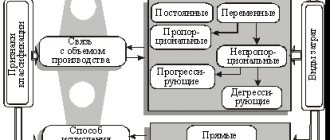
Large holdings and networks are developing an incentive system and often pursue an active social policy: they help employees financially, give gifts for holidays and birthdays.
The same thing happens in small businesses, just with a difference in scale and approach. The principles of accounting are the same everywhere. If you organize it correctly, the tax base will be reduced or at least it will be possible to avoid subsequent problems during the audit.
One-time payments include in particular:
- Prizes - any, incl. not related to work.
- Financial assistance - for an event upon application in connection with a difficult life situation and others.
- Gifts - in kind (even such as a car and real estate), cash and others.
We write accounting policies and regulations
Some specialists, especially in the creative field, high-quality professionals who have a choice of offers, are attracted by the social package.
In order for employees to see what they will get from working for the company, in addition to salary, it is worth clearly describing the incentive options and determining what you are willing to spend on. Then collect the data in a separate statement, which will become part of the accounting policy. It also specifies the nuances of accounting and tax accounting.
Note! Each employee must be familiarized with the document against signature.
If personal bonuses are established for someone (usually managers), they are prescribed in a separate clause of the employment contract. In other cases, the text simply refers to the provision (there is no need to bloat the document).
You can also provide general language. For example, “an organization has the right to reward an employee for work, achievement of professional results and for other reasons.” However, this option is not supported by the tax authorities; they require specifics and clear definitions of when and for what the employee receives incentives.
As an example of a bonus clause, you can use our sample.
What does tax accounting and the calculation of contributions from incentives look like?
When developing accounting policies and local regulations, remember the following principles:
- To accept cost amounts in tax accounting, indicate them as part of the payroll, tie them to work activity, but you will have to impose contributions on them. If, on the contrary, you reflect the costs of incentives as payments not related to work, then they will not fall into the base for contributions, but it will be impossible to accept them as expenses. We choose from two evils what is more profitable for you.
Note! Bonuses from targeted funds, at the expense of trade unions, remuneration to employees and managers beyond those mentioned in the concluded agreements will not be included in expenses. The basis is clauses 21 and 22 of Article 270 of the Tax Code.
- Holiday bonuses and other non-working payments to employees cannot be included in expenses. You can try to reformulate them in order to still include them in costs. For example, birthday bonuses should be correlated with length of service in the organization and a gradation should be created - the longer the period of work, the greater the incentive. True, there remains a possibility that the approach will not suit the tax authorities, and you will have to go to court for a solution. There is positive judicial practice for the employer.
- The calculated contributions, regardless of the payments themselves, will be fully included in the costs - paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Financial aid, regardless of the size and purpose, will definitely not be included in tax expenses (clause 23 of Article 270 of the Tax Code). But for some of its types there will be no need to charge insurance premiums. For example, they do not tax assistance in the amount of up to 50,000 at the birth of a child (the main thing here is to meet the deadline - make the payment within the first year after birth). You can get by without charging contributions if you provide assistance of up to 4,000 rubles per year to your employees in other situations. Links - pp. 3 and 11 p. 1 p. 422 NK.
- Regardless of the form, any gifts require the execution of a gift agreement if the value of the gift is more than 3 thousand rubles (clause 2 of Article 574 of the Civil Code), but to document the transaction it is recommended to always draw it up, even when the amount is less.
- The Labor Code establishes that one of the reward options can be a valuable gift (Article 191). Having established this type of incentive in the company and designated it as part of the payroll, you will have to charge insurance premiums for it.
- When, in accordance with the GPC agreement, a transfer of ownership is carried out (for example, a company donates a car, an apartment), contributions will not be charged (clause 4 of Article 420 of the Tax Code).
- The donation transaction is subject to VAT (clause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code). An exception is the gift of money (subclause 3, clause 1, article 39 of the Tax Code). Payers will be companies that work for OSNO. An organization (or individual entrepreneur) that uses UTII, does not conduct other activities and has not switched to the simplified tax system, is also required to pay VAT.
