With accounting, the process is streamlined: they hire an accountant, he handles everything. Sometimes they try to blame the management on the accountant as well. Usually, because they don’t see the difference, but it’s like asking a developer to fix Wi-Fi in the office, because “well, he’s a computer guy.”
Let's face it - accounting is a scary thing and no one wants to get into it. Accountants are holy people, without whom a business will be mired in penalties, fines and audits.
There is no need to put management accounting on the shoulders of an accountant. Yes, a great accountant will be able to do both, but these are two different forms of reporting and two functions in the company. You don’t want an accountant to do twice as much work, which will take twice as long, require twice as many skills and a completely different frequency. It's just not his job.
Let's try to figure out whose and why to complicate our lives so much.
Why you need to keep both records, why different specialists should do this, how to build a full-fledged accounting system in a company and not spend millions on it, Mikhail Smolyanov (“Finologist”) and Alexey Fitiskin (“My Business”) will tell you at the free webinar “Accounting and management accounting: how do large companies keep records and why does small business need it?” September 11 at 17:00 Moscow time
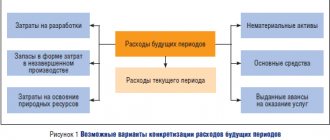
Purposes of each type of accounting
Accounting records transactions and transactions, financial results and cash flows.
It gives a rough idea of what is happening in the business. The main goal of an accountant is to correctly calculate taxes and report on the financial position of the organization on time. Accounting is focused on the past, since accounting works only with what has already happened or is happening now. It is unlikely that your accountant will predict revenue for at least the next month. Accounting does not have this capability, so it is not suitable for management.
Management accounting is aimed at operational analysis, understanding the state of affairs and planning further work.
It is important for management to collect information to make decisions that will help gain benefits in the future. Analysis of past periods helps to see the factors affecting the organization and predict the level of profit and loss in the future. The dynamics are monitored by three basic management reports:
- about cash flow;
- about financial results;
- forecast balance.
Knowledge and competencies
Reporting has different functions, so the knowledge of the specialists who deal with each also differs.
Financial statements
The accountant speaks the language of the state and knows the rules of the state. It brings business actions into compliance with government regulations. Let's look at two life situations: employee business trips and acquiring.
1. Business trips
Nikolai and Alexey go to Moscow for negotiations on the project. Everything is paid for by the company. After negotiations, Nikolai leaves, and Alexey remains on his business in Moscow for two more days and demands that the company pay for his return tickets, accommodation and travel allowances.
The accountant’s task is to pay travel allowances to both employees and deal with Alexey separately. What an accountant needs to do:
- Understand whether it is legal to include additional hotel expenses and daily allowance for Alexey.
- Calculate daily allowance for each employee.
- Monitor the preparation of an advance report for each employee and generate payments for overruns.
To understand whether it was possible to pay Alexey for two days in Moscow, the accountant studied the legislation, internal documents on employees and business trips and was convinced that he could:
- pay for tickets from Moscow with a date shift of two days;
- include this expense in reducing taxable income;
- not to pay Alexey travel allowances for two extra days;
- not to pay for Alexey’s hotel for two extra days.
2. Acquiring
A simple operation “attached a card - the purchase price was written off - returned the goods” in the world of an accountant looks like this:
1. The client paid for goods in the store with a card. Postings are generated about the write-off of goods and the bank's debt to the organization, because the money arrives at the bank with a delay of 1-3 days.
2. The money arrived in the company’s bank account within 1-3 days. The bank deducts its acquiring fee. Postings are generated about the write-off of the bank's debt to the organization.
3. The bank commission must be allocated because it is withheld from the buyer's money. It is issued in a special way - as part of the proceeds.
The accountant sets up the cash register for the taxation system, and in addition to the cash register, an acquiring terminal appears. At the end of the day, the devices issue reports, on the basis of which the accountant makes accounting entries and draws up a cash book, in which he receives revenue and deposits it with the bank.
Management reporting
A financial model is a language for describing a business through numbers. A specialist who deals with management accounting must understand business processes.
When a person knows how marketing, sales and production work, he understands the essence of the processes and knows how to digitize them. He can ask the right question, talk to every manager, find an error in the calculations. Unlike an accountant, he is not required to thoroughly understand taxes.
