From the article you will learn:
The dismissal of a chief accountant is a serious event for almost any organization. The chief accountant is one of the key employees in the company who is responsible for accounting for business transactions, timely transfers to the state budget and extra-budgetary funds. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, separation from such employees is carried out on practically the same grounds and rules as the termination of employment contracts with any other hired entities. However, some differences in terminating contracts with chief accountants still exist. We'll talk about this in more detail in our article.
Grounds for dismissal of the chief accountant
The chief accountant can be dismissed on the same grounds as other employees.
These grounds are listed in Art. 77–81, 83 and 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, the legislator provides additional grounds for terminating the employment relationship with the chief accountant, namely: However, the specifics of the position dictate the specifics of the dismissal of the chief accountant. The chief accountant is one of the key figures in any company. The scope of responsibilities of this specialist is established by legal acts (for example, the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 402-FZ), the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia “On approval of the Regulations on Accounting”, etc.), local regulations of the company, employment contract and job description.
The main tasks of the chief accountant are to organize accounting of the company's business operations in accordance with legal requirements, ensure timely fulfillment of obligations for payments to the budget and extra-budgetary funds.
The procedure and features of dismissal of the chief accountant - step by step
There are no special requirements for the procedure for dismissal of this category of workers in the current labor legislation. Therefore, when parting with the chief accountant, the employer’s action algorithm will depend on the reasons for the employee’s dismissal (at his own request, by agreement of the parties, at the employer’s initiative).
At the same time, the dismissal of the chief accountant is undoubtedly different from the dismissal of an ordinary employee. The dismissal of this specialist for any reason must be accompanied by the transfer of files and documents to a new employee. Due to the lack of regulation of this process in the current legislation, it is advisable to provide for such a procedure in the local legal act of the company. And in the absence of such a document, regulate in detail the procedure in the order on the transfer of affairs from the resigning employee to the one appointed to his position.
As for the rules for formalizing the termination of employment relations with an employee, they are enshrined in Art. 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and assume the following:
Responsibility of the enterprise management
Dismissal of a chief accountant is a complex procedure that requires serious legal justification. If this issue is approached superficially, and the offended financial manager files a lawsuit, then it is quite possible that the dismissal will be declared illegal, and the employer will be punished financially (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- fine to the manager in the amount of up to 1,500 rubles;
- fine to the enterprise from 30 to 50 thousand rubles;
- suspension of the company's activities.
The most reasonable thing to do is, by presenting undeniable evidence of the chief accountant’s guilt or incompetence, to persuade him to pay at his own request.
Dismissal of the chief accountant at his own request
The procedure for dismissing a chief accountant at his own request (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is not fundamentally different from the dismissal of any other employee on this basis (see the article “Procedure for dismissal at his own request step by step”).
If an accountant decides to resign, he is obliged to notify the company administration about this 2 weeks before the date of planned departure by submitting a written application. The said period begins the next day after the employer receives the employee’s application (Part 1 of Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Note! A resignation letter can be sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt and a description of what was sent. In this case, the countdown of the period begins from the date of receipt of the letter by the employer (a mark about this should be on the delivery notice), and not the date of its sending.
Before the end of the notice period for dismissal, the employee has the right to withdraw his application, unless another specialist is officially hired in his place (Part 4 of Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
As mentioned above, a feature of the dismissal of the chief accountant is his transfer of affairs and documents to the successor according to the act. But the manager should remember that he does not have the right to detain an employee if it was not possible to complete the procedure on time or there are unfinished matters, such as submitting reports or balance sheets.
We recommend! The procedure for transferring cases upon termination of an employment contract can be specified in the contract itself and/or the job description. This will simplify and speed up the process of submitting cases.
Responsibility after dismissal
The procedure for receiving and transferring cases is quite capacious and does not always fit within the two-week work period. Therefore, the accountant may be held liable even after the day of dismissal.