By the way! Some taxpayers and even judges have a different opinion regarding VAT. Alternatively, you can take into account gifts that are specified in the company’s internal documents as part of the Payroll Fund, and not calculate VAT. In practice, it is safer, of course, not to argue with inspection authorities, especially when it comes to rare and small gifts.
The line between rewarding for work achievements and the desire to please employees “just because” is thin, so you will have to defend yourself and firmly justify your own point of view (with documentation, of course). The Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund are also interested in non-taxable payments; they are especially attentive to them during an on-site inspection.
How are gifts made?
To give gifts to employees, you need to draw up an appropriate administrative document - an order from the director. If the cost of the gift is more than 3,000 rubles, the donation is formalized by a written agreement in accordance with Art. 574 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The agreement can be formalized as a multilateral one if there are many employees (Article 154 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, you need to create a statement for the transfer of gifts - in it, the staff will confirm with a signature the receipt of the gift.
In general, gift processing is carried out using the following steps:
- issuance of an order, which the staff reads and signs;
- generation of a statement and signature by each employee at the time of receipt of the gift;
- execution of a gift agreement when the value of the gift is more than 3,000 rubles.
The contract specifies the name of the gift, the date and place of preparation, information about the company and employees, a description of the gift with characteristics and cost, and the signatures of the parties.
We understand the withholding and calculation of personal income tax
The bonuses will have to be taxed in full and there are no exceptions for them.
We list some exceptions from the taxable base, the list is incomplete, others can be found in Article 217 of the Tax Code, with references to items specifically from it in parentheses.
- Financial assistance paid to a working or former employee (if his dismissal is related to retirement) - in the amount of up to 4,000 per year (clause 28).
- Assistance provided by an organization to an employee at the birth (adoption, receipt of guardianship) of a child (up to a year after birth) - up to 50,000 rubles (clause 8).
- Any assistance to veterans and disabled people of the Great Patriotic War; for former prisoners (detailed list in paragraph 33) - up to 10,000 rubles during the year.
- Any other gifts from organizations and individual entrepreneurs received by the taxpayer during the year in a total amount not exceeding 4,000 rubles (clause 28).
By the way! You can give gifts to the child and another relative of the employee, not just himself. There will be a limit of 4,000 per year for each person. The main thing is to draw up a gift agreement in the name of the appropriate person.
“Gift” personal income tax
A gift is income in kind, which is taken into account when determining the tax base for personal income tax (Clause 1, Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, paragraph 28 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation exempts from taxation gifts received by individuals from organizations whose value does not exceed 4,000 rubles per year. It is unlikely that a children's New Year's gift will cost more. This means that the employee most likely will not have any obligation to withhold personal income tax. In this case, the organization is required to keep personalized records of these incomes (see, for example, letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 20, 2017 No. 03-04-06/2650). Important! Recommendation from ConsultantPlus The transfer of the gift must be documented, otherwise the income will not be considered a gift (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/28/2020 N 03-04-06/14371, dated 08/12/2014 N 03-04-06/40051). Such documents are... For more details, see K+. Trial access is available for free.
If a gift costs more than 4,000 rubles, or the organization gives gifts not only to children, but also to the employees themselves, and not only on New Year, but also on other holidays, and the total cost of gifts for the year exceeded the tax-exempt amount, for this income the organization becomes a tax agent (clause 1 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But only in relation to the excess amount, from which the tax must be calculated.
An example of calculating personal income tax when issuing several gifts in a calendar year from ConsultantPlus Situation: An organization gave three gifts to an employee (tax resident of the Russian Federation) during the calendar year: the first gift - by March 8 in the amount of 1,500 rubles; the second gift in June for a professional holiday in the form of a vase worth 2,000 rubles; the third gift in December for the New Year in the amount of 1,000 rubles. The issuance of each gift is formalized by order of the manager. Calculation of personal income tax can be viewed in K+. Trial access to the system is free.
See also “Are gifts under 4,000 rubles reflected in 6-NDFL?”