At the free webinar “Accounting and management accounting: how do large companies keep records and why does small business need it?” On September 11 at 17:00 Moscow time, Mikhail Smolyanov (“Finologist”) and Alexey Fitiskin (“My Business”) will analyze in detail when, where and for what purpose accounting and management accounting are used, what is the difference between them:
— Specialist competencies and tools for accounting automation.
— Specialist competencies and tools for automation of management accounting.
Is it possible to combine all functions in one person or service and how much does it cost? Three examples of companies for which management accounting helped solve and avoid problems will be given.
Open data and trade secrets in accounting
Accounting is needed by tax authorities, statistics services, suppliers and other external users. Accounting data is no secret. They are even published publicly on the statistics website.
Management accounting is maintained for internal use by the director, manager or owner. Its data often becomes a trade secret, so even within the organization not everyone has access to it.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
What does management accounting provide?
Well-constructed management accounting:
- contributes to the successful operation of enterprises;
- ensures high rates of their strategic development;
- allows management to quickly obtain the necessary accounting and analytical information;
- provides the organization with competitive advantages through cost management, business activities and general management;
- structures different types and areas of activity of the enterprise;
- provides an assessment of the contribution to the final result of various structural divisions.
Sources:
- https://upr.ru/article/upravlencheskij-uchet-opyt-vnedreniya-s-nulya/
- https://www.1CashFlow.ru/upravlencheskiy-uchet-na-predpriyatii
- https://www.B-Kontur.ru/enquiry/751-chto-takoe-upravlencheskij-uchet
- https://assistentus.ru/upravlencheskij-uchet/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/buhgalterskij_uchet/vedenie_buhgalterskogo_ucheta/v_chem_otlichie_buhgalterskogo_ucheta_ot_upravlencheskogo/
- https://finacademy.net/materials/article/etapy-vnedreniya-upravlencheskogo-ucheta
- https://www.audit-it.ru/terms/accounting/upravlencheskiy_uchet.html
Fixed and free forms of accounting
Accounting requirements are defined in detail: it is regulated by laws, regulations, standards, tax clarifications and other documents. The deadlines for compiling and the form of reporting are strictly defined. Accounting is mandatory for all organizations; you simply have no choice whether to do it or not.
Management accounting is simply your right. It is not subject to rules from above; it can be conducted in a way that is convenient for you, based on the specifics of the activity and your own goals. The main thing is that you understand the reports and indicators yourself. The frequency of compilation can be any: week, quarter or even year.
Objectives of management accounting, methods and means of their implementation
The introduction of management accounting allows you to effectively and efficiently solve a set of problems:
- Carry out planning of economic activities through budgeting;
- Control and optimize costs by promptly obtaining information;
- Analyze the deviation of actual indicators from planned ones based on management reports.
Ways to implement management accounting tasks:
- Management (internal) and financial (external) reporting;
- Operational accounting;
- Budgeting.
The reality of data in accounting
We reflect in accounting what is written in the contract. And in management accounting we focus on the real meaning of the operation.
For example, sale with subsequent repurchase: the contract is concluded with the condition that the seller can buy the goods from the buyer at any time and retains all the risks and benefits of owning the goods. Such a transaction is a disguised loan or financing. There is no point in recognizing revenue from such a transaction in management accounting, since the revenue figure will be higher than in reality. But in accounting you will have to do this.
How to build management accounting
If a company, as part of improving management efficiency, wants to implement a management accounting system, it will have to go through a number of successive stages.
You will have to start by defining the basis of management data, that is, a specific financial base. In domestic companies, the primacy of management accounting is a rather rare phenomenon, so most often it has to be built on the basis of an already functioning financial accounting system. In such cases it is necessary:
- clearly state the current situation (number of reports, their information content, analytics features, efficiency of information generation, etc.);
- predict the planned organization of accounting (reports on management needs instead of standard ones, changing the system of evaluation indicators, optimizing information, operating not only with past data, but also with forecasts).
The right level of detail
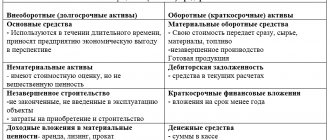
Accounting evaluates the entire enterprise and combines information about all departments, products, and employees.