If such an employee does not submit the acceptance and transfer certificate, then the employer, within a year after the termination of the employment contract, has every right to file a lawsuit against such an accountant.
The management can file a claim even if there is an act, but in this case it will be very difficult to prove the guilt of the former employee, because the fact that he did his job efficiently will be documented.
Work off upon dismissal of the chief accountant at his own request
How long should the chief accountant work upon dismissal? For this specialist, service upon dismissal is standard and is 2 weeks (how to correctly calculate the period of service, read the article “Work upon dismissal”). By agreement between the employee and the employer, the employment contract can be terminated before the end of the notice period for dismissal. That is, if the parties do not object, then they can separate on the day the application is submitted. This does not contradict labor laws. But do not forget that the position of chief accountant involves the transfer of affairs to a new employee, which undoubtedly takes time.
Note! If the employee has been placed on probation and its term has not yet ended, he can notify about the termination of the employment contract 3 days before the planned date of dismissal (Part 4 of Article 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In some cases, the employer is obliged to terminate the employment contract within the period specified in the employee’s application. These situations are listed in Part 3 of Art. 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and are relevant for any employee resigning at his own request:
- impossibility of continuing to work (retirement, health status and other cases, subparagraph “b” of paragraph 22 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 2));
- a violation of labor legislation, internal documents or an employment contract recorded by the employer (by the state labor inspectorate, the prosecutor's office or the court).
What should be transferred?
Documenting the process of transferring cases when the chief accountant resigns at his own request is interesting for all parties in as much detail as possible. Both the incoming and outgoing specialist will be able to protect themselves from the boss and inspectors with a detailed list of documents and information listed in the act. Therefore, when the question arises about what should be included in the final document, you need to use a simple rule: if there is an accounting entry, there must be a primary document. In other words, if at one time the chief accountant entered a figure into the accounting registers or used it to prepare reports, then he must present the new employee taking office with the paper from which it was taken. Those who have experience working as an accountant or auditor understand perfectly well how much primary documentation and documentation compiled on its basis can accumulate in an enterprise even over a short period of work. It’s good if the enterprise has already undergone a documentary audit relatively recently, then documents only for the subsequent period after the audit are subject to transfer. You can simply read the report following the inspection to make sure that the predecessor has fulfilled all the requirements set out in it and paid all penalties.
Main list
Regardless of the specifics of the enterprise’s activities, there is a constant list of transferred documents and valuables that the chief accountant must hand over upon dismissal:
- cash documents and reports;
- bank statements;
- accounting registers and turnover accounting statements;
- receipt and expenditure documents for inventory items;
- certificates of work performed and services received;
- inventory cards for accounting, depreciation and movement of fixed assets, inventory sheets and inventories of the latest inventory;
- acts of write-off of valuables, replenishment or reconstruction of fixed assets;
- advance reports and supporting documents;
- documents on targeted or government financing, if such transactions took place in the company;
- loan agreements and annexes thereto;
- statements of accrual and payments to employees;
- estimates, calculations and technological maps.
The transfer act must also record the balances of the accounting accounts as of the date of division of responsibility specified in the order:
- the balance of funds in the cash register and on current accounts of the enterprise, and it is advisable to immediately carry out a sudden inventory of them;
- decipher accounts receivable and payable in the context of counterparties (consumers of the enterprise’s products and suppliers of goods and services);
- balances or overexpenditures on accountable amounts in the context of financially responsible persons;
When drawing up the act, it would be useful to include information that the new chief accountant is familiar with the order on accounting policies, the job description of the chief accountant, the regulations on bonuses and incentives for employees, the collective agreement and the charter of the enterprise. Also, all items and intangible assets stored by the previous chief accountant are transferred against signature. Sample order for acceptance and transfer of the chief accountant's file:
Act on the acceptance and transfer of cases by the head office:
Sample entry in a work book:
Deadlines
If the company from which the chief accountant is leaving is quite young and its period of activity does not exceed a couple of years, then you need to transfer documents for the entire period of work. If the life of the company is much longer, then the parties to the transfer need to decide on the depth of verification and inventory of the archive:
| Date of last check | Document transfer period | Base |
| Less than three years ago | The original audit report and all documents for the subsequent period are transferred | Art. 113 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Three to five years ago | For the entire period from the date of the last inspection | Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 23. Responsibilities of taxpayers, paragraphs. 8 clause 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 29 402-FZ |
| More than five years ago or never | For the last five complete annual reporting periods | Art. 29 402-FZ |
| Regardless of the timing of the inspection | Long-term storage documents (from 10 years), such as personal files of employees and salary slips, are submitted for the entire period of operation of the enterprise | Order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia No. 558 |
It is unlikely that absolutely all the primary documents of the enterprise are in the custody of the chief accountant, but knowing their storage periods will be useful for conducting an inventory in departments and areas in the accounting department. The new specialist only needs to submit those papers that were in the personal charge of the old chief accountant.