Who will pay the tax?
We withhold personal income tax from the employee’s income. If we give out money, it is done directly from it. If the remuneration is in kind - payment for a spa, swimming pool, some goods, then from other income.
Let’s imagine a generous employer and a lucky employee who received something valuable as a gift: an apartment, a car, expensive jewelry. The cost of such things is high, which means that the tax will be rather large.
Despite the gratuitous basis of the gift agreement, do not forget to indicate the value of the gift, otherwise it is impossible to determine income. If the employee’s income does not allow personal income tax to be withheld until the end of the year, then the tax agent is not obliged to fulfill his duties indefinitely. You just need to inform the Federal Tax Service with a certificate 2-NDFL (sign “2”) before March 1 of the next year that there is a balance of uncollected tax, it will send the taxpayer a notification about the amount of the debt and the deadline for payment.
Explain to the employee the nuances of taxation to avoid disagreements in the future.
The timing of personal income tax transfer depends on the form in which the payment is made.
- we issue money - we deduct it directly from income and transfer it no later than the next day;
- we give an item, a certificate, pay for something - we transfer personal income tax to the budget no later than the day following the day of actual tax deduction.
Accounting entries
In different cases, accounting methods are similar, but there are differences in the types of payments and other incentives. We give gifts, give out financial assistance or bonuses not related to work, using the transactions below.
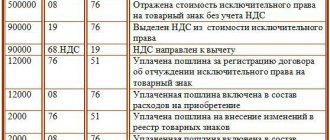
Option 1. Goods purchased from a supplier with VAT. Organization - VAT payer:
- D 10 K 60 – purchases received.
- D 19 K 60 – input VAT is taken into account.
- D 60 K 51 (71) – paid for the purchase to the supplier with a settlement account (or through an accountable person).
- D 68 VAT K 19 – VAT is accepted for deduction.
- D 73 (76) K 10 – issuing incentives to employees (other individuals).
- D 91.2 K 73 (76) - the cost of purchased items is written off as other expenses. Sometimes postings No. 5 and No. 6 combine D 91.2 K 10, but this is not correct.
- D 91.2 K 68 VAT – VAT charged.
- D 99 K 68 NP – reflects the permanent tax liability (PNO) for income tax (PBU 18/02), calculated by the formula (amount of incentive in the form of an item + VAT) * 20%.
- D 73 K 68 – personal income tax is charged.
- D 91.2 K 69 – contributions accrued.
- D 70 K 73 – personal income tax is withheld from wages.
Note! PBU 18/02 is not applied by those who do not pay income tax (for example, organizations using the simplified tax system, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax) and is optionally applied by companies maintaining simplified accounting (for example, small businesses).
Similar entries are made when an organization “pays” with goods that it usually trades (account 10 will replace another - 41 “Goods”) or transfers its own products (instead of 10 “Materials” account 43 “Finished Products” and there are no first 4 entries).
Option 2. Certificates, tickets, gift cards and other monetary documents, which are used to subsequently provide services or purchase goods:
Here everything is exactly the same as in Option 1, only count 10 changes to 50.3 “Cash documents”.
Option 3. Money:
- D 73 (76) K 50 (51) – funds were issued from the cash register or transferred through the bank.
- D 91.2 K 73 (76) - writing off the amount as other expenses.
- D 99 K 68 Income tax - PNO.
- D 73 K 68 – personal income tax.
- D 91.2 K 69 – insurance premiums are charged.
Option 4. In-kind form of encouragement. We pay for the benefit of the employee for services or goods:
- D 73 K 76 – reflects the employee’s debt to the creditor.
- D 76 K 51 (50, 71) – services, work or goods paid for by the employer.
- D 91.2 K 73 – payment is written off.
- D 99 K 68 NP – PNO.
- D 73 K 68 – personal income tax.
- D 91.2 K 69 – contributions.
- D 70 K 73 – personal income tax is withheld from wages.
