:
1) statement by Shmeleva N.E. requesting financial assistance; 2) a copy of the child’s birth certificate.
General Director Romanov A.N. Romanov
Amounts not subject to personal income tax are stated in paragraph 8 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The terms of family law contained in the Tax Code are used in the meaning in which they are used in this branch of law (clause 1 of article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
According to the Ministry of Health and Social Development (see letter dated March 23, 2010 No. 647-19), payments not specified in the employment contract are subject to insurance contributions
On a note. Financial assistance and average earnings
To calculate government benefits, an accountant has to calculate average earnings. It includes all payments and rewards in favor of the employee, which are taken into account in the base for calculating insurance premiums (clause 2 of article 14 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ). It turns out that if, for example, financial assistance in connection with registering a marriage is allocated in the amount of 10,000 rubles, then it will only be included in the average earnings in part - in the amount of 6,000 rubles. According to subparagraph 11 of paragraph 1 of Article 9 of Law No. 212-FZ, financial assistance, the amount of which does not exceed 4,000 rubles, is not subject to insurance contributions.
But when calculating average earnings for other cases provided for by the Labor Code (for example, accrual of vacation pay), they are guided by the Regulations on the specifics of the procedure for calculating average wages, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2007 No. 922. In accordance with paragraph 3 of this document, when determining average earnings do not take into account payments not related to wages, including financial assistance
Brothers and sisters who have only one common parent are considered half-siblings.
According to paragraph 2 of Article 346.16, only expenses that meet the criteria of paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are accepted for accounting under the simplified tax system.
Table. Fragment of filling out the Income and Expense Book of Tornado LLC for the second quarter of 2010
| No. | Date and number of the primary document | Contents of operation | Income taken into account when calculating the tax base | Expenses taken into account when calculating the tax base |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 68 | Payment order No. 43 dated 05/05/2010 | Pension contributions transferred | — | 840 |
| 69 | Payment order No. 44 dated 05/05/2010 | Contributions in case of injury are listed | — | 20 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
In 2010, “simplified people” do not pay social insurance contributions in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity and health insurance contributions (subclause 2, clause 2, article 57 of Law No. 212-FZ)
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
Who pays a lump sum benefit upon the birth of a child?
Since the beginning of 2022, only one benefit payment system has been in force - direct payments. In this case, the employer accepts a package of documents from the employee and transfers them 5 days in advance to the Social Insurance Fund at the place of registration of the employer. The authority itself will transfer the required amount to the parent within 10 days from the date of receipt of the documents necessary to assign the benefit. Direct payments are a pilot project, which all regions of Russia joined from January 1, 2022.
Previously, along with direct payments, there was an offset system: the employee wrote an application for benefits, the employer paid it from his own funds, and then applied to the Social Insurance Fund to reimburse the expenses incurred. The company had to pay the entire amount within 10 days.
If the parents do not work, then the benefit is paid through the social security authorities.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
To receive financial assistance at work
- Make sure your employer provides this support and find out the terms and conditions.
- Collect documents that confirm the circumstances in connection with which you are asking for financial assistance.
- Write an application and attach supporting documents to it.
- If you do everything correctly, as provided in the organization’s documents, the manager will consider your request and, possibly, issue an order to provide assistance.
- You can ask for financial assistance even when it is not provided for in the company documents. In this case, the manager may refuse, or may agree to provide assistance.
Source: T—J
Documents for payment of child benefit
When applying for benefits, the employee must provide the following documents to the accounting department:
- information about the insured person. They can be requested from the employee upon employment or during work. They are submitted in the form approved by the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and are drawn up on paper or in the form of an electronic document;
- original birth certificate of the child from the registry office in form 24;
- a copy of the child's birth certificate;
- details for transferring money;
- a certificate stating that the second parent did not receive benefits. It can be obtained from the accounting department at work or from the social security office if the spouse does not work.
In addition, the employee writes a statement addressed to the employer. We recommend the following form.
The child’s parents may be divorced and do not live together, then the mother may have difficulty obtaining a certificate of non-receipt of benefits by the father. In this case, a copy of the divorce certificate and a document confirming the fact that the child lives with the applicant are attached to the application. You can get it at the passport office after registering the child at the place of residence.
A new parent should not delay receiving the payment. If he does not have time to submit documents in 6 months , it will be very difficult to receive benefits: you will have to prove that you were seriously ill, you were prevented by natural disasters, it was a long and difficult move, or the employer is to blame for everything.
Documents for the Social Insurance Fund from the employer
The employer submits documents (information) to the Social Insurance Fund within five calendar days after the employee’s application. They can be submitted:
- on paper or electronically, if the average number of employees does not exceed 25 people;
- only electronically if the average number of employees is more than 25.
When submitting documents on paper, in addition to the main list of papers, you will need an inventory of them. The inventory form is approved by the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation (clause 3 of the Regulations on the specifics of the appointment and payment of VNiM benefits in 2022).
If you submit documents electronically, you only need to submit a register of information. The register is compiled electronically on the basis of data available to the employer and documents submitted by the employee (clauses 1.2, 1.4 of the Procedure for filling out the register of information). In column 19, mark all information that is not included in the register form, but is important when assigning benefits. For example, the name of the district or locality, if the benefit needs to be increased by the district coefficient.
If the employer does not submit all the documents or makes errors during preparation, the Social Insurance Fund will not award benefits. First, he will send a notice to provide the missing information. In addition, the official may be fined 300-500 rubles.
What is financial assistance
Financial assistance is a social benefit. You receive money not for work, but due to life circumstances - I will tell you more about them below.
You can receive financial assistance at your place of work if your employer has provided this type of support. Some companies provide assistance to family members of employees and even former employees, but this is rare.
To whom it is due. Since the employer is not obliged to provide financial assistance to employees, he decides who and how to pay it. He can enshrine support measures in a local act if he wants to clearly indicate to whom and when he can provide assistance.
The document may be called, for example, a provision on financial assistance. But this is not necessary - the employer can include the conditions and amount of payments in the internal labor regulations, in the regulations on remuneration or other internal document. If a collective agreement has been concluded with employees, financial assistance may be a section of such an agreement.
Documents on financial assistance indicate what types of assistance the employer provides, in what amount and in what order employees receive it.
You can find out whether your company provides financial assistance from an accountant or HR officer. Typically, such documents are introduced during employment, and if a local act is adopted later, at the time of adoption. But you can view them at any time. The document must be shown within three working days after your written request.
Who pays? Financial assistance is paid by the employer - an organization or an individual entrepreneur. In this article I will tell you in detail about this type of support.
Members of trade union organizations can also count on the help of a trade union if it has a provision on providing financial assistance. An educational institution can provide assistance to undergraduate and graduate students. And in emergency situations, you can receive financial assistance from the budget - I’ll also tell you briefly about this type of help.