The responsibility of the resigning chief accountant to transfer affairs applies only to those documents that are under his direct control or provided to him under a custody agreement.
Dismissal by agreement of the parties
Any employee, including the chief accountant, has the right to terminate the employment contract at any time by agreement with the employer (Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The dismissal of the chief accountant by agreement of the parties requires the signing of a separate document indicating the conditions of separation. Employees often resort to this form of dismissal in order to receive additional compensation (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, see article “Compensation for dismissal by agreement of the parties”).
Is it necessary to pay it? The Consultant Plus system answers this question in a ready-made solution. If you do not yet have access to the ConsultantPlus system, you can register for free for 2 days.
Often, the provision for additional payments to the employee is written directly into the text of the agreement on termination of the employment contract. Judges' opinions on the possibility of such fixation of compensation payments were divided:
- Some judges believe that the employer, who has assumed the obligation to pay the employee severance pay as part of the agreement to terminate the employment contract, has no grounds for refusing to provide the employee with the specified compensation (see the ruling of the Moscow City Court dated February 20, 2019 No. 33-3102/2019) .
- Another position is that mere agreement between the parties is not enough. Payment of compensation to an employee, including those related to termination of an employment contract, must be provided for by law or the remuneration system used in the organization, which is established by a collective agreement, local regulations (decision of the Zavolzhsky District Court of Tver dated November 26, 2018 No. 2-2047/ 2018).
Note! An agreement on termination of contracts with chief accountants of state corporations, state-owned companies, state extra-budgetary funds cannot contain provisions on the payment of severance pay and any compensation (Part 3 of Article 349.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Payments
In 2022, an accountant will receive standard payments in the form of compensation for unused vacation days, as well as wages.
In addition to them, there may be additional payments specified in local regulations or collective agreements of companies. Their presence may also be specified in the agreement of the parties.
It is possible to receive severance pay, but only in a few cases. These may include dismissal due to the liquidation of the company or due to a reduction in the number of its employees. In such cases, benefits will not go to only those who worked on the basis of a fixed-term contract.
Table: types of compensation payments provided for by law depending on the reason for dismissal
| Reason for dismissal | Compensation payment |
| Change of owner of the organization's property | Compensation in the amount of not less than three average monthly earnings - Art. 181 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Liquidation of an organization | Severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings and preservation of average monthly earnings for the period of employment, but not more than two months from the date of dismissal - Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Reduction in the number or staff of an organization's employees | Severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings and preservation of average monthly earnings for the period of employment, but not more than two months from the date of dismissal - Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
| Inconsistency of the employee with the position held or the work performed due to a health condition that prevents the continuation of this work (if the dismissal is initiated by the employer) | Severance pay in the amount of two weeks' average earnings - Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
This is also important to know:
Certificates upon dismissal of an employee in 2022: what certificates does the employee receive?
So, from the point of view of economic feasibility, a chief accountant who voluntarily resigns is much better than someone who is fired “without guilt.”
Is it possible to fire the chief accountant when changing the head of the company?