Procedure for taxation of gifts to staff or contractors
Personal income tax
Income tax is calculated on amounts over RUB 4,000. Moreover, personal income tax is calculated on both tangible and intangible income.
When calculating personal income tax you need to:
- summarize the cost of all gifts given to an employee in the reporting year;
- subtract 4,000 rubles from the result. — the amount of tax-free income;
- calculate personal income tax at a rate of 13% (for residents) and 30% (for non-residents).
If the gift is in the form of money, then personal income tax is withheld immediately on the day of payment, and is transferred no later than the day following the day the gift is given.
If the gift is not monetary, then personal income tax is withheld from the cash payment that is closest in date, and is transferred no later than the day following the day of withholding.
Insurance premiums
Regardless of how much the gift costs, insurance premiums do not need to be charged on it. This is stated in Art. 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation or in Art. 20.1 of Law No. 125-FZ.
VAT
According to Art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT must be charged on gifts, and on their purchase price without VAT. If a company donates its own products, then VAT is charged on its cost.
For all gifts according to the completed statement, you need to generate one invoice. Input VAT can only be deducted if there is a supplier invoice.
Income tax
According to Art. 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there is no need to charge income tax on a gift. The fact is that it is transferred to the employee free of charge, and therefore its value does not need to be taken into account when calculating tax.
Summary of taxes and fees
In general, the following main points regarding taxes and fees can be identified:
- Personal income tax is paid on amounts greater than 4,000 rubles, calculated on an accrual basis. For residents the tariff is 13%, for non-residents - 30%;
- insurance premiums are not calculated and paid;
- VAT is charged on the cost of the gift without VAT or on the cost price;
- income tax is not calculated.
Features of accounting for financial assistance
Various sources can be used for payment. Including the company's profit remaining after taxation and not previously distributed. Let's assume that the organization decided to issue financial assistance from retained earnings of previous years (account 84). How to carry out such a business transaction? I would like to emphasize that the Ministry of Finance is against such manipulations; in its opinion, the expression “retained earnings” implies that the founders have not yet made a decision on these funds.
In order not to irritate the Ministry of Finance, you need to hold a meeting and draw up a protocol with a decision on allocating part of retained earnings to such expenses. This will be easier to do if there is only one participant in the organization, then his sole decision is sufficient. The postings will be similar to the postings above, but count 91 will replace count 84.
Office decoration
An integral part of holiday expenses is the cost of decorating the premises. Of course, regarding March 8 and February 23, this is not very relevant, which cannot be said, for example, about the New Year. Should there be a chance to recognize these costs as expenses? Let's say right away that it is small. The Ministry of Finance considers such expenses economically unjustified.
However, you can try to justify them. This will not work for simplifiers, since their tax system assumes a closed list of costs . But subjects on OSN can try it. There are such cases in judicial practice. But you need to take into account that to a greater extent this applies to premises visited by counterparties - business partners, clients, customers. The meaning of the costs in this case is that they are aimed at creating a positive image of the organization, and this, in turn, strengthens its position in the market.
It should be taken into account that the FAS opposes the recognition of such expenses as advertising. The antimonopoly authority believes that they do not meet the definition given in the advertising law No. 338-FZ of March 3, 2006. Taking this into account, it is recommended that the costs of office decoration be reflected in accounting as other costs associated with production (subclause 49 of clause 1 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Again, entities using the simplified tax system do not have the opportunity to take such costs into account as expenses, even though they can justify them.
Reporting
Sometimes confusion arises when reporting non-taxable payments. Some do not include them at all in reports and 2-NDFL certificates, others show them everywhere. How to correctly fill out reports in accordance with the rules and legislation?
First of all, look at the instructions for the forms, they are quite detailed, and you can find answers to most questions there. Secondly, note for yourself the difference between payments that are not taxable under the law and those that are not subject to tax or conditional contributions. For example, dividends are not taxable amounts and are not shown at all in the RSV-1 report. At the same time, financial assistance is generally subject to contributions and is exempt from them only in the form of certain exceptions, which means that it should appear in the report.