Management accounting can look at the entire company or individual divisions - in depth and in more detail. This allows you to better understand the business from the inside and know what is happening in it and why. You see not just the overall flow of funds in the company, but also indicators by department and even employee. Not just see the profit, but understand its sources. Don’t just take into account goods, but divide them into groups and types.
Basic principles of policy for organizing a management accounting system
The organization of management accounting is based on certain principles of the company’s management policy. These include:
- Frequency corresponding to production cycles.
- Continuity of information and its repeated use.
- Formation of reporting indicators acceptable for all levels of management.
- Application of budgeting.
- Evaluation of the performance of individual structural divisions (CFD).
- Reliability, completeness, efficiency of information, possibility of analysis.
- Use of common units of measurement.
Metrics to Track
Accounting is carried out in monetary terms and is governed by numbers. Management accounting includes natural and even verbal indicators: the number of defects, productivity, customer and employee satisfaction, staff turnover, average order size and others. These indicators affect the business just as much as numbers, so they need to be monitored and adjusted. Often this becomes the main tool in optimizing the operation of the entire enterprise.
A web service for small businesses, Kontur.Accounting, helps you keep records, pay salaries and submit reports, and also generates five management reports. Monitor business development and automate routine accounting operations. All new users can get acquainted with the system and work in Accounting for free for two weeks.
Management reports in Excel
Excel tables have almost unlimited reporting functionality. You can create any types of tables and graphs that will reflect exactly the indicators that the manager wants to see.
True, to organize management accounting here, you will need a considerable amount of preliminary work and good knowledge of the program.
When starting to organize reports in Excel, it is important to determine by what criteria the data will be analyzed. It depends on what the manager wants to see . Expenses and income can be combined by projects, divisions, retail outlets, or other characteristics.
Then it is necessary to think through the classification and assign codes to operations so that all accounting users perceive the information in the same way. The next step is to create expense and income items, describe them in detail and indicate which accounting indicators they correspond to.
In order for the program to show the necessary results, it is necessary to spend a lot of time mastering the available functions, drawing up formulas for calculations and regulating data entry algorithms. If you plan to automate your work a little, you can't do without learning the basics of Visual Basic for creating macros.
At all stages of working with reports in Excel, it is important to carefully monitor each user action. One awkward deletion or transfer of data can create errors in formulas that lead to incorrect results. Management reports in Excel require daily manual entry of actual and planned operations - the program does not provide tools for automatic data loading. It is also impossible to avoid the “human factor” - when entering operations, there is a high probability of errors.
After implementation. Support and bug fixes
Only exemplary employees will definitely fill out the forms correctly, not try to reduce the time for filling out and not skip important steps (remember about the key employee responsible for communication with the implementation group in each department?).
Several months after the active phase, the implementation group should have a user support hotline open. Key employees in departments should show by example how to correctly fill out the database. The database should be regularly checked for errors, which should be clearly explained to users. Sooner or later the influx of errors and questions will subside. And it took us six months.
Managerial balance: examples from life
- 1. A young, actively developing trading and manufacturing company. After two years of operation, funds are needed for expansion.
One of the owners has an economic education. He created a system of tables for generating indicators and basic reports, but without a Balance Sheet. Primary data is stored in 1C.
The second investor is a foreigner who asked for a balance before making new investments. It seems to be easy to compile, because records are kept. However, when trying to build a report, we realized that Asset and Liability do not add up to large amounts. Nobody knows where to look for errors over two years of work, what to correct in accounting.
The result: the investor did not want to give money until the accounting was in order. When receiving investments and loans, everyone requires a balance sheet.
- 2. Individual entrepreneur with a trade turnover of $25,000 per month. We prepared reports in Google spreadsheets using method 3. Quickly and beautifully. But no one checked the results, and over 9 months there was a difference in the Money item of more than $3,500 (more in the Balance than in fact).
After searching, we found unaccounted expenses of $2,500, which reduced the final profit. This upset the owners. But they also reduced the creditor: it turned out that it had been paid a long time ago. This made everyone happy.
There was a discrepancy of $2,000 for an item as a result of the item being written off in CRM, but CRM did not show the amount of the write-off. And no one took them into account in the reporting. Only during reconciliation did we realize that it was important to improve this automation point. And we understand that write-off could involve elementary theft. There is no alternative to the balance sheet to control current activities.
- 3. The company provides design services - this is a long-term process.