A specific reason for terminating an employment relationship with such a company specialist as the chief accountant is a change of owner of this company (clause 4, part 1, article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
It is important to distinguish between dismissal when there is a change in the owner of the company and the dismissal of the chief accountant when there is a change in manager. A change in the ownership of a company (as opposed to a change in management) involves a transfer of ownership of the assets of that company from one person to another person(s). Clause 32 of Resolution No. 2 explains in what cases dismissal under clause 4, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is possible, and in which it is not allowed:
The new owner has the right to dismiss the chief accountant no later than 3 months from the date of his ownership rights (Part 1, Article 75 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If, after the specified period, the employee continues to work, then subsequently it is impossible to dismiss him on this basis.
If the employment contract is terminated on the grounds under consideration, the chief accountant has the right to receive compensation. The minimum amount of payments is 3 average monthly earnings (Article 181 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). By agreement between the parties it can be increased. The exception is the employees named in Art. 349.3 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For them, the amount of compensation cannot be higher than 3 average monthly earnings.
“Goodbye” they said to the Chief Accountant
The dismissal of the chief accountant may take on a less “voluntary” nature when it comes to systematic violations of discipline, as well as a whole list of other acts aimed at causing harm to the company. As an example, here are some of them:
- Regular lateness to work can be regarded as a violation of discipline, and therefore the internal regulations established in the company;
- Errors in reporting made by the chief accountant personally or by his subordinates, which subsequently resulted in the imposition of significant fines on the organization;
- Loss of primary documents and irresponsible attitude towards their restoration. He is in charge of storing these and many other papers;
- Implementation of fraudulent schemes related to the transfer of funds to unreliable counterparties without the knowledge of the director;
- Endorsement of invoices without the knowledge of the manager in the absence of the right to sign.
This list can be continued for a long time. It is important to understand that the chief accountant is in charge of all the affairs of the organization. Plus, he has a complete understanding of its business activities. Any action that causes material damage can ultimately turn out sadly for the chief accountant. Unfortunately, when hiring any employee, it is impossible to know 100% for sure how cooperation with him may turn out. Here it’s only according to Stanislavsky: “I believe” or “I don’t believe.”
Dismissal of the chief accountant at the initiative of the employer
Labor legislation includes a large list of grounds on which an employer has the right to dismiss an employee, including the chief accountant. Conventionally, they can be divided into groups:
- Objective, not related to the employee’s guilty behavior. This is dismissal on the grounds stated in paragraphs. 1–4 hours 1 tbsp. 81, art. 83, art. 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (liquidation, reduction of staff (numbers), etc.).
- Dismissal due to the employee’s guilty behavior (clauses 5–7, 9, 11, part 1, article 81, article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Important! Dismissal of a chief accountant for guilty behavior requires compliance with both the general procedure for terminating an employment contract (Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and the procedure for bringing a specialist to disciplinary liability under Art. 192, 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, it is necessary to remember the restrictions and special conditions for dismissal of such categories of employees as:
- a woman expecting a child;
- a woman with children under 3 years of age;
- a single parent raising a child under the age of 14 (a disabled child under the age of 18);
- the sole breadwinner of a disabled child under 18 years of age or a child under 3 years of age in a large family.
Procedure for transferring cases
Important! Please keep in mind that:
- Each case is unique and individual.
- A thorough study of the issue does not always guarantee a positive outcome. It depends on many factors.
To get the most detailed advice on your issue, you just need to choose any of the options offered:
- Use the online chat in the lower corner of the screen.
- Call: Federal number: +7 (800) 511-86-74
A written statement begins the difficult and thorny path of transferring business from the outgoing employee to the new one. Since the law does not contain clear requirements regarding the mandatory nature and form of the act of acceptance and transfer of cases, it can be approved and the details of the process can be specified in the order of the head (Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- Full names and positions of the participants in the transfer (a new chief accountant, deputy, any other employee, or the head of the enterprise himself can be appointed as a successor).
- Timing of the procedure and completion.
- Date of division of responsibility (the last period is determined, which must be completely closed by the old chief accountant, including the last reporting period and its list).
- Range of questions for verification (balance sheet, balances on accounting accounts, statements of synthetic and analytical accounting, breakdown of receivables and payables, etc.)
- List of property, documents and other valuables that are subject to responsible storage by the new head of the accounting department (originals of title documents, carriers of information about electronic signatures, seals and stamps, keys to safes and their contents).
- Data of officials entitled to be present at the transfer.
- Form of the final document.
Even if a new chief accountant has already been found and is ready to start work, this will not be enough to sign the document acceptance certificate. The fact is that signing such a document means accepting all papers and valuables for storage and use, and only an employee of the enterprise can do this. This means that on the date of signing the act, an employment contract must be drawn up with the person. Since two chief accountants at one enterprise are nonsense, it is better to accept a candidate for the position of chief accountant as his deputy or one of his deputies. And then transfer him to the already vacated post. If there is no desire to produce personnel orders, then the transfer act can be signed by the manager himself. Moreover, paragraph 1 of Art. 7 402-FZ directly obliges him to organize the safety of documentation in the company. Please remember that in this case you will need to go through the transfer procedure again. Now the act will be signed between the manager and the new chief accountant who has taken office. Otherwise, it will not be possible to hold him responsible for documents and valuables.
Dismissal upon liquidation of an enterprise
The dismissal of the chief accountant during the liquidation of an enterprise is one example of termination of an employment contract with an employee at the initiative of the employer due to the occurrence of objective reasons (Clause 1, Part 1, Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Liquidation can be voluntary, by decision of the company's owners, or forced, by a court decision. The adoption of a decision on liquidation is accompanied by the appointment of a liquidation commission, to which all powers to manage the legal entity are transferred (clause 4 of Article 62 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
When a company is liquidated, in accordance with the law, employment contracts with all employees are terminated. However, as a rule, a chief accountant is necessary during the liquidation process.
We recommend! In this case, you can formalize your relationship with him according to the following scheme:
- Terminate the previous employment contract in compliance with the general procedure for dismissal during liquidation).
- Conclude a fixed-term employment contract. Or a civil contract.
How to fire an accountant based on an article
An employee, including the chief accountant, who has already been brought to disciplinary liability, in case of repeated violation of labor discipline, may be dismissed on the basis specified in clause 5 of part 1 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (repeated failure to fulfill labor duties). You can be fired regardless of what the first punishment was (a reprimand or reprimand).
The procedure for applying a disciplinary sanction in the form of dismissal requires the employer to:
- record a violation;
- conduct an internal inspection, taking into account the severity of the act and accompanying circumstances (part 5 of article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 53 of resolution No. 2);
- comply with the deadlines for applying disciplinary sanctions set out in Part 3 and Part 4 of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (within a month after the discovery of the offense, but no more than 6 months from the date of its commission, and based on the results of an audit, inspection of financial and economic activities or an audit - no more than 2 years);
- complete all documents correctly.
The algorithm of actions is described in detail in the article “Dismissal for repeated failure to fulfill job duties.”
Audit as a way to reconcile the parties
It is unlikely that the chief accountant will suddenly decide to resign of his own free will. The brief and streamlined formulation often hides the idea of changing jobs that has been mulled over for weeks or months, as well as accumulated mutual dissatisfaction with management. In this case, it may be acceptable for both parties to conduct an audit of the enterprise’s activities over the past few years. Firstly, auditors will perform a complete review of all documentation instead of a selective one, which is practiced during the standard transfer of cases between accountants. Secondly, if deficiencies are detected, the company will be given recommendations on correcting them or restoring missing papers. Thirdly, under an agreement with the audit company, responsibility for all detected violations of tax or other legislation during the audited period will be assigned to the involved auditors.
Is it possible to fire a chief accountant for lack of trust?