When starting a new project, each time they took an advance for half the work. There was always enough money in circulation, and at the end of the month it was withdrawn entirely as dividends. Until the crisis arrived and new agreements practically ceased. It turned out that there was nothing to pay for the costs of projects that had already been paid for by clients. And they must be continued.
With the help of the Balance Sheet, they easily explained to the owners that their business was supported by a creditor - this must be analyzed before issuing dividends and creating reserves.
If the profit is small, but there is a lot of money, most likely the business has a large creditor. And the balance sheet often shows what type and duration it is.
The most common business question is: why is there always not enough money? This is especially strange if there is profit. Looking at the Balance Sheet, you can immediately say that the money is in receivables, or goods, or fixed assets. To release money from freezing you need to:
- work more actively with clients to return money;
- urgently sell the product and order less, but more often in the future;
- consider the issue of turnover and financial cycle, etc., which are also calculated on the basis of the Balance Sheet.
If there is profit but no money, then the Balance Sheet will show where the company’s money is.
Management Balance Analysis
Balance sheet analysis can quickly tell what a business is, where and at what speed it is moving:
- how much money, raw materials, goods, fixed assets (buildings, equipment), intangible assets (programs, licenses);
- how much is owed to the business and how much does the business owe to someone (in aggregate, to whom exactly);
- how much profit or loss has accumulated during the operation of the enterprise;
- how much money, own and borrowed, has been put into circulation by the business - whether the owner owns his business or everything already belongs to creditors.
That is, the second function of the Balance is informational and analytical.
It is on the basis of the Balance Sheet items that a financial analysis of a business’s operation is carried out:
- business speed indicators: goods turnover, debt, operating and financial cycles;
- return (profitability) of assets and equity;
- financial leverage (for credit);
- liquidity, solvency, etc.
Payment schedule
Let’s take a closer look at an equally important financial management tool – the payment calendar. The payment calendar built into 1C: Accounting creates a daily plan for cash receipts and expenditures in the following sections:
- Payment from buyers;
- Other supply;
- Taxes and fees;
- Payments to suppliers;
- Salary;
- Periodic payments.
For the payment calendar to work fully, you must enable the payment planning functionality in the program settings and set default payment terms.
Various configuration documents can be used as a basis for adding a payment to the calendar. For example, such as “Invoice to buyer”, “Sales (acts, mortgages)”, “Invoice from supplier” or “Receipt (acts, invoices)” and others.
The amount of taxes and contributions is calculated in accordance with completed declarations and accruals entered in accounting entries. A dash in the amount column means that the deadline for paying the current tax has come, but there is no declaration or tax accrual in the database.
The payment calendar in 1C Accounting is a simple and visual management report with which you can manage cash flows, prevent cash gaps and control the payment of taxes and other mandatory payments.
External specialized and universal reports for 1C
External reports allow you to implement the required appearance and structure of data presentation. Each company can develop its own unique management reports that will use existing information in 1C: Accounting. External reports can be developed by almost any 1C specialist. Their use will allow, without making changes to the application solution, to receive the necessary reports in the shortest possible time in the form required by the company manager or owner.
Universal reports work on a different principle - using the existing report form generation engine, a 1C:Accounting user, for example, a financial director and an accountant, can use a special setting to interactively create the required type of report, without resorting to the help of developers. Basically, these reports are generated on the basis of accounting entries between specified accounting accounts.
For each report line assigns a specific rule, for example:
- Total - sum by substrings
- Account balance - allows you to display the balance of a specific account in the context of sub-accounts. Allows you to create separate debit/credit balances
- Account turnover - allows you to display data on specific transactions between accounts
- Sum of other lines - allows you to make simple calculations between lines
- Additionally, in the line settings, you can specify the need to display a transcript for the subcontract selected accounts.
Thus, a 1C user can create several different settings for a universal report, save them and use the constructed management accounting model in all 1C: Accounting databases.
Managerial Balance: advantages for the company
- 1. The balance sheet is the only way to control the current activities of the enterprise and the correctness of the data in all other reports.
- 2. The balance sheet helps to analyze what the business is, where and at what speed it is moving.
- 3. The company is required to provide a Balance Sheet if it wants to attract investments or loans.
Without drawing up a Balance Sheet, you are deprived of the opportunity to conduct very important analytical research, draw conclusions, find errors and, most importantly, manage the enterprise.