Dismissal under clause 7, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is applicable only to an employee servicing monetary or commodity valuables: receiving, accounting, storing goods and money, transporting them, distributing them, etc. (clause 45 of Resolution No. 2). We are talking about financially responsible employees holding positions or performing work contained in the lists approved. Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 No. 85.
The chief accountant is not an employee who directly works with monetary or commodity assets, therefore he cannot be dismissed on this basis. This point of view is set out in paragraph 4 of the Review of Legislation and Judicial Practice of the RF Armed Forces for the third quarter of 2006 (definition of the RF Armed Forces No. 78-B06-39).
Note! It is still possible to dismiss the chief accountant on the grounds under consideration, but only if he was entrusted with work (labor function) involving the direct servicing of monetary (commodity) assets (at present there is no ban on such a combination). Moreover, it is important that the fact of performing two different job functions is officially assigned to the employee (for example, in an employment contract or additional agreement).
Regarding dismissal under clause 7.1, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then it applies exclusively to employees whose positions are designated in the relevant regulations (for example, in the laws “On Anti-Corruption” dated December 25, 2008 No. 273-FZ, “On State ...” dated July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ ).
Read about the nuances of the procedure in the article “Dismissal due to loss of trust - features of the procedure.”
Consequences
Even if offenses were discovered after the chief accountant left, administrative or criminal liability may be imposed on him.
Also, in the event that the organization suffered material damage as a result of the discharged person fulfilling or not fulfilling his duties, he must compensate for the damage in full.
What may be the responsibility for after leaving a position?
| Legislative act | Article | Violation committed | Deadlines |
| tax code | 120 | Violations related to accounting and reduction of tax payments | 3 years from the date of submission of the report |
| 122 | Violation of tax payment deadlines | ||
| Code of Administrative Offenses | Chapter 15 | Violation of registration requirements, submission of reports, etc. | Within 1 year from the date of discovery |
| Criminal Code | 198, 199 | Evasion of tax duties and payments | Depending on the seriousness of the offense - 2 years, 6 and 10 years |
| 165 | Causing damage as a result of breach of trust | ||
| 201 | Abuse of official position | ||
| 293 | Negligence at work | ||
| 327 | Forgery of documents | ||
| Labor Code | 238 | Causing damage | 1 year from the date of discovery of the fact |
It is possible to prove the guilt of a dismissed person only after an appropriate court decision has been made.
Employer's liability
Controversial situations often arise when the manager does not want to let go of a valuable worker and tries in every possible way to keep him at work.
- If the employer does not accept the resignation letter . In this case, the application is drawn up in 2 copies, one of which is registered in the personnel department or with the secretary in the journal of incoming correspondence and remains with the employee. The service period begins to count from the date of registration. The second option is to send an application to the manager by registered mail. Processing will begin from the day the letter is received by the addressee, the date is indicated in the tear-off notice.
- If you haven't found a replacement . It is not legal to delay the departure of a worker for this reason. The chief accountant transfers all documentation to the manager.
- The person being dismissed is not given his or her work book back . Such actions are illegal and are grounds for appealing to the labor inspectorate or court.
Making an unreasonable decision is grounds for dismissal of the chief accountant
How to fire a chief accountant for lack of trust? Due to the absence in the legislation of the possibility of dismissing the chief accountant for lack of trust, the employer can terminate the employment contract with him on another basis - the chief accountant making a decision that led to a violation of the safety of property, its misuse or other damage to the company’s property (clause 9, part 1, article 81 of the Labor Code RF).
To dismiss an employee on this basis, a set of conditions must be present (clause 48 of Resolution No. 2):
- Negative consequences should occur precisely as a result of the decision made by the specialist.
Note! Based on the literal interpretation of this norm, it is impossible to dismiss the chief accountant in the event of his inaction (failure to make a decision) on the basis in question.
- The consequences could have been avoided if a different decision had been made.
- The chief accountant's guilt has been proven. Since dismissal on this basis is a disciplinary sanction, it can only be applied if the specialist’s guilt is established. The presence of guilt means that he knew or should have known about the possible consequences of his decision. When conducting an internal investigation, you need to request a written explanation from the employee (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The dismissal order is issued on the basis of collected documents confirming the occurrence of negative consequences and the cause-and-effect relationship between them and the accountant’s decision (decision of the Moscow City Court dated January 18, 2011 in case No. 33-807).
Transfer of cases when changing the chief accountant
The obligation of a resigning employee to submit files and draw up reports on the work done is not established by the labor legislation of the Russian Federation. Therefore, it is extremely important to formalize issues related to this procedure in the company’s local regulations. When developing such a document, as an example, you can use the “Instructions on the procedure for accepting and submitting cases by chief accountants (senior accountants with the rights of chief accountants) ...”, approved. Ministry of Health of the USSR 05.28.1979 No. 25-12/38.
It is also advisable to provide for the obligation to hand over and accept cases in the employment contract and job description of the chief accountant (see the article “Transfer of cases and other nuances upon dismissal of the chief accountant”).
The administrative document for the procedure for transferring cases when changing the chief accountant is the order of the manager. It states:
- the basis for issuing the order (dismissal of the chief accountant);
- employee accepting cases (new accountant, manager, other employee);
- other persons involved in the transfer of affairs (for example, auditors);
- timing of the procedure;
- the procedure for conducting and processing the procedure for submitting and accepting cases (if it is not established by a local act).
Is an inventory required when the chief accountant is dismissed?
A change in accounting management may be accompanied by an inventory and audit of the company's assets and liabilities. Inventory is carried out if:
- as determined by the employer (in a local act or order, paragraph 3 of Article 11 of Law No. 402-FZ);
- the chief accountant is assigned financial responsibility by a labor contract or agreement (Article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 4, paragraph 1.5 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory..., approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49).
Read even more details and a sample transfer document in the Consultant Plus system (ready-made solution “How to organize the transfer of affairs of the chief accountant”). If you do not yet have access to the ConsultantPlus system, you can obtain it free of charge for 2 days.
Financial liability to the employer
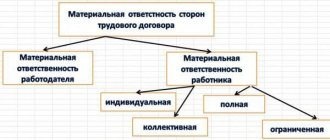
The opportunity to recover material damage from an employee, provided for in Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, provides only for cases of direct calculable financial harm. The favorite topic of some employers about lost profits is completely excluded from the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Since Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation limits the amount of liability to the average salary, and the chief accountant is not included in the list of positions with which a separate agreement on full financial liability can be concluded, the obligation to compensate for damage can only be prescribed in an employment contract (Article 243 of the Labor Code). But even then, the employee retains the right to refuse to deduct material damage from his salary. In such circumstances, the employer will be forced to prove the need for compensation and the amount of damage in court (Article 248 of the Labor Code).
If there is no one to delegate matters to
If the chief accountant’s own desire has become an unpleasant surprise for the employer, difficulties may arise with the search for a new specialist and the smooth transfer of affairs. The boss will simply sabotage the process by not appointing a successor and not signing the act himself. And although his actions can be indirectly regarded as an attempt to detain a specialist, it will be problematic to prove this in the same court. After all, the Labor Code does not say a word about how exactly this process should be organized; the enterprise is given complete freedom in this matter (Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
You can partially try to protect yourself with the help of your subordinates, because the position of chief accountant most often implies the presence of several more accountants in the company. Each of them is responsible for their own area of work, and, if these employees are loyal, you can try to sign with each of them your own copy of the act on the integrity of documents for the current and previous periods.
If the enterprise is large enough and has an archival service in its structure, then it is best to hand over the papers to the archivist. In any case, it is better to spend the two-week warning period for the chief accountant to check and put all the files in order, even if there is no one to hand them over to.
Unlike the retiring manager, it will be difficult for the chief accountant to transfer the archive for storage to a third-party organization or take the documents with him for self-